Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
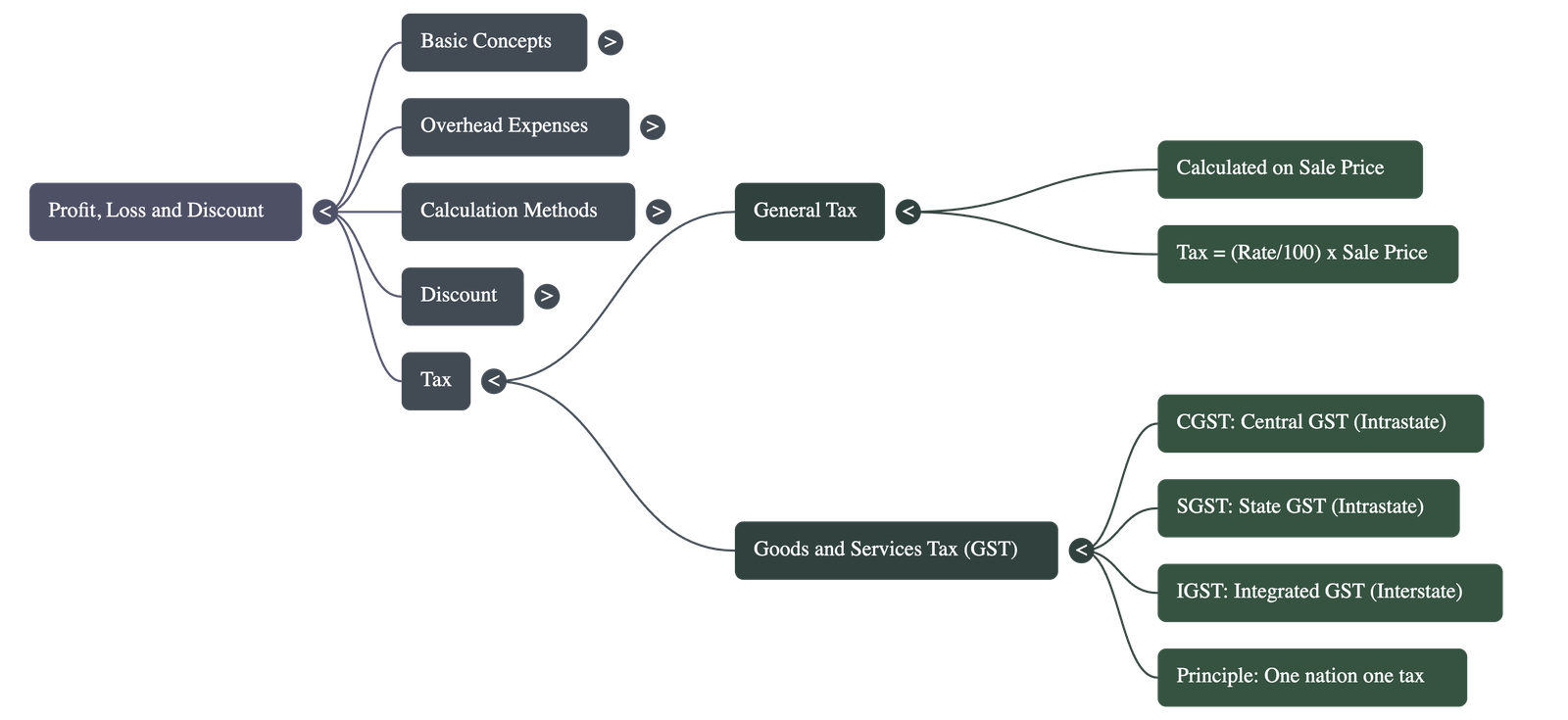
Chapter 8: Profit, Loss and Discount
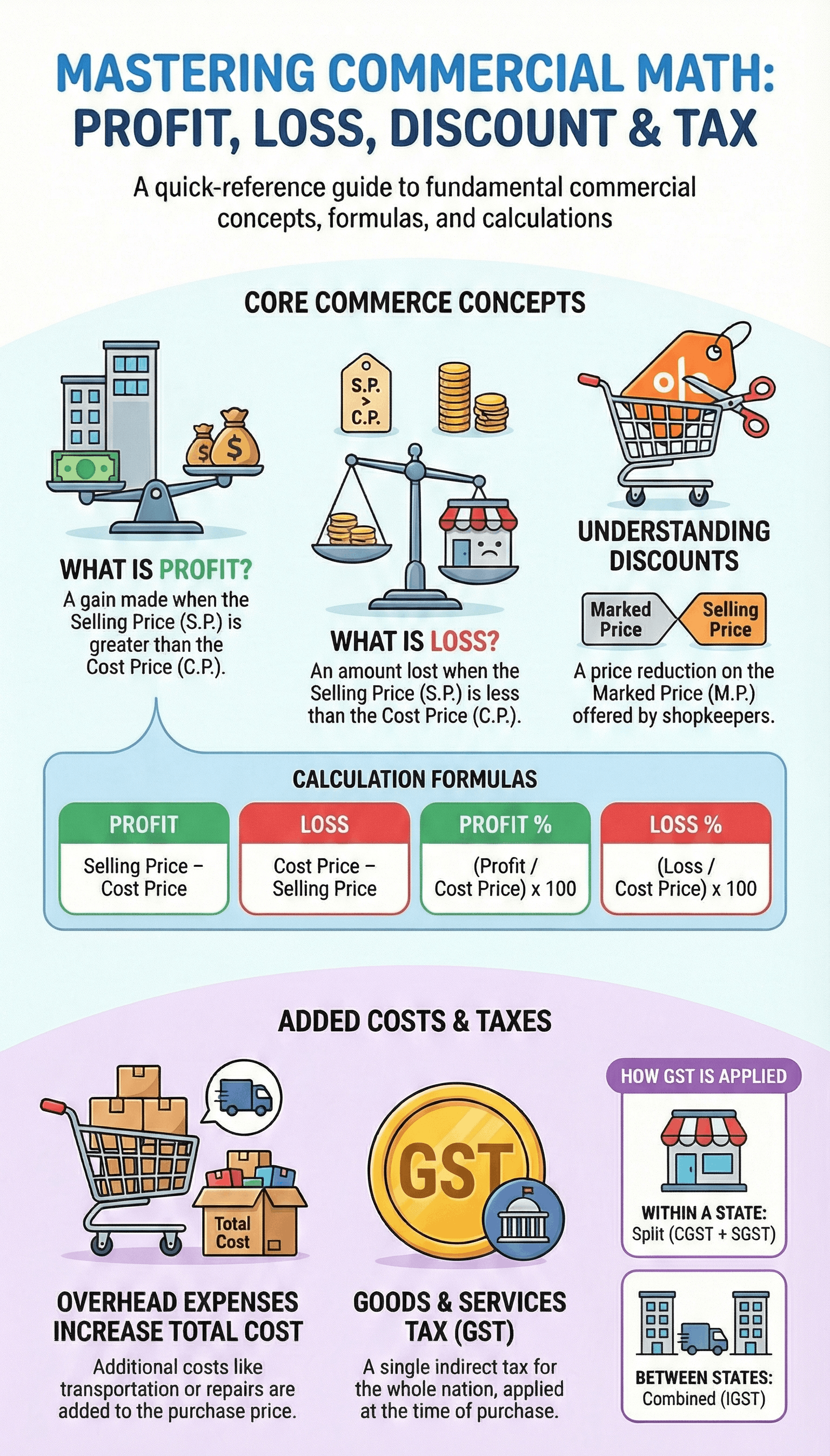
1. Fundamental Concepts of Profit and Loss
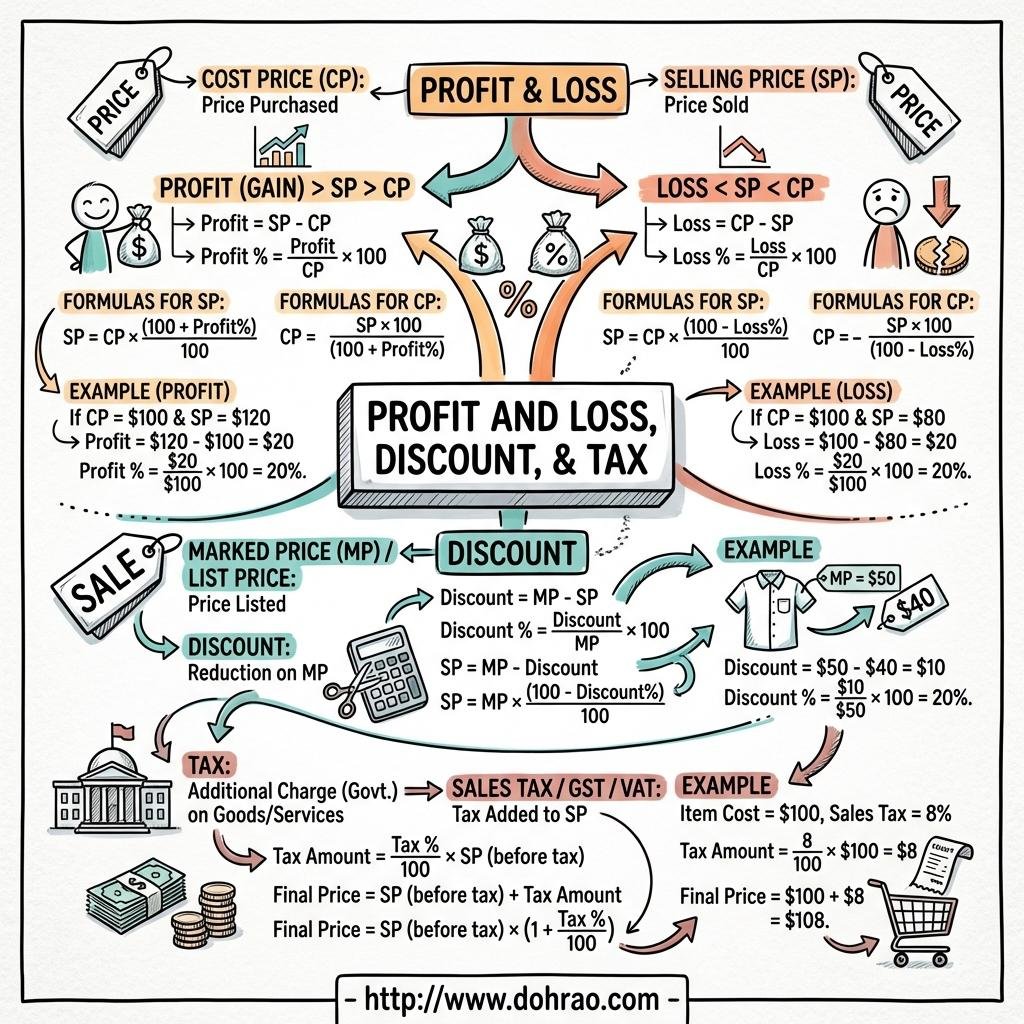
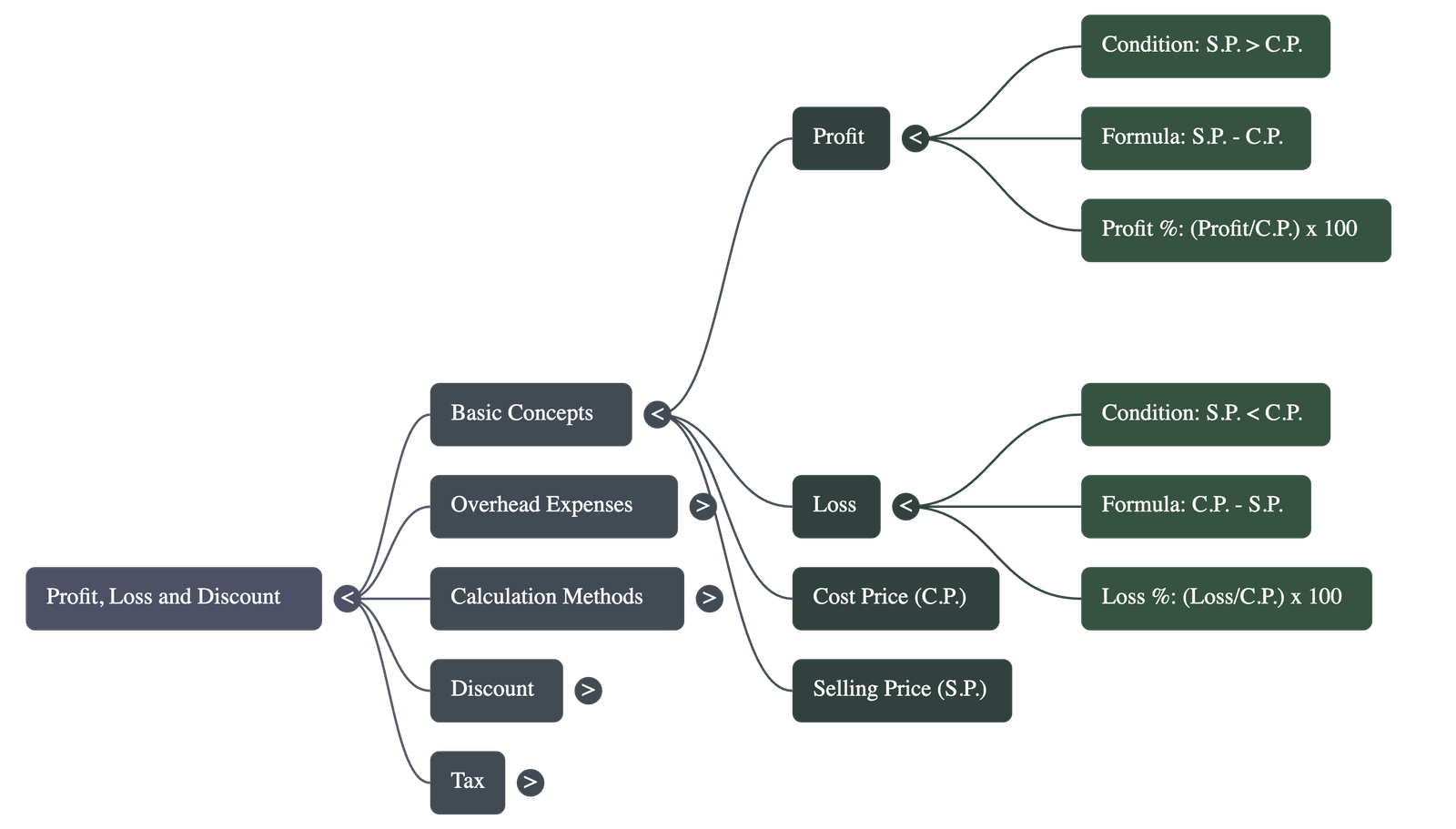
- Profit (Gain): Realized when the Selling Price (S.P.) of an item is higher than its Cost Price (C.P.).
- Loss: Realized when the Selling Price (S.P.) is lower than the Cost Price (C.P.).
- Crucial Rule: Both Profit percentage and Loss percentage are always calculated on the Cost Price (C.P.).
• Profit = S.P. - C.P.
• Loss = C.P. - S.P.
• Profit % = (Profit / C.P.) × 100
• Loss % = (Loss / C.P.) × 100
• Loss = C.P. - S.P.
• Profit % = (Profit / C.P.) × 100
• Loss % = (Loss / C.P.) × 100
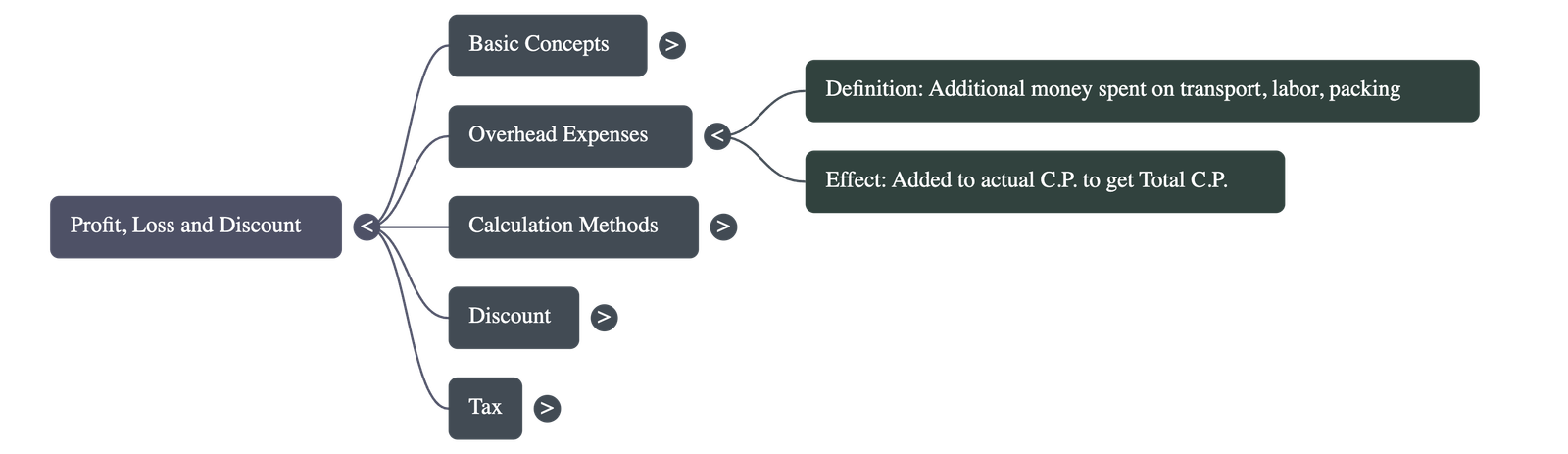
2. Overhead Expenses
- Definition: Extra costs incurred after the purchase of an item, such as transportation, labor, repairs, or packing.
- Total Cost Price: To find the actual profit or loss, these overheads must be added to the original purchase price to determine the Total Cost Price.
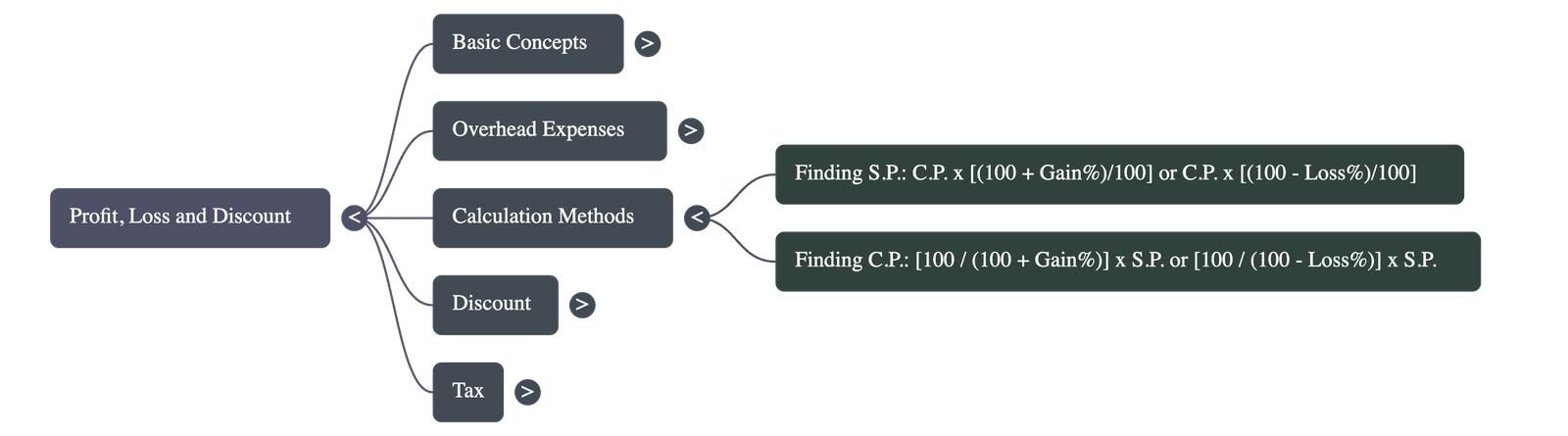
3. Mathematical Relations (S.P. and C.P.)
- If C.P. and Gain/Loss % are known, S.P. can be calculated directly using specific formulas.
- If S.P. and Gain/Loss % are known, C.P. can be derived by reversing the percentage calculation.
• S.P. = [(100 + Gain%) / 100] × C.P.
• S.P. = [(100 - Loss%) / 100] × C.P.
• C.P. = [100 / (100 + Gain%)] × S.P.
• C.P. = [100 / (100 - Loss%)] × S.P.
• S.P. = [(100 - Loss%) / 100] × C.P.
• C.P. = [100 / (100 + Gain%)] × S.P.
• C.P. = [100 / (100 - Loss%)] × S.P.
4. Discount and Marked Price
- Marked Price (M.P.): Also known as the list price or printed price; it is the price displayed on the item before any reduction.
- Discount: A reduction offered on the Marked Price to encourage sales or dispose of old stock.
- Basis of Calculation: Unlike profit/loss, Discount is always calculated on the Marked Price (M.P.).
- Successive Discounts: When two or more discounts are applied sequentially, the first is applied to the M.P., and the second is applied to the reduced price. These can be converted into a single equivalent discount.
5. Taxation and GST
- Sales Tax: A tax levied by the government on the sale of goods to fund public services like roads and hospitals. It is calculated on the sale price.
- Goods and Services Tax (GST): Introduced in India on July 1, 2017, to replace multiple indirect taxes under the principle of "one nation and one tax."
- GST Components:
CGST (Central GST) Levied on intra-state transactions; goes to the Central Government. SGST (State GST) Levied on intra-state transactions; goes to the State Government. IGST (Integrated GST) Levied on inter-state transactions (between different states). - Current GST Rates: The standard applicable rates are 0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%.
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |