Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
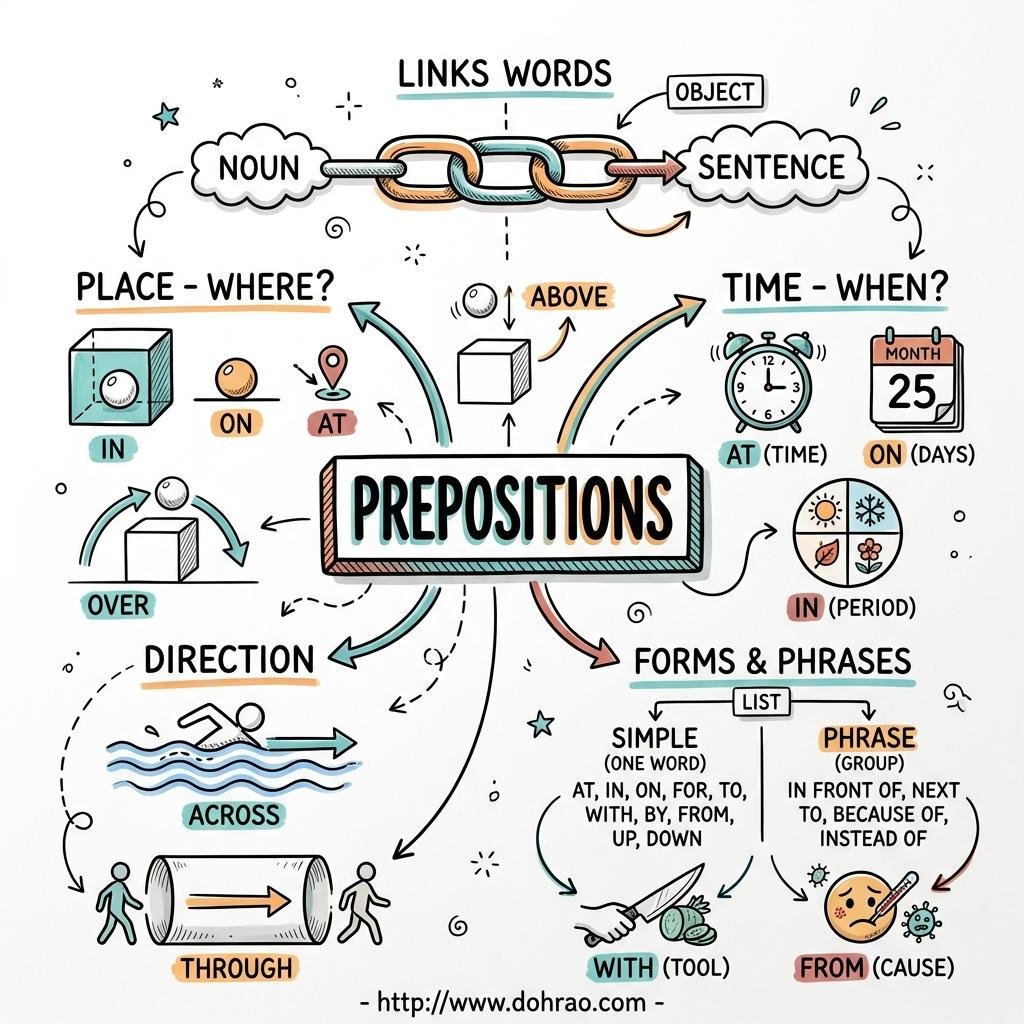
Prepositions
Core Functions and Objects
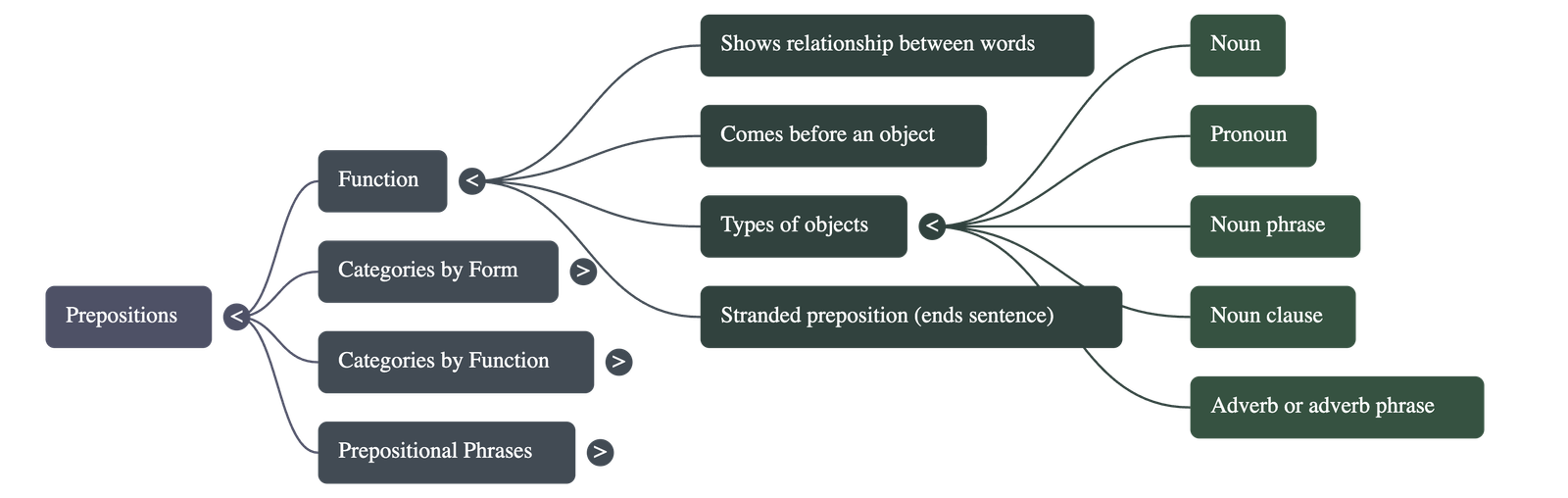
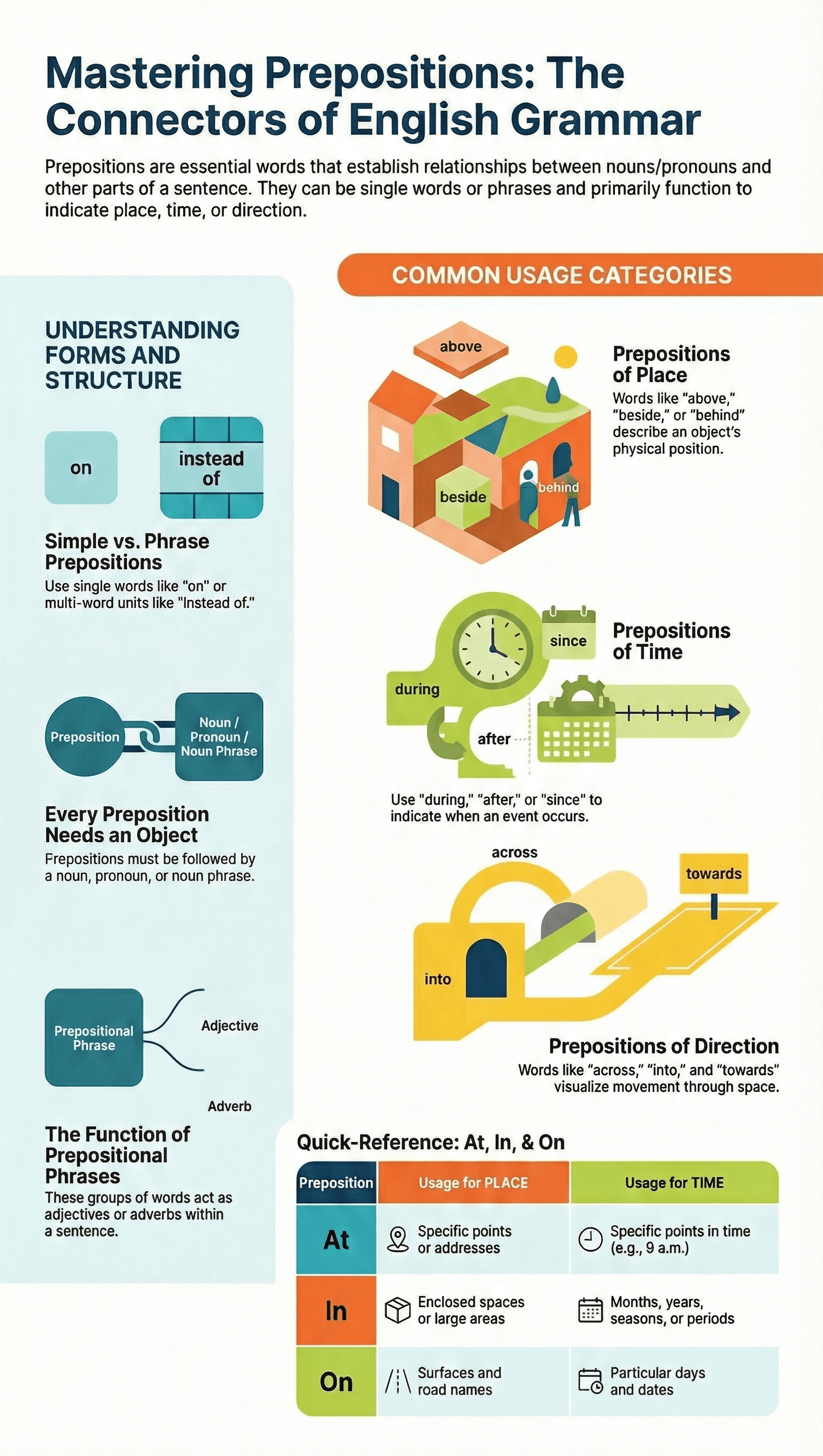
- Definition: A preposition is a word typically placed before a noun or pronoun to show its relationship with other words in a sentence.
- The Object: The word or phrase following a preposition is called its object. This can be a noun, pronoun, noun phrase, noun clause, or occasionally an adverb.
- Stranded Prepositions: These occur when a preposition appears at the end of a sentence, often used with relative or interrogative pronouns or to provide emphasis to the object.
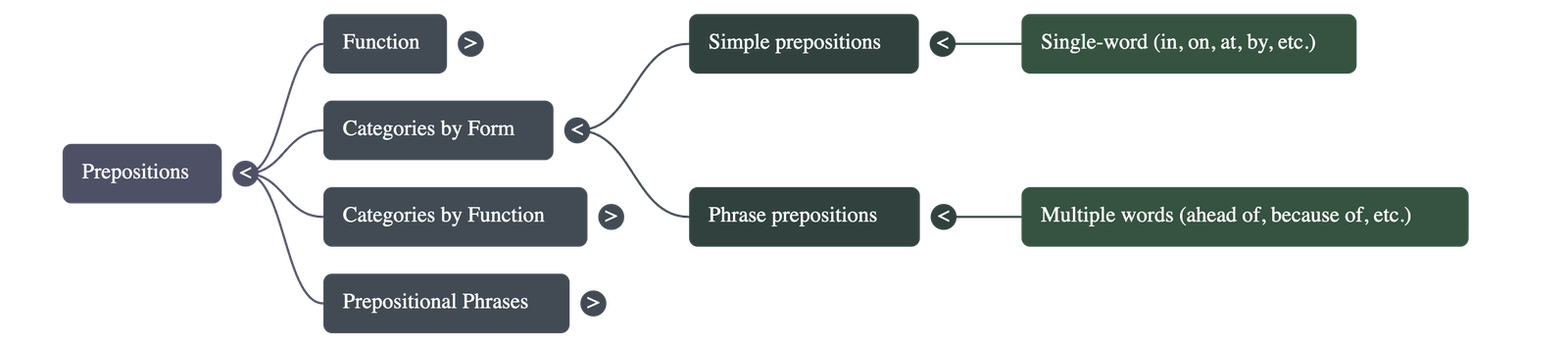
Classification by Form
- Simple Prepositions: Single-word prepositions such as in, on, at, by, from, with, and between.
- Phrase Prepositions: Groups of words that function as a single preposition, such as ahead of, because of, in front of, and on behalf of.
Classification by Function
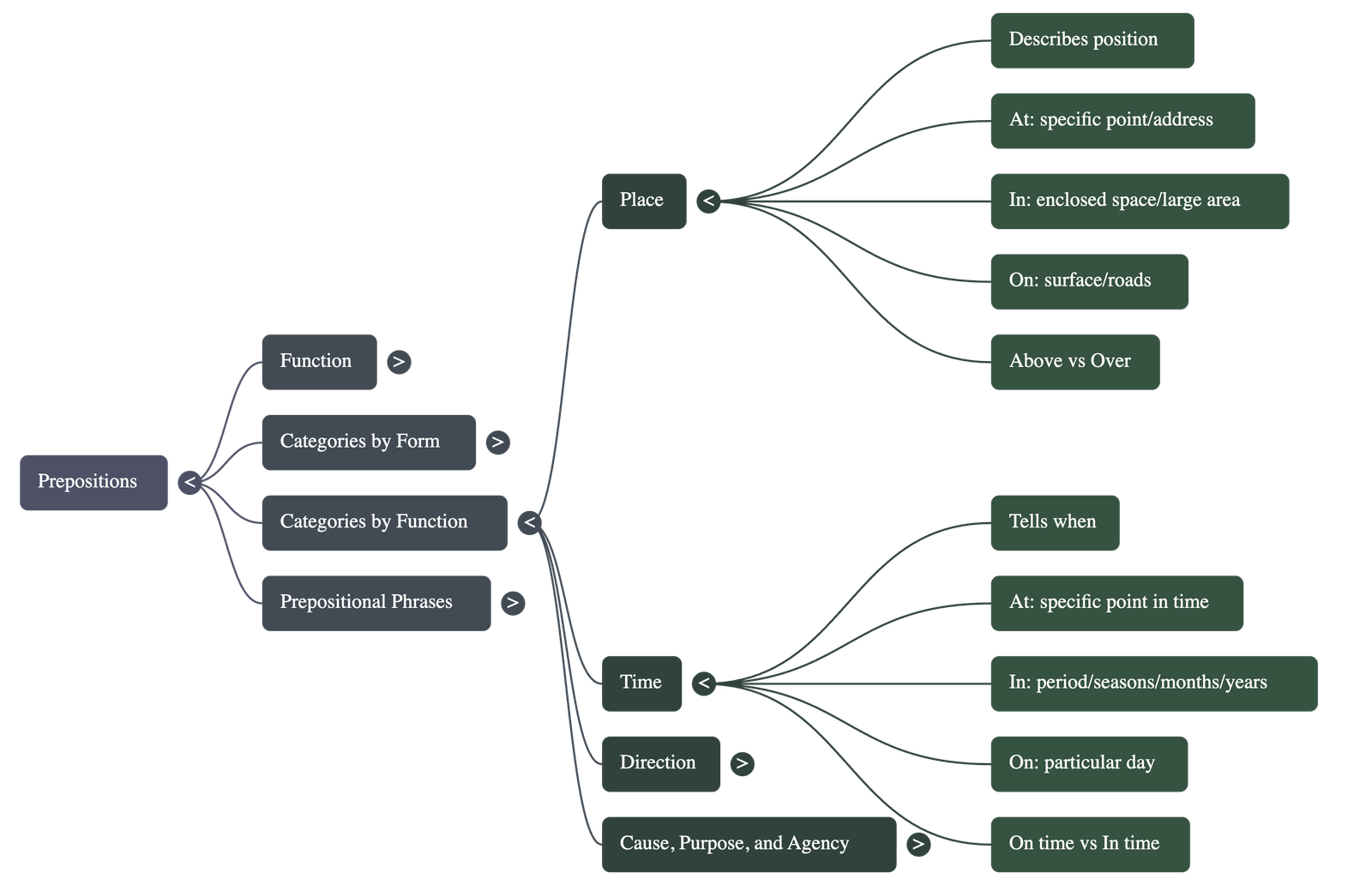
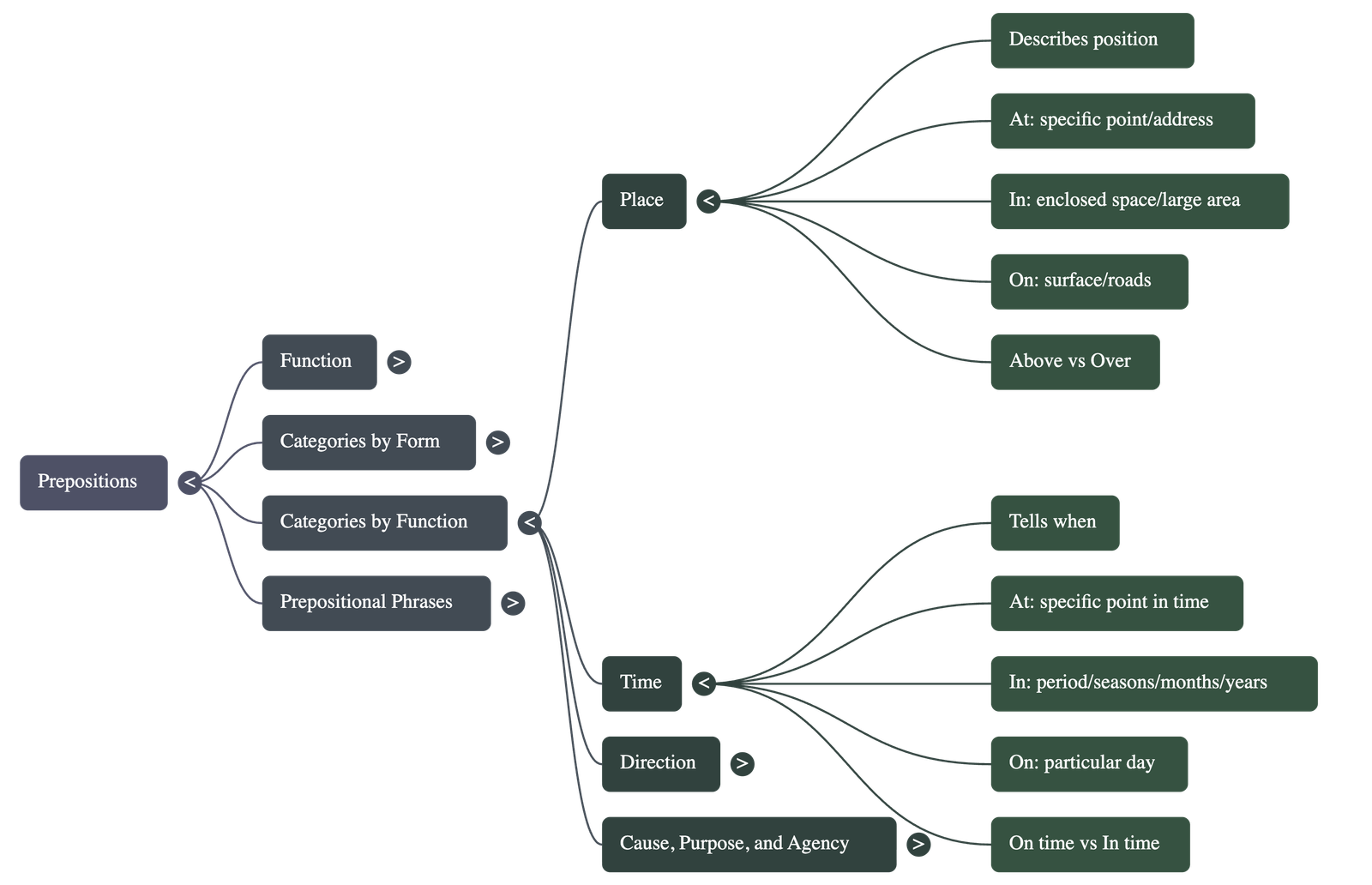
- Prepositions of Place: Used to describe the position of a person or thing. Examples include above, below, beside, and near.
- At: Used for specific points or addresses.
- In: Used for enclosed spaces or large areas like cities.
- On: Used for surfaces and the names of roads.
- Prepositions of Time: Indicate when an action occurs.
- At: Used for specific points in time (e.g., 9 a.m.).
- In: Used for periods of time (minutes/hours), times of day, seasons, months, and years.
- On: Used for particular days and dates.
- On time vs. In time: "On time" refers to a specific scheduled moment, while "in time" means not too late.
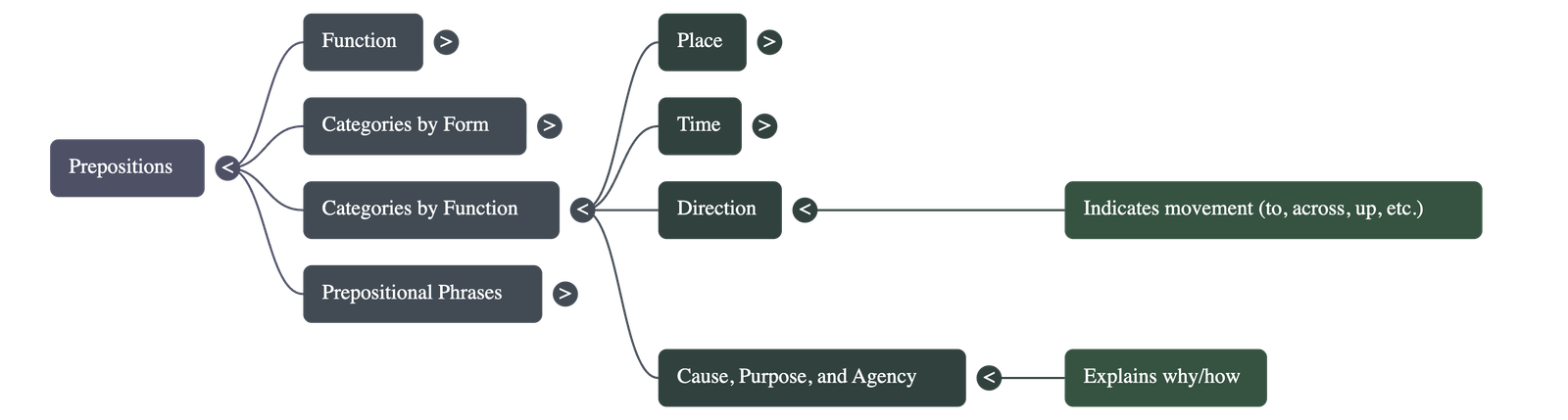
- Prepositions of Direction: Indicate movement toward a destination, such as to, towards, through, across, into, and up.
Usage Nuances (Above vs. Over)
- Both words mean "higher than," but over is used when one thing is moving or touching/covering another.
- Above is preferred when one thing is at a higher level but not directly over another.
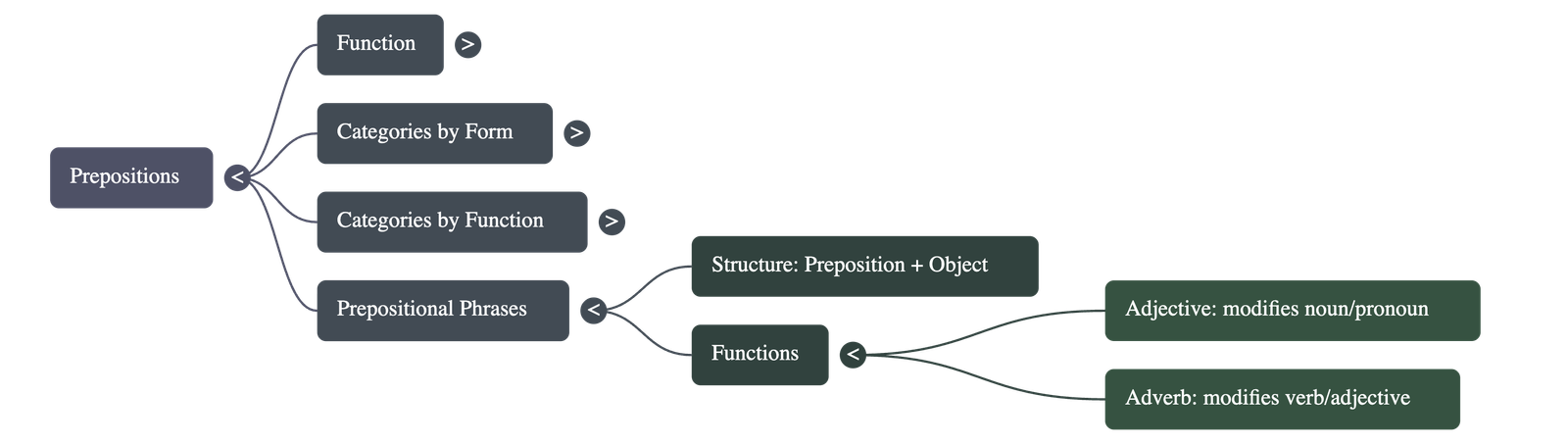
Prepositional Phrases
- Structure: A prepositional phrase consists of a preposition, its object, and any associated modifiers.
- Adjectival Function: When a phrase modifies a noun or noun phrase, answering the question "which one?"
- Adverbial Function: When a phrase modifies a verb or adjective, answering questions like "how?", "when?", "why?", or "where?"
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |