Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Summary of Chapter 4: Cubes and Cube-Roots
1. Fundamentals of Cubes
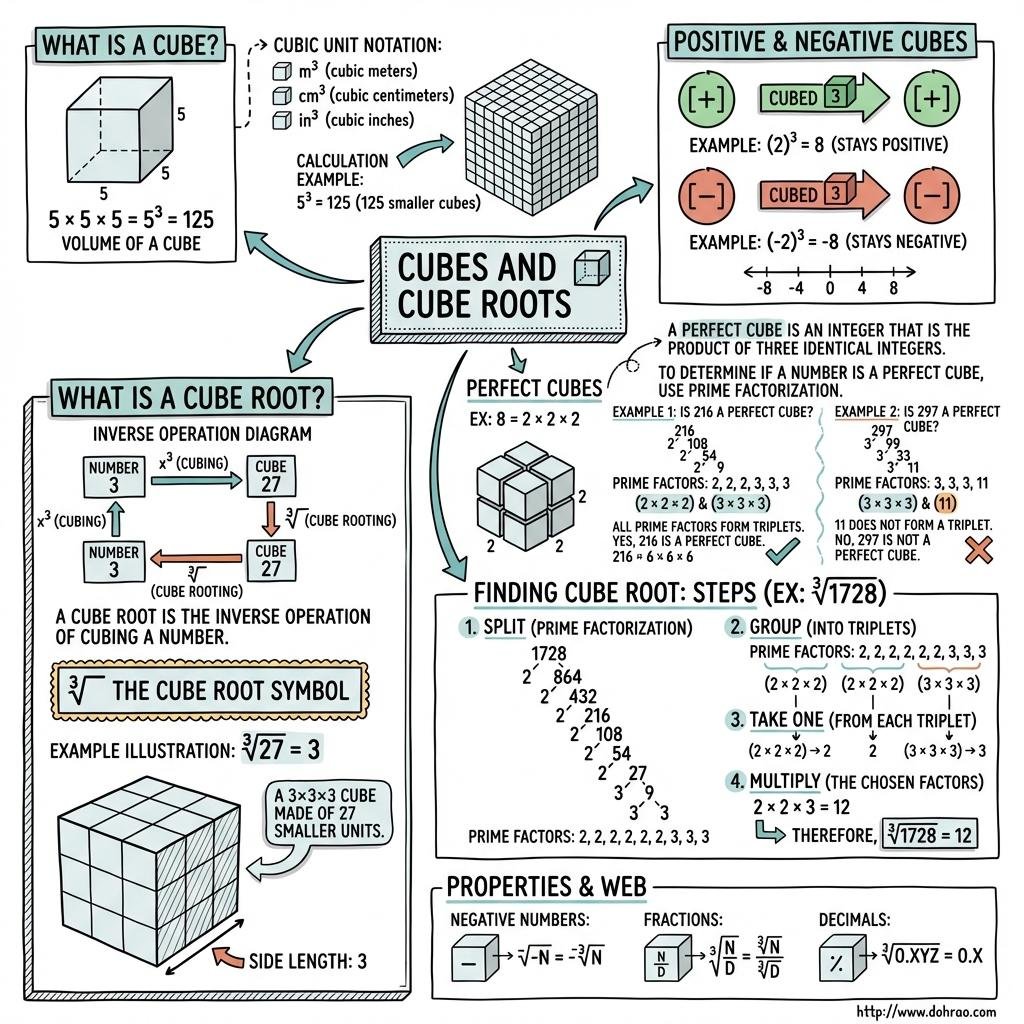
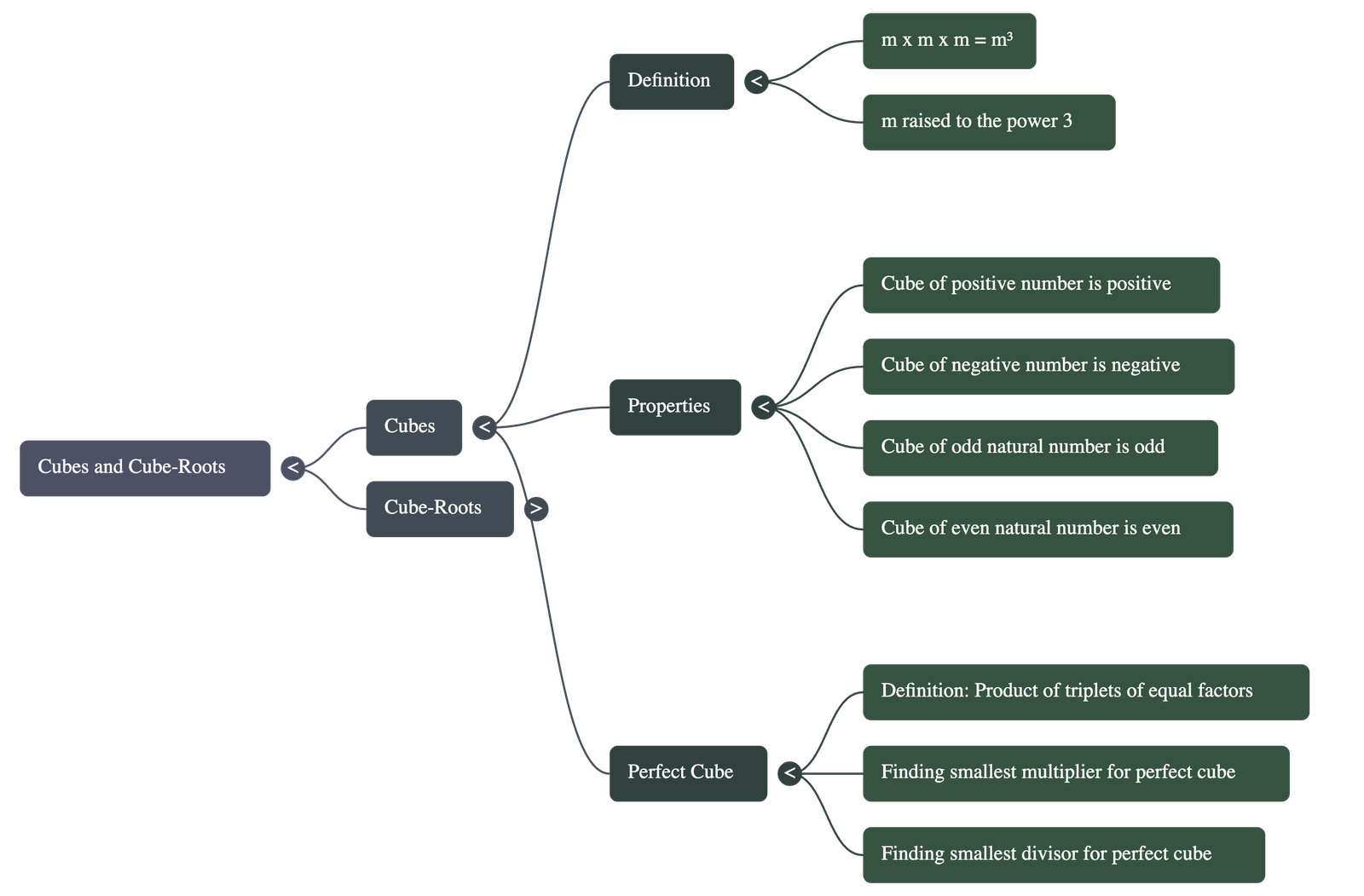
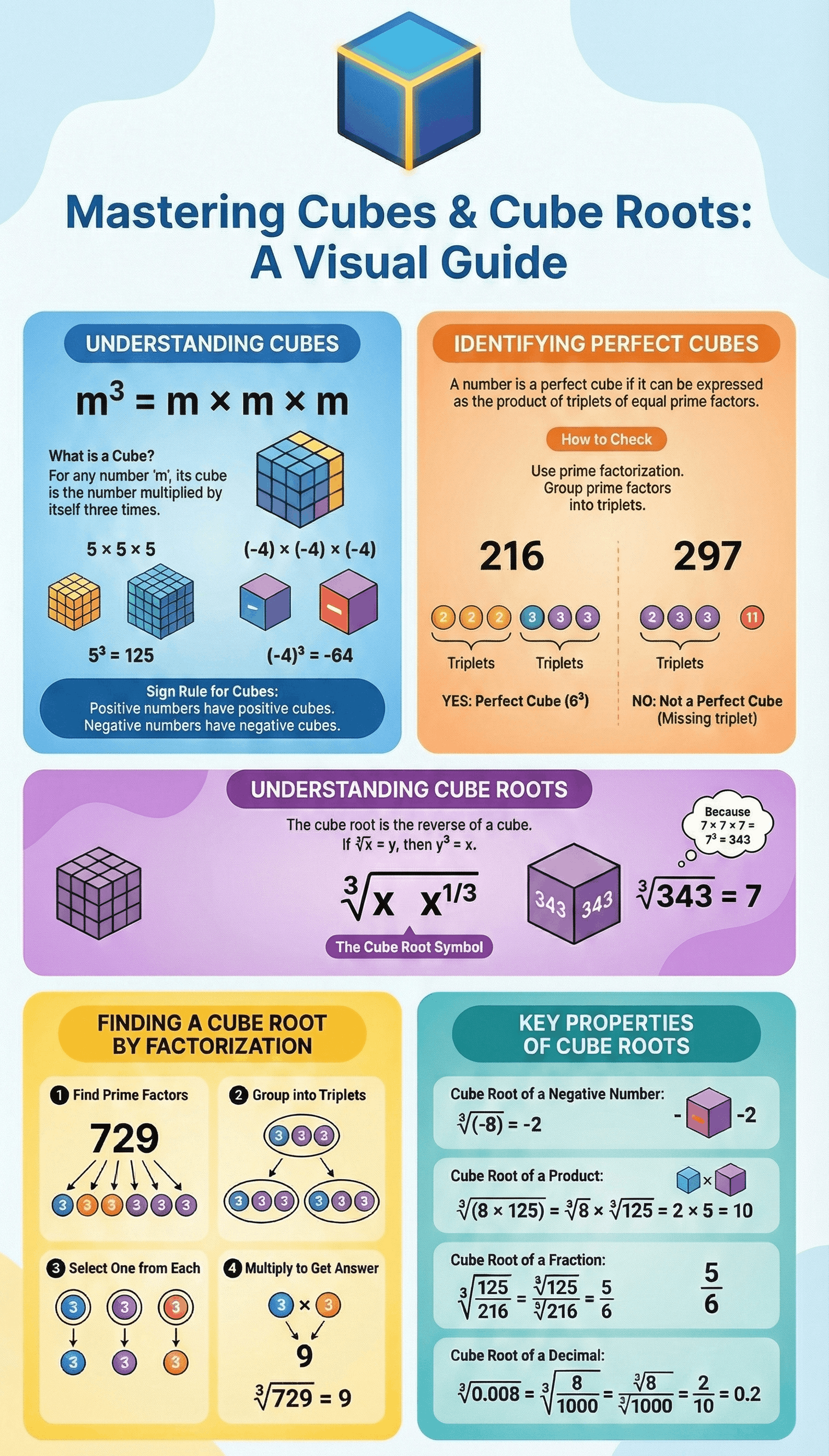
- Definition: For any number m, the product obtained by multiplying the number by itself three times (m × m × m) is called the cube of m, written as m3.
- Perfect Cubes: A natural number is a perfect cube if it can be expressed as the product of triplets of equal prime factors. For instance, 216 is a perfect cube because it factors into (2 × 2 × 2) × (3 × 3 × 3).
- Parity of Cubes: The cubes of even natural numbers are always even (e.g., 83 = 512), and the cubes of odd natural numbers are always odd (e.g., 53 = 125).
- Signs of Cubes: The cube of a positive number is positive, while the cube of a negative number is always negative.
2. Transforming Numbers into Perfect Cubes
- Prime Factorization Method: To determine if a number is a perfect cube, you must find its prime factors. If any factor does not appear in a group of three (a triplet), the number is not a perfect cube.
- Adjusting Numbers: If a number is not a perfect cube, you can find the smallest number to multiply or divide it by to make it one. This is done by identifying which prime factors are missing from a triplet (to multiply) or which factors are extra (to divide).
3. Understanding Cube-Roots
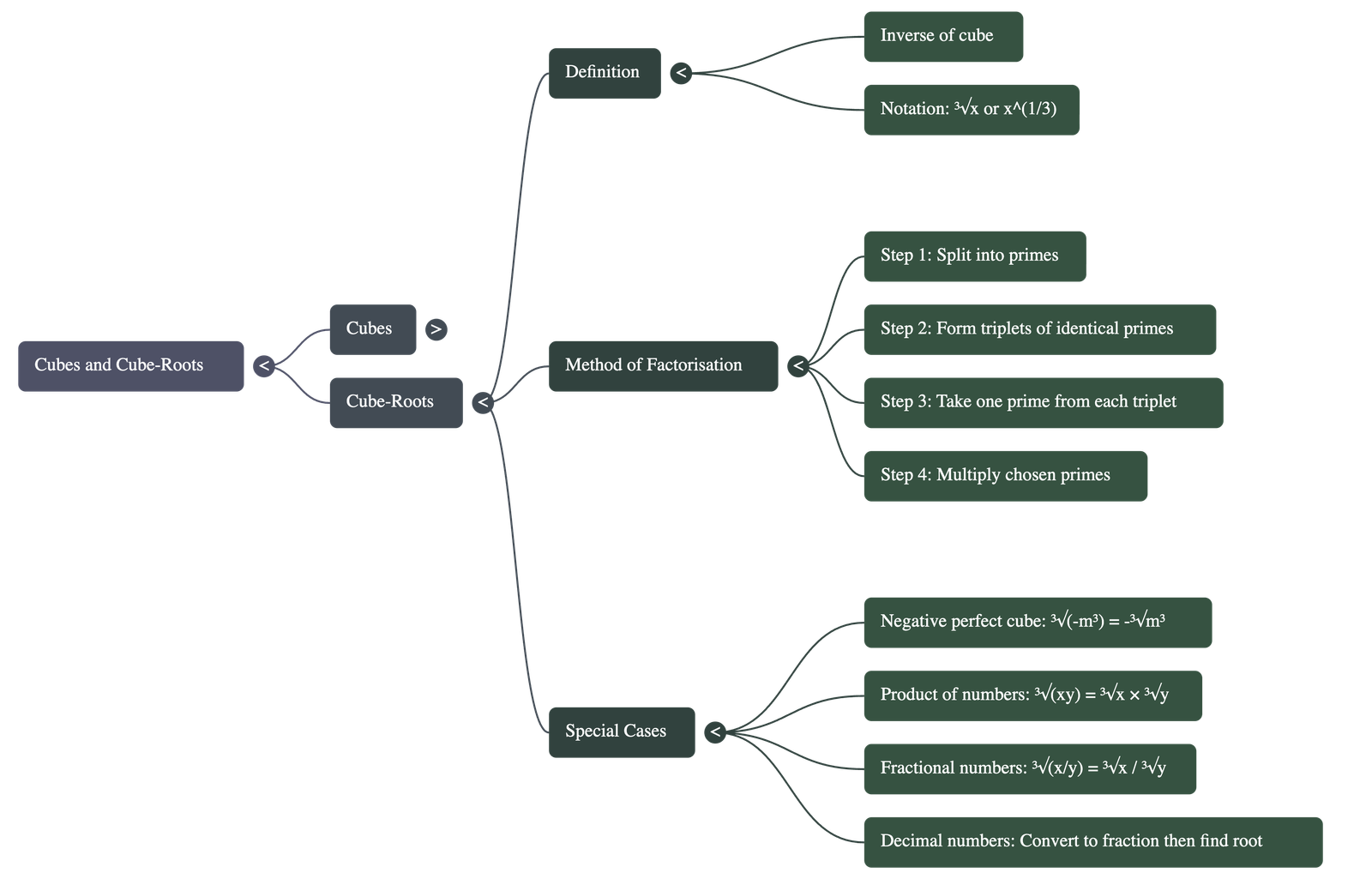
- Mathematical Definition: The cube-root of a number x is the value y such that y3 = x. This is denoted by the symbol ³√x or x1/3.
- The Factorization Process: To find a cube-root manually:
- Resolve the number into its prime factors.
- Group these identical primes into triplets.
- Take one factor from each triplet.
- Multiply these factors together to find the cube-root.
4. Specific Rules for Cube-Roots
- Negative Perfect Cubes: The cube-root of a negative perfect cube is simply the negative of the cube-root of its absolute value. For example, ³√(-8) = -2.
- Product Rule: The cube-root of a product of numbers is equal to the product of their individual cube-roots: ³√(xy) = ³√x × ³√y.
- Fraction Rule: The cube-root of a fraction is the cube-root of the numerator divided by the cube-root of the denominator: ³√(x/y) = ³√x / ³√y.
- Decimal Rule: To find the cube-root of a decimal number, it is best to convert the decimal into a fraction first (e.g., 0.027 becomes 27/1000) and then calculate the cube-root of both parts.
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |