Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
A point-wise summary of the chapter titled Subject and Predicate:
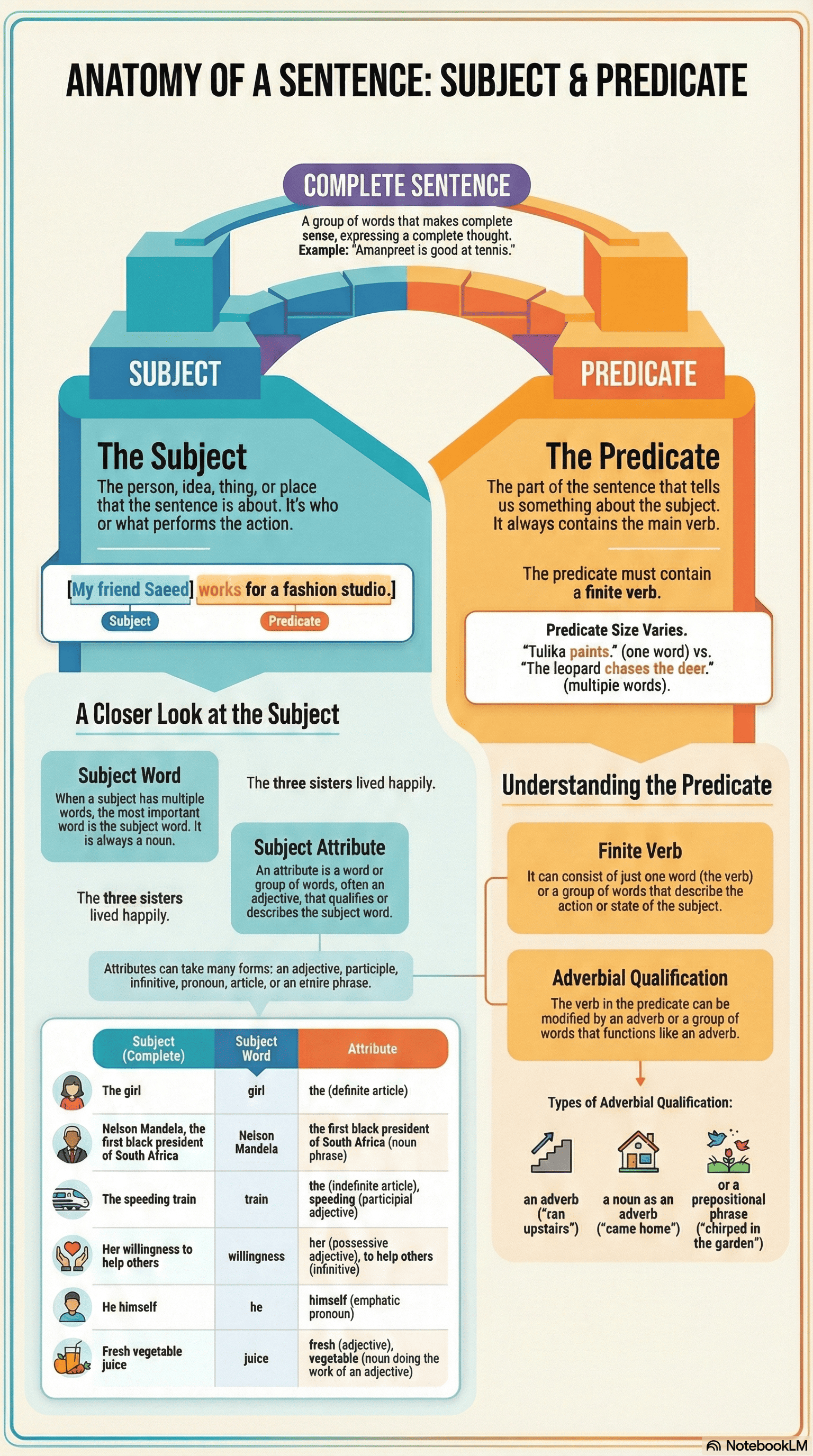
- Definition of a Sentence: A sentence is a group of words that makes complete sense.
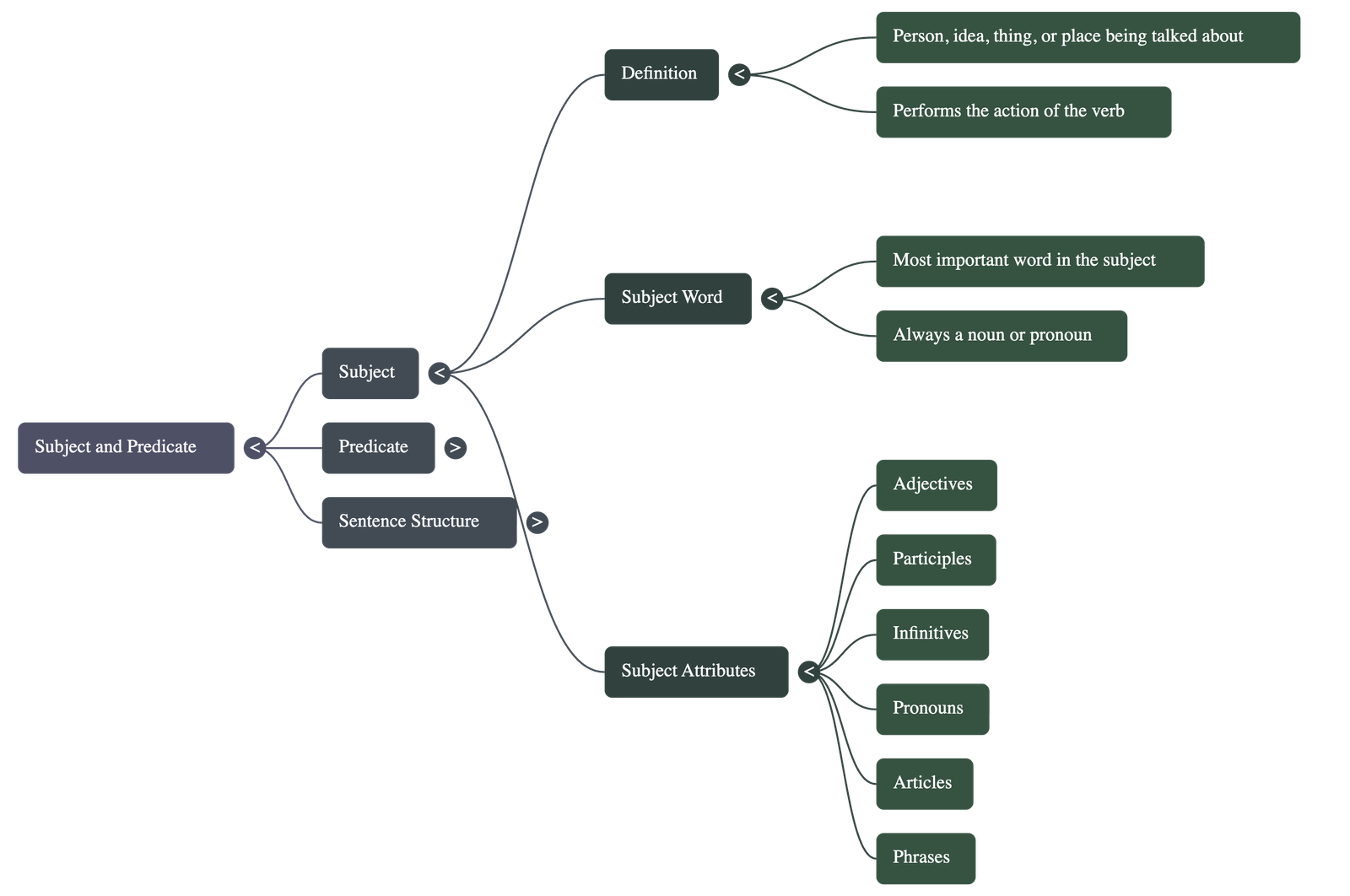
- The Subject: This is the person, idea, place, or thing that is being talked about or that performs the action expressed by the verb.
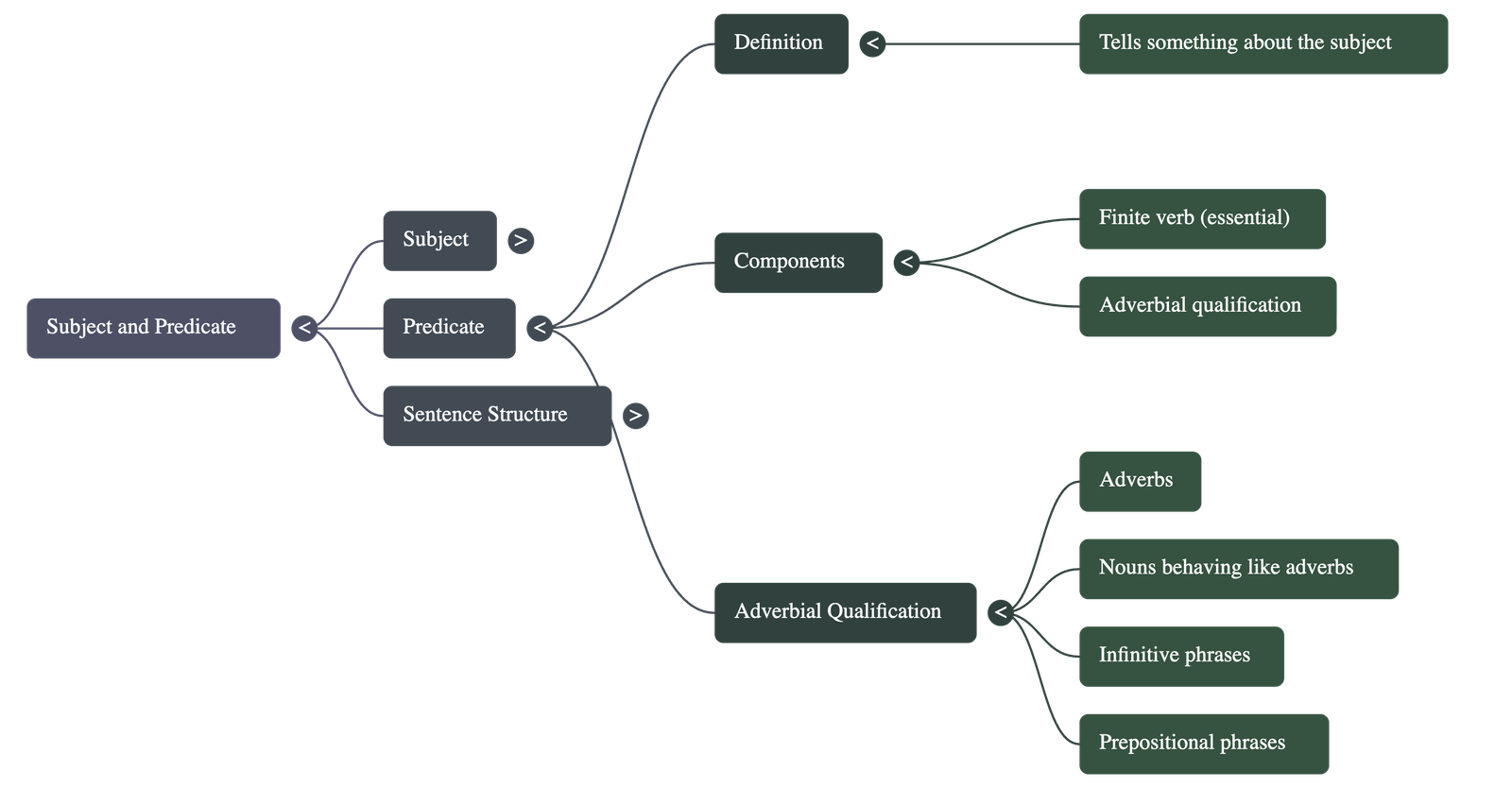
- The Predicate: This is the part of the sentence that tells us something about the subject.
- The Subject Word: In a subject consisting of multiple words, the most important word is called the "subject word," and it is always a noun.
- Subject Word Attributes: The subject word is often qualified by an adjective or words functioning as an adjective; this is known as an attribute.
- Types of Attributes: An attribute can take several forms, including:
- Articles (e.g., "the," "a").
- Adjectives or participial adjectives (e.g., "fresh," "speeding").
- Noun phrases or infinitives (e.g., "to help others").
- Emphatic pronouns or possessive adjectives.
- Components of the Predicate: A predicate can be a single word or a group of words, but it must always contain a finite verb.
- Adverbial Qualification: In the predicate, the verb may be qualified by an adverb or a group of words (such as a prepositional phrase or infinitive phrase) that performs the work of an adverb.
Analogy To understand this structure, think of a sentence like a directed play: the Subject is the lead actor (the "who" or "what"), the Attributes are the actor's costume and description, and the Predicate is the action they perform on stage to tell the story.
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |