Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
1. Introduction to Variations
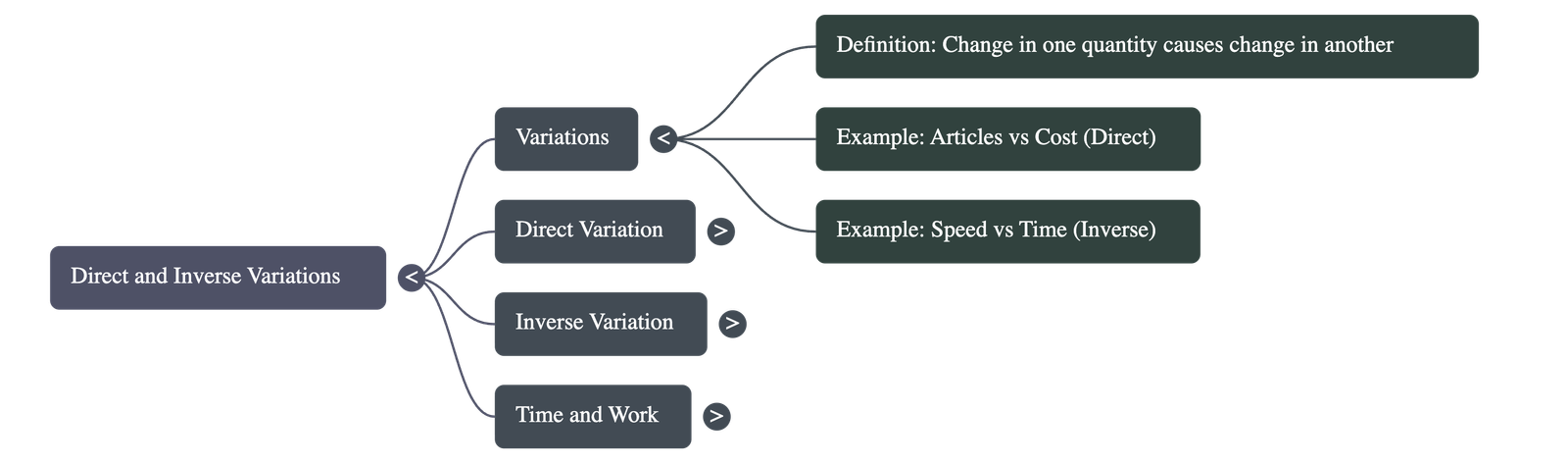
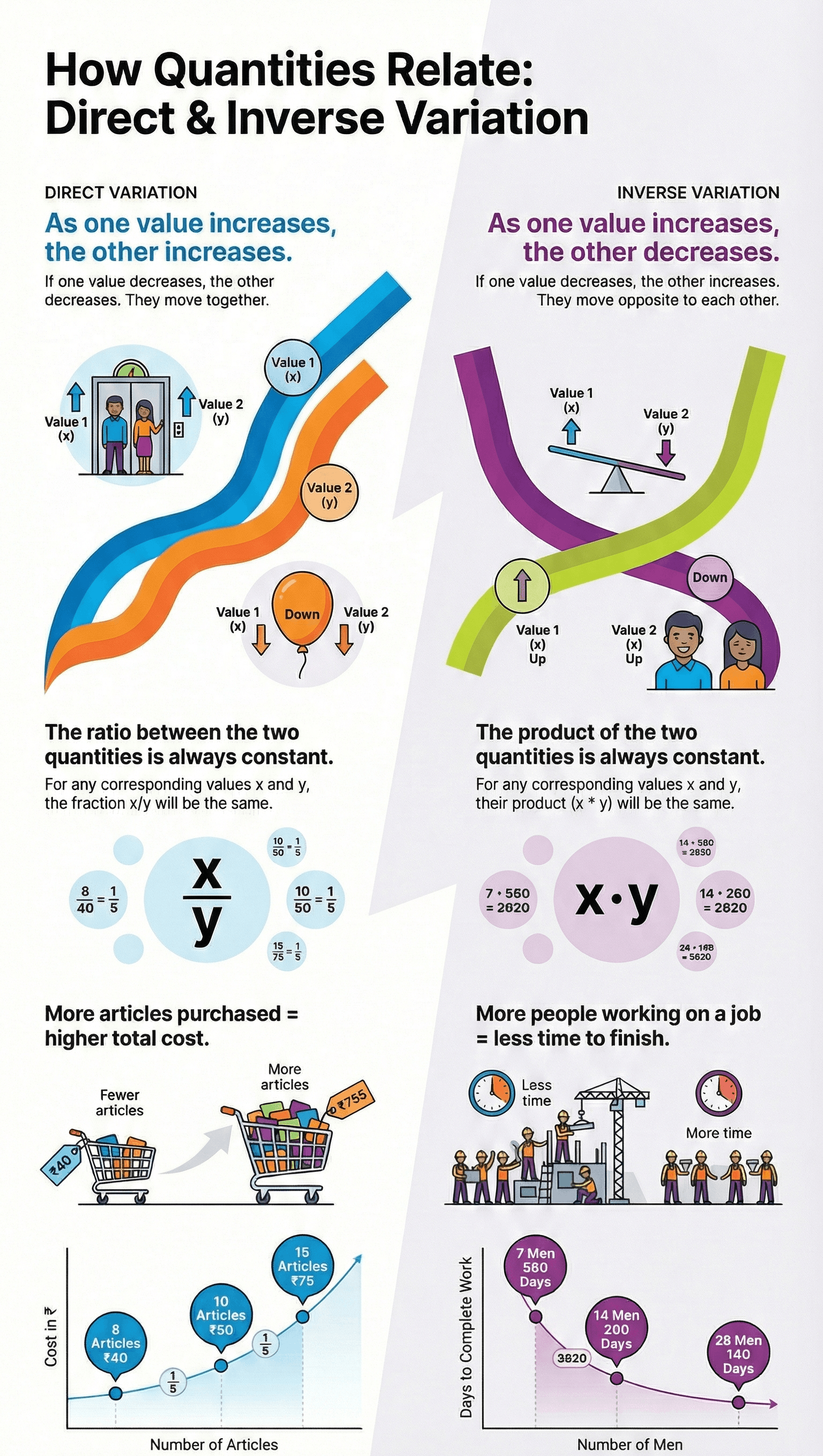
- Definition: Two quantities are in variation if a change in one quantity causes a corresponding change in the other.
- Common Examples:
- The more articles you buy, the higher the total cost.
- The more money deposited in a bank, the more interest is earned.
- The higher the speed of a car, the less time it takes to cover a specific distance.
2. Direct Variation
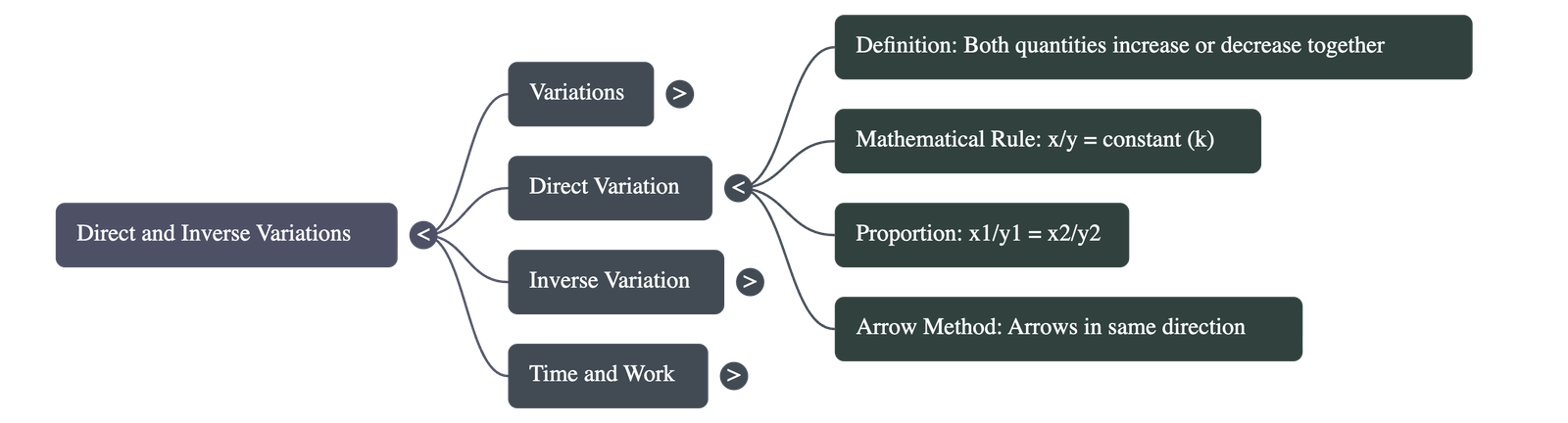
- Concept: Direct variation occurs when an increase in one quantity causes an increase in the other, or a decrease in one causes a decrease in the other.
- Mathematical Rule: If two quantities x and y vary directly, their ratio (x/y) remains constant.
- Formula: x₁ / y₁ = x₂ / y₂ = constant.
- Arrow Method: When solving problems, arrows for both quantities are marked in the same direction (either both upward or both downward).
3. Inverse Variation
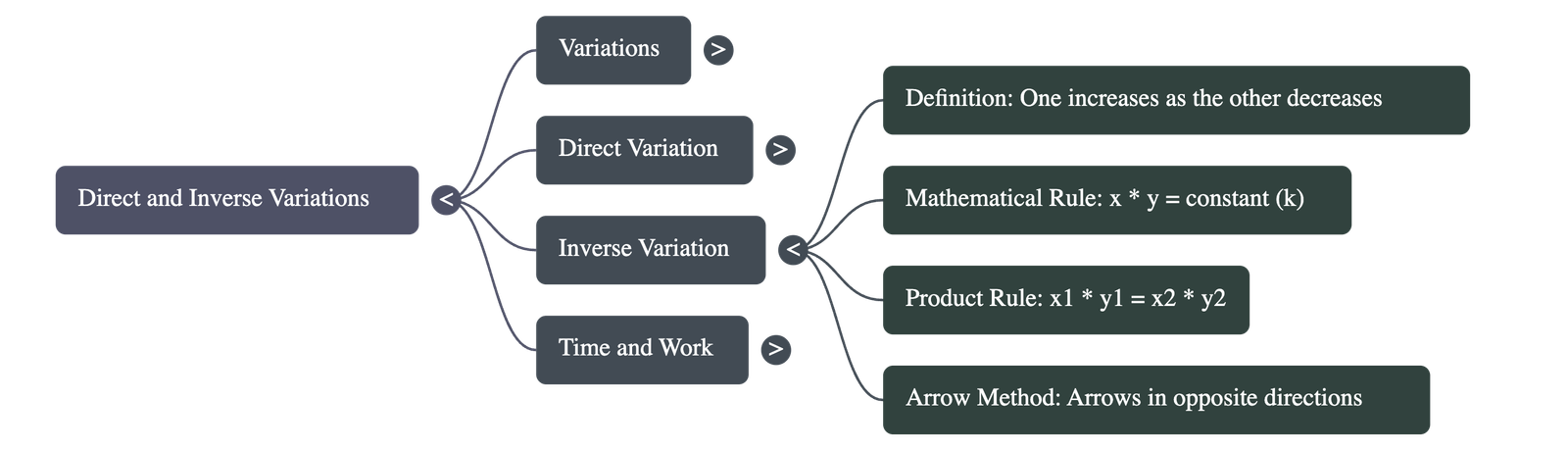
- Concept: Inverse variation occurs when an increase in one quantity causes a decrease in the other, or a decrease in one causes an increase in the other.
- Mathematical Rule: If two quantities x and y vary inversely, their product (x × y) remains constant.
- Formula: x₁y₁ = x₂y₂ = constant.
- Arrow Method: In calculations, arrows are marked in opposite directions (one upward and one downward).
4. Time and Work Concepts
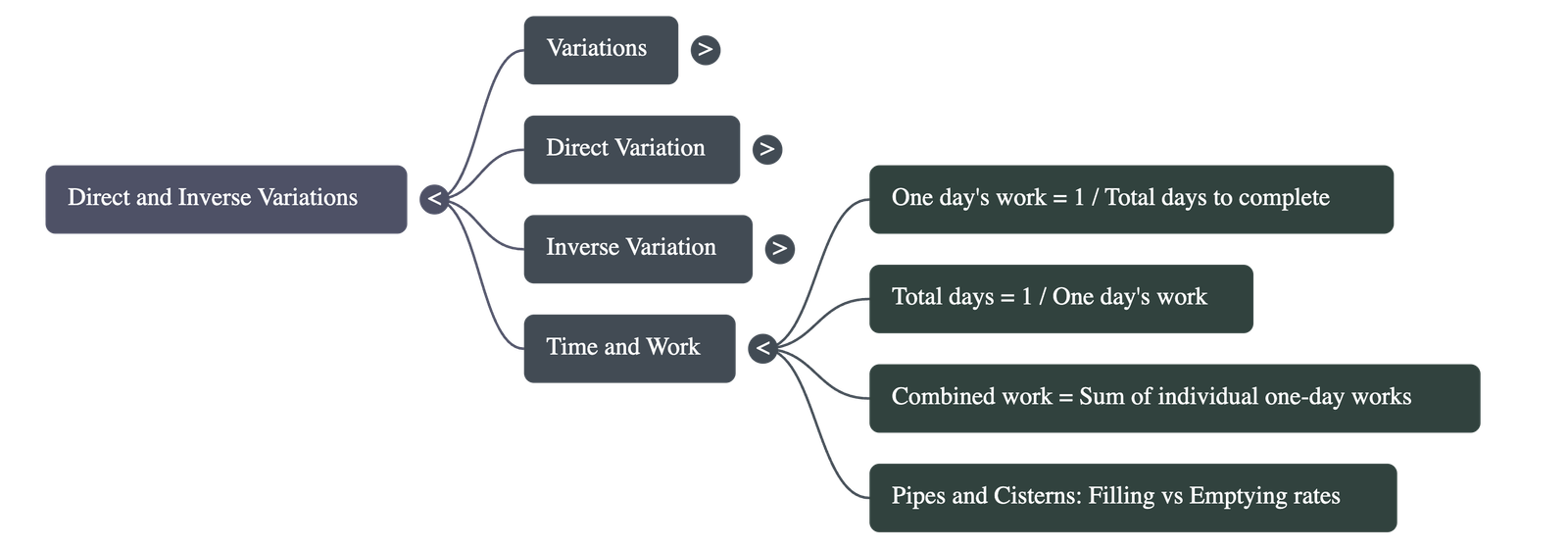
- One Day's Work: If a person can complete a piece of work in n days, then the work done in one day is 1/n.
- Total Time: Conversely, if a person's one day's work is 1/n, they will require n days to finish the entire task.
- Combined Work: When multiple people work together, their individual one-day work rates are added to find the total work done in one day.
- Formula for Time: Number of days required = (Total work to be completed) / (One day's work).
5. Pipes and Cisterns
- Filling Pipes: The work done by a pipe filling a tank is considered positive. If a pipe fills a tank in x minutes, it fills 1/x part of the tank in one minute.
- Emptying Pipes (Waste Pipes): The work done by a pipe emptying a tank is considered negative. If a pipe empties a full tank in y minutes, it empties 1/y part of the tank in one minute.
- Net Work: If multiple pipes are open at once, the net rate of filling or emptying is the sum of the rates of the filling pipes minus the rates of the emptying pipes.
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |