Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Rational Numbers - Summary
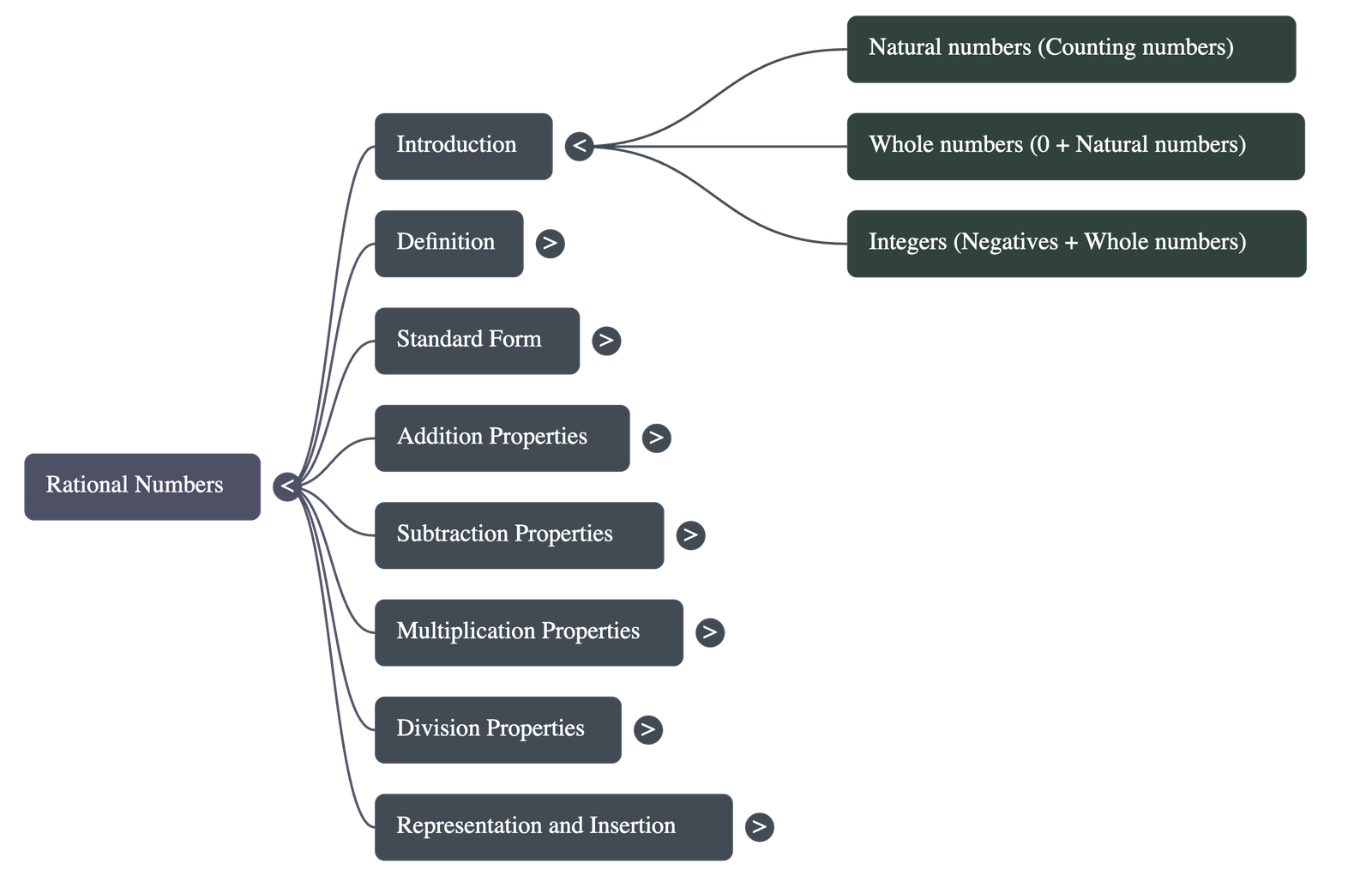
- Basic Number Categories and Definitions
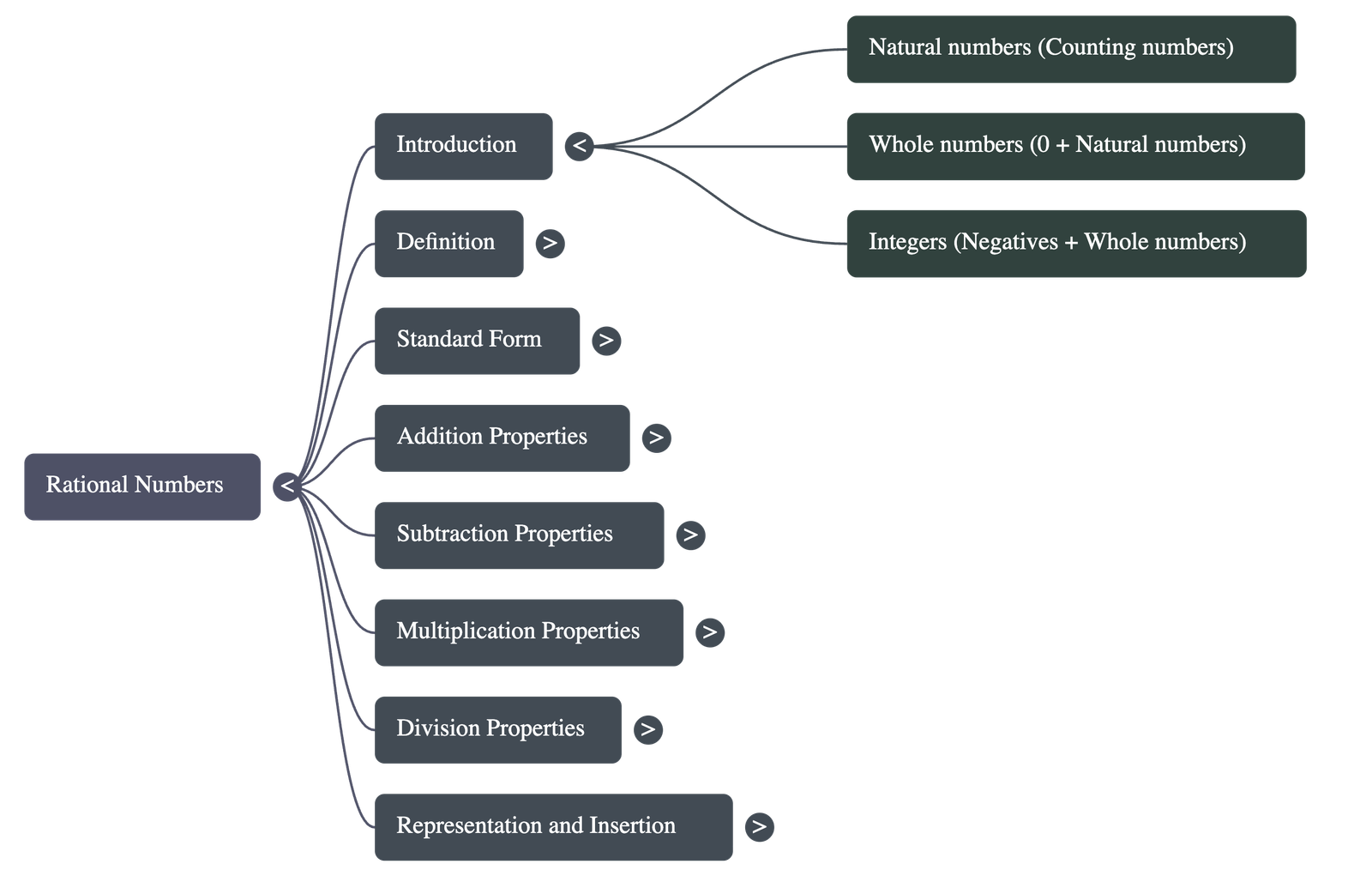
- Natural Numbers: These are counting numbers like 1, 2, 3, 4, 5....
- Whole Numbers: Includes 0 (zero) along with all natural numbers.
- Integers: Consist of negative natural numbers combined with whole numbers.
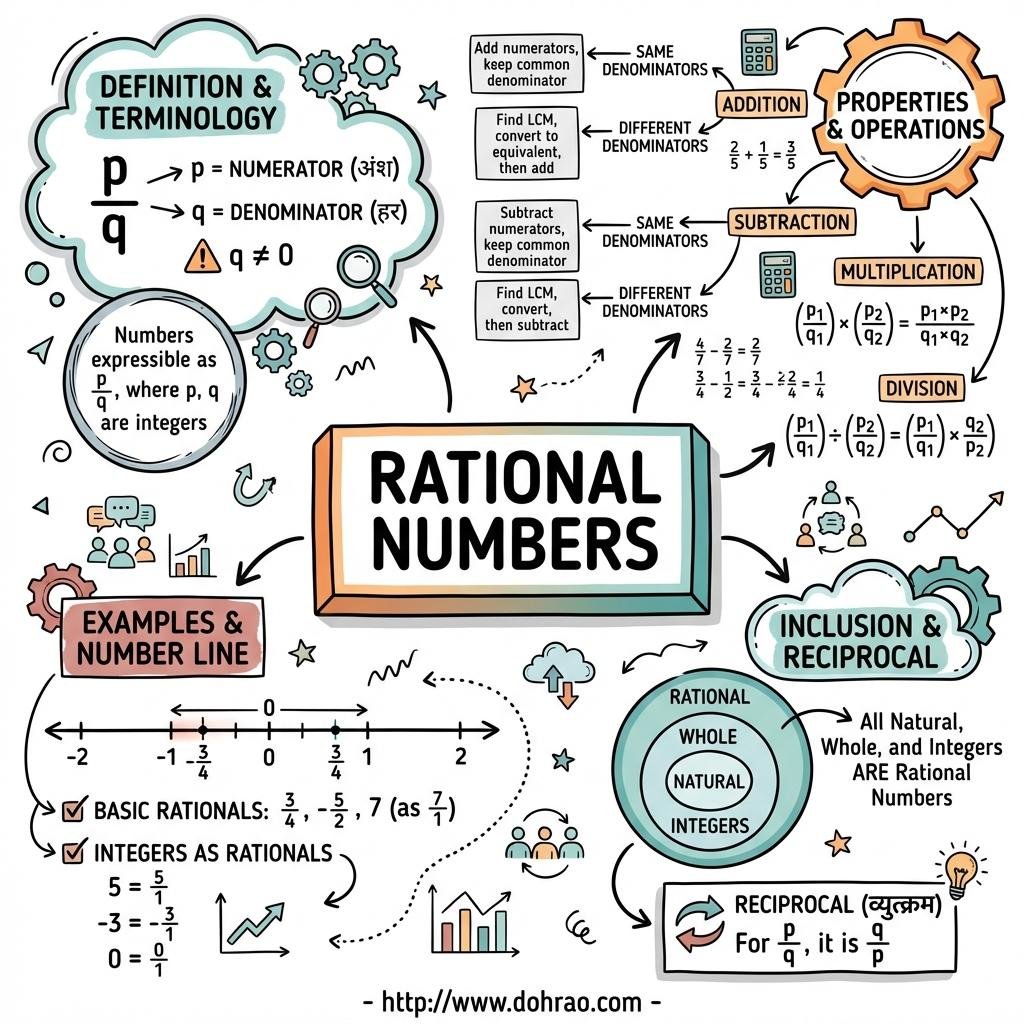
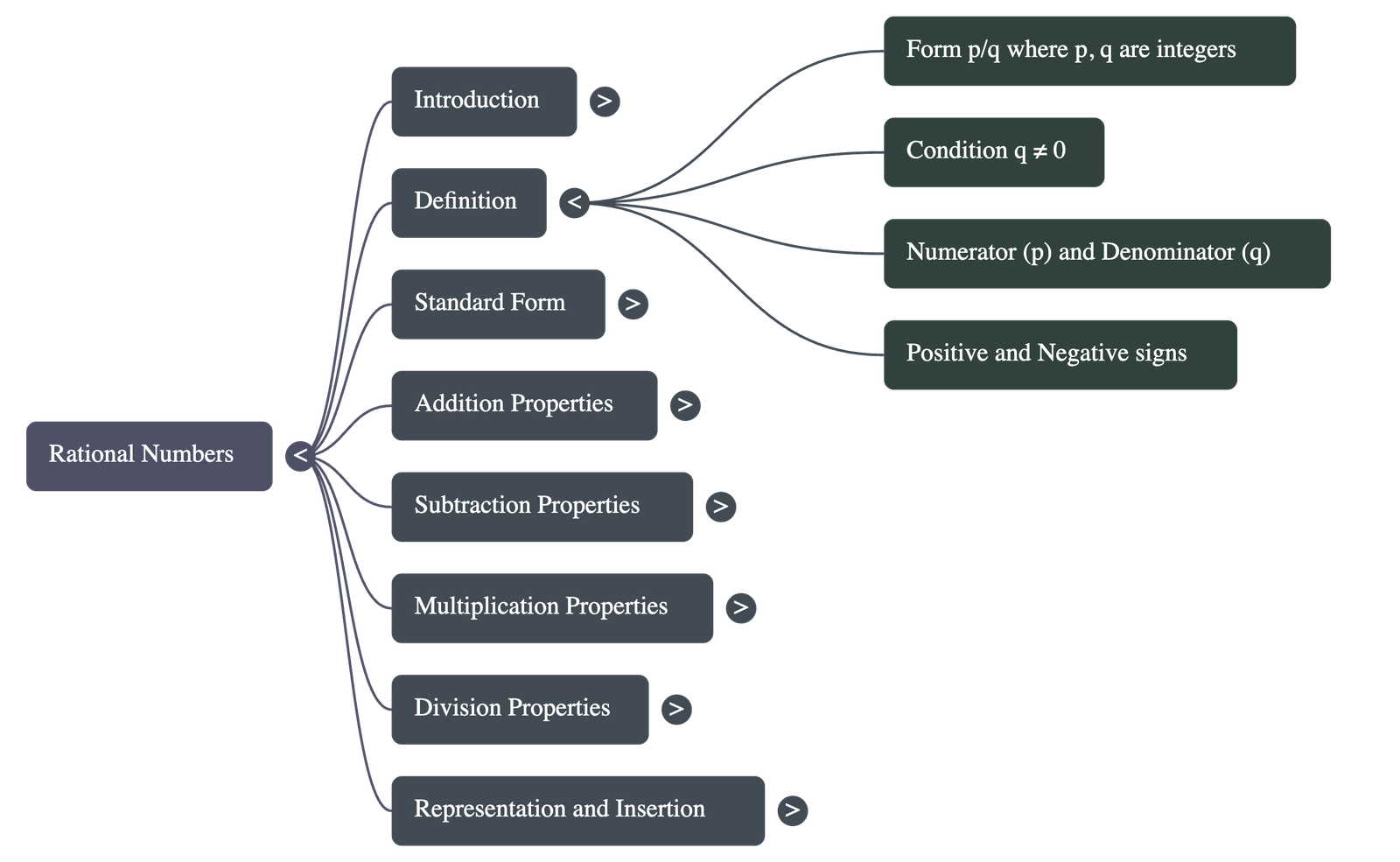
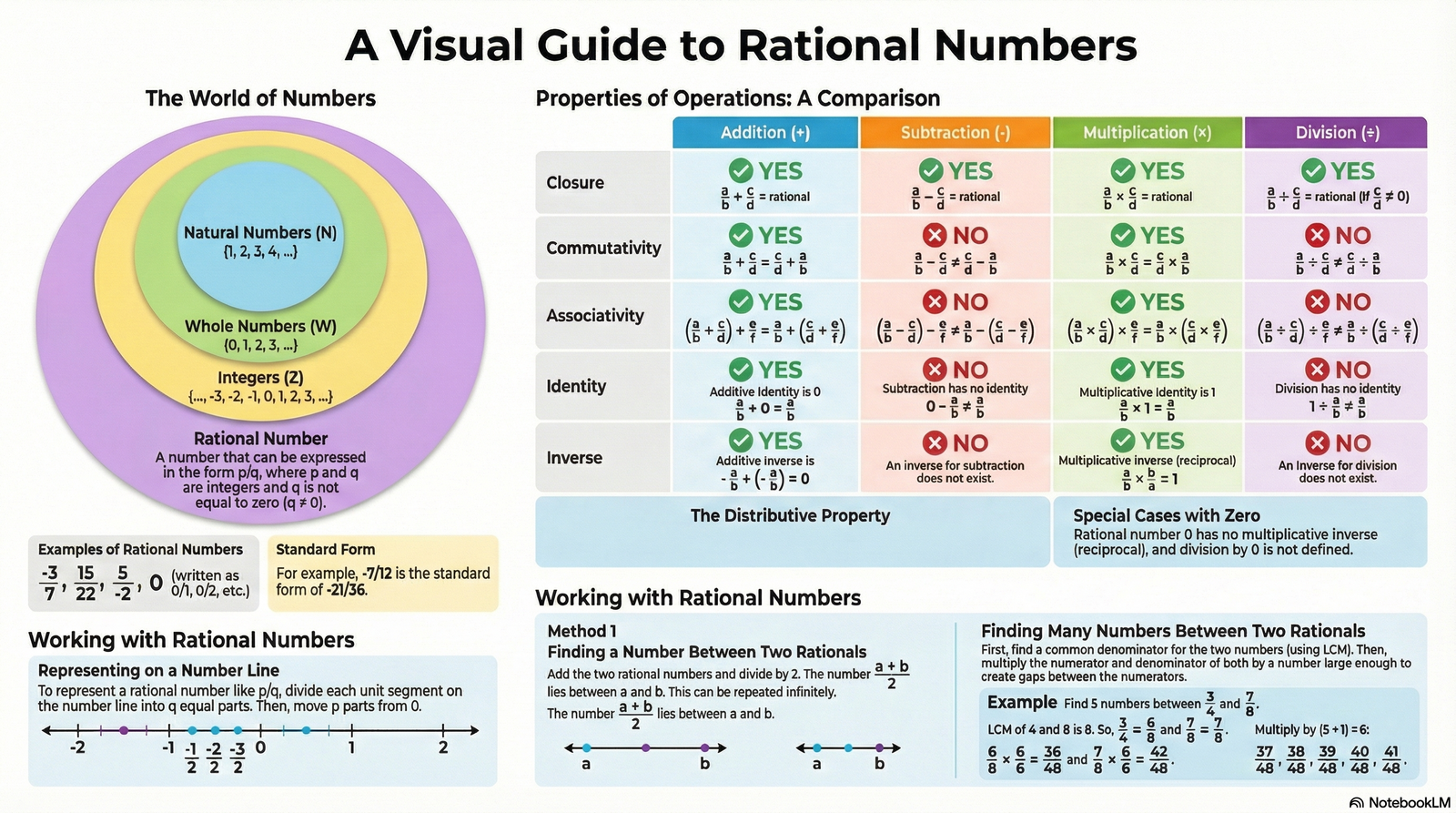
- Rational Numbers: Any number that can be expressed in the form q p , where p and q are integers and q =0.
- Inclusions: Every natural number, whole number, integer, and fraction is a rational number; zero (0) is also a rational number because it can be written as 1 0 , 5 0 , etc.
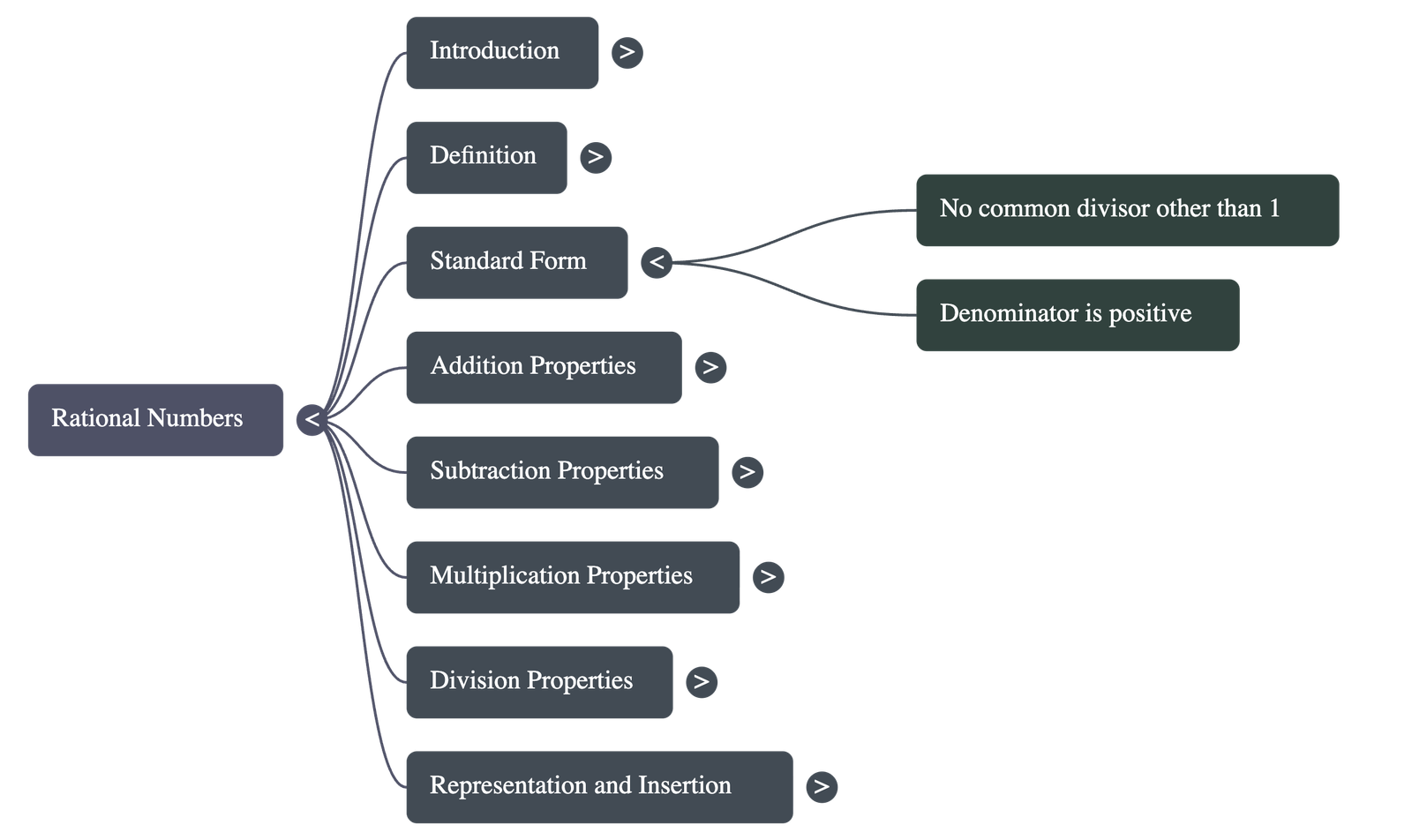
- Standard Form: A rational number is in standard form if p and q have no common divisor other than 1 and the denominator q is positive.
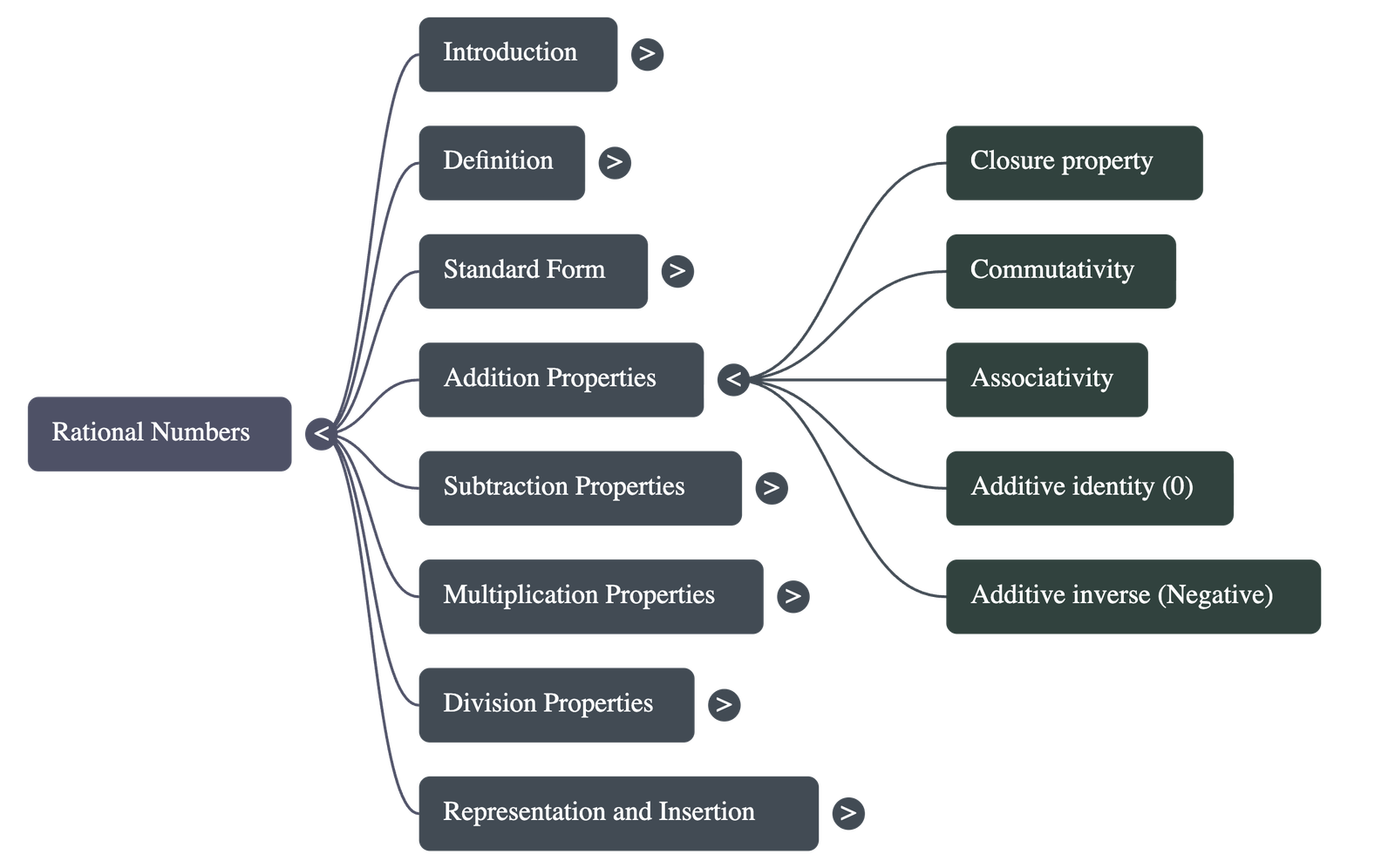
- Properties of Addition
- Closure: The sum of two rational numbers is always a rational number.
- Commutativity: The order of addition does not matter: b a + d c = d c + b a .
- Associativity: The grouping of numbers does not change the sum.
- Additive Identity: Zero (0) is the identity element; adding it to any rational number leaves the number unchanged.
- Additive Inverse: Every rational number b a has an inverse − b a such that their sum is zero.
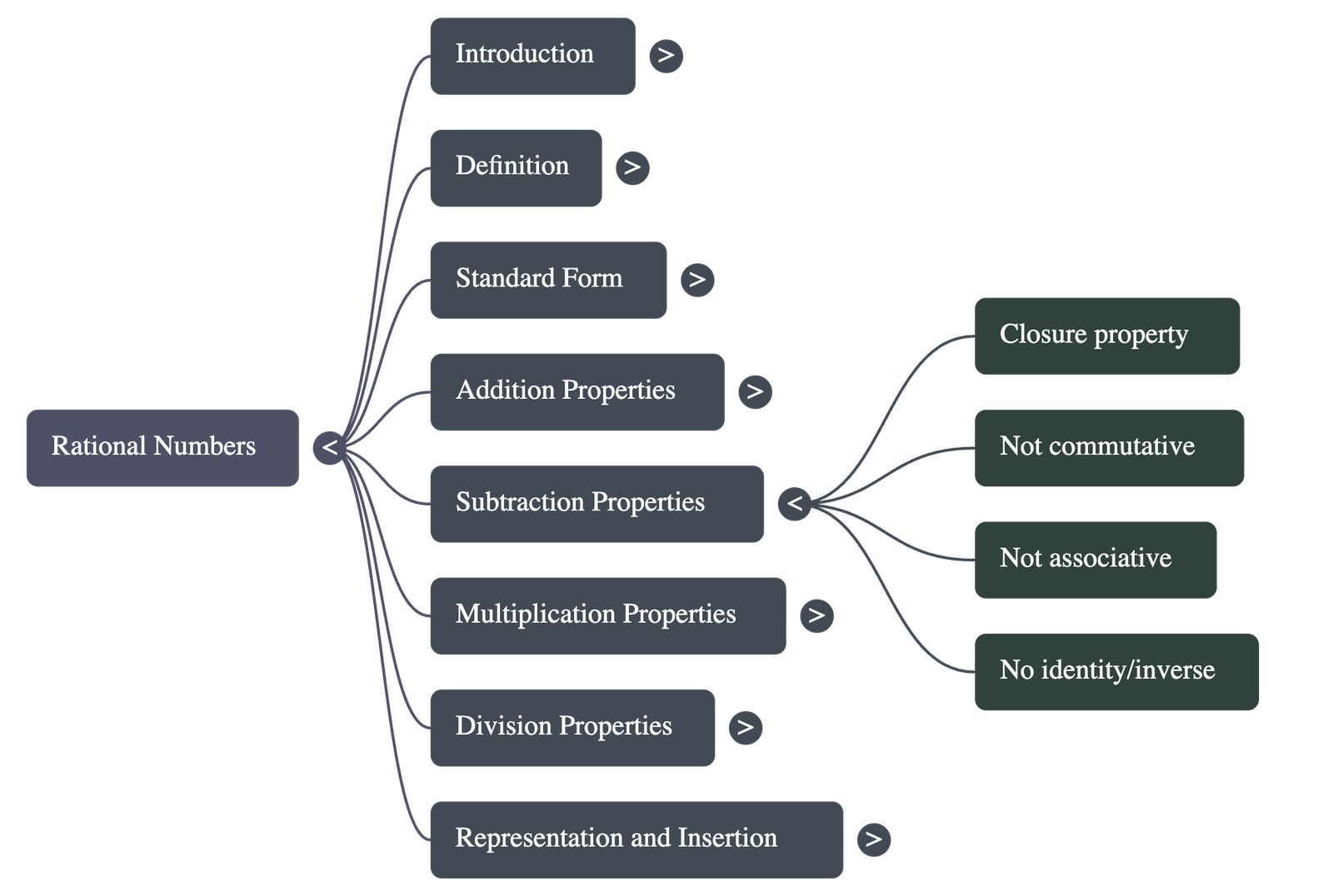
- Properties of Subtraction
- Closure: Subtraction of two rational numbers results in a rational number.
- Non-Commutative and Non-Associative: Unlike addition, the order and grouping of numbers do matter in subtraction.
- Identity/Inverse: Subtraction has no general identity element and no existence of inverse.
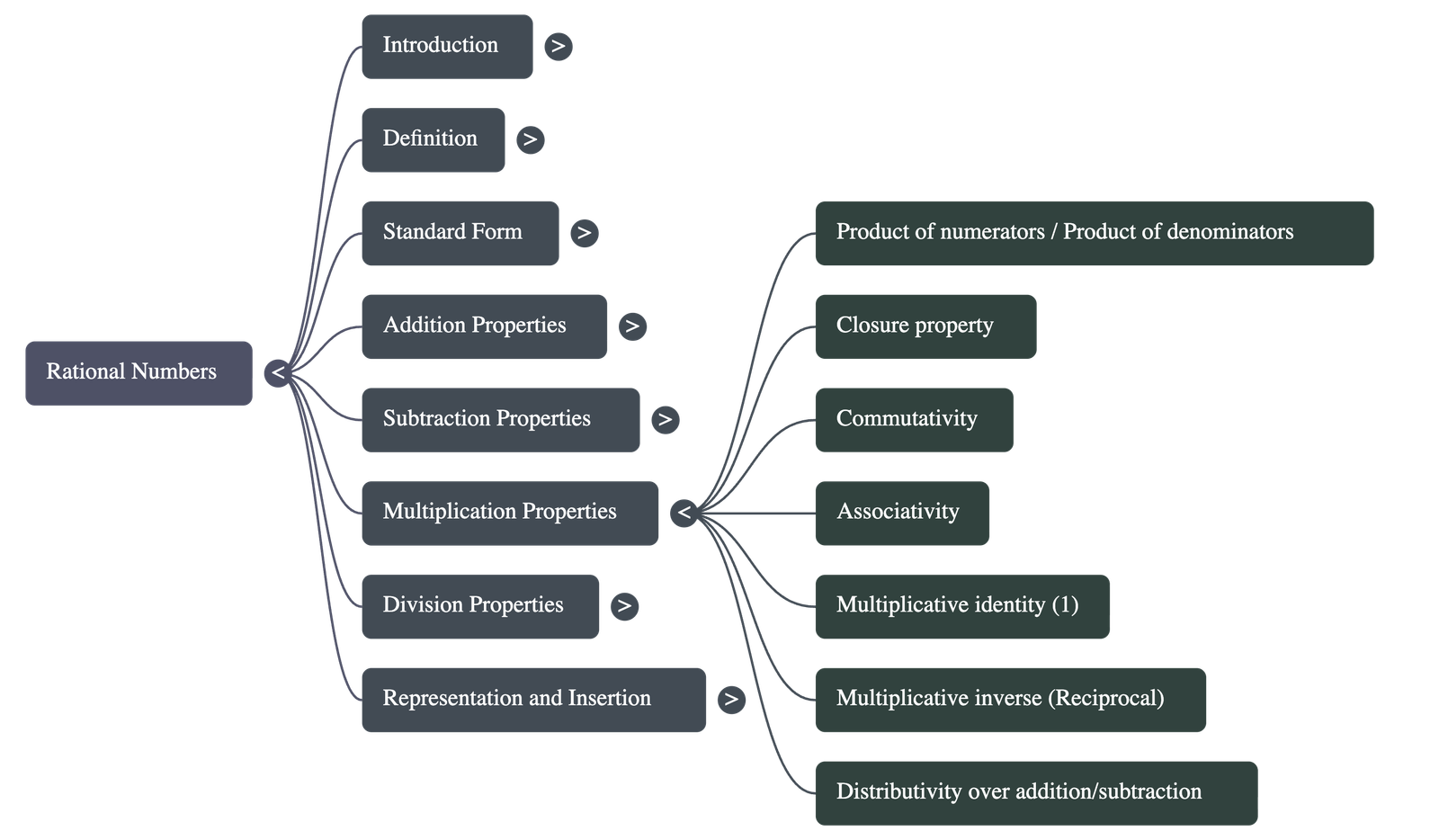
- Properties of Multiplication
- Calculation: The product is found by multiplying the numerators together and the denominators together.
- Closure: The product of two rational numbers is always a rational number.
- Commutativity and Associativity: Multiplication follows both properties, meaning order and grouping do not affect the result.
- Multiplicative Identity: One (1) is the multiplicative identity.
- Multiplicative Inverse (Reciprocal): For a non-zero rational number
b
a
, the reciprocal is
a
b
. Their product is 1.
- Note: Zero (0) has no multiplicative inverse.
- Distributivity: Multiplication is distributive over both addition and subtraction.
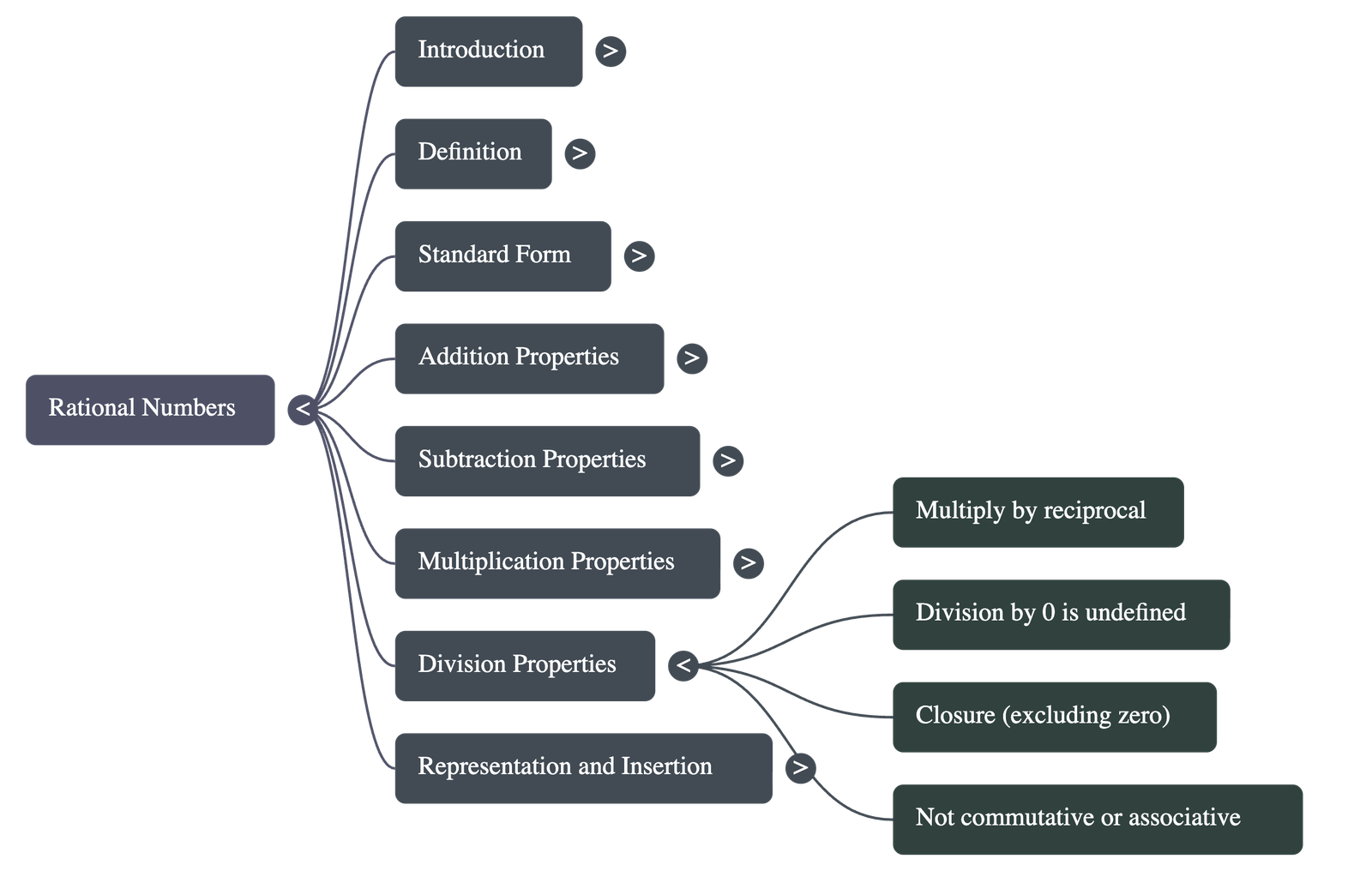
- Properties of Division
- Calculation: Dividing by a rational number is equivalent to multiplying by its reciprocal.
- Division by Zero: Division by zero is not defined.
- Non-Commutative and Non-Associative: Division does not follow these properties.
- Closure: Division is closed for all rational numbers except when dividing by zero.
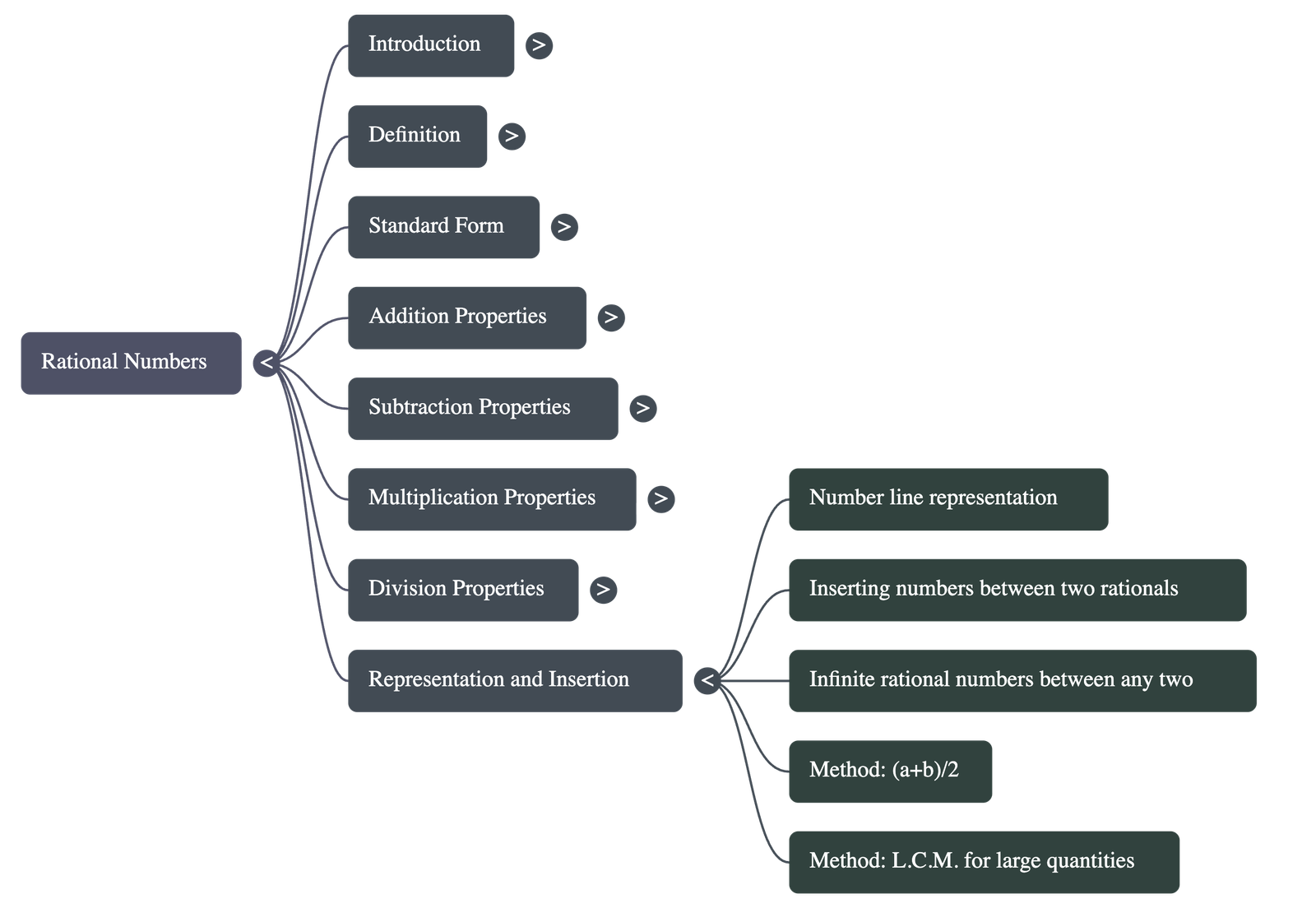
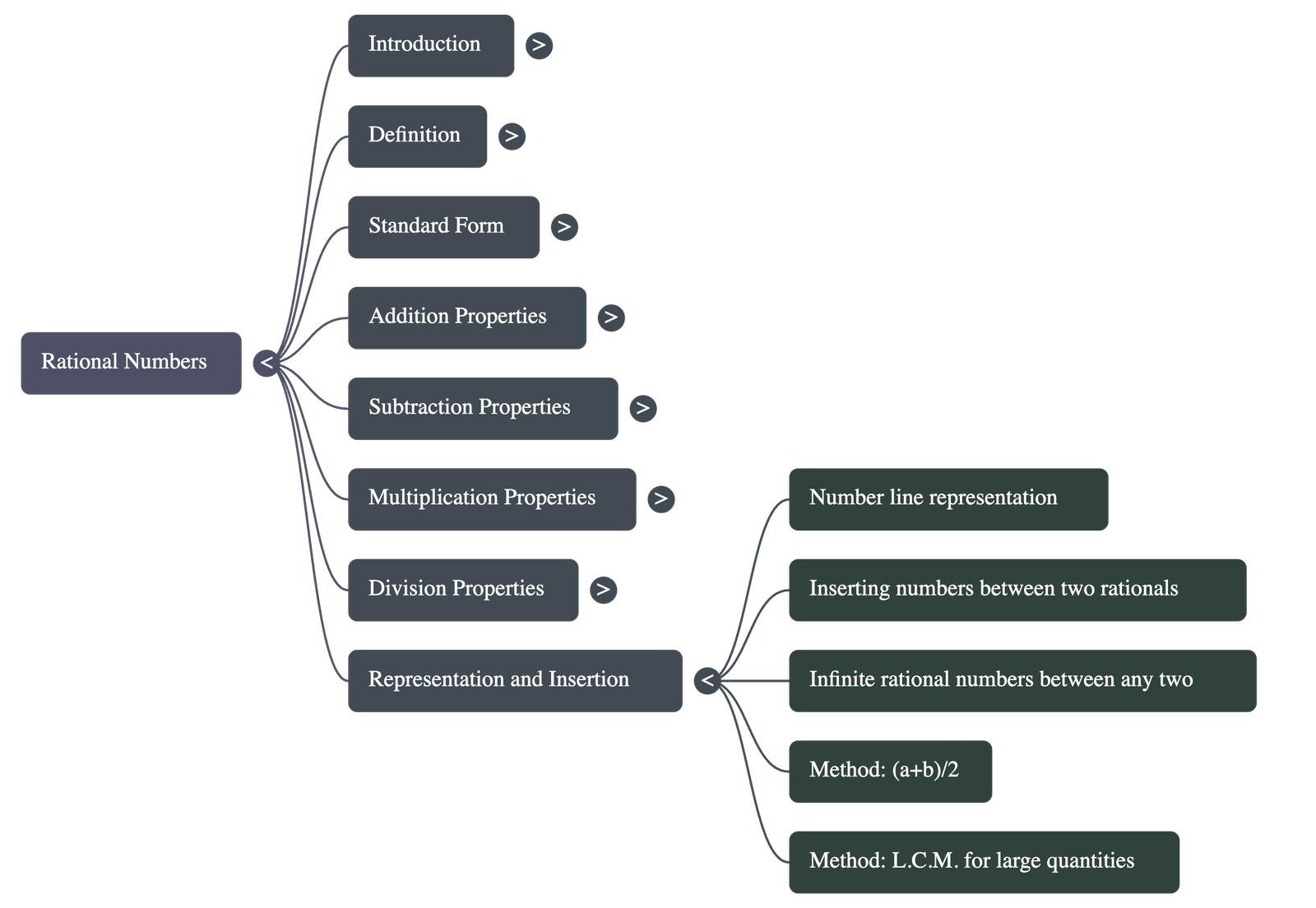
- Representation and Insertion
- Number Line: Rational numbers can be represented on a number line by dividing the distance between integers into equal parts based on the denominator.
- Density: There are infinitely many rational numbers between any two given rational numbers.
- Finding Numbers Between:
- One method is using the average: 2 a+b .
- Another method for finding many numbers involves making the denominators equal (using LCM) and then increasing the numerator and denominator to create a larger range.
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |