Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Chapter Summary: Probability
This chapter introduces the fundamental concepts of probability, dealing with uncertainty, chance, and the prediction of outcomes in random experiments.
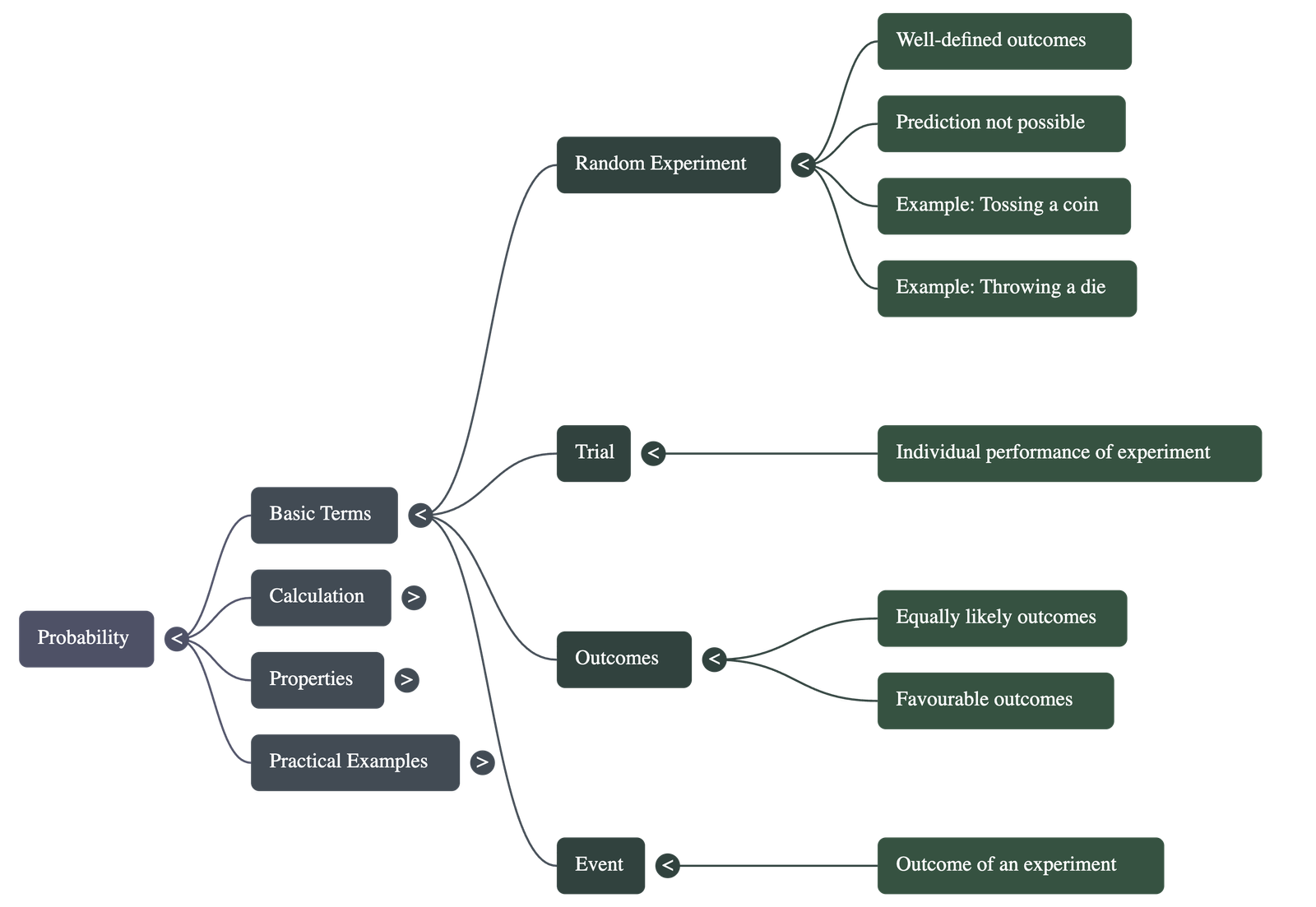
1. Fundamental Concepts
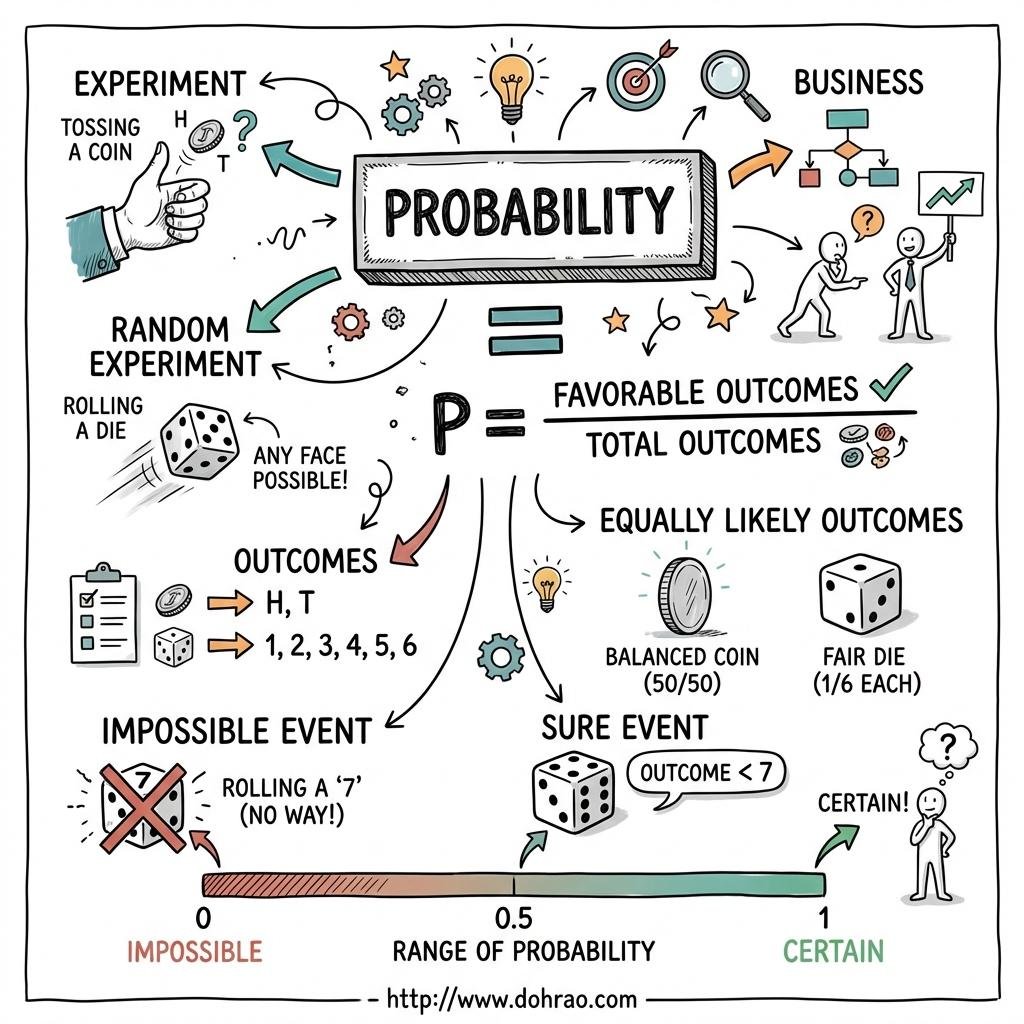
- Probability: A measure of uncertainty regarding the occurrence of an event. It quantifies the chance of an event happening.
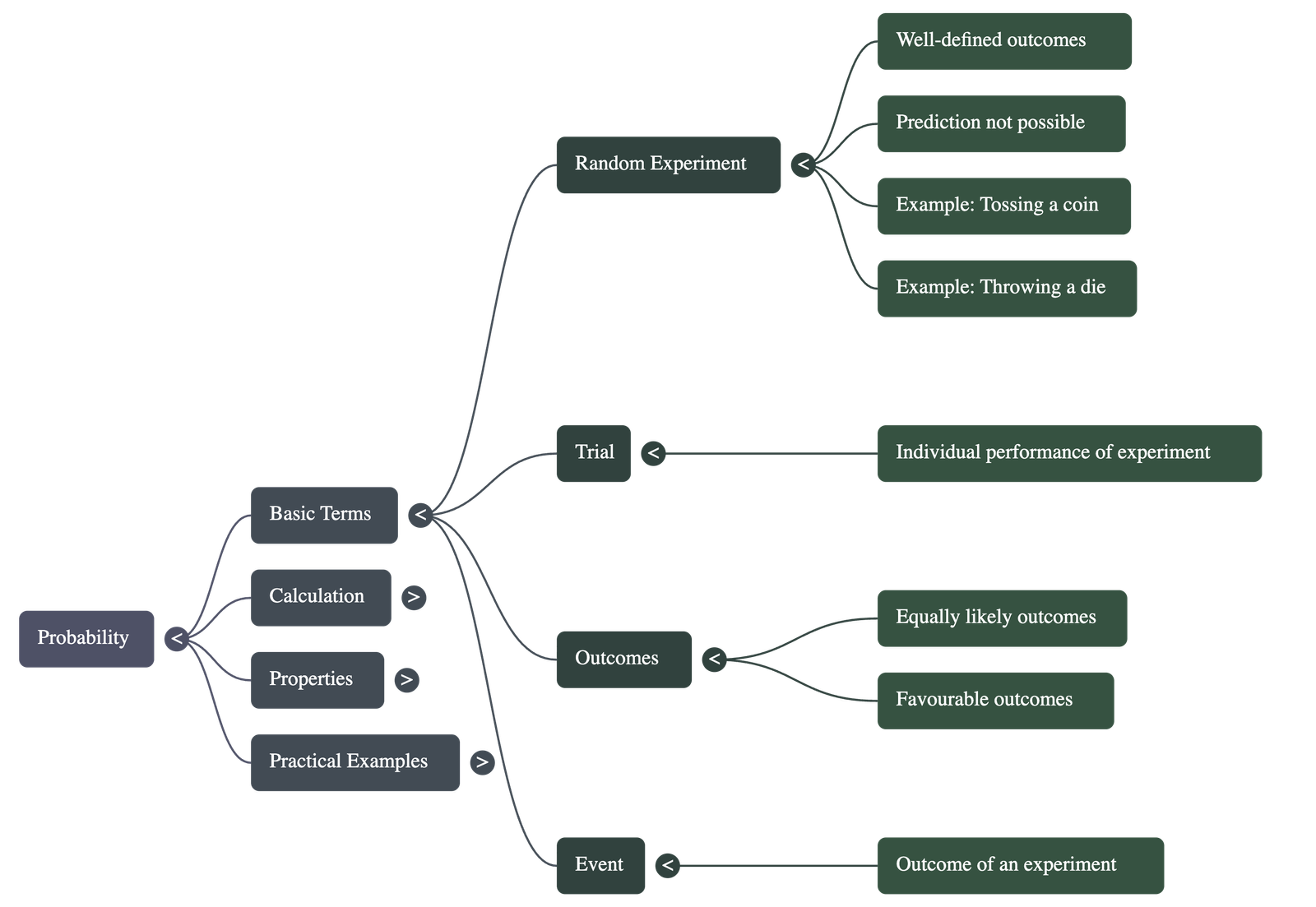
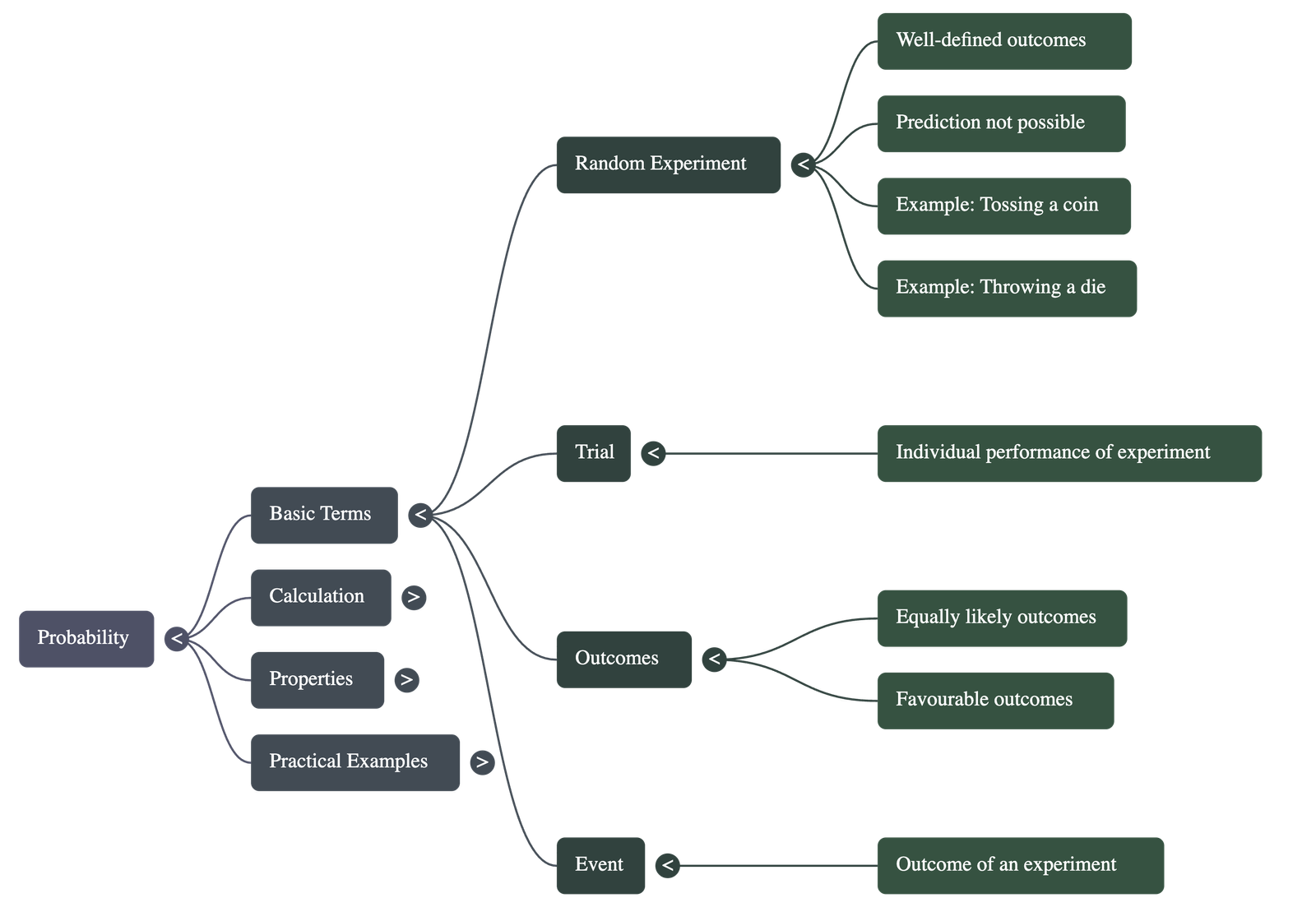
- Experiment: An action that results in well-defined outcomes.
- Random Experiment: An experiment where:
- There is more than one possible outcome.
- All possible outcomes are known in advance.
- The specific outcome cannot be predicted beforehand.
- Trial: A single performance of an experiment (e.g., one toss of a coin or one throw of a die).
- Event: Each outcome of an experiment is called an event.
- Equally Likely Outcomes: When all outcomes of an experiment have an equal chance of occurring (e.g., a fair coin or a fair die).
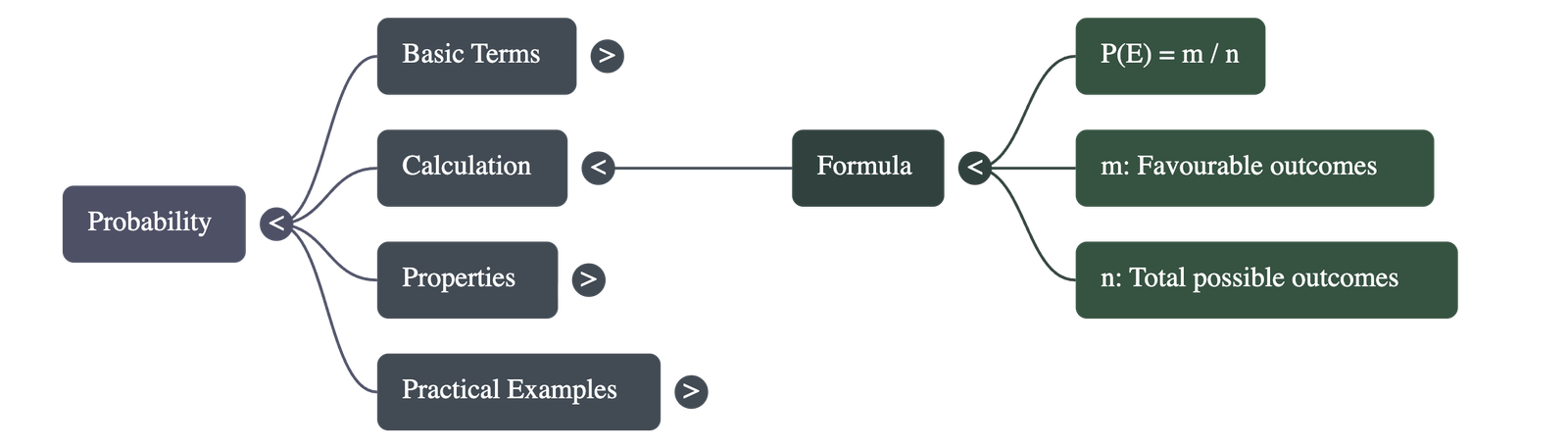
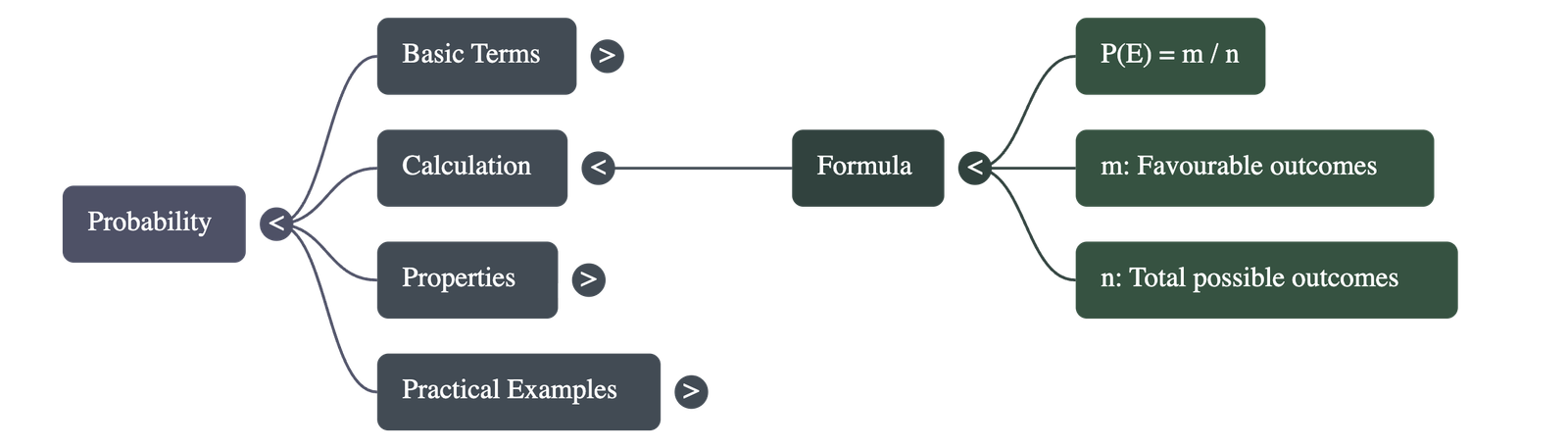
2. Calculation of Probability
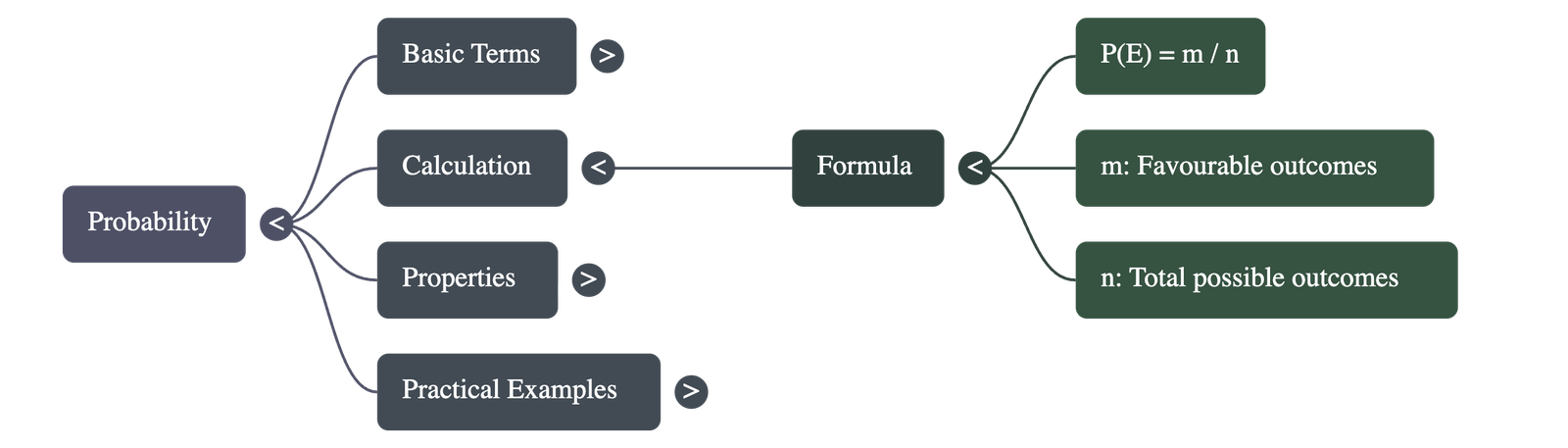
If there are n total possible outcomes and m outcomes are favourable to a specific event E, the probability of E happening is denoted by P(E).
P(E) =
Number of favourable outcomes
Total number of possible outcomes = m / n
Total number of possible outcomes = m / n
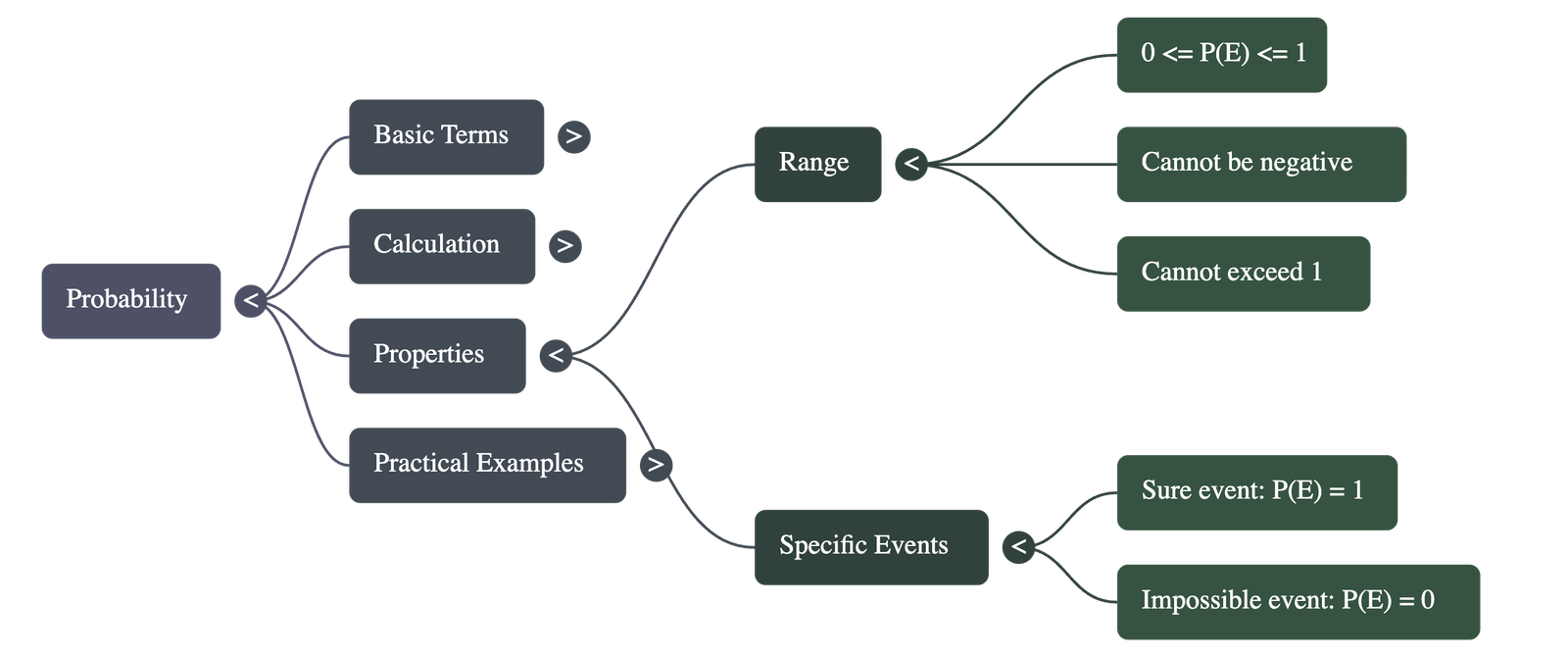
3. Important Properties of Probability
- Range: The probability of an event always lies between 0 and 1 (inclusive).
Mathematically: 0 ≤ P(E) ≤ 1 - Sure Event: An event that is certain to happen has a probability of 1.
Example: Getting a natural number less than 7 when throwing a standard die. - Impossible Event: An event that can never happen has a probability of 0.
Example: Getting a number greater than 6 when throwing a standard die. - Sum of Probabilities: The sum of the probabilities of all possible outcomes of an experiment is always 1.
- Validity: Probability can never be negative and can never be greater than 1. Answers like -2 or 1.25 are impossible.
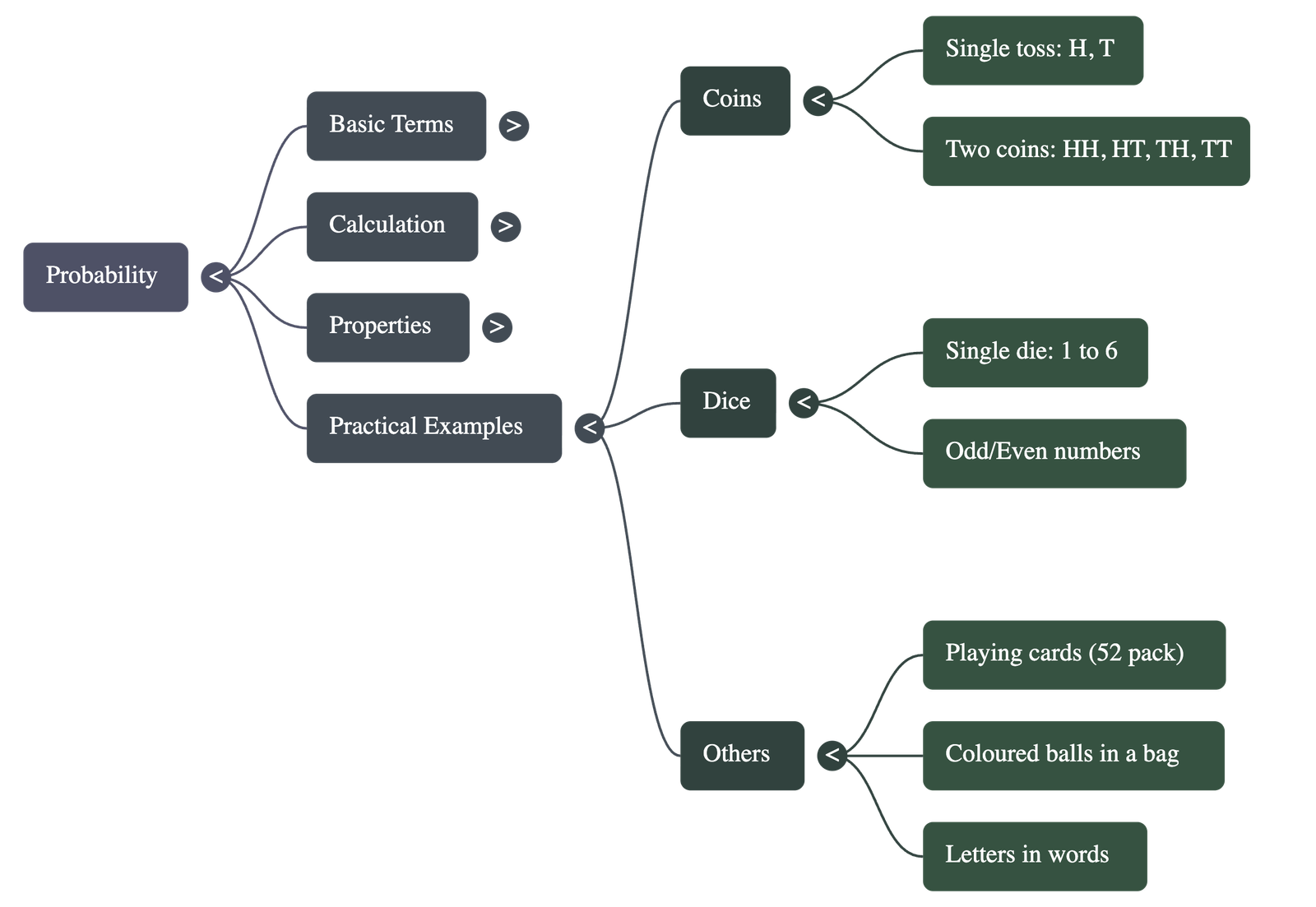
4. Common Sample Spaces (Outcomes)
Tossing Coins
- 1 Coin: Total outcomes = 2 (Head, Tail).
- 2 Coins (or 1 coin tossed twice): Total outcomes = 4 (HH, HT, TH, TT).
- 3 Coins: Total outcomes = 8 (HHH, HHT, HTH, HTT, THH, THT, TTH, TTT).
Throwing Dice
- 1 Die: Total outcomes = 6 (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6).
- Even numbers: 2, 4, 6
- Odd numbers: 1, 3, 5
- Prime numbers: 2, 3, 5
- 2 Dice: Total outcomes = 36 (Pairs ranging from (1,1) to (6,6)).
Playing Cards
- A standard deck contains 52 cards.
- Calculations are based on suits (Hearts, Diamonds, Spades, Clubs), colors (Red, Black), or face cards (King, Queen, Jack).
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |