Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
1. Multiplication of Binomials
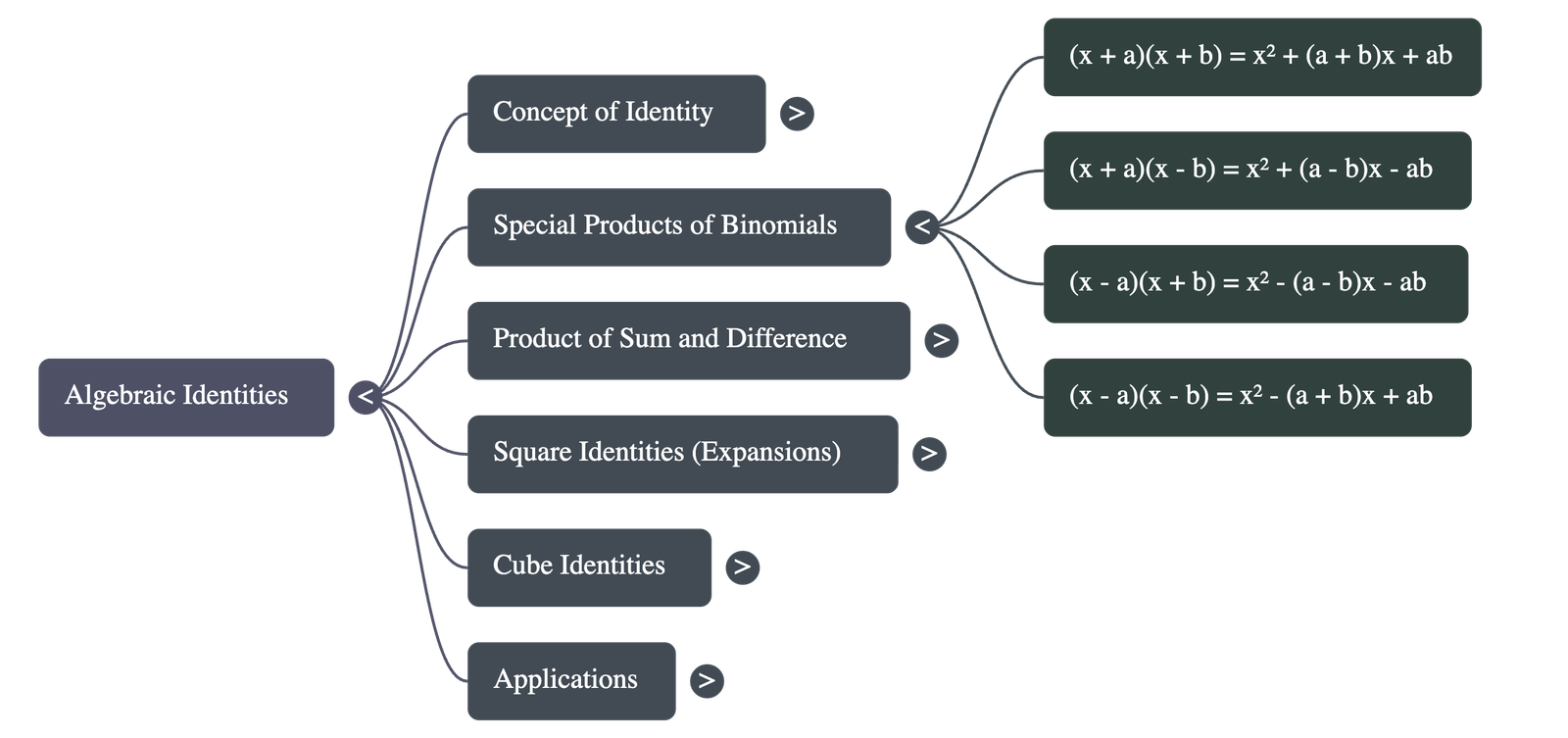
- Direct Multiplication: Binomials can be expanded by distributing each term of the first expression into the second. For example, (x - a)(x + b) = x² + (b - a)x - ab.
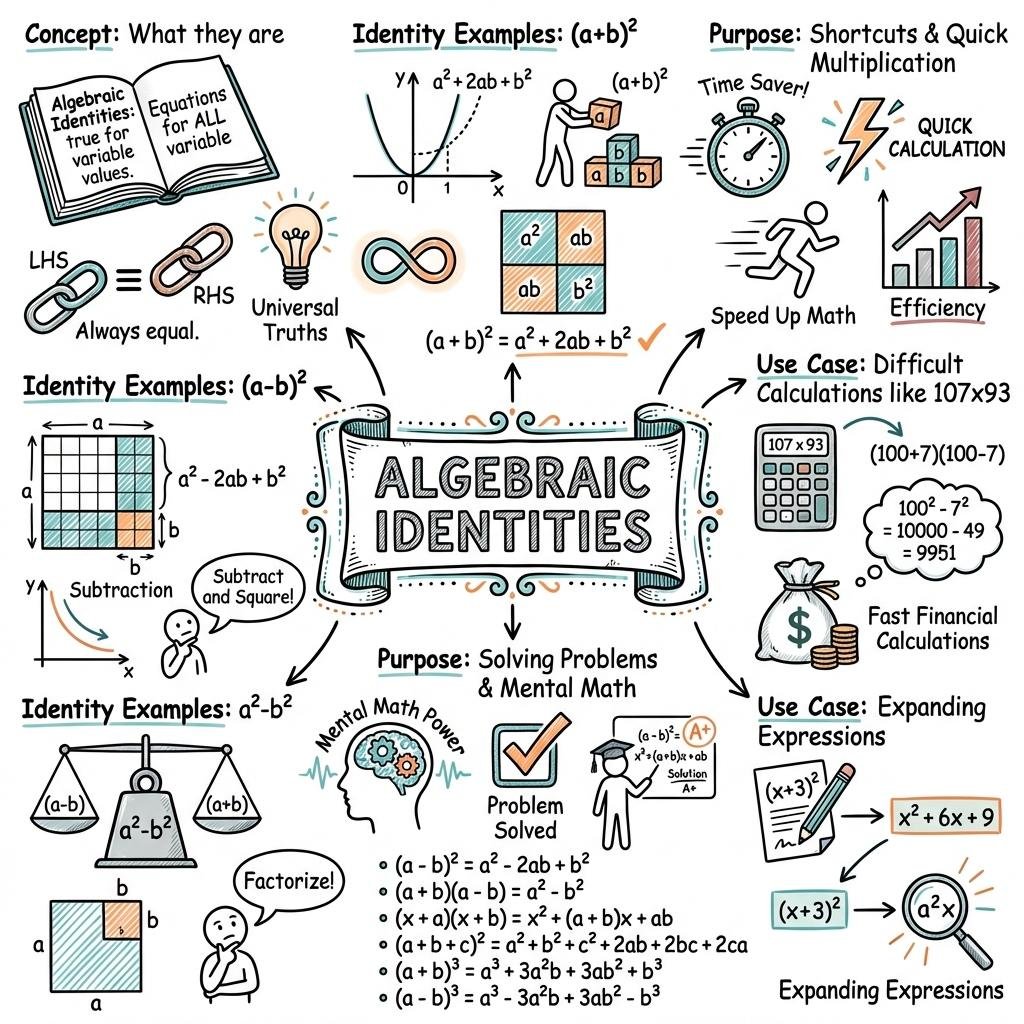
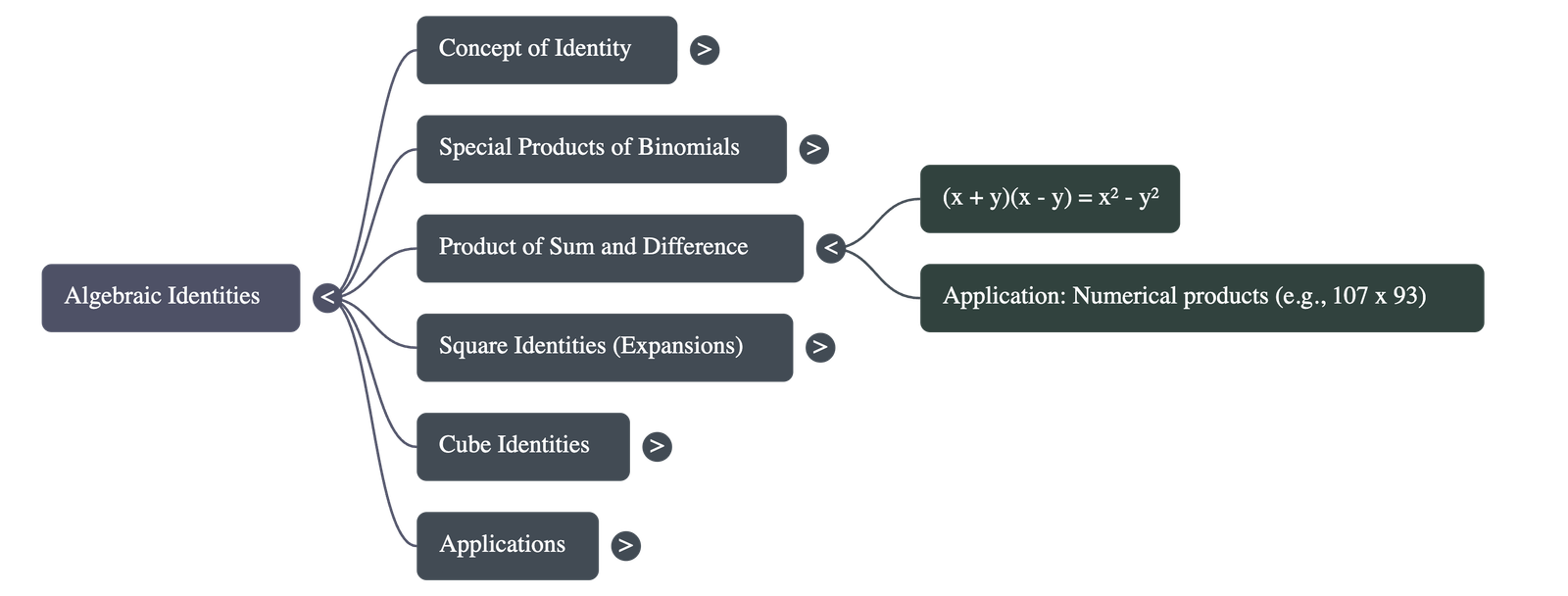
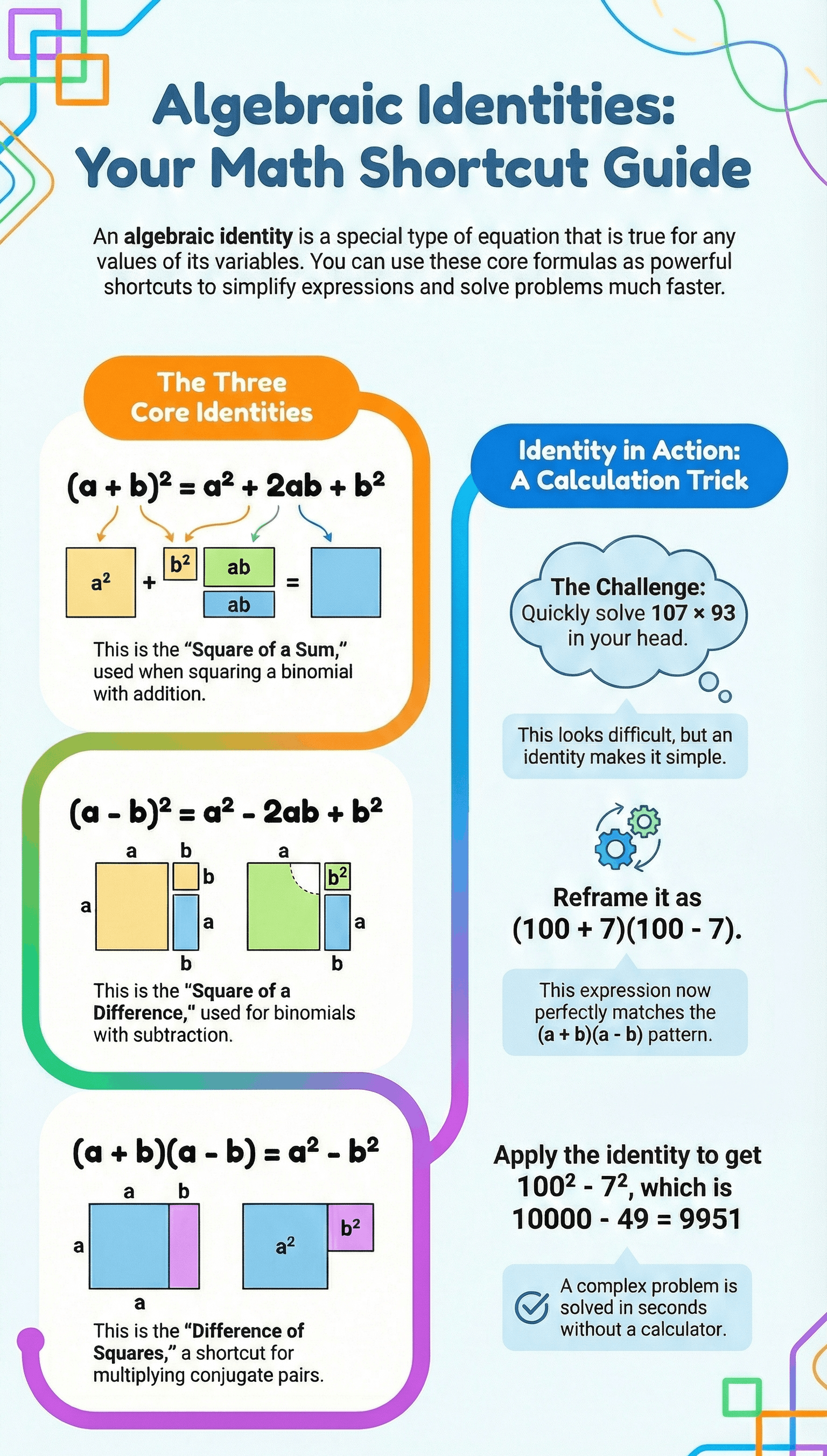
- Product of Sum and Difference: A fundamental identity where the product of the sum and difference of two terms equals the difference of their squares: (x + y)(x - y) = x² - y².
2. Squaring Identities (Expansions)
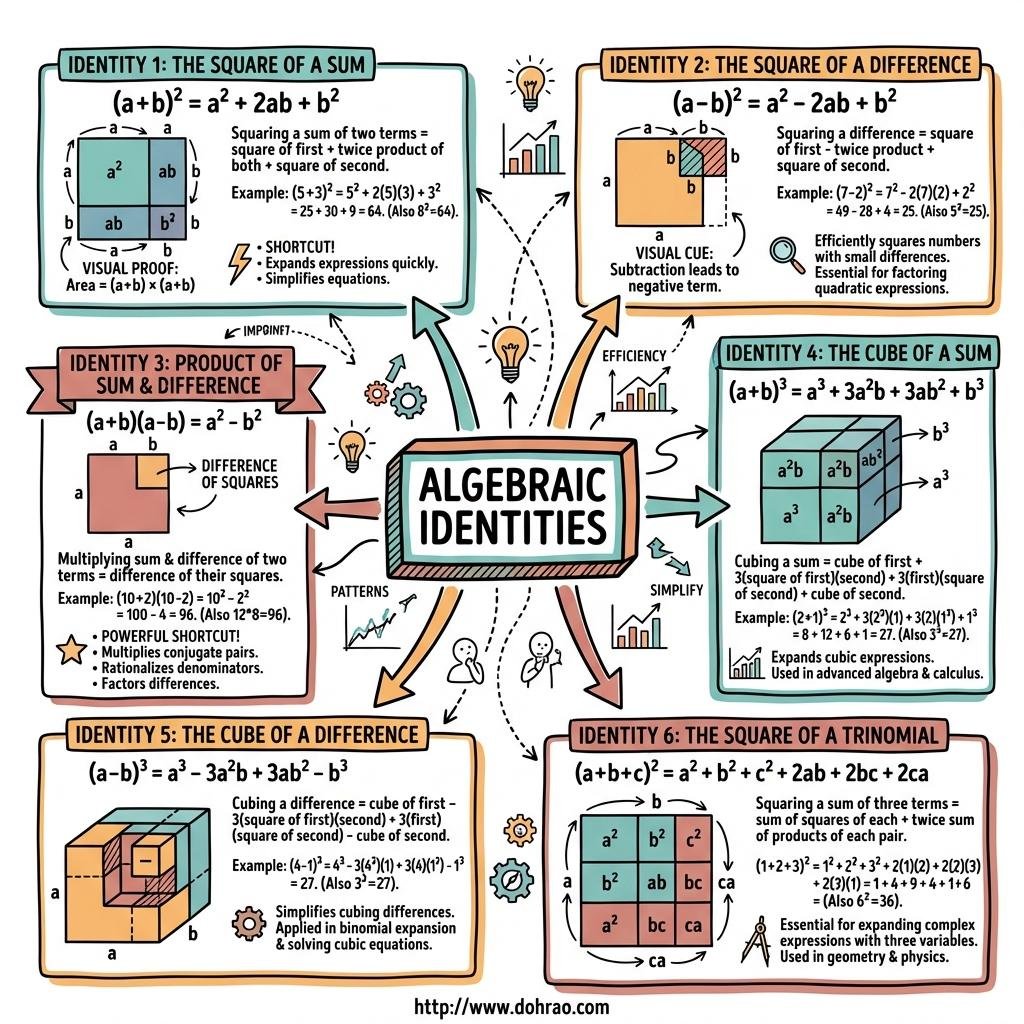
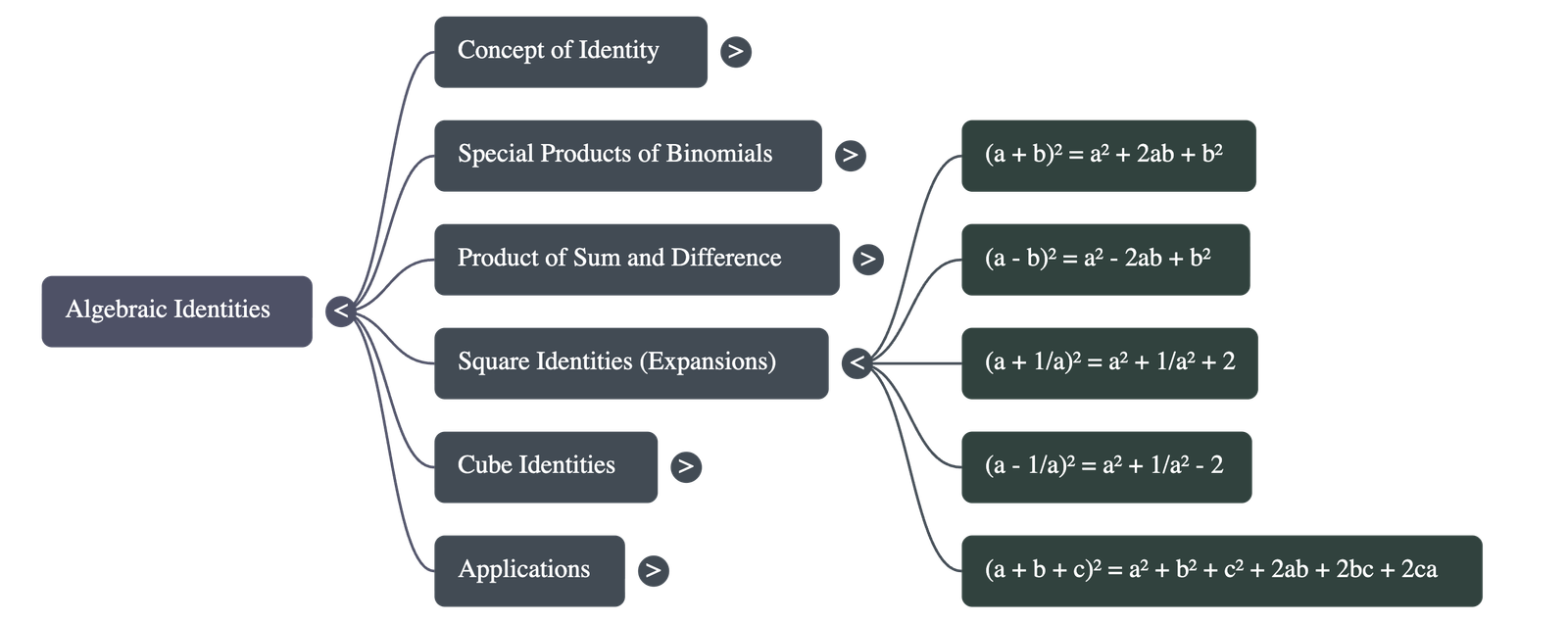
- Square of a Sum: The expansion follows the pattern (a + b)² = a² + 2ab + b².
- Square of a Difference: The expansion follows the pattern (a - b)² = a² - 2ab + b².
- Reciprocal Squares: Special cases involving a variable and its reciprocal include:
- (a + 1/a)² = a² + 1/a² + 2
- (a - 1/a)² = a² + 1/a² - 2
3. Squaring Trinomials
- Expansion of (a + b + c)²: When squaring a three-term expression, the result is the sum of the squares of each term plus twice the product of each pair: a² + b² + c² + 2ab + 2bc + 2ca.
- Variations in Signs: If a term in the trinomial is negative, such as (a + b - c)², the signs of the pair-products involving that term change accordingly (e.g., a² + b² + c² + 2ab - 2bc - 2ca).
4. Cubes of Binomials
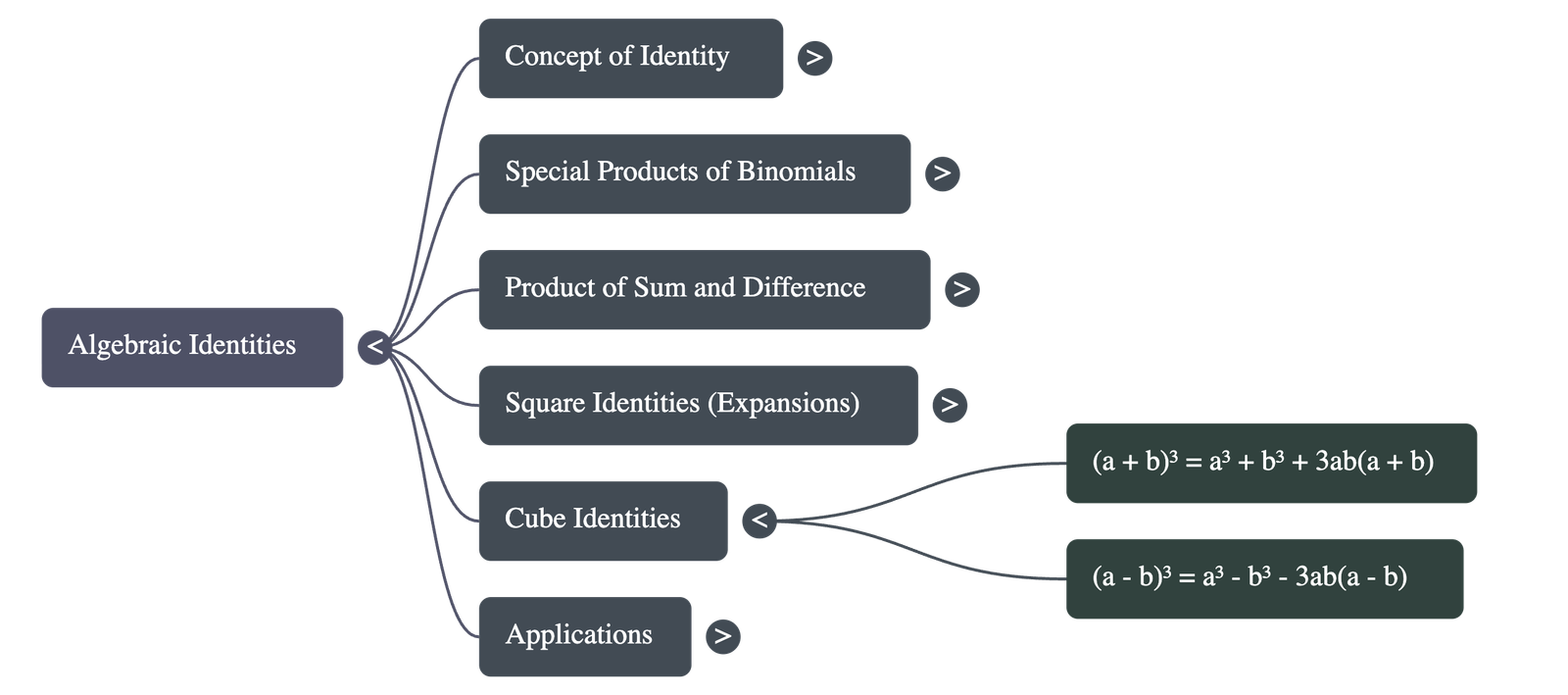
- Cube of a Sum: Expanded as (a + b)³ = a³ + 3a²b + 3ab² + b³, which can also be written as a³ + b³ + 3ab(a + b).
- Cube of a Difference: Expanded as (a - b)³ = a³ - 3a²b + 3ab² - b³, which can also be written as a³ - b³ - 3ab(a - b).
5. Practical Applications
- Numerical Calculations: Identities are used to simplify mental math, such as calculating 107 × 93 by treating it as (100 + 7)(100 - 7) = 100² - 7².
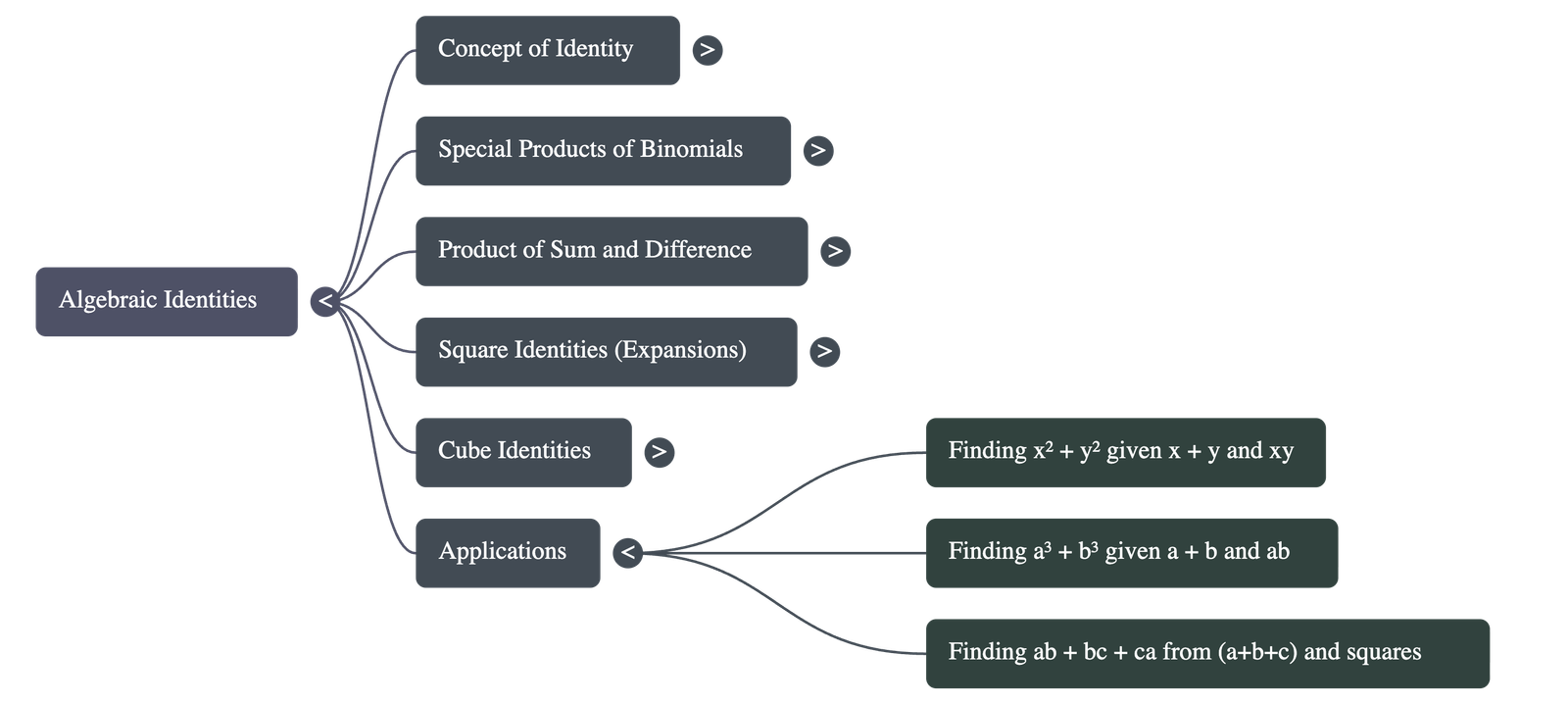
- Value Finding: Using known values like a + b and ab to find unknown expressions like a² + b² or a³ + b³ without finding the individual values of 'a' and 'b'.
- Simplification: Algebraic identities help in simplifying complex expressions and proving equality between different mathematical statements.
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |