Chapter Summary: Surface Area, Volume, and Capacity
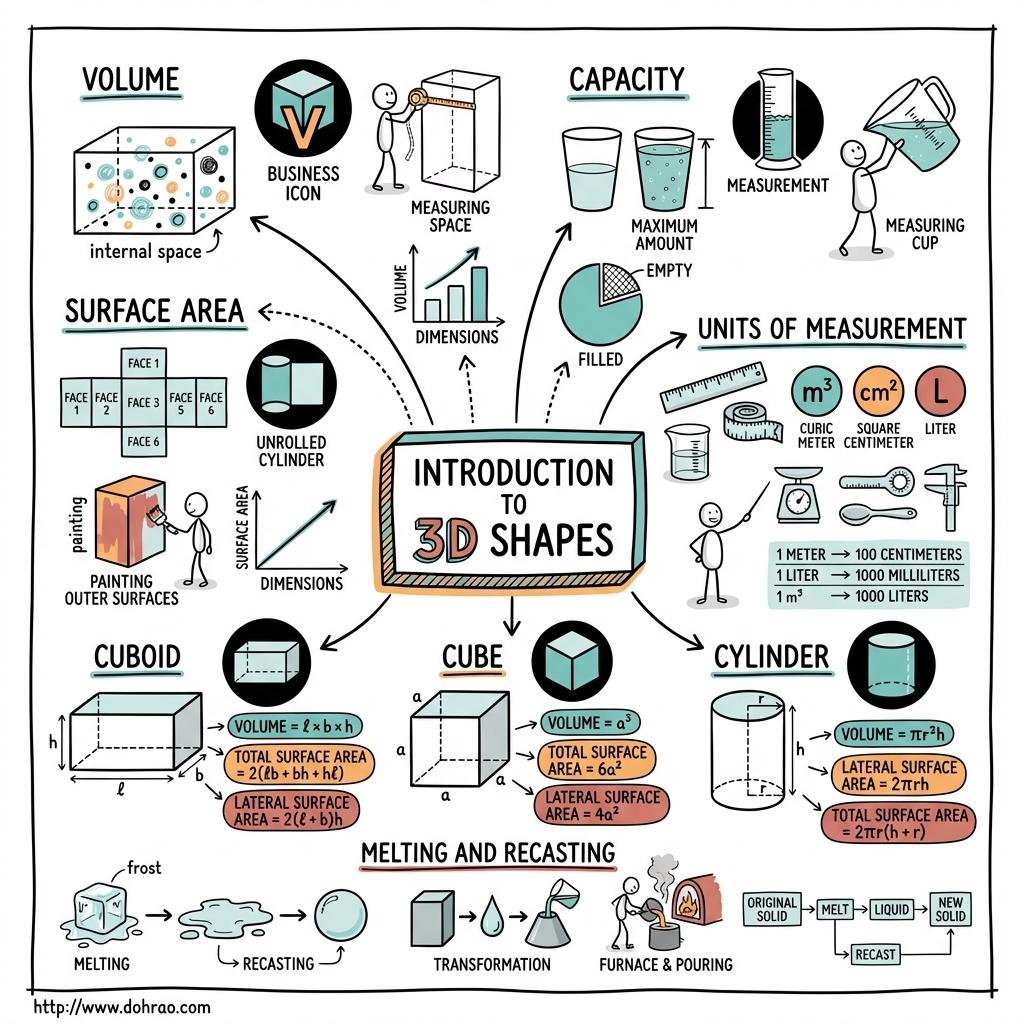
This chapter covers the mathematical properties of three-dimensional solids: the Cuboid, the Cube, and the Cylinder. It details how to calculate the space they occupy (volume) and the total area of their outer surfaces.
1. Introduction and Basic Concepts
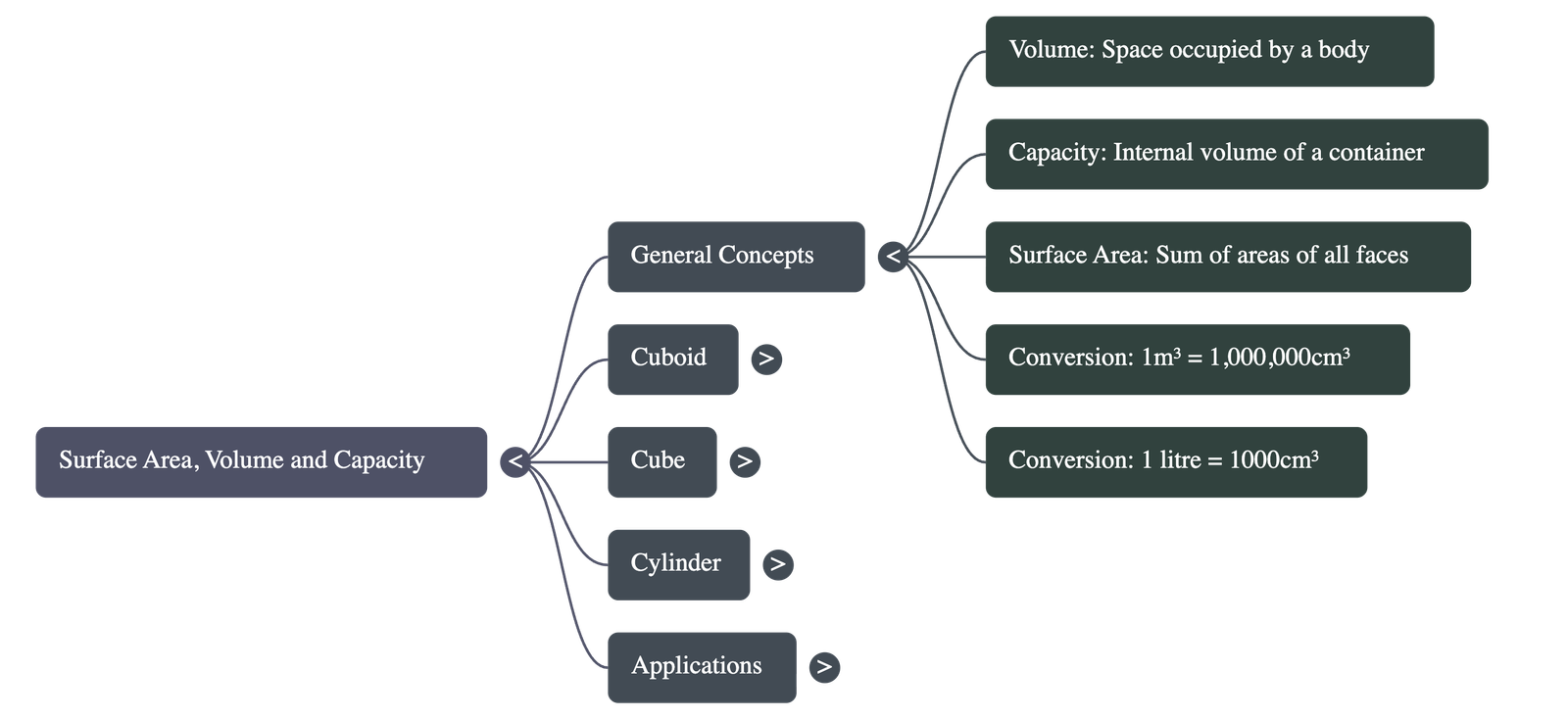
- Volume: The amount of space occupied by a solid body.
- Capacity: The internal volume of a container (how much it can hold).
- Surface Area: The sum of the areas of all faces of the solid body.
Important Unit Conversions
- Volume Conversion: 1 m3 = 1,000,000 cm3
- Capacity Conversion: 1 litre = 1,000 cm3
- Volume to Capacity: 1 m3 = 1,000 litres
2. The Cuboid
A cuboid is a rectangular solid bounded by six rectangular faces. It has length (l), breadth (b), and height (h).
- Volume: l × b × h
- Total Surface Area (TSA): 2 (lb + bh + hl)
- Lateral Surface Area: 2 (l + b) × h
- Diagonal Length: √(l2 + b2 + h2)
3. The Cube
A cube is a special type of cuboid where the length, breadth, and height are all equal. Each face is a square with side a.
- Volume: a × a × a = a3
- Total Surface Area: 6 × a2
- Lateral Surface Area: 4 × a2
- Diagonal Length: a√3
4. Applications: Boxes and Material Volume
When dealing with boxes made of material with a specific thickness, we distinguish between external and internal dimensions.
- Closed Box: If the material has thickness x:
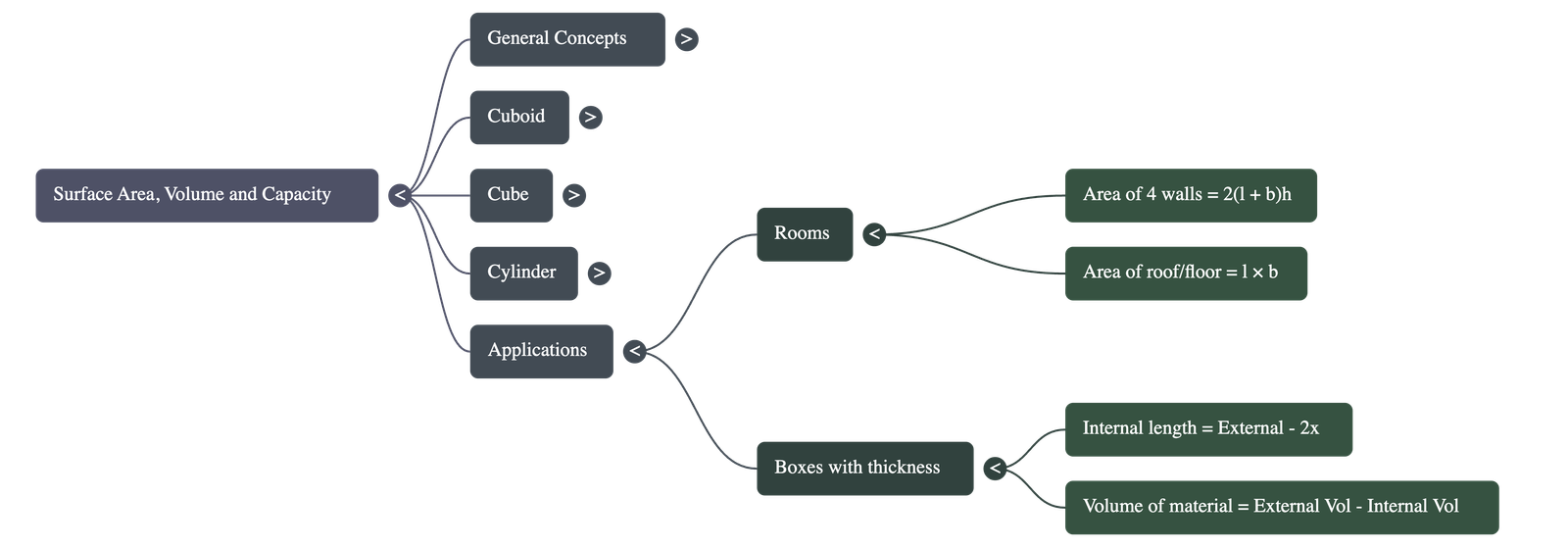
- Internal Length = External Length − 2x
- Internal Breadth = External Breadth − 2x
- Internal Height = External Height − 2x
- Volume of Material Used: Calculated by subtracting the internal volume from the external volume.
Volume of Material = External Volume − Internal Volume - Melting and Recasting: When a solid is melted to form a new shape, the volume remains constant.
Volume of solid melted = Volume of new solid formed
5. The Cylinder
A cylinder is a solid with a uniform circular cross-section. It is defined by the radius of its base (r) and its height (h).
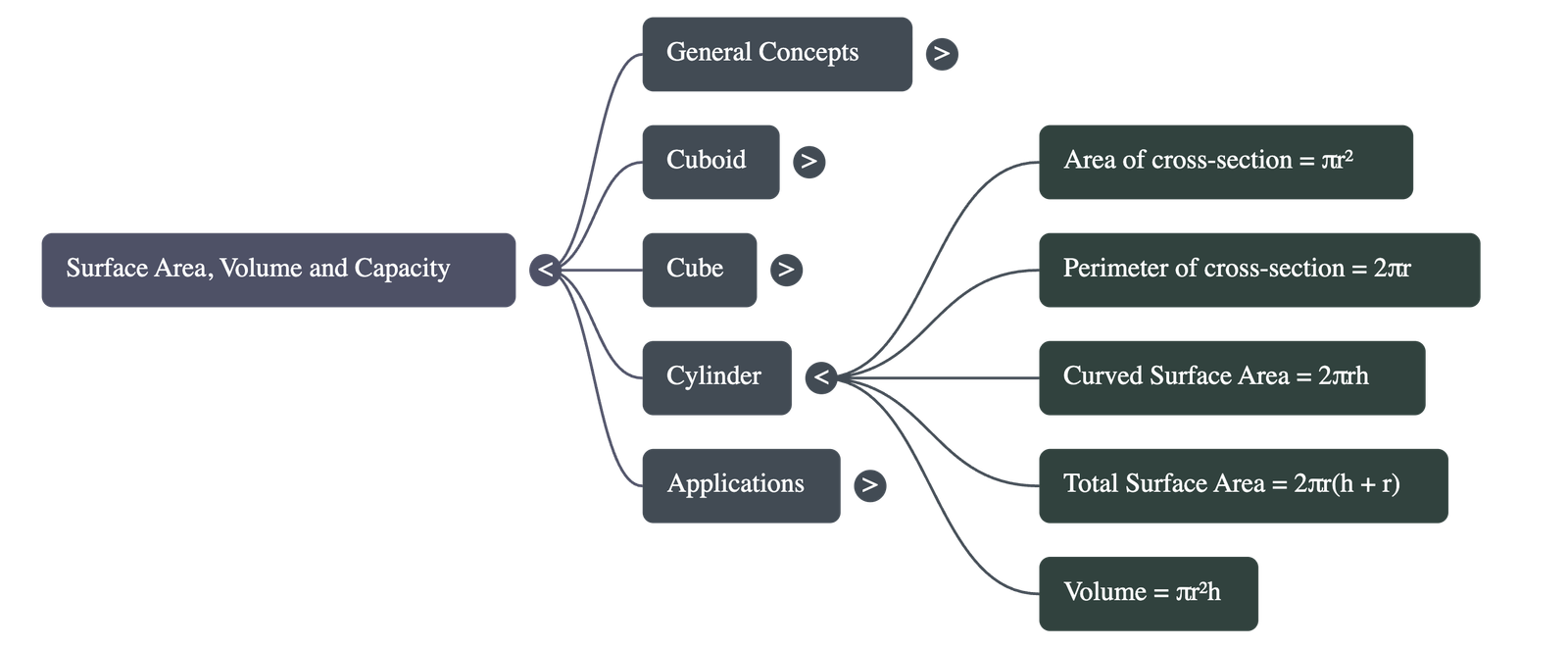
- Area of Cross-section: πr2
- Perimeter of Base: 2πr
- Curved Surface Area (CSA): 2πrh (Perimeter × Height)
- Total Surface Area (TSA): 2πr(h + r) (CSA + 2 × Base Area)
- Volume: πr2h (Area of Base × Height)