Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Direct and Indirect Speech
1. Definitions
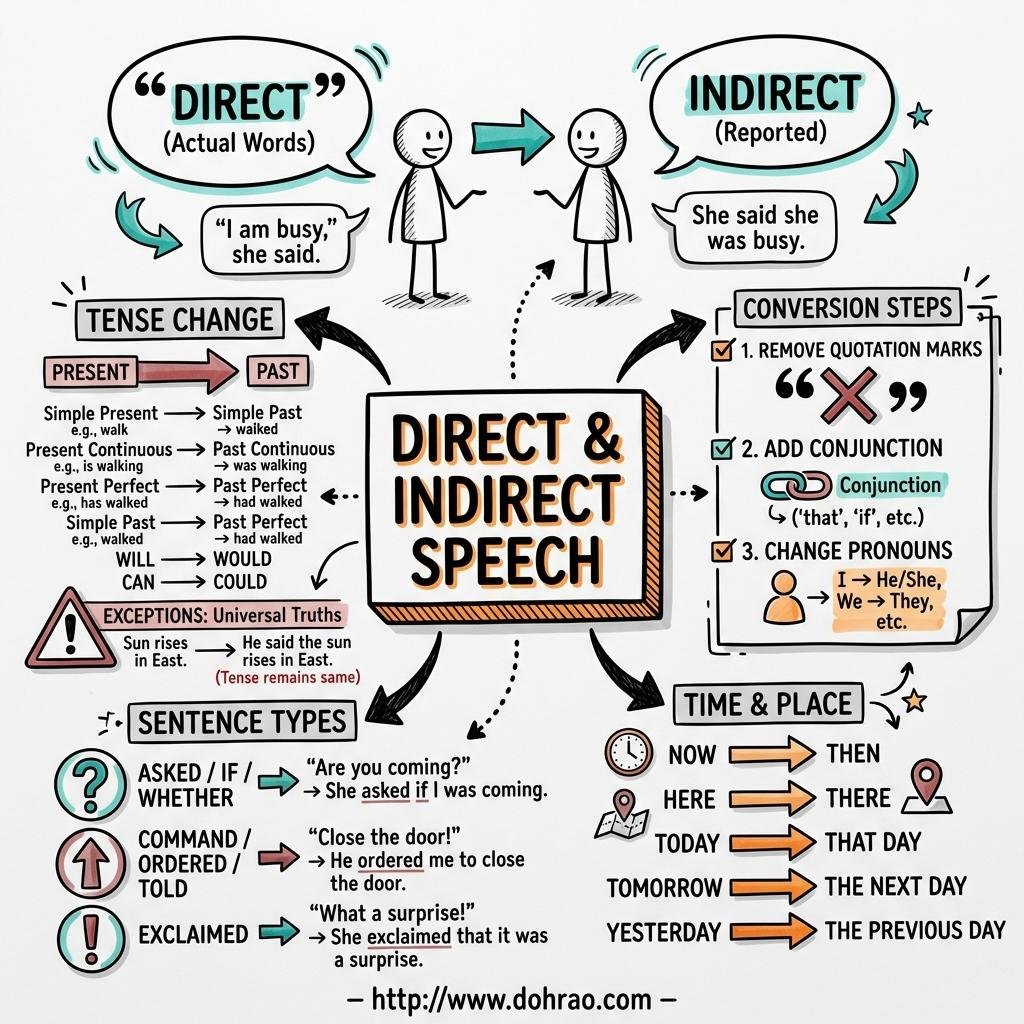
- Direct Speech: Reporting exactly what someone said by quoting their actual words within inverted commas.
- Indirect (Reported) Speech: Reporting the substance of what was said without repeating the speaker's exact words.
2. Key Rules for Conversion
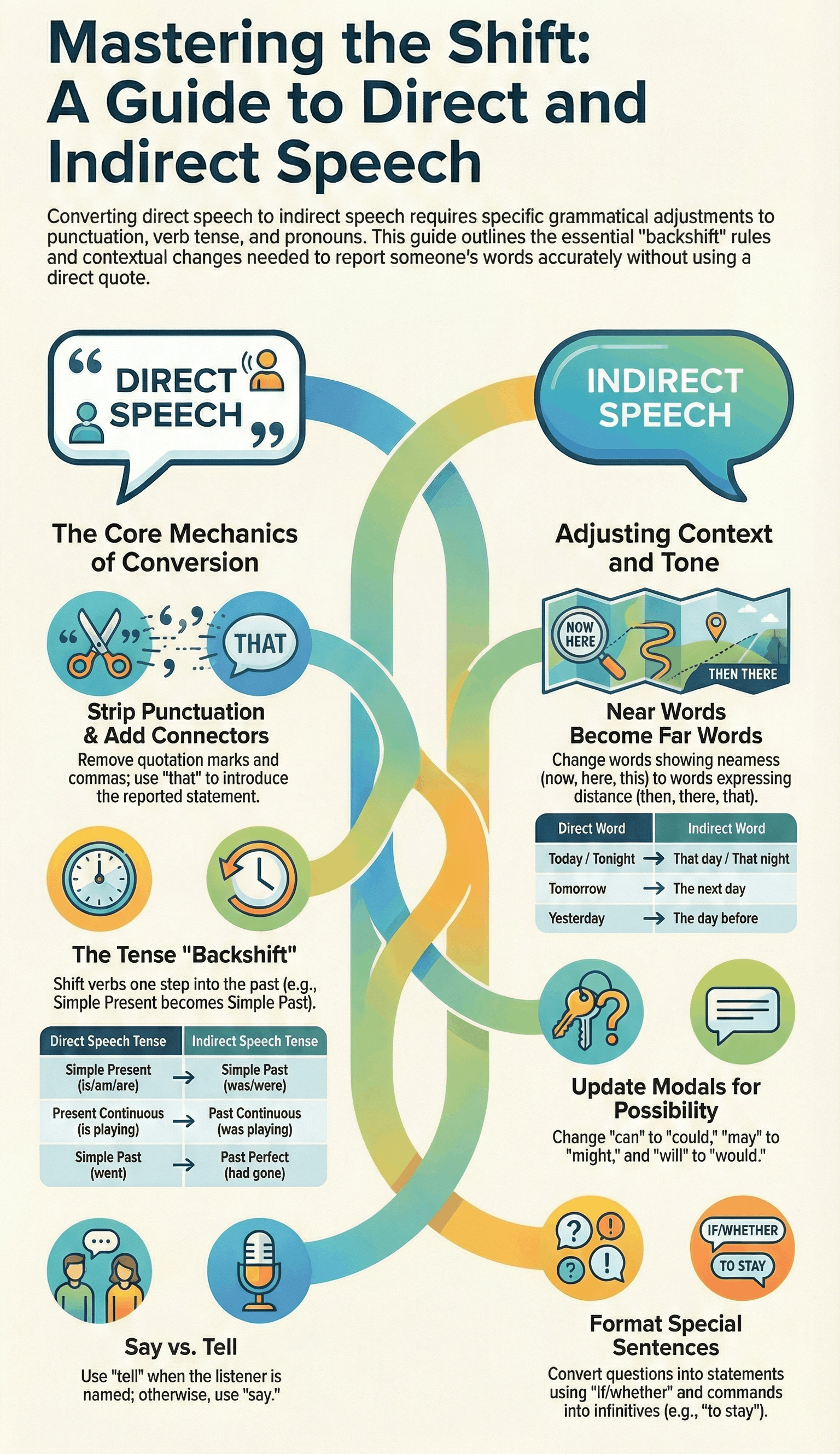
- Punctuation: Inverted commas and the comma separating the reporting verb are removed in indirect speech.
- Conjunctions: A conjunction like that, if, or whether is often used to introduce the reported statement.
- Sentence Structure: All types of sentences (questions, exclamations, commands) are converted into assertive statements ending with a full stop.
- Pronouns: Personal pronouns change based on who is reporting and who is being addressed (e.g., first person usually changes to third person).
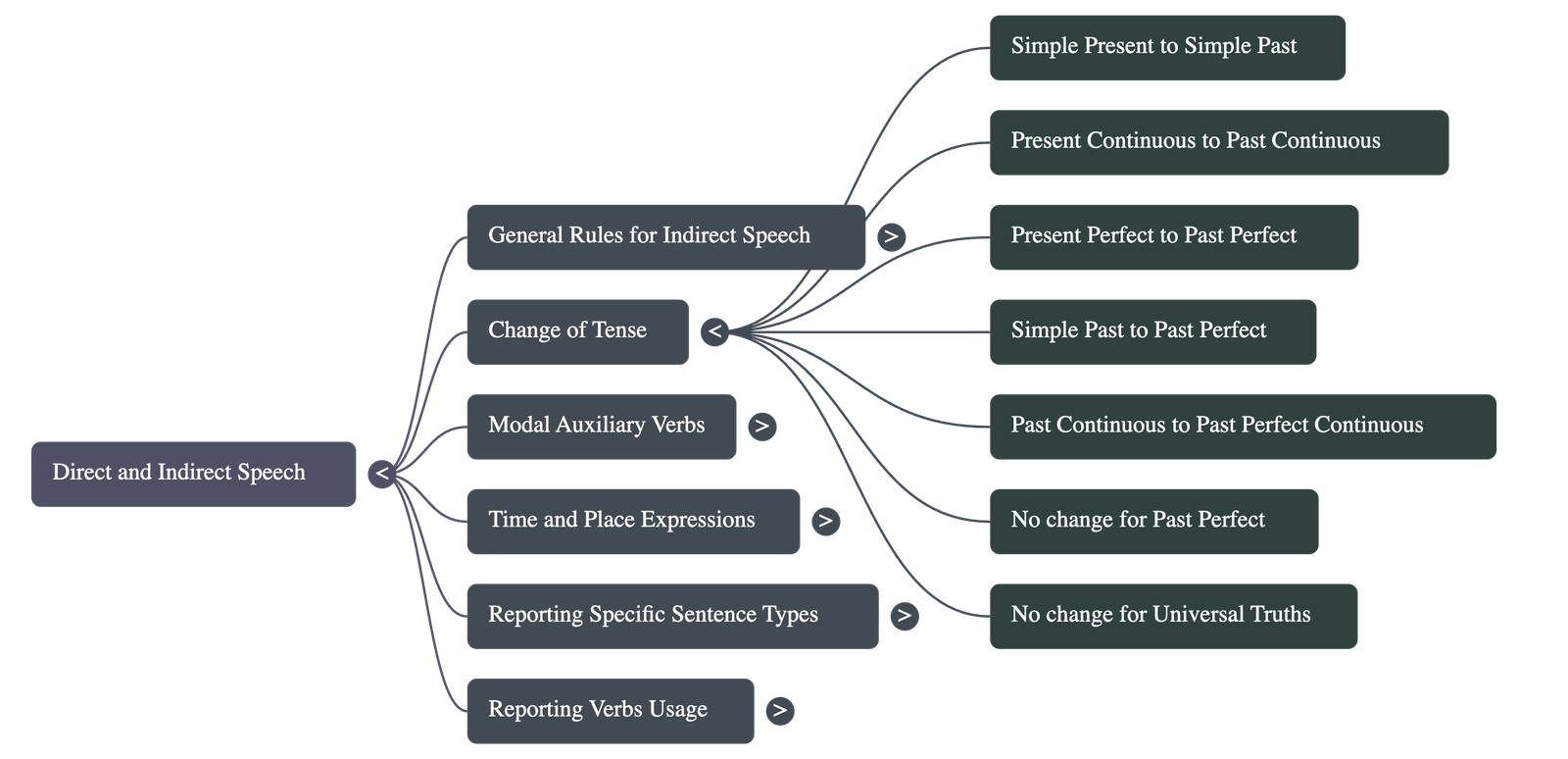
3. Tense Changes
When the reporting verb is in the past tense, the tense of the direct speech usually shifts back:
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
|---|---|
| Simple Present | Simple Past |
| Present Continuous | Past Continuous |
| Present Perfect | Past Perfect |
| Simple Past | Past Perfect |
| Past Continuous | Past Perfect Continuous |
| Modals (can, may, will, shall) | Past Modals (could, might, would, should) |
Exceptions: No tense change occurs if the reporting verb is in the present/future tense, or if the statement expresses a universal truth or remains true at the time of reporting.
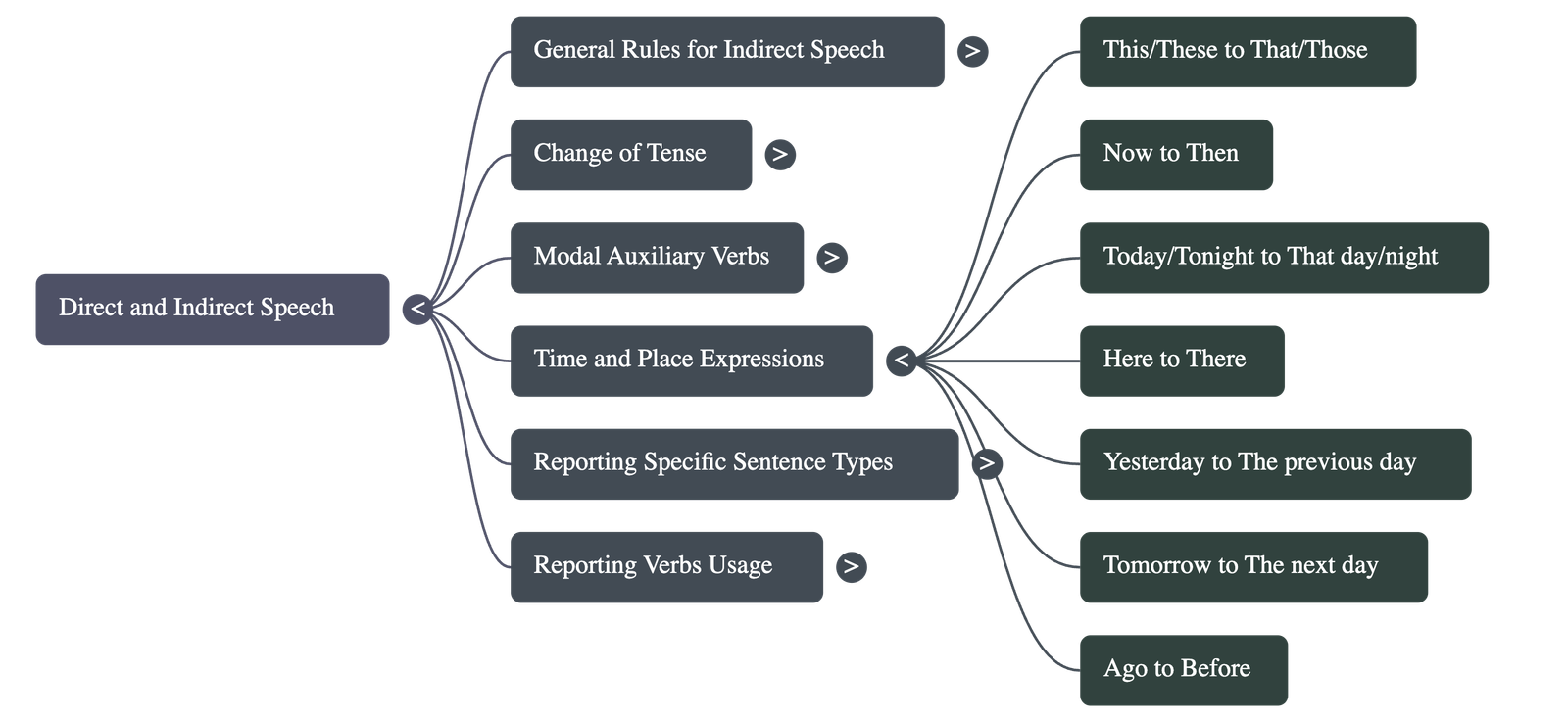
4. Changes in Time and Place
Words expressing nearness in time and place change to words expressing distance:
- This/These becomes That/Those
- Now becomes Then
- Today/Tonight becomes That day/That night
- Yesterday becomes The day before/The previous day
- Tomorrow becomes The next day/The following day
- Here becomes There
- Ago becomes Before
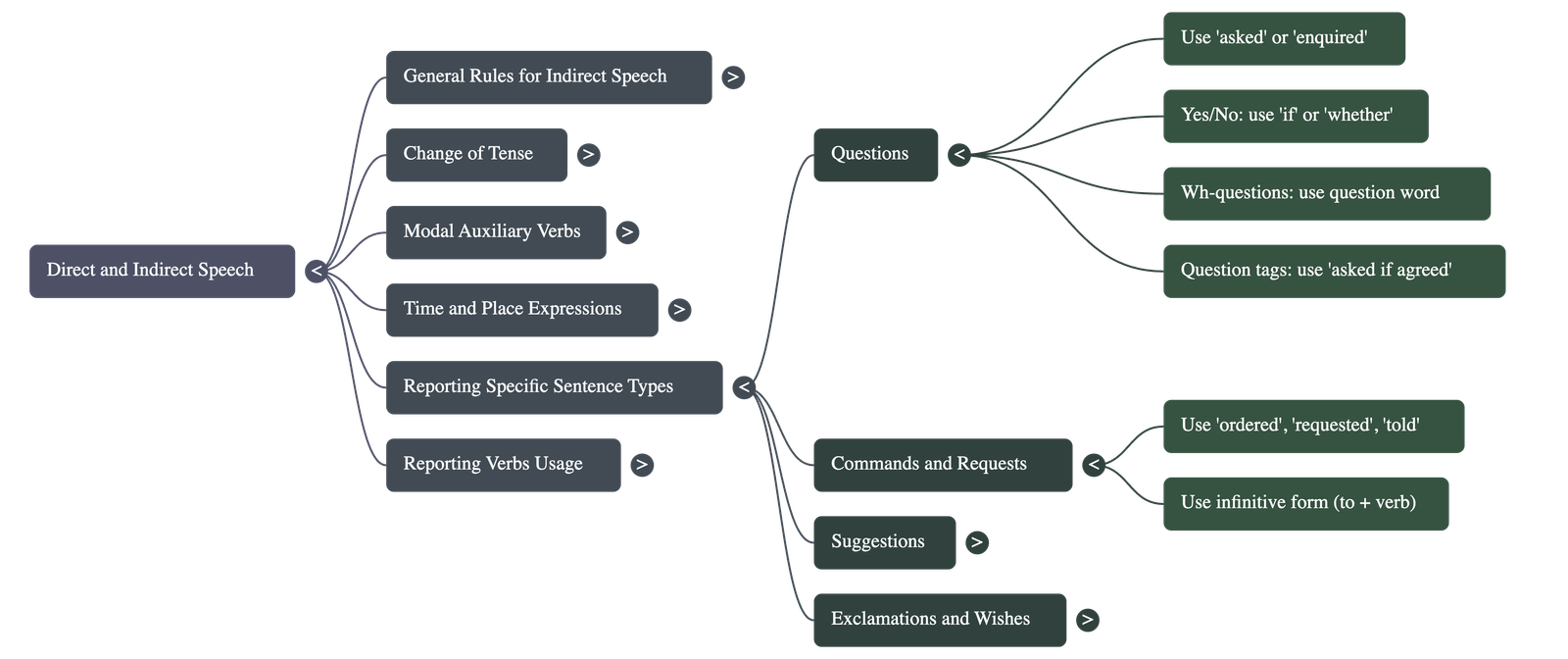
5. Reporting Different Sentence Types
- Questions: Use reporting verbs like asked, enquired, or wondered. For Yes/No questions, use if/whether. For Wh-questions, the question word remains the same but the word order becomes assertive.
- Question Tags: The tag is removed, and the sentence is reported based on the meaning conveyed (e.g., "asked if I agreed").
- Commands and Requests: Use reporting verbs like ordered, requested, or commanded. The main verb is changed into its infinitive form (e.g., "to leave").
- Suggestions: Use the reporting verb suggested. The word 'let' is often replaced with "that we should."
- Exclamations and Wishes: Use reporting verbs like exclaimed, praised, or regretted. Expressions of feeling (with joy, with sorrow) are added to capture the mood.
6. Reporting Verbs: Say vs. Tell
- Use tell if the reporting verb is followed by the name or pronoun of the person being spoken to.
- Use say if the person being spoken to is not mentioned.
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |