Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
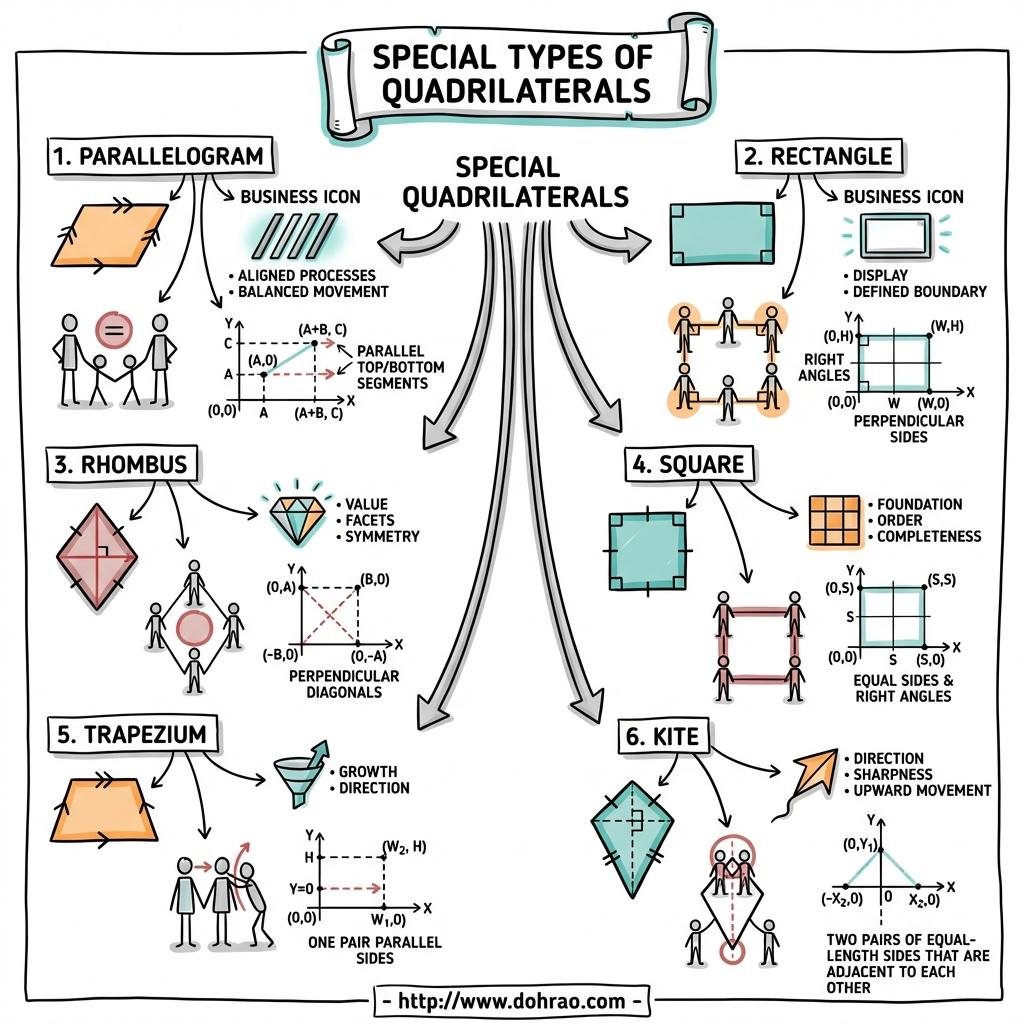
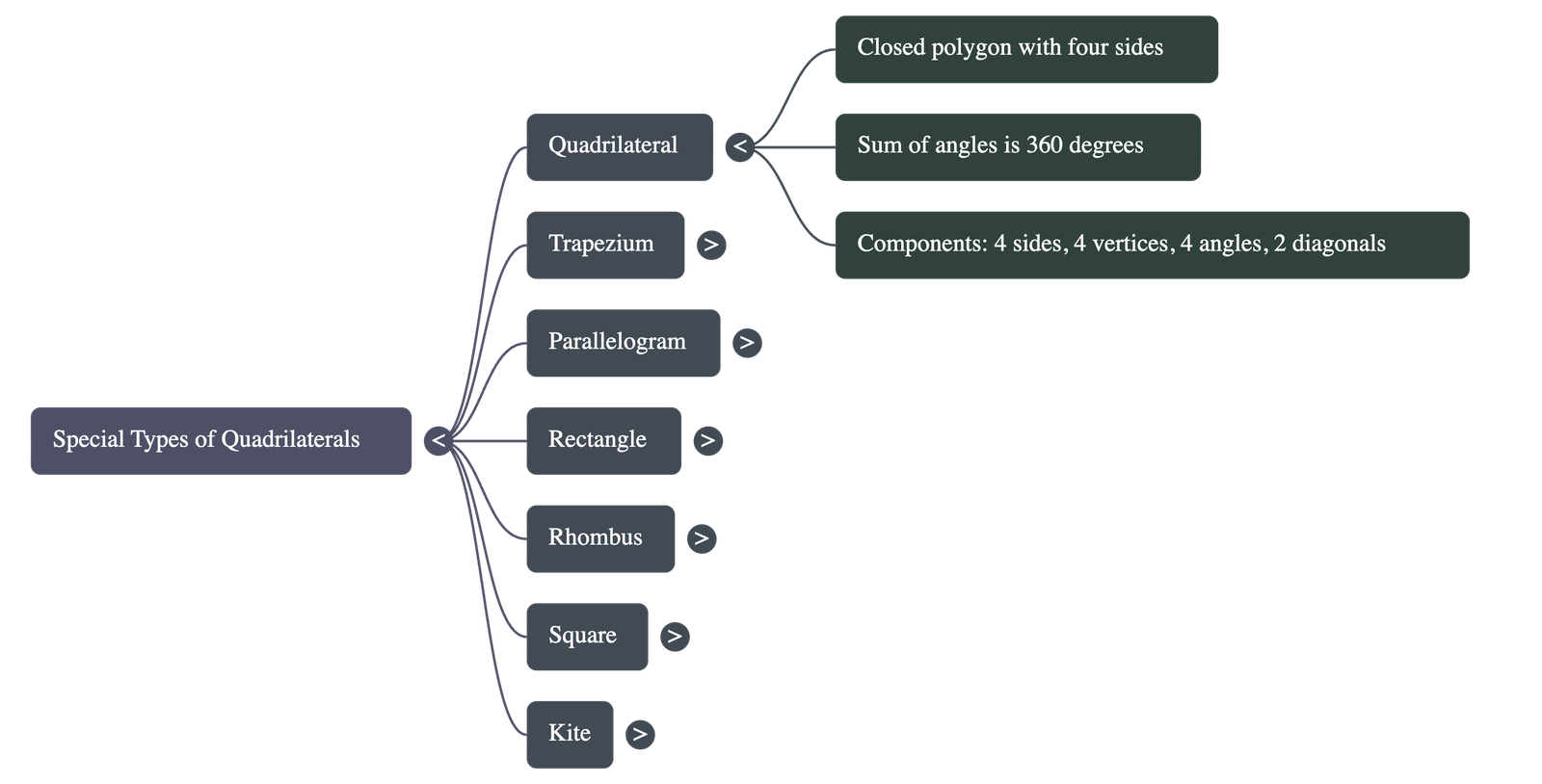
1. General Quadrilateral
- A quadrilateral is a closed polygon with four sides.
- It consists of four vertices, four angles, and two diagonals.
- The sum of the interior angles of any quadrilateral is always 360° (equal to four right angles).
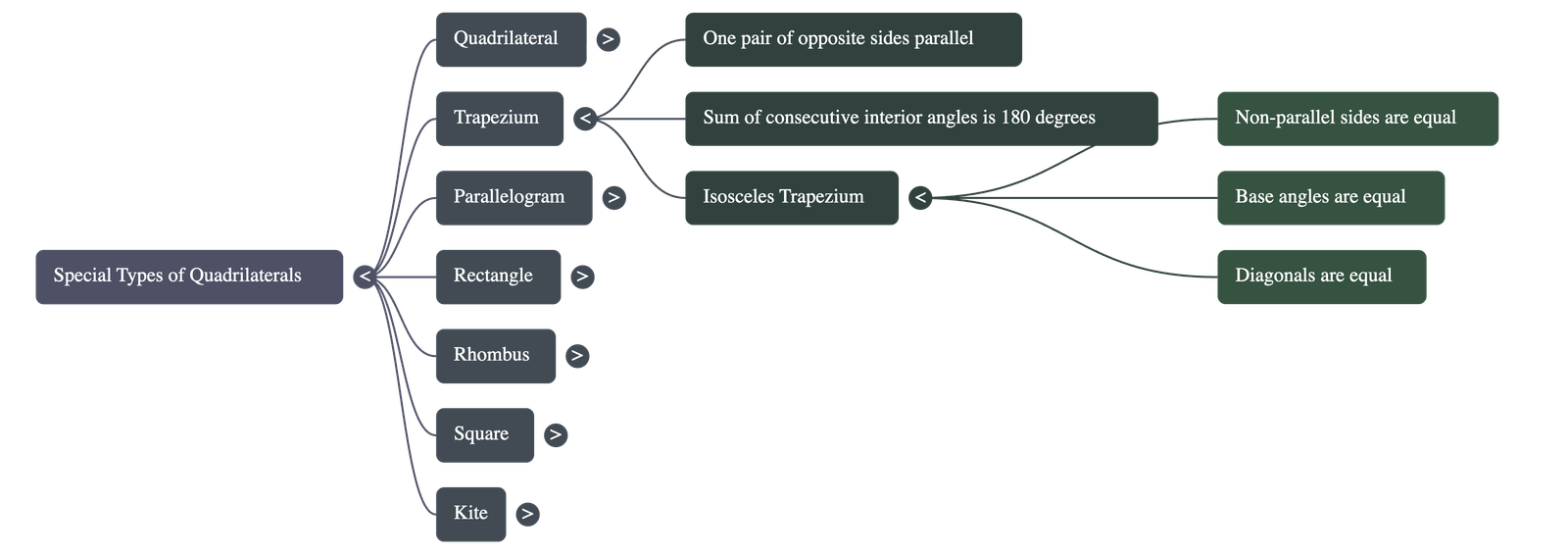
2. Trapezium
- A quadrilateral with one pair of opposite sides parallel and the other pair non-parallel.
- In a trapezium, the angles between a parallel side and a non-parallel side are supplementary (sum to 180°).
- Isosceles Trapezium: A specific type where the non-parallel sides are equal. In this case, the base angles are equal and the diagonals are of equal length.
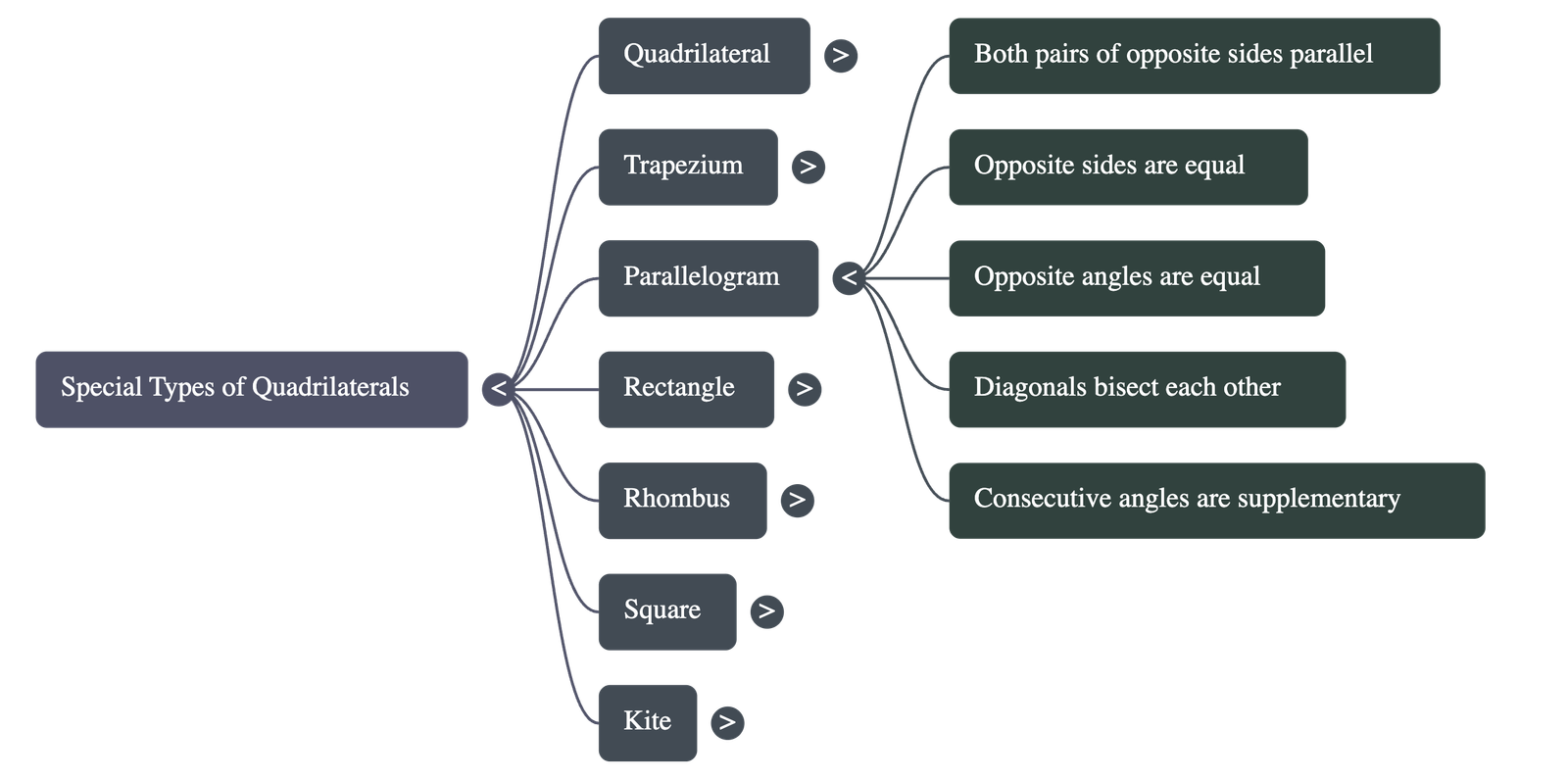
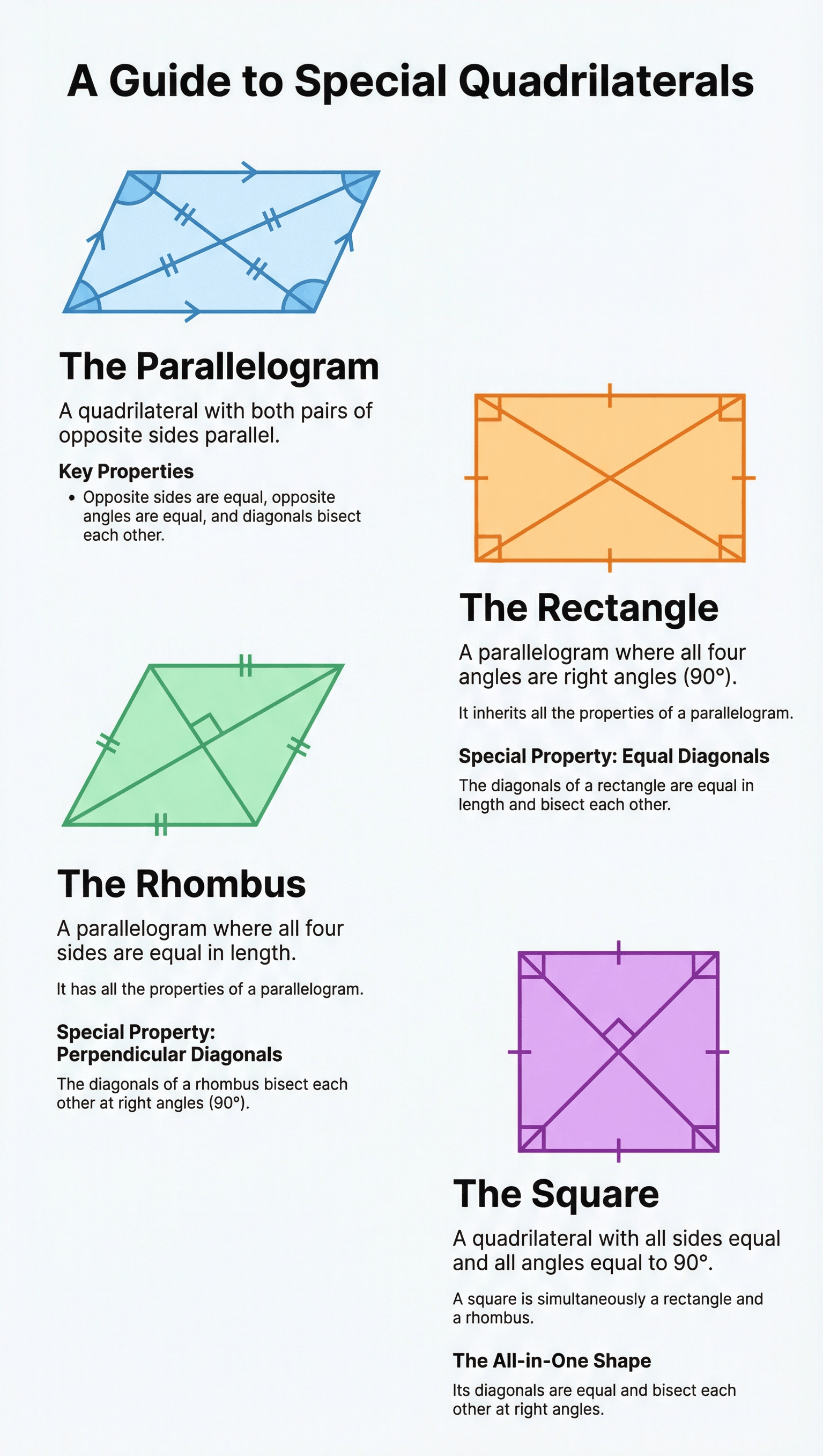
3. Parallelogram
- A quadrilateral where both pairs of opposite sides are parallel.
- Key Properties:
- Opposite sides are equal in length.
- Opposite angles are equal.
- Each diagonal bisects the parallelogram into two congruent triangles.
- Diagonals bisect each other. - To prove a quadrilateral is a parallelogram, one can show that opposite sides are equal, opposite angles are equal, diagonals bisect each other, or one pair of opposite sides is both equal and parallel.
4. Rectangle
- A parallelogram in which each angle is a right angle (90°).
- Since it is a parallelogram, its opposite sides are equal and parallel.
- A unique property of a rectangle is that its diagonals are equal and they bisect each other.
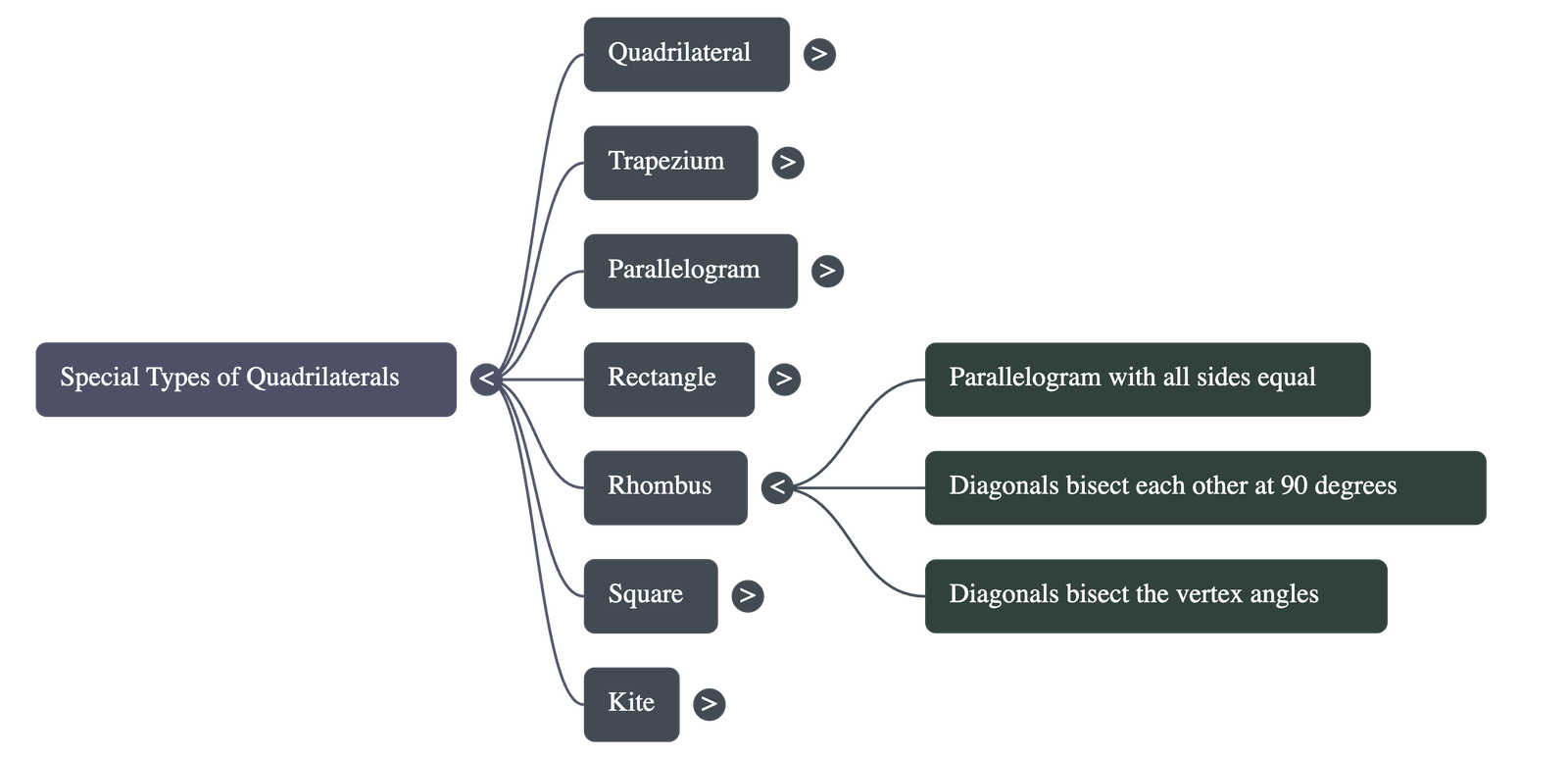
5. Rhombus
- A quadrilateral where all four sides are equal in length.
- It is a special type of parallelogram; therefore, its opposite angles are equal and opposite sides are parallel.
- Distinctive Property: The diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at right angles (90°).
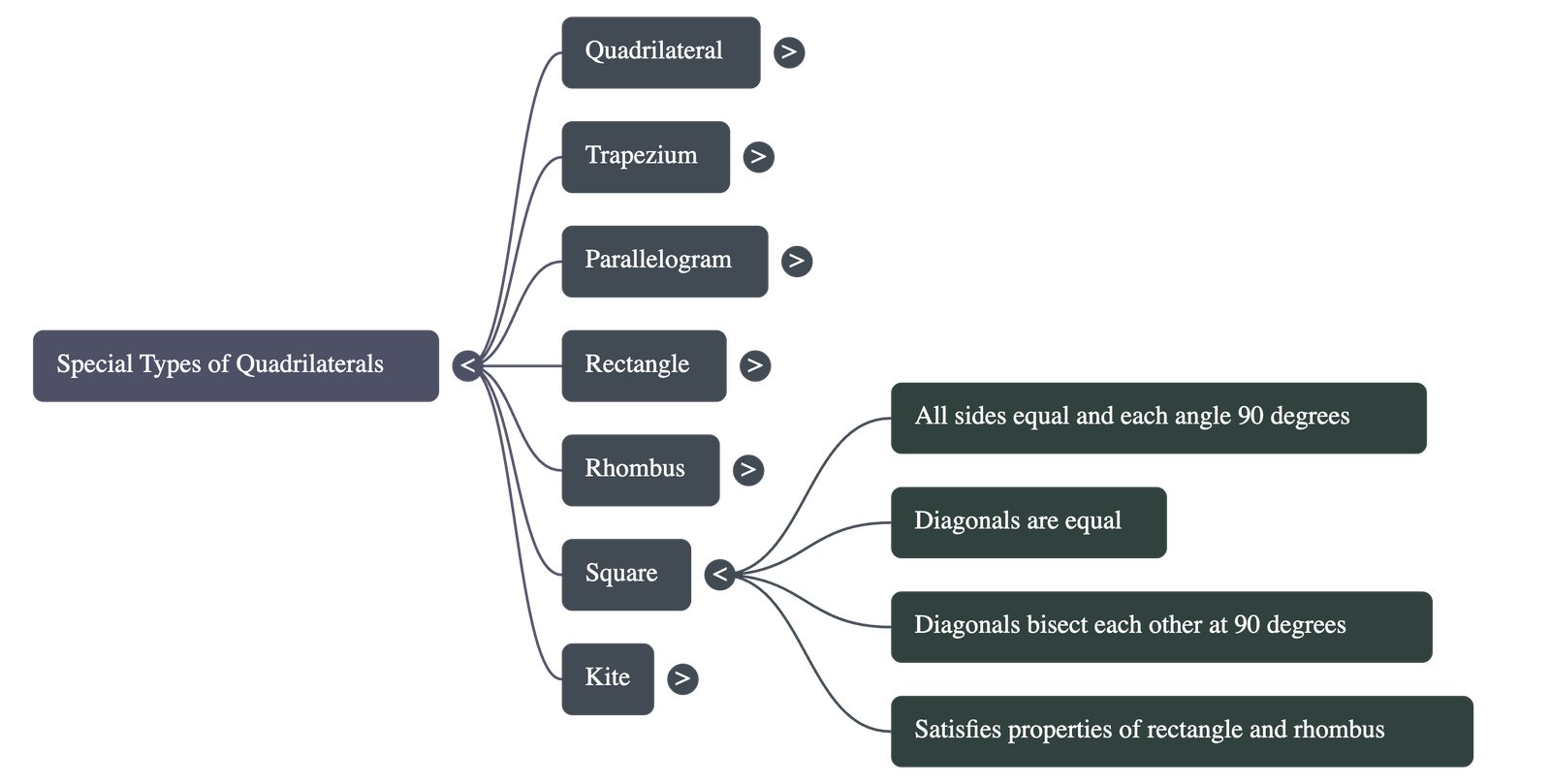
6. Square
- A quadrilateral where all sides are equal and each angle is 90°.
- A square is the most "complete" quadrilateral, satisfying the properties of a rectangle, a rhombus, and a parallelogram.
- Diagonals: They are equal in length and bisect each other at right angles.
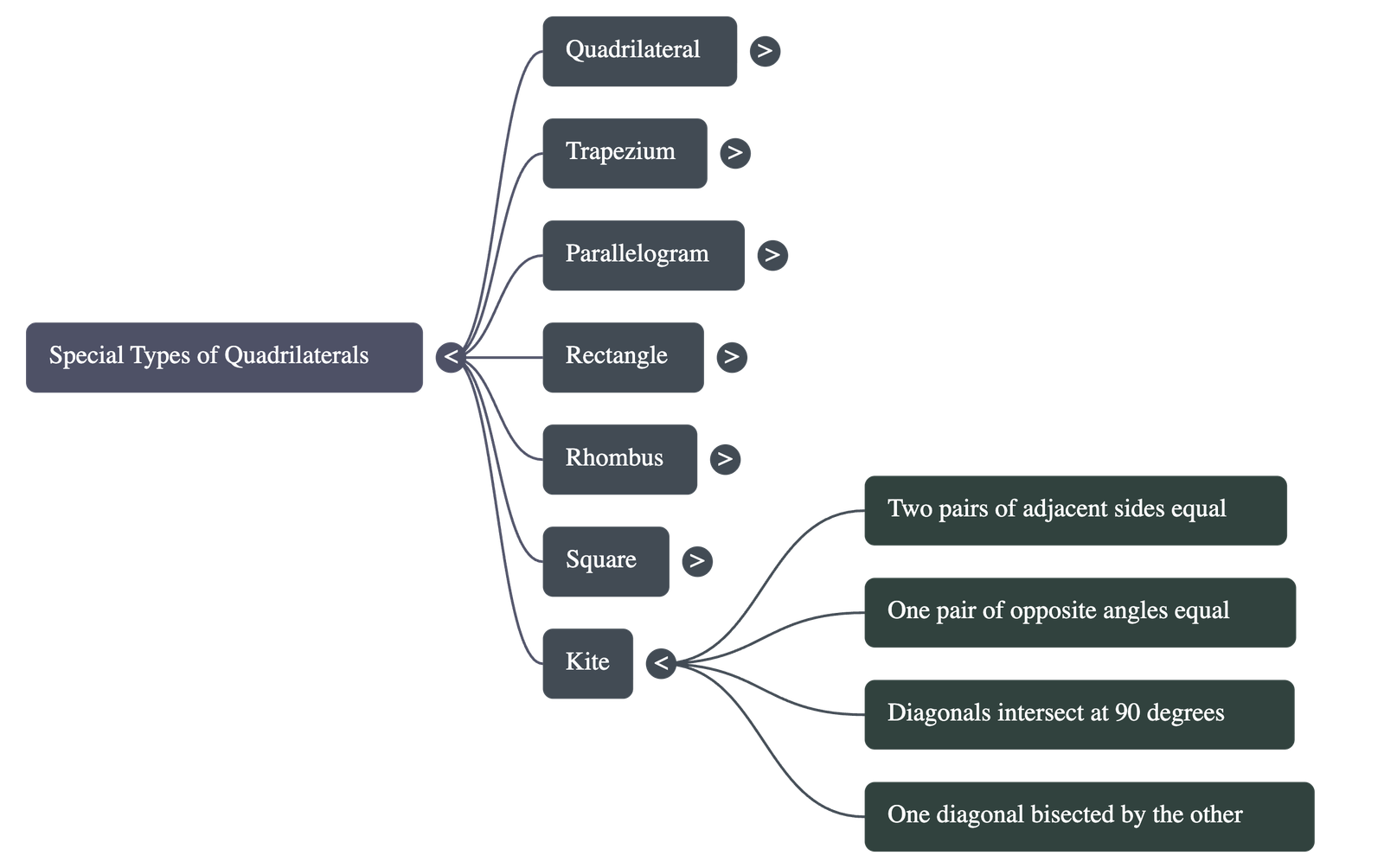
7. Kite
- A quadrilateral with two pairs of equal adjacent sides.
- Properties:
- One pair of opposite angles is equal.
- Diagonals intersect each other at right angles.
- One diagonal is bisected by the other.
- One diagonal bisects the interior angles at the vertices it joins.
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |