Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Understanding Shapes (Including Polygons)
1. Introduction to Curves
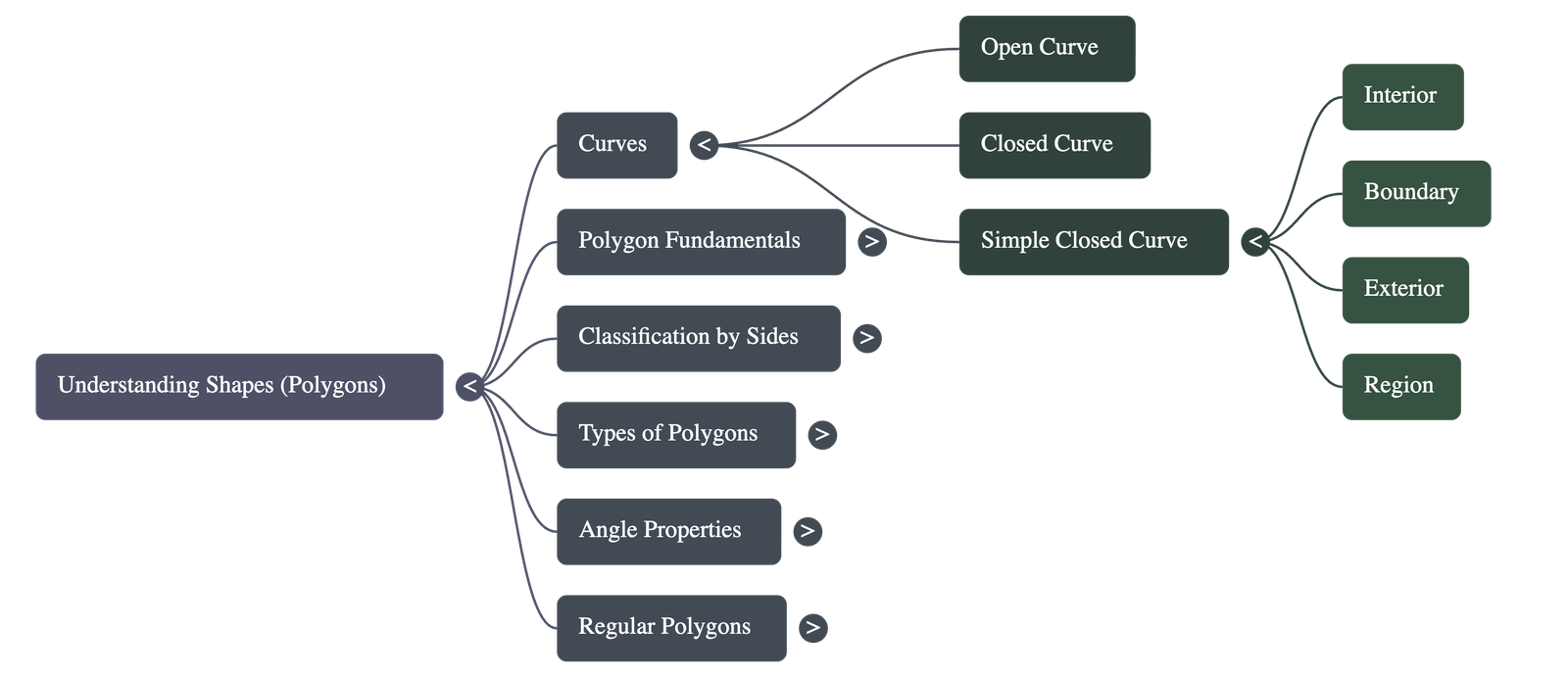
- Mathematical Definition: In geometry, even a straight line is considered a curve.
- Open Curve: A curve that does not cut itself.
- Closed Curve: A curve that cuts itself to enclose a space.
- Simple Closed Curve: A closed curve that does not pass through any of its points more than once.
- Regions: A simple closed curve divides a plane into three parts: the interior, the boundary, and the exterior. The interior combined with the boundary is known as the region.
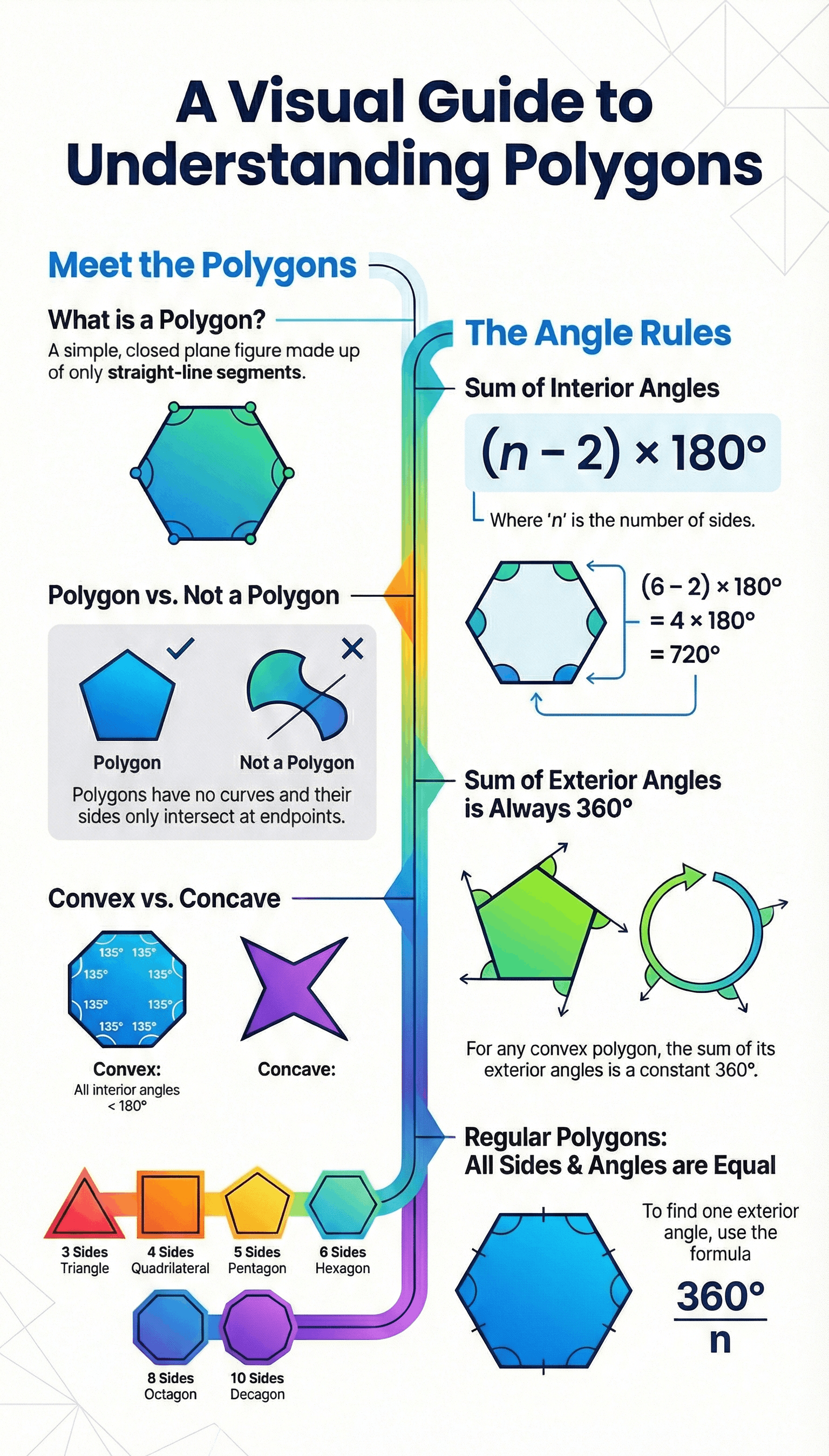
2. Polygons and Their Classification
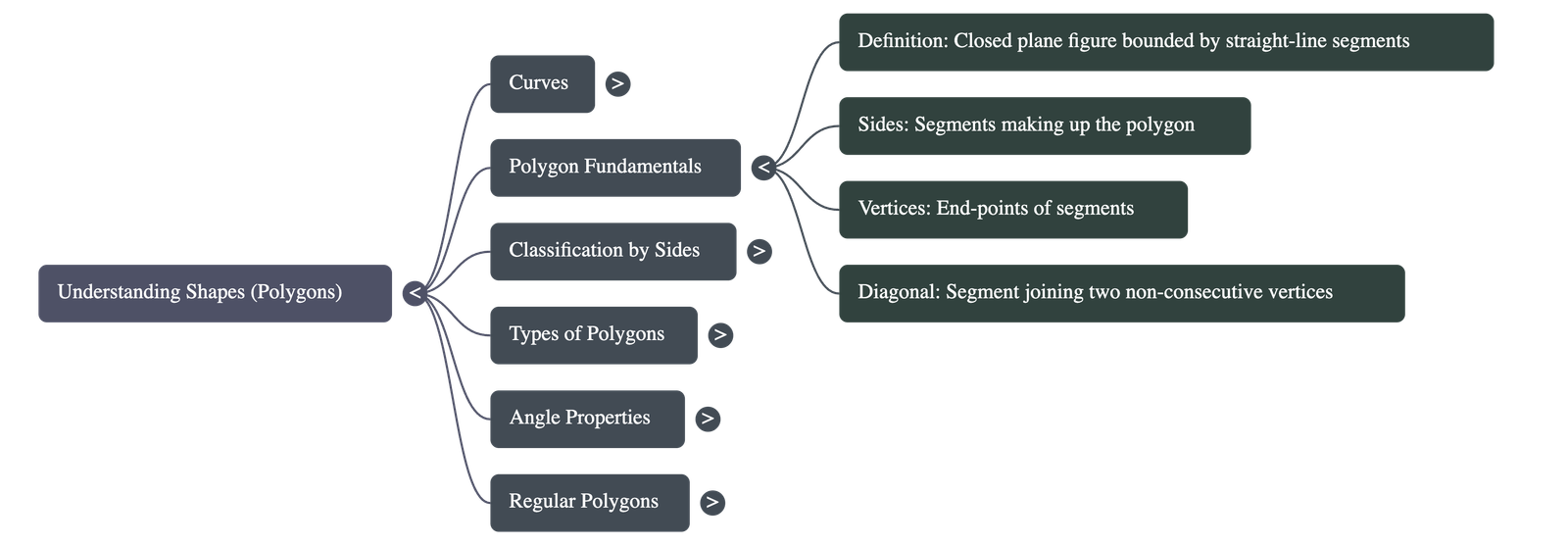
- Definition: A polygon is a closed plane figure bounded by straight-line segments. The segments must intersect only at their endpoints, and each endpoint must be shared by exactly two segments.
- Components: The segments forming the polygon are sides, and their endpoints are vertices.
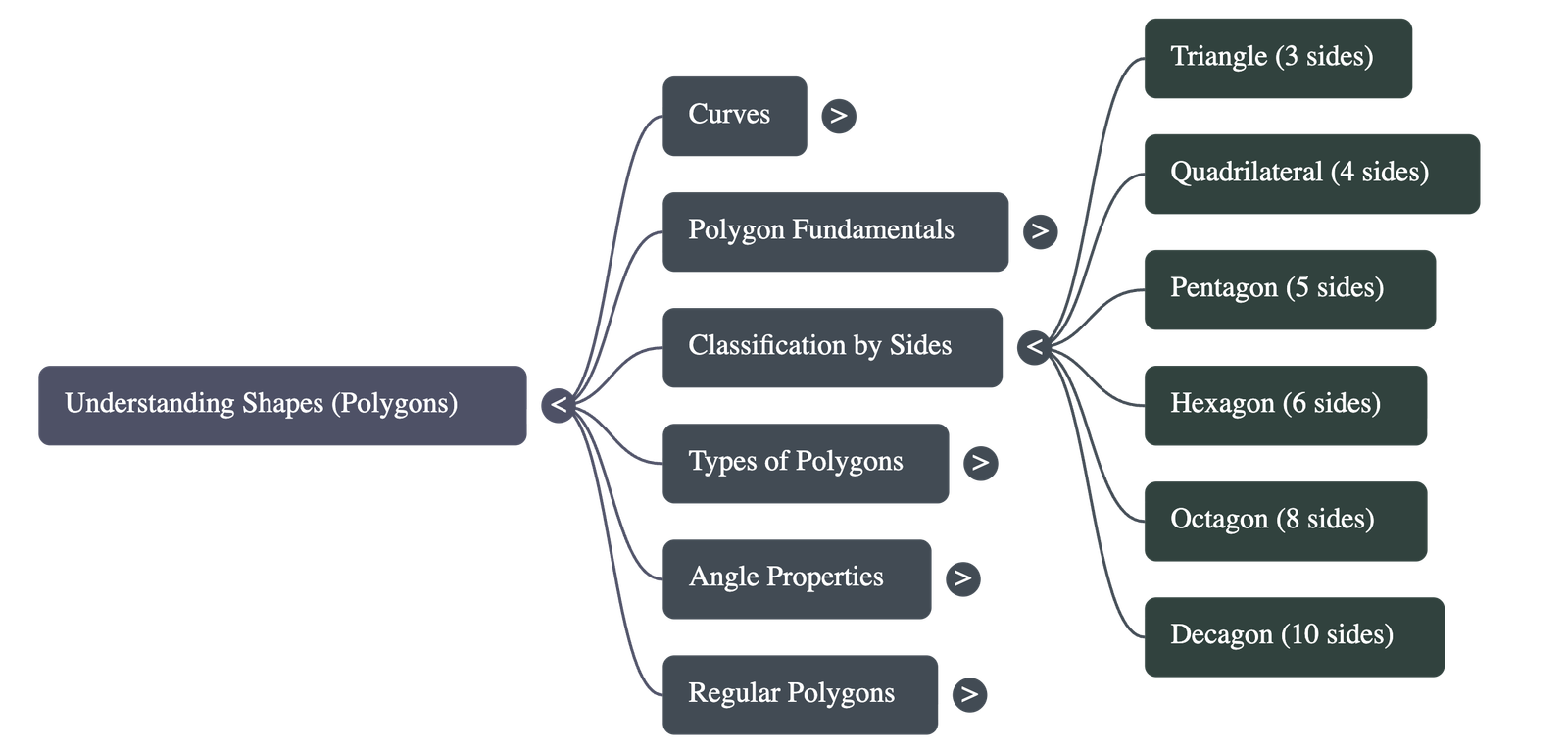
- Naming Conventions: Polygons are named based on their number of sides:
- 3 Sides: Triangle
- 4 Sides: Quadrilateral
- 5 Sides: Pentagon
- 6 Sides: Hexagon
- 8 Sides: Octagon
- 10 Sides: Decagon
- Diagonal: A line segment joining any two non-consecutive vertices.
3. Types of Polygons
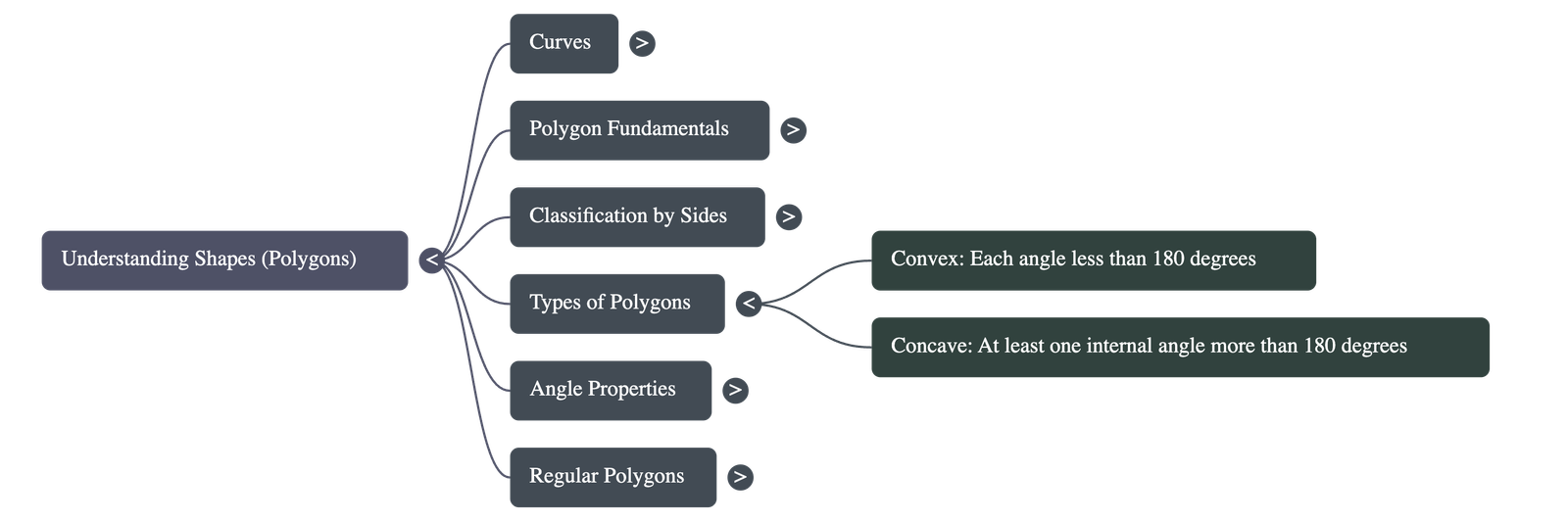
- Convex Polygon: A polygon where every internal angle is less than 180°. (Unless stated otherwise, "polygon" usually refers to a convex one).
- Concave (Re-entrant) Polygon: A polygon where at least one internal angle is more than 180°.
4. Key Angle Formulas
- Sum of Interior Angles: For a polygon with n sides, the sum is calculated as:
(n - 2) × 180° OR (2n - 4) right angles
- Sum of Exterior Angles: If the sides are produced in order, the sum of all exterior angles is always 360° (4 right angles), regardless of the number of sides.
- Side Constraints: The number of sides in a polygon must be a natural number and cannot be less than 3.
5. Regular Polygons
- Definition: A polygon is "regular" if all its interior angles are equal, all its sides are equal, and all its exterior angles are equal.
- Individual Angle Formulas: For a regular polygon with n sides:
- Each Interior Angle:
[(2n - 4) × 90°] / n - Each Exterior Angle:
360° / n
- Each Interior Angle:
- Calculating Sides: If the exterior angle is known, the number of sides n is:
n = 360° / Exterior Angle
- The Linear Pair Property: At any vertex of a polygon, the Interior Angle + Exterior Angle = 180°, as they form a straight line.
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |