Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
1. Fundamental Components
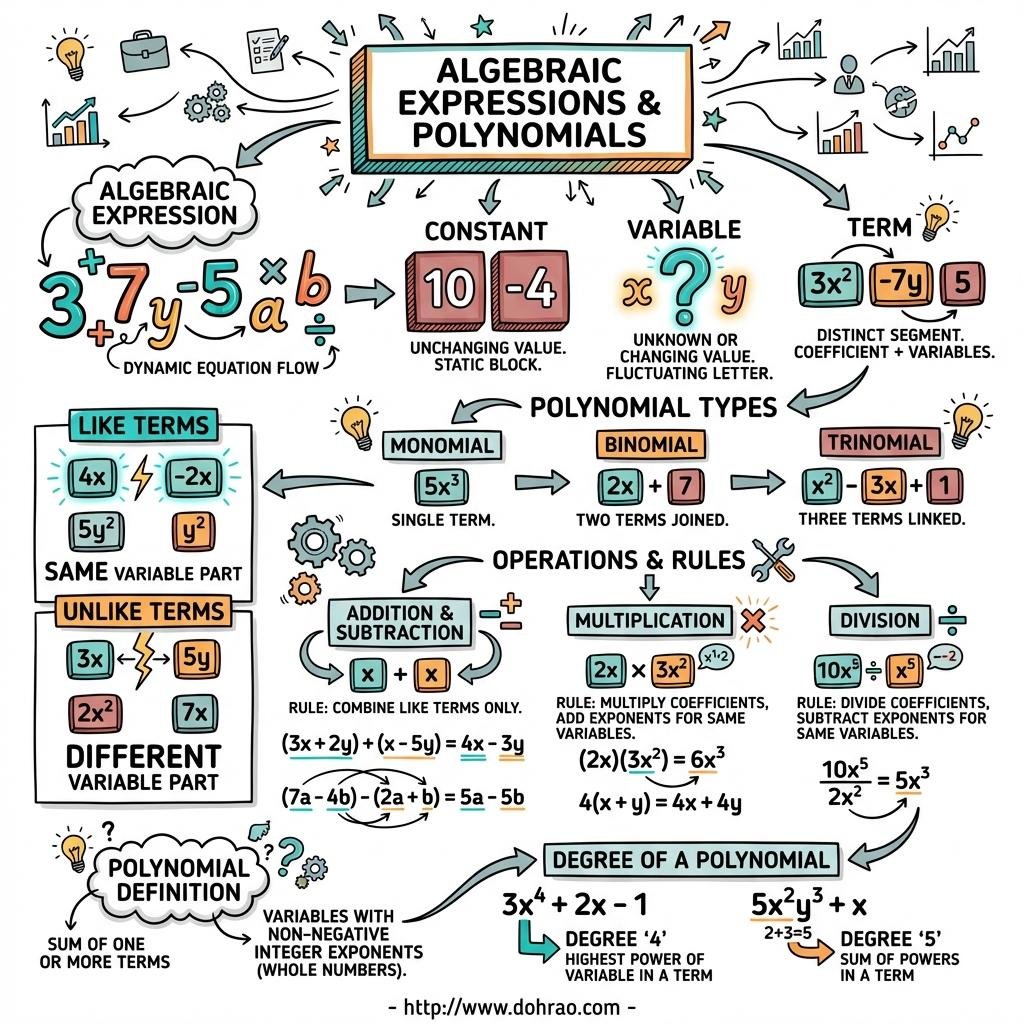
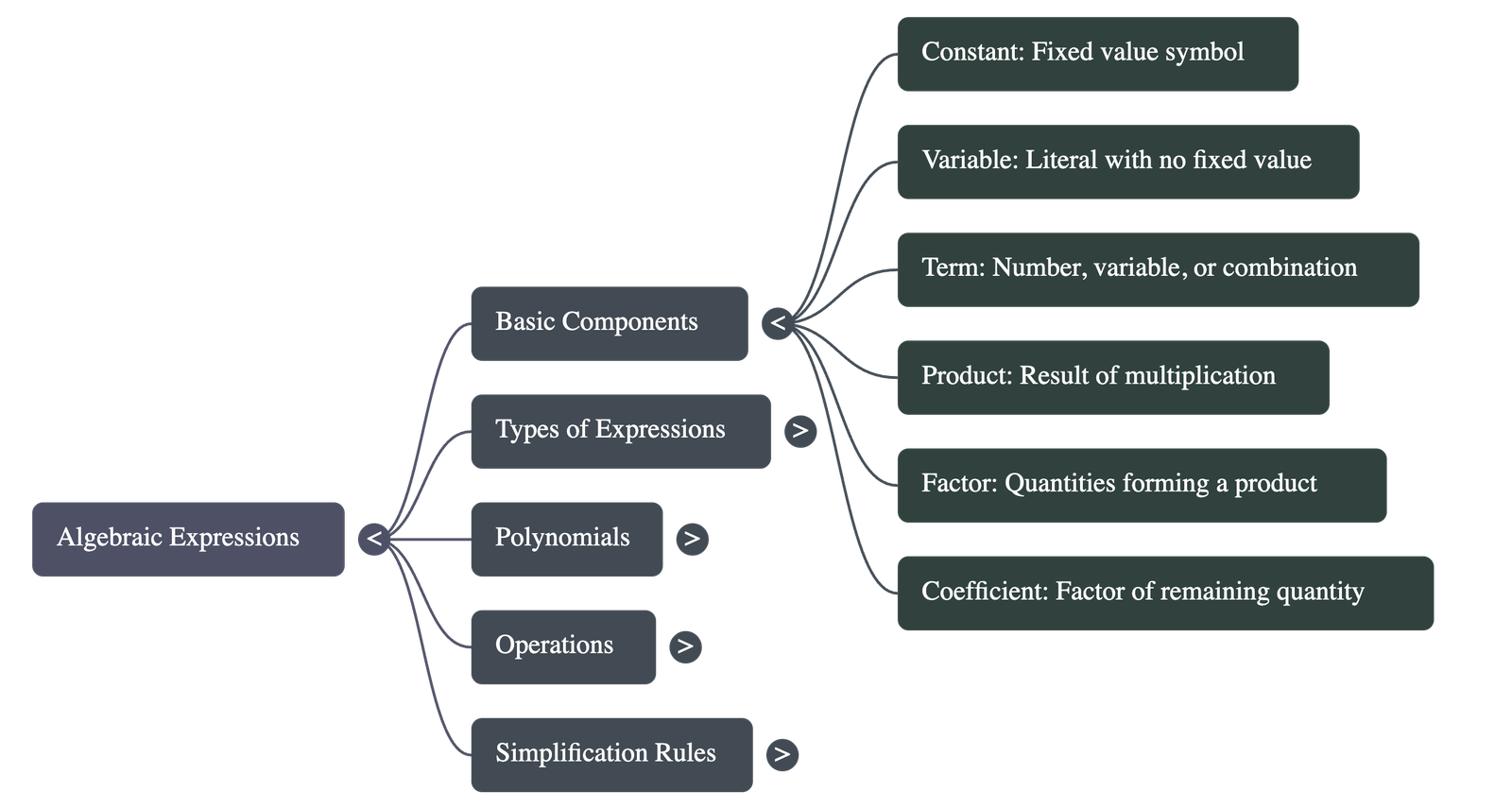
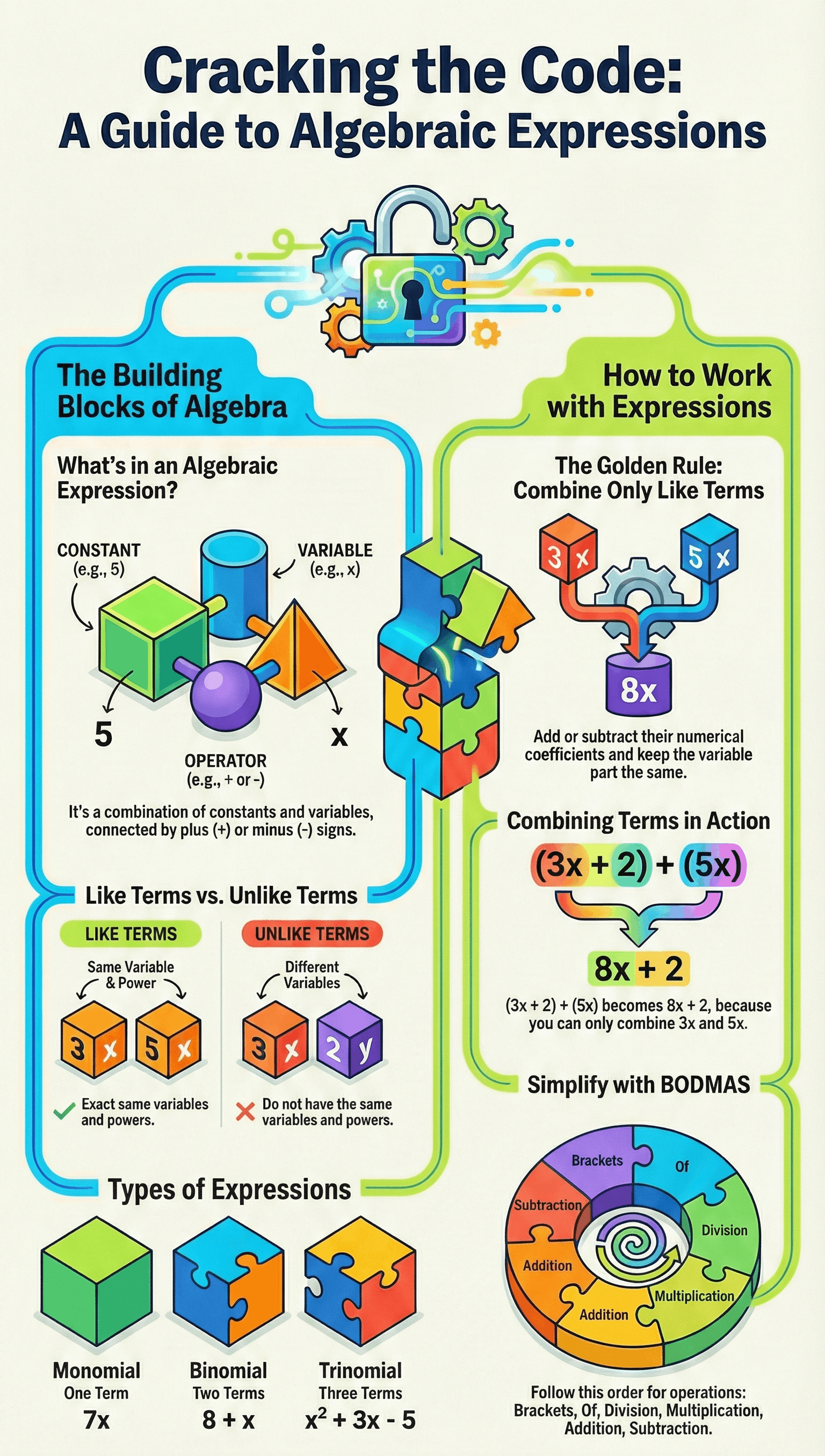
- Constants: Symbols that have a fixed numerical value (e.g., 8, -15, √3).
- Variables (Literals): Symbols that do not have a fixed value and can be assigned various values based on requirements (e.g., x, y, z).
- Terms: A number, a variable, or a combination of them in the form of a product or quotient (e.g., 7x, 3xy, -6/x).
2. Types of Algebraic Expressions
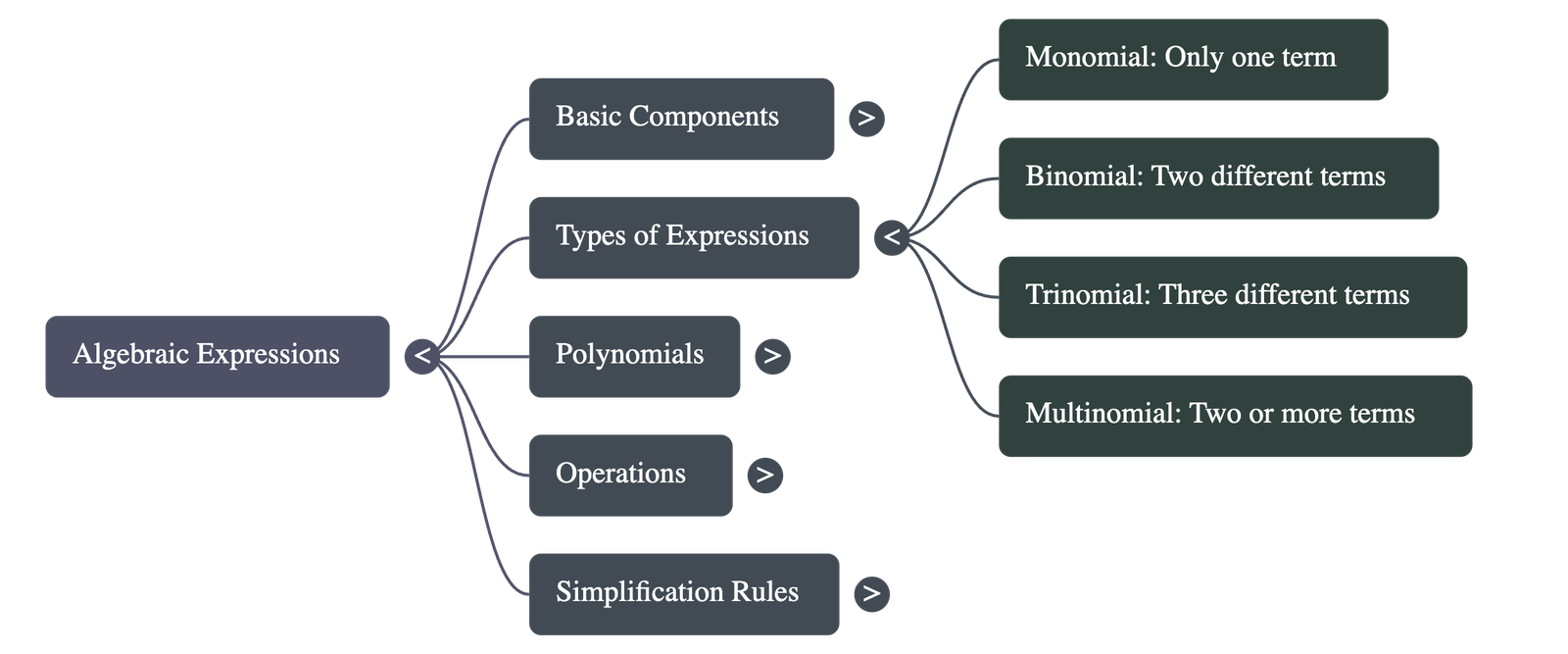
- Algebraic Expression: A collection of terms connected by addition (+) or subtraction (-) signs.
- Monomial: An expression containing only one term.
- Binomial: An expression containing exactly two different terms.
- Trinomial: An expression containing exactly three different terms.
- Multinomial: An expression containing two or more terms. Every binomial and trinomial is also a multinomial.
3. Concept of Polynomials
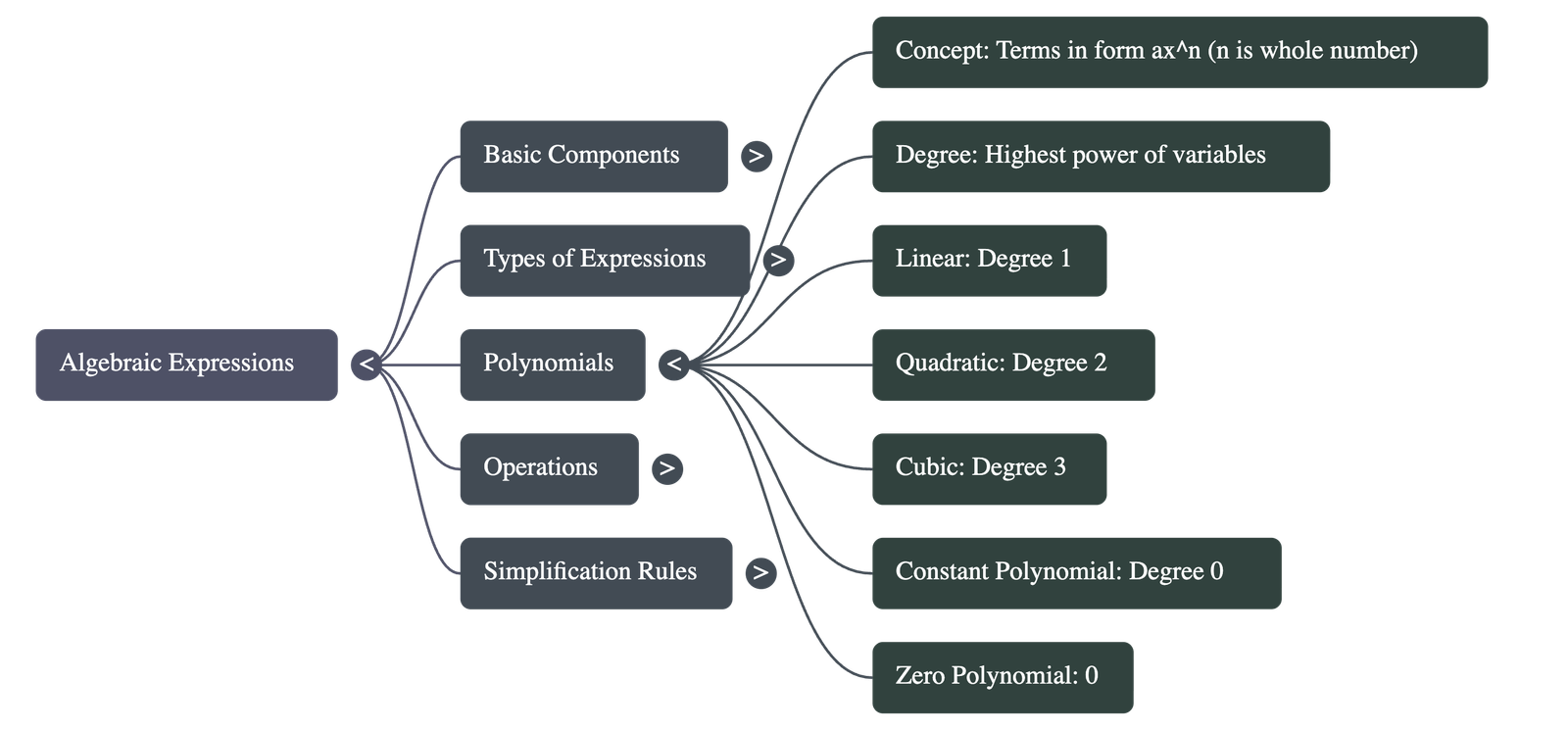
- Definition: An algebraic expression where each term follows the form axn, and n must be a whole number. If the exponent is negative or a fraction, it is not a polynomial.
- Degree of a Polynomial:
- For a single variable, it is the highest power of that variable.
- For multiple variables, it is the highest sum of the powers of variables in any single term.
- Classification by Degree:
- Linear: Degree 1
- Quadratic: Degree 2
- Cubic: Degree 3
- Constant: Degree 0
4. Factors and Coefficients
- Factors: Each quantity (constant or variable) that is multiplied to form a product. The constant part is the numeral factor, and the variable part is the literal factor.
- Coefficients: Any factor of a term is called the coefficient of the remaining part of that term.
- Like Terms: Terms that have the exact same literal coefficients (variables and powers). Only like terms can be added or subtracted.
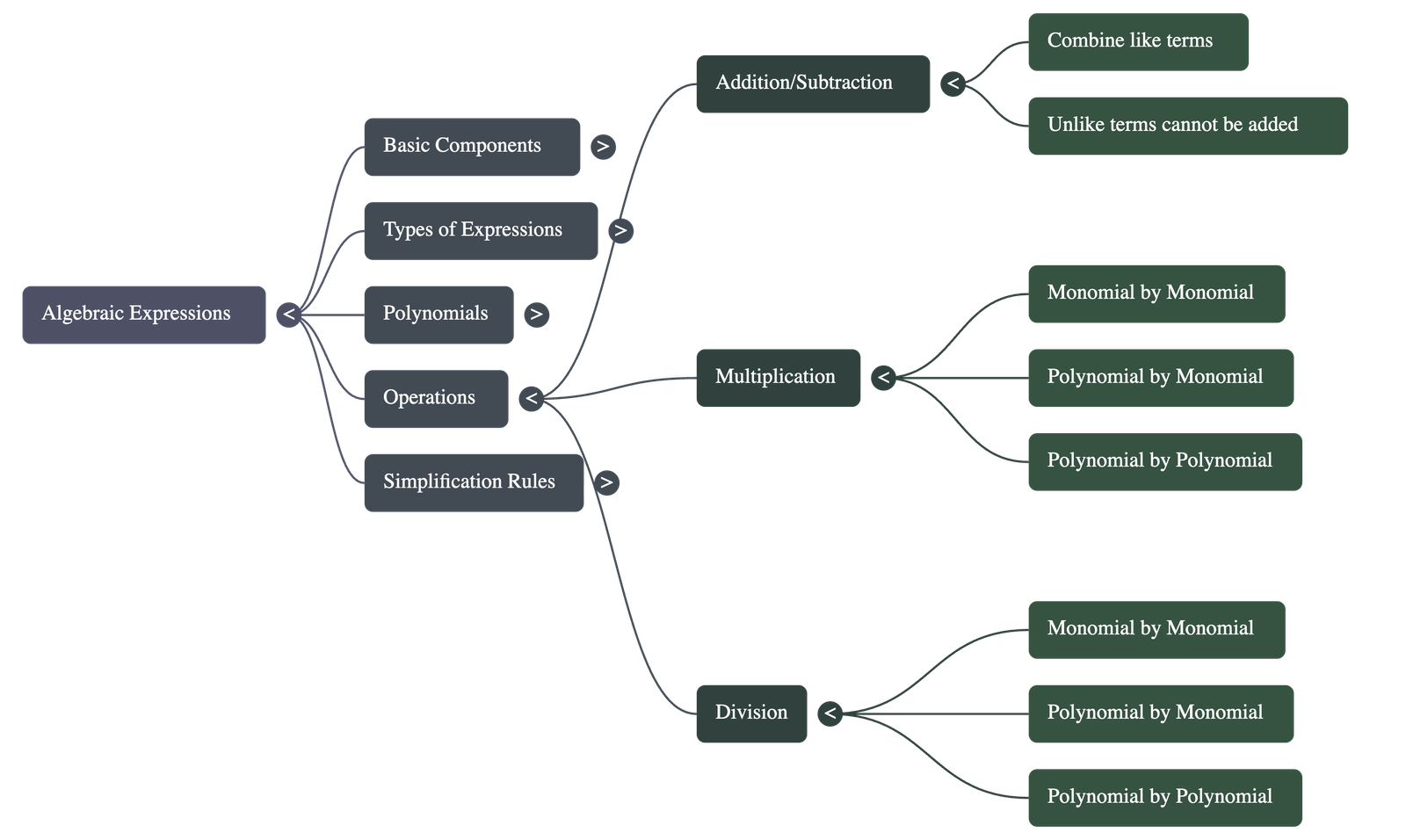
5. Basic Operations
- Addition & Subtraction: Performed by combining the numerical coefficients of like terms. Unlike terms must be kept separate.
- Multiplication:
- When multiplying literals, powers are added: xm × xn = xm+n.
- Polynomial multiplication involves multiplying each term of one expression by every term of the other.
- Division:
- When dividing literals, powers are subtracted: xm ÷ xn = xm-n.
- The relationship holds: Dividend = (Quotient × Divisor) + Remainder.
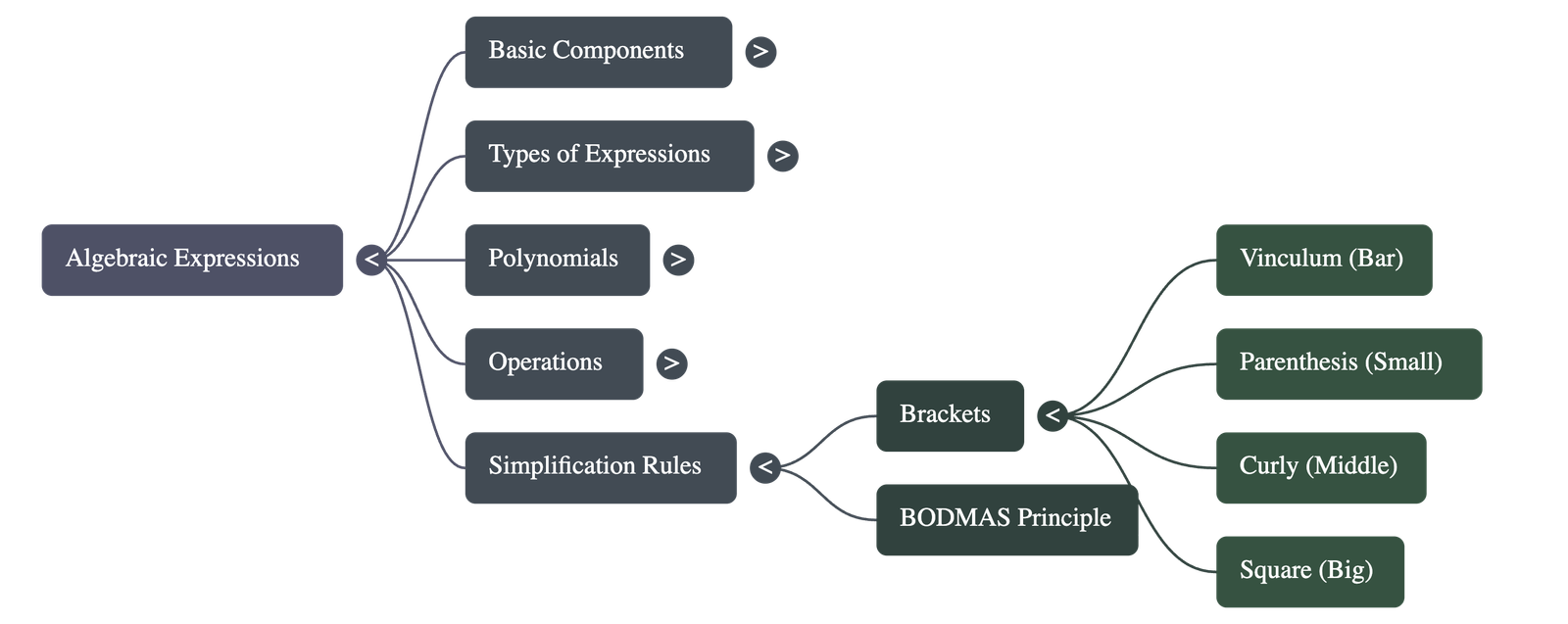
6. Simplification and BODMAS
- Brackets: Operations must follow a specific order of removal: 1. Vinculum (bar), 2. Parenthesis (round), 3. Curly brackets, 4. Square brackets.
- BODMAS Principle: The order of operations is Brackets, Of, Division, Multiplication, Addition, and Subtraction.
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |