Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Chapter 22: Area of a Trapezium and a Polygon
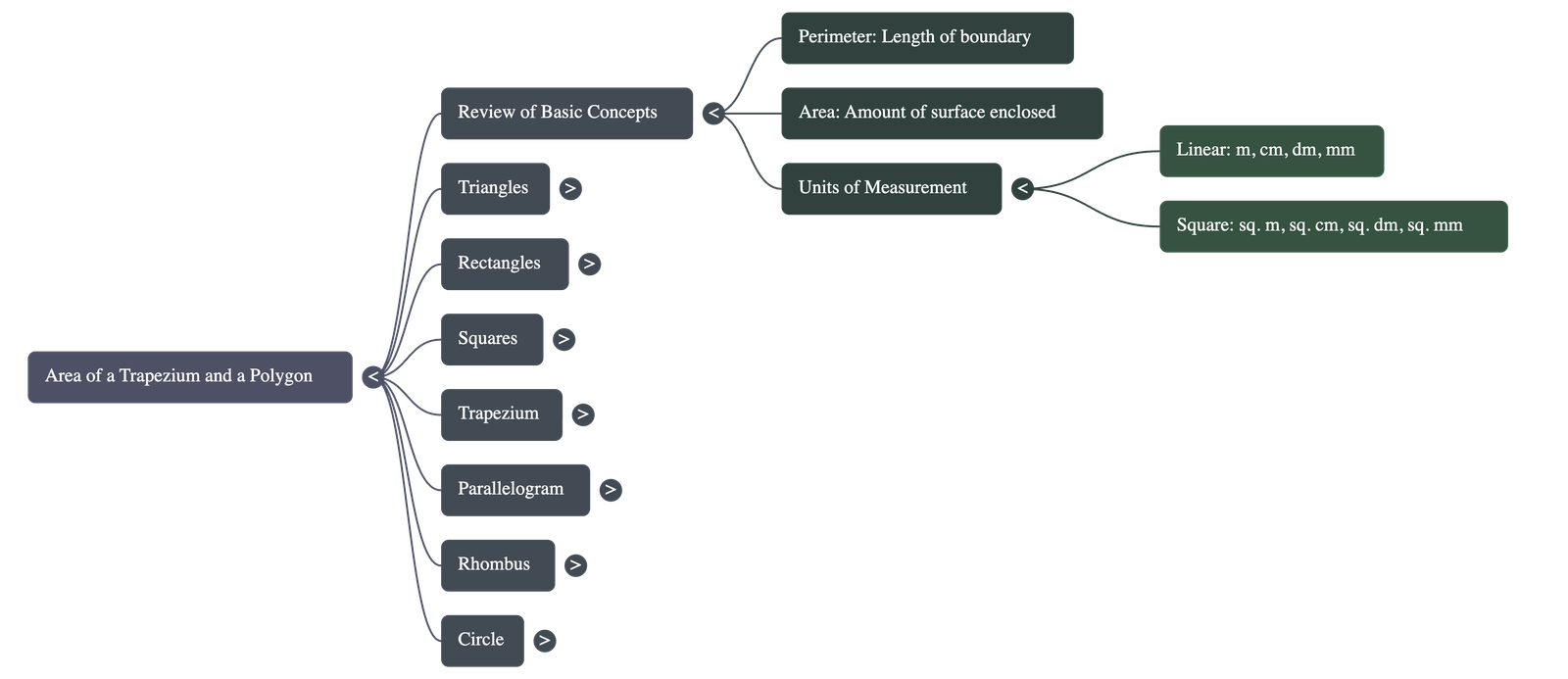
1. Fundamentals of Mensuration
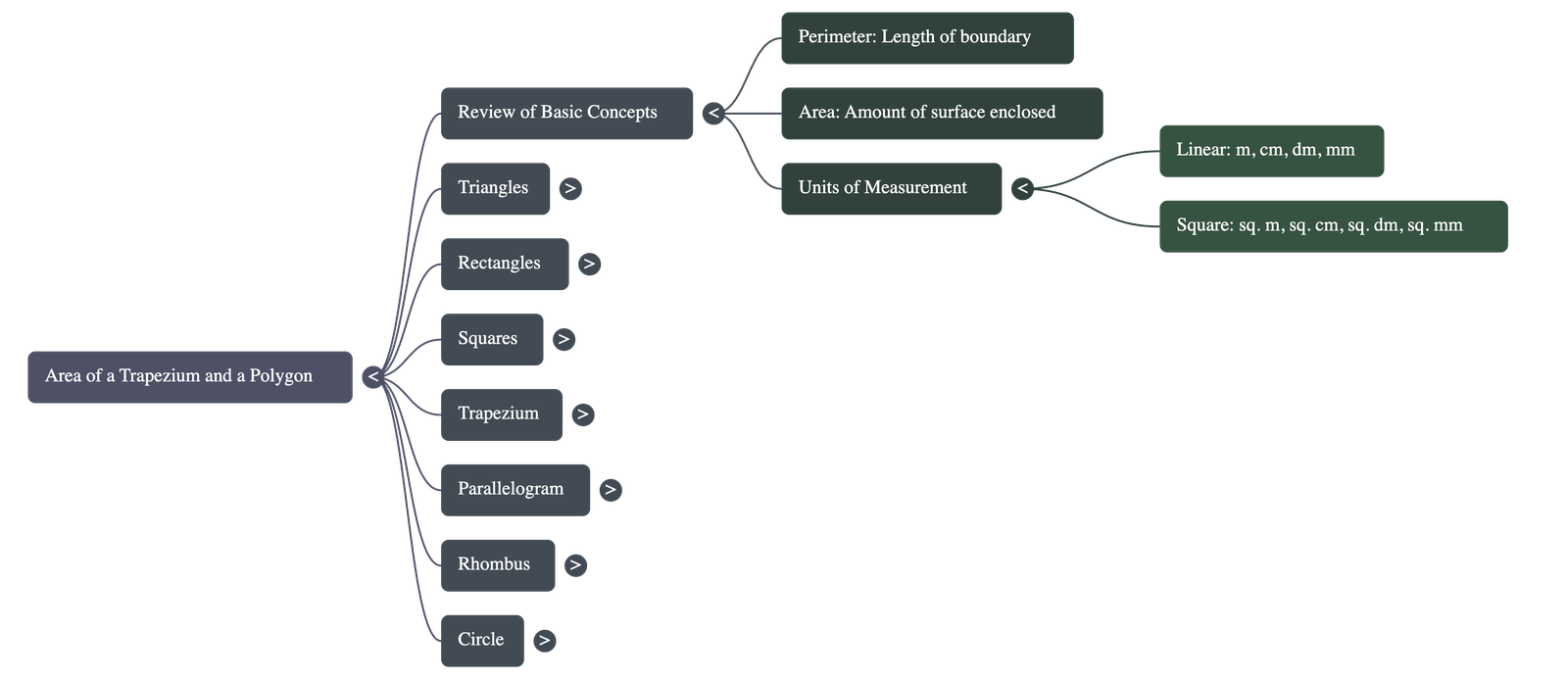
- Perimeter is defined as the total length of the boundary of a plane figure.
- Area represents the total amount of surface enclosed by the boundaries of a figure.
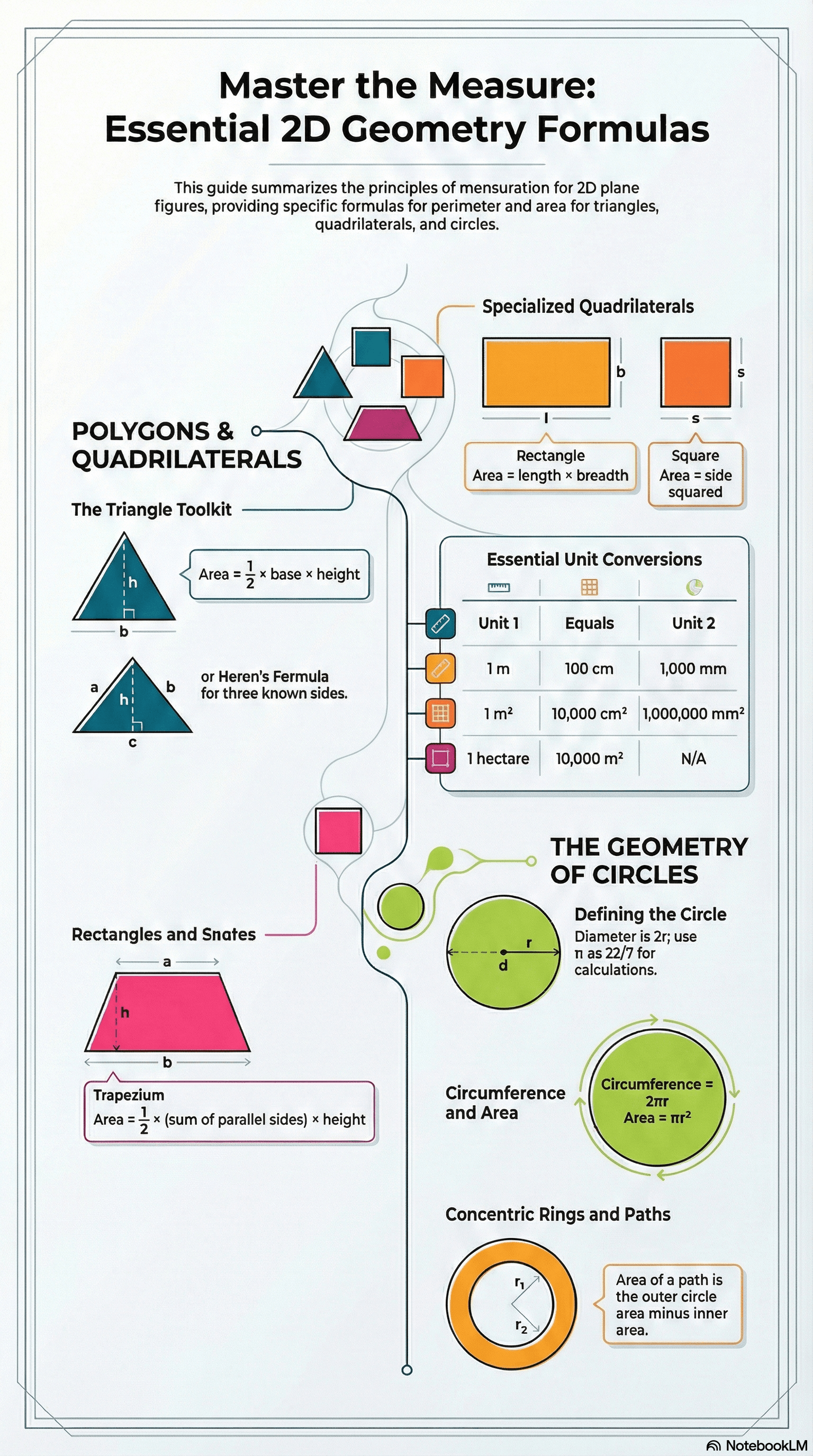
- Standard units for length include metres (m), centimetres (cm), millimetres (mm), and decimetres (dm).
- Area is measured in square units, such as square metres (m²) or square centimetres (cm²).
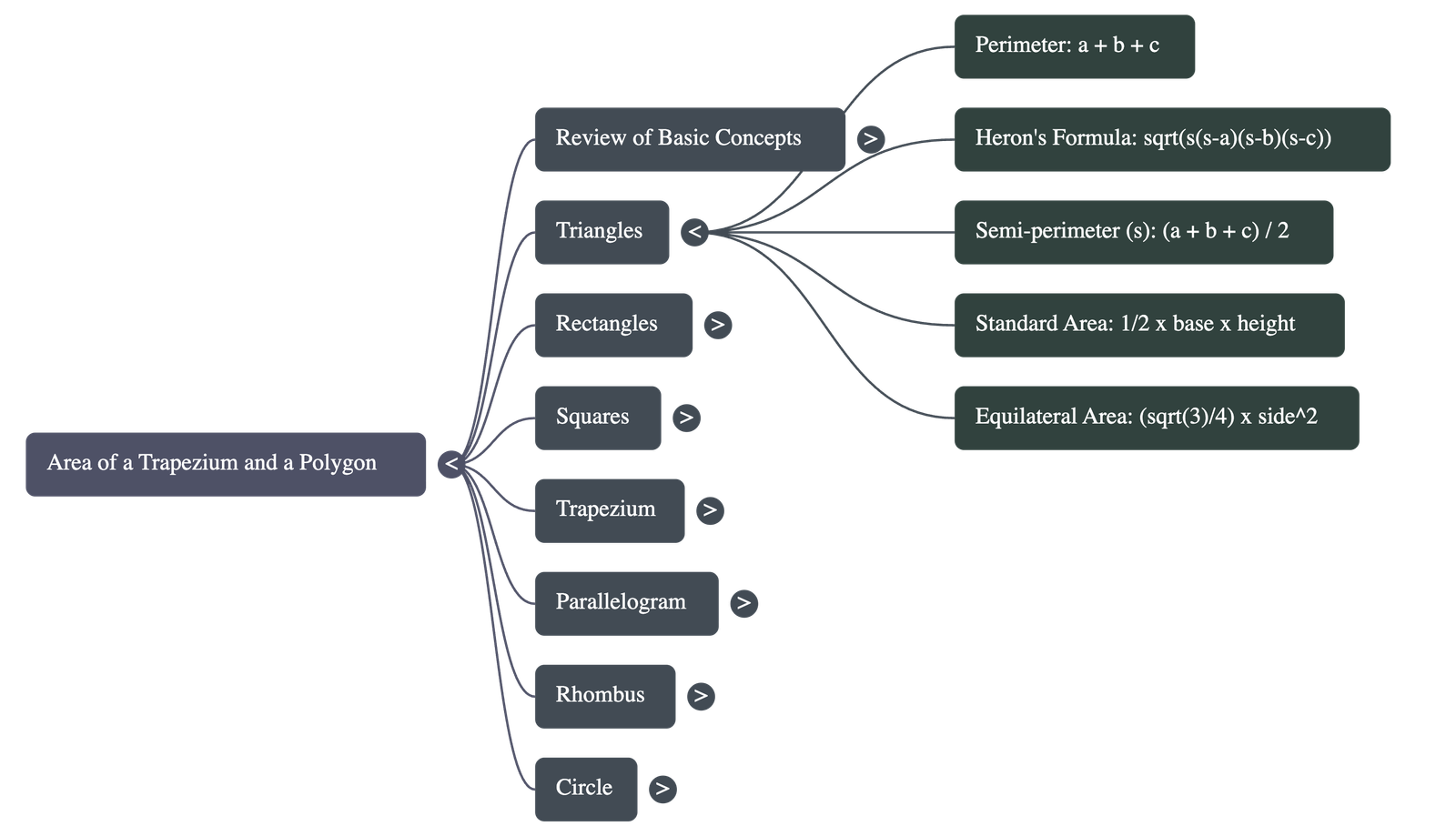
2. Perimeter and Area of Triangles
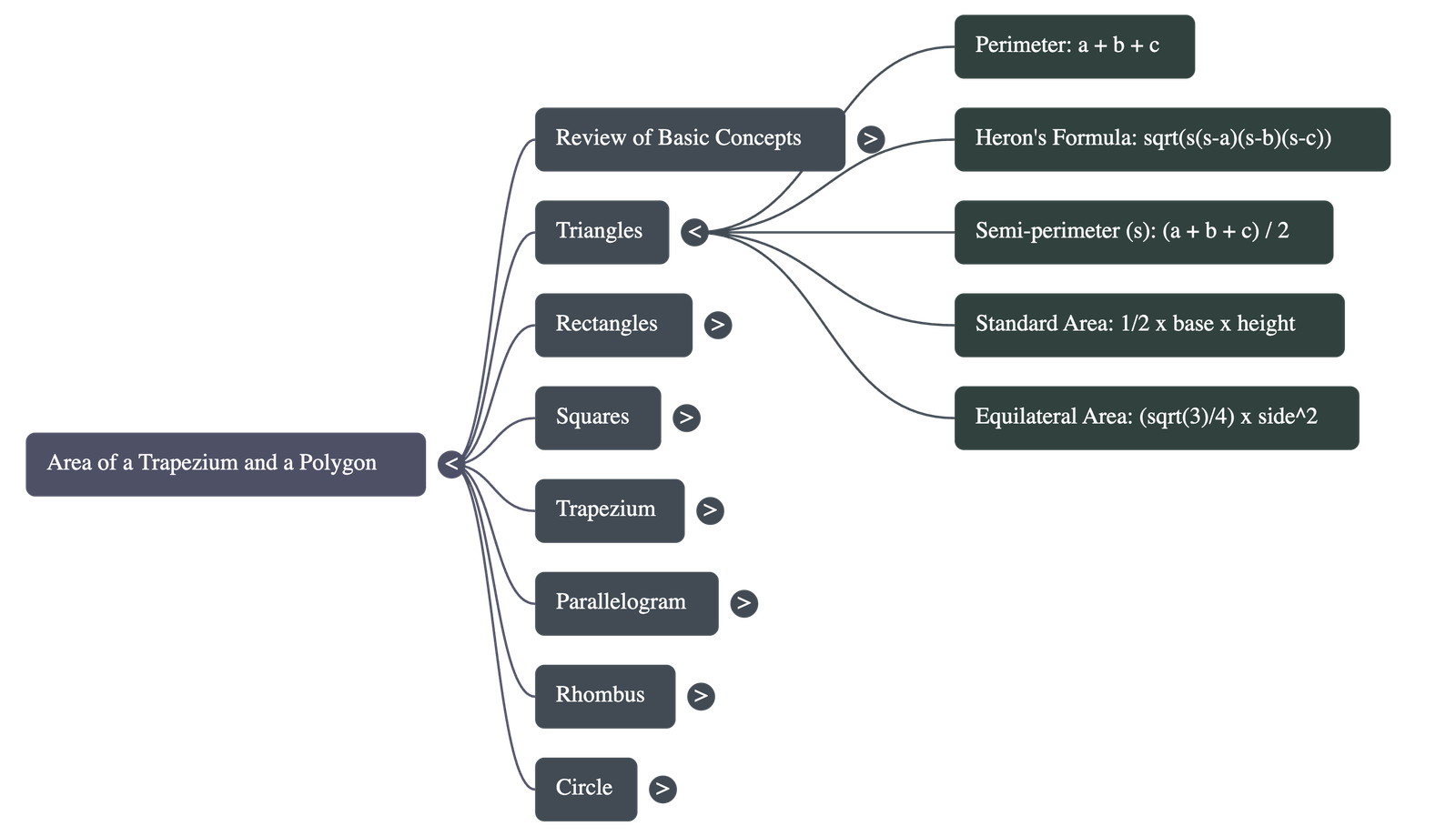
- For a triangle with sides a, b, and c, the perimeter is a + b + c.
- Heron’s Formula: Used when all three sides are known.
Area = √[s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)], where s (semi-perimeter) = (a + b + c) / 2.
- Base-Height Formula: Used when the base and corresponding altitude (height) are known.
Area = 1/2 × base × height
- Equilateral Triangles: For a triangle where all sides are a:
Area = (√3 / 4) × a²
3. Rectangles and Squares
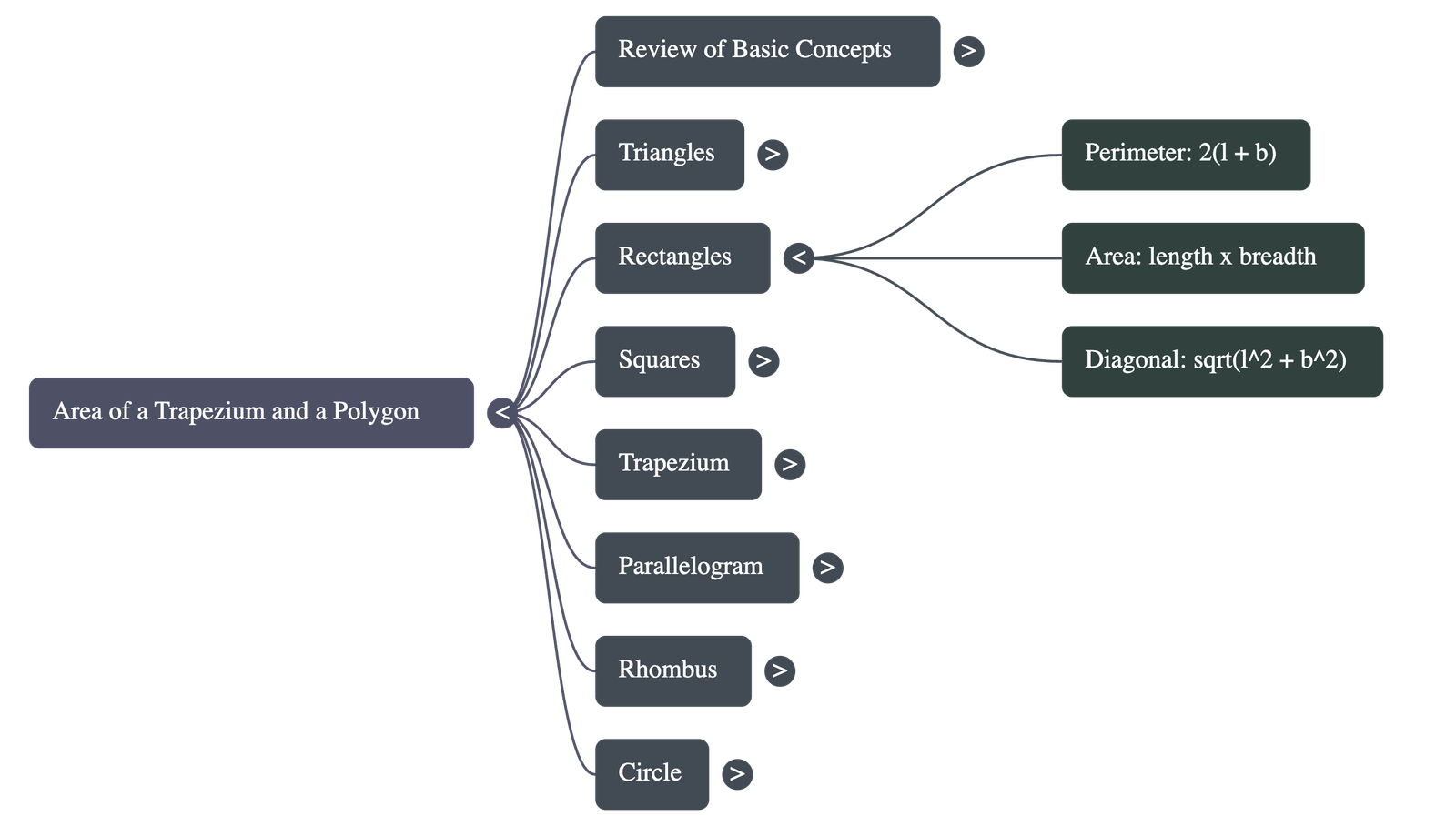
- Rectangle:
Perimeter = 2(length + breadth)
Area = length × breadth
Diagonal = √(length² + breadth²) - Square:
Perimeter = 4 × side
Area = (side)² or 1/2 × (diagonal)²
Diagonal = side × √2
4. Special Quadrilaterals
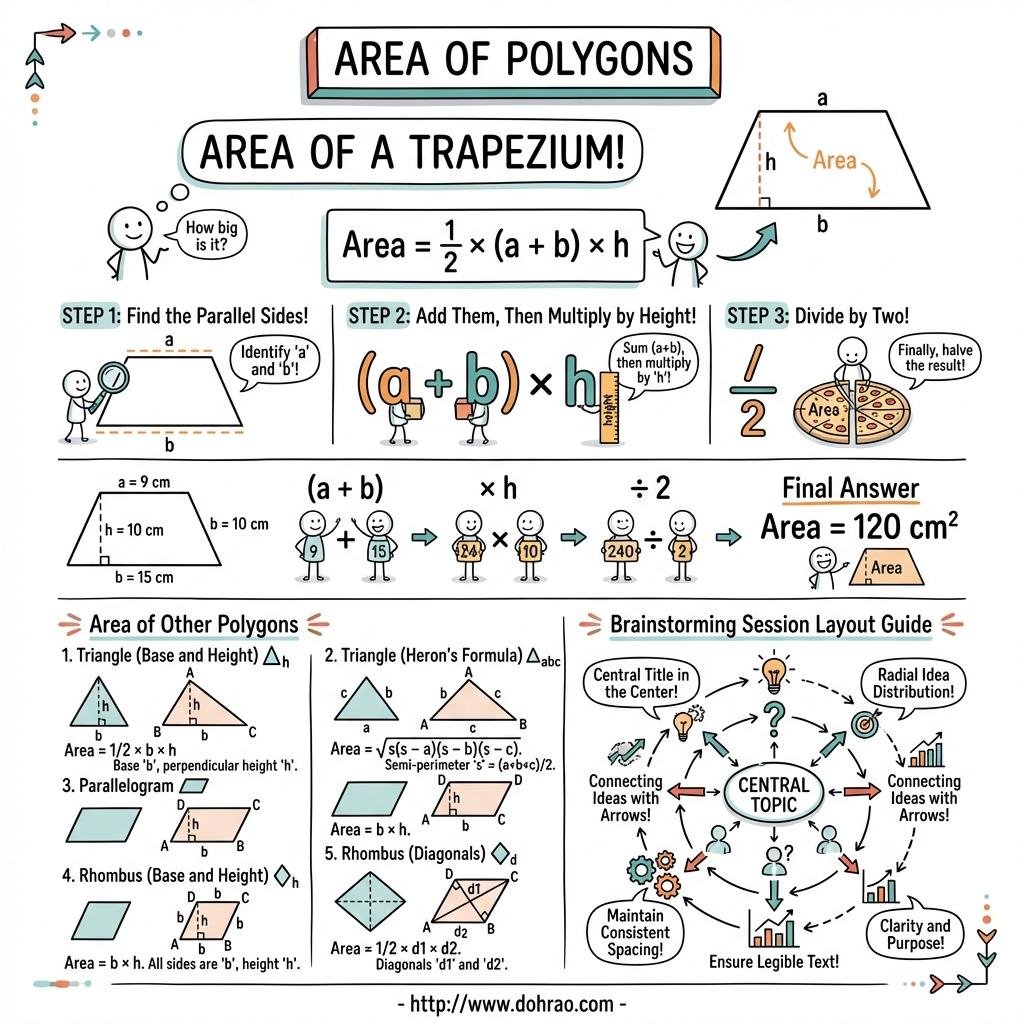
- Trapezium: A figure with one pair of parallel sides.
Area = 1/2 × (sum of parallel sides) × height
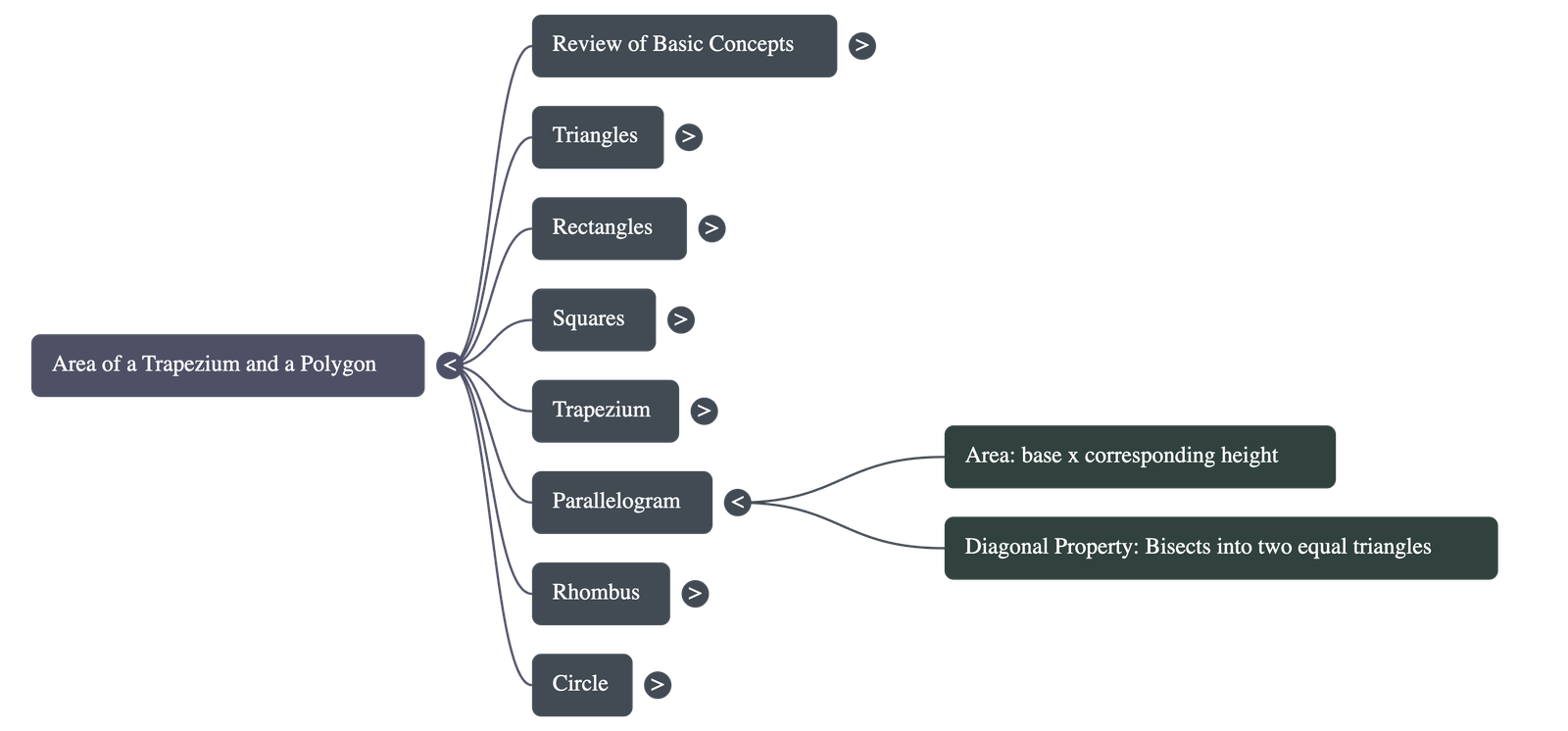
- Parallelogram:
Area = base × corresponding heightNote: A diagonal divides a parallelogram into two triangles of equal area.
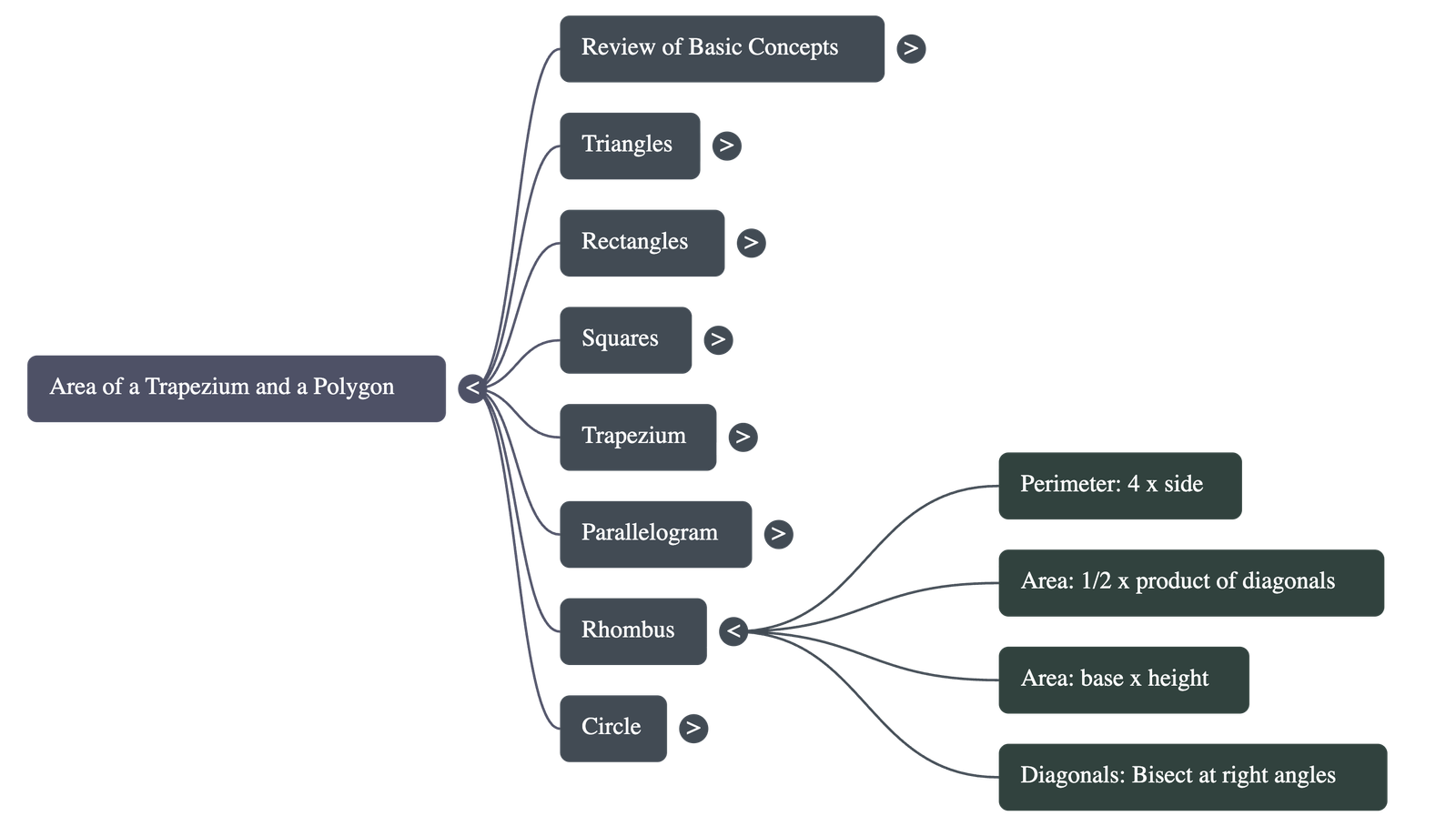
- Rhombus: A parallelogram with all sides equal.
Area = 1/2 × product of diagonals (d1 × d2)Note: Diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at right angles (90°).
Area = base × height
5. Circles
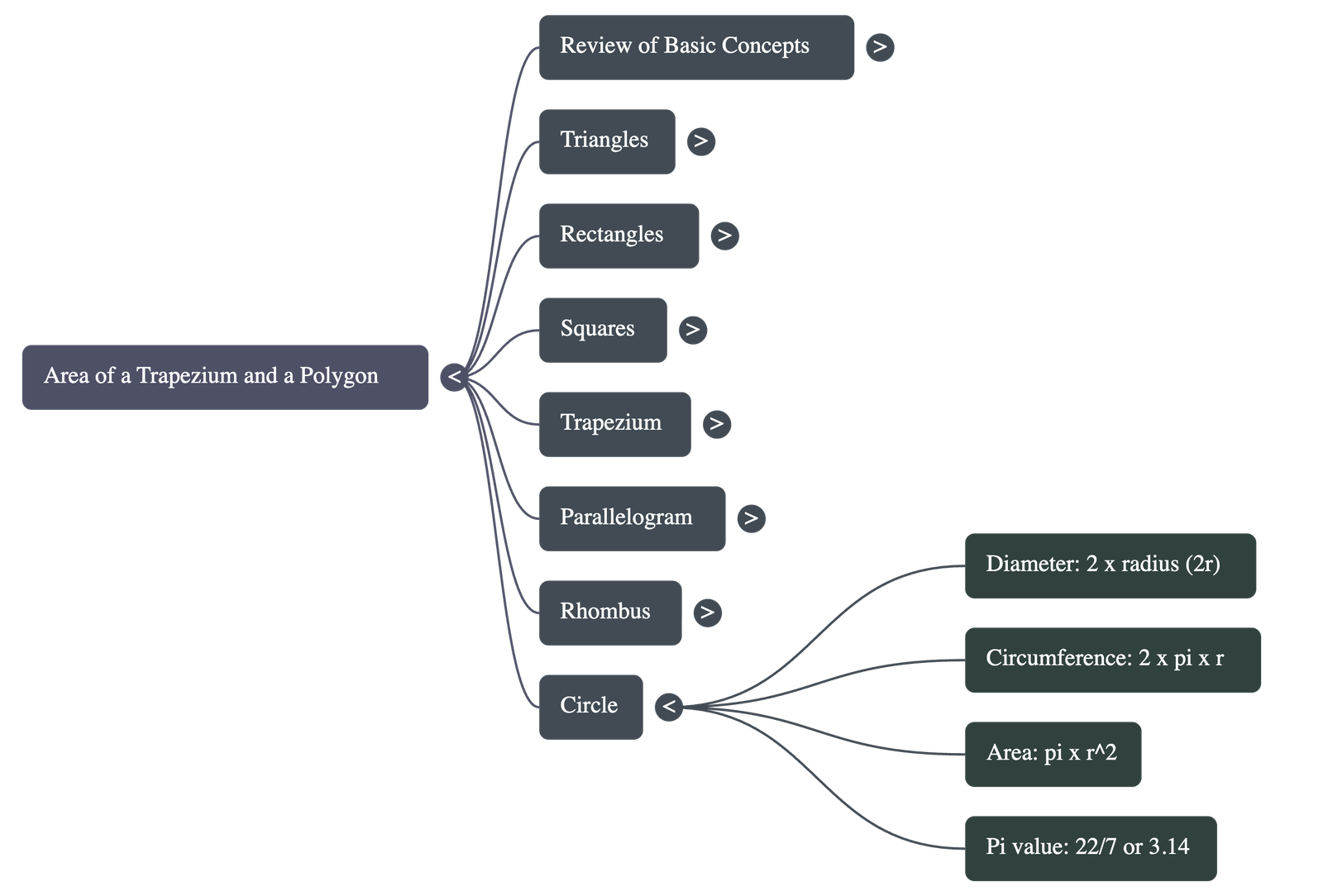
- Diameter (d): Twice the length of the radius (r).
- Circumference (C): The perimeter of a circle.
Circumference = 2πr (where π ≈ 22/7 or 3.14)
- Area: The surface enclosed by the circle.
Area = πr²
6. Practical Applications
- The sources discuss calculating the area of paths by subtracting the area of the inner rectangle/square from the outer one.
- Costing: To find the total cost for flooring, tiling, or levelling, the area is multiplied by the rate per unit area.
- Wheel Rotations: The distance travelled by a wheel in one revolution is equal to its circumference.
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |