Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Chapter Summary: Participles
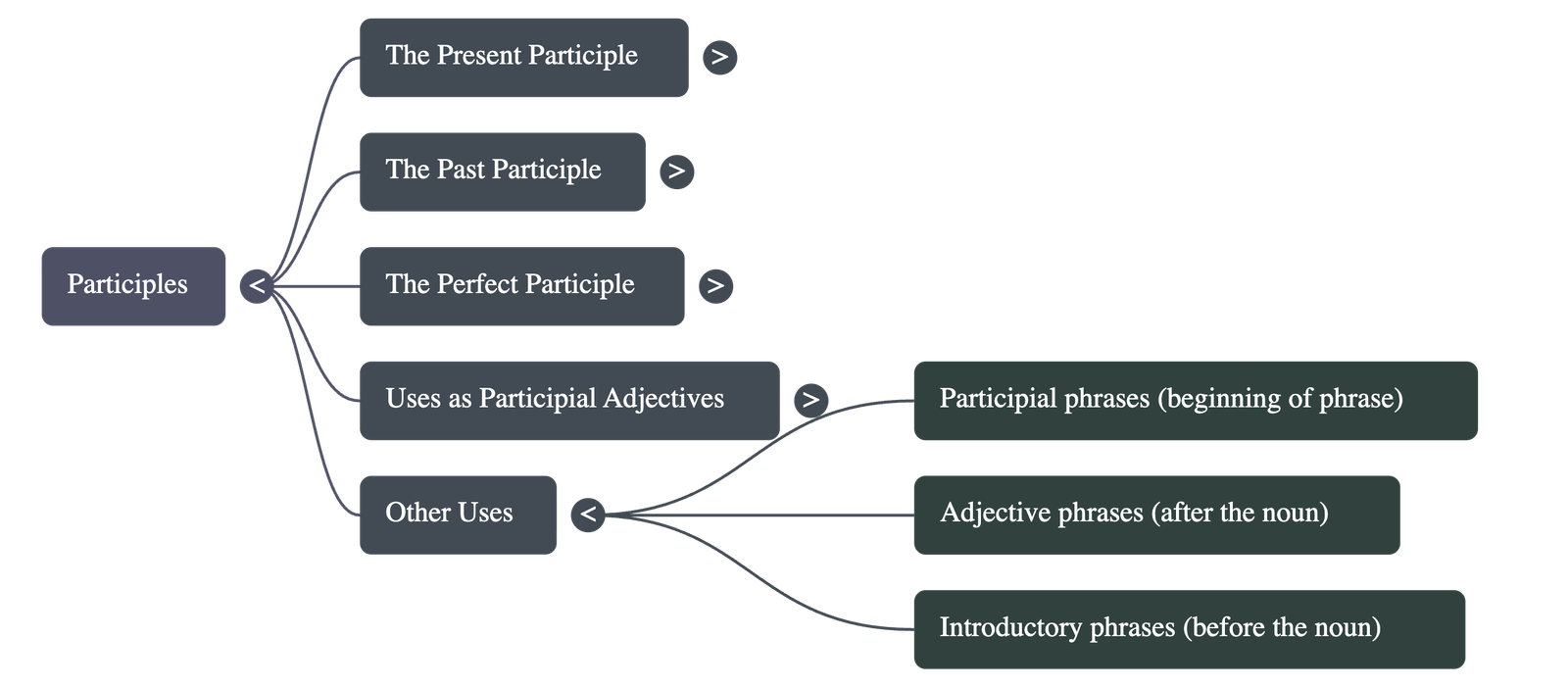
1. Overview of Participles
- Dual Nature: Participles are words that function as both verbs and adjectives depending on their context.
- Classification: There are three primary categories: the present participle, the past participle, and the perfect participle.
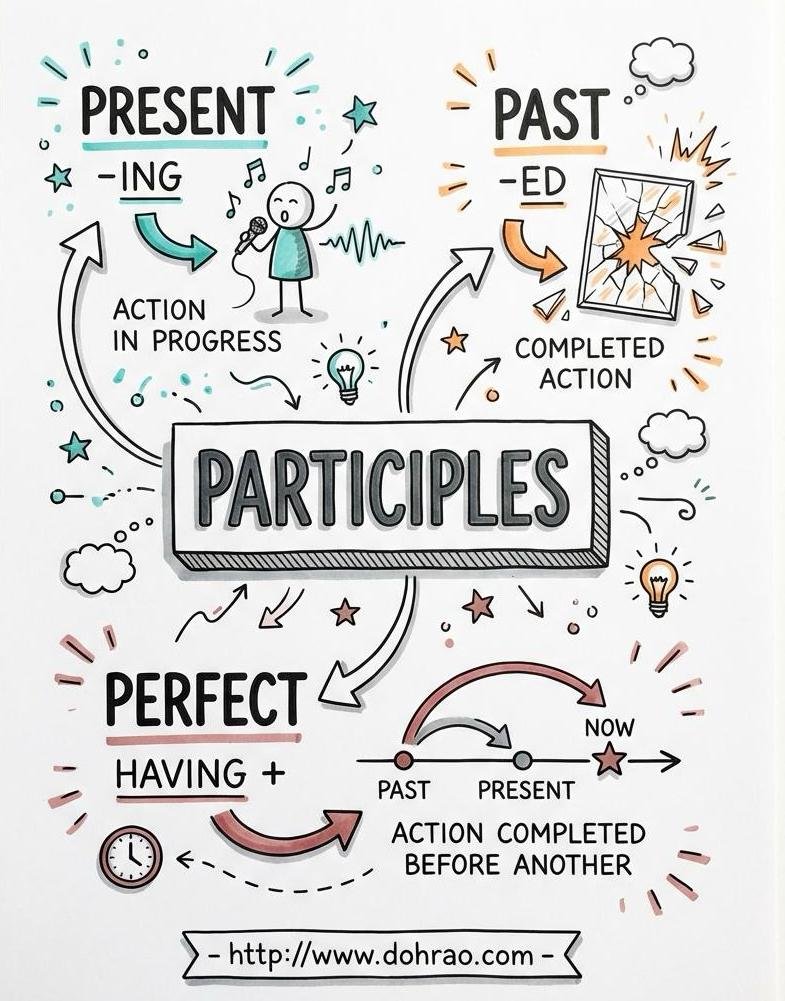
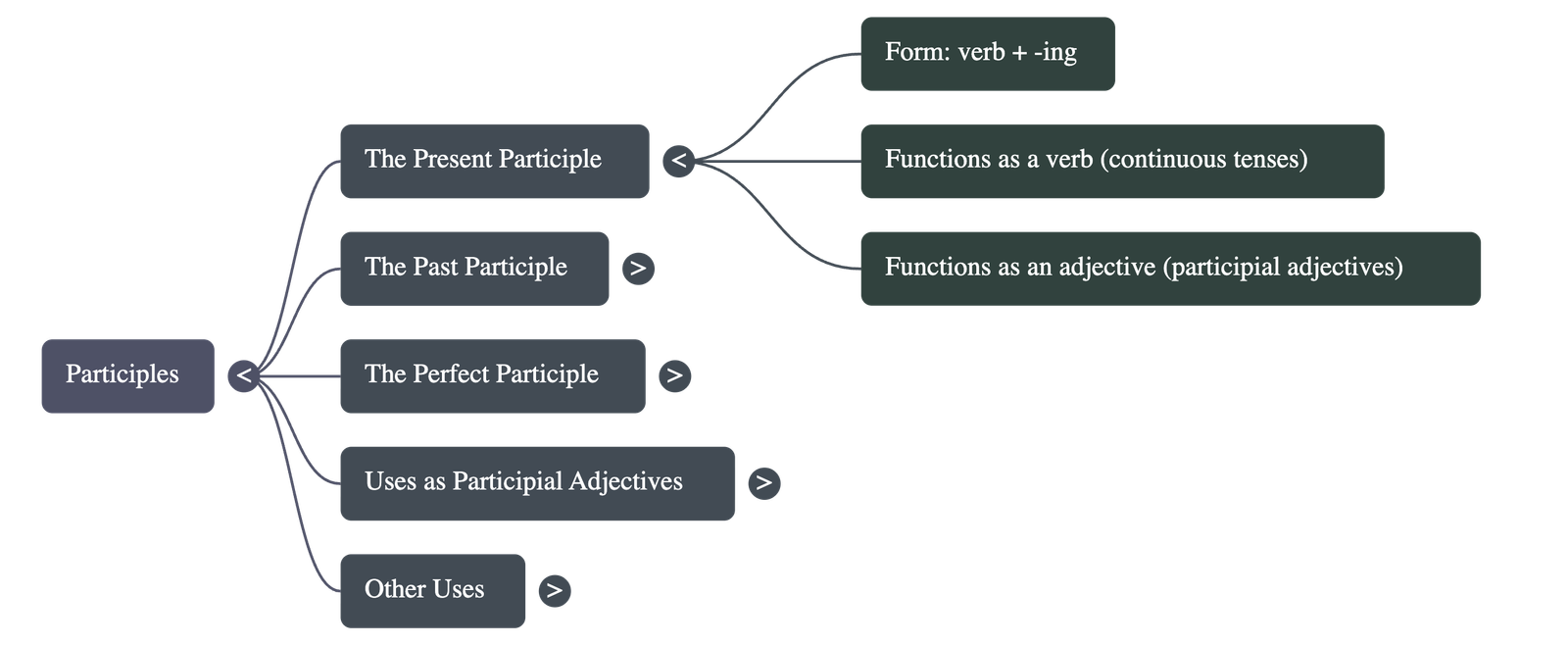
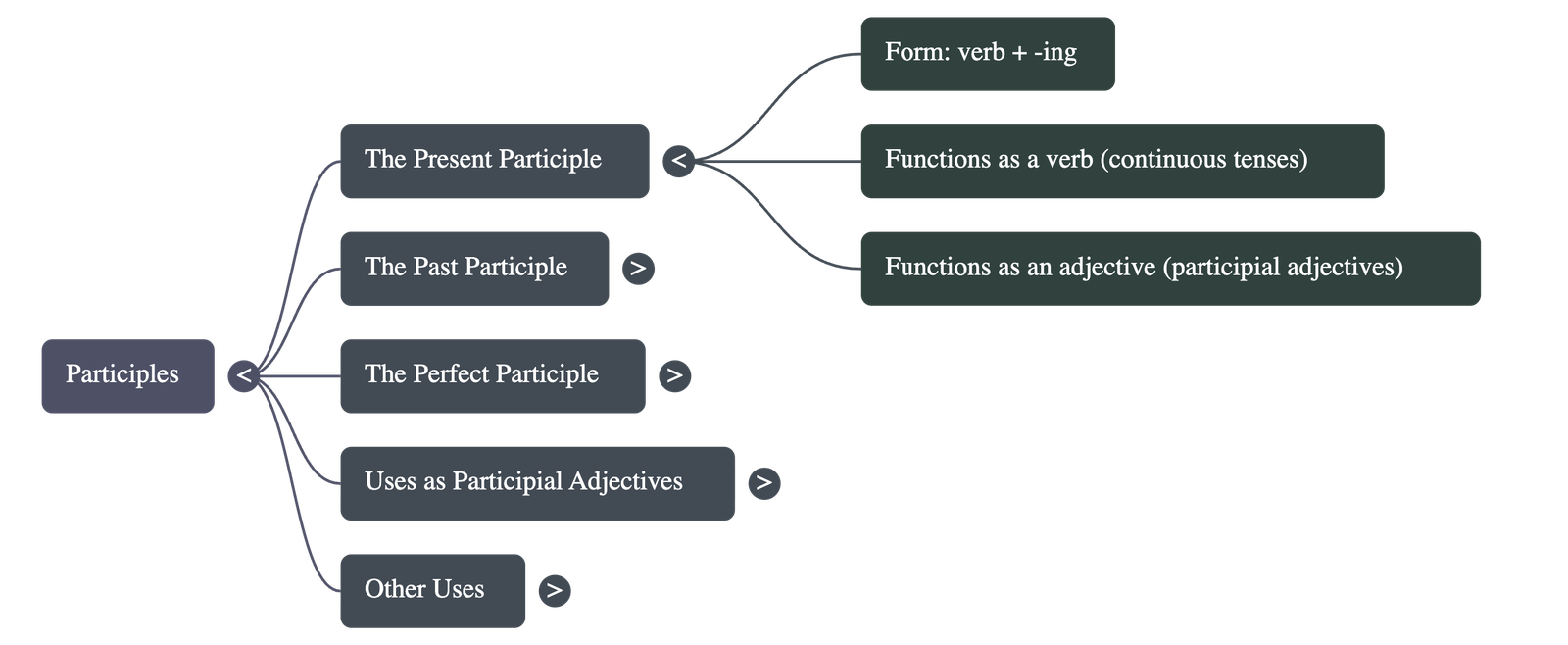
2. The Present Participle
- Form: Always ends in -ing (e.g., singing, moving, laughing).
- As a Verb: Used to form continuous tenses to show that an action is currently in progress.
- As an Adjective: Also known as a verbal adjective, it describes a noun (e.g., "the moving water").
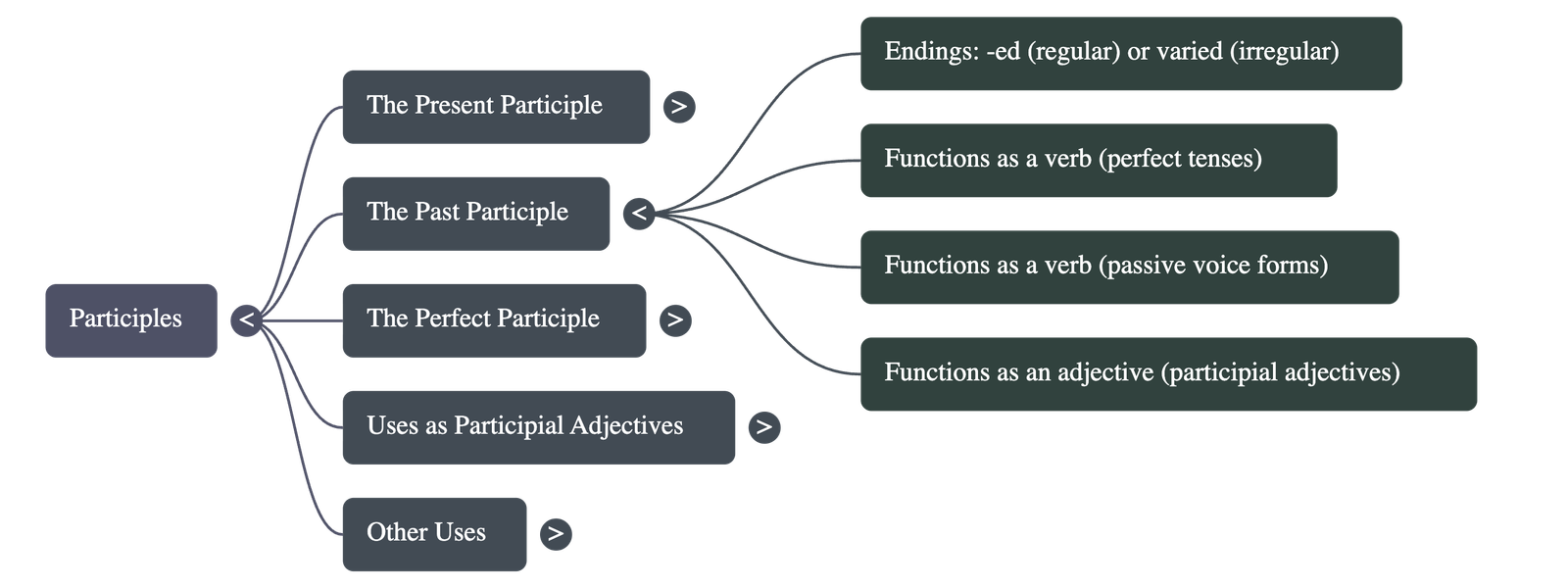
3. The Past Participle
- Form: Regular verbs end in -ed, while irregular verbs have varied endings (e.g., taught, broken, flown).
- As a Verb:
- Used to form perfect tenses (e.g., "has repaired").
- Used to form the passive voice (e.g., "was given").
- As an Adjective: Functions as a participial adjective to describe the state of a noun (e.g., "broken glass").
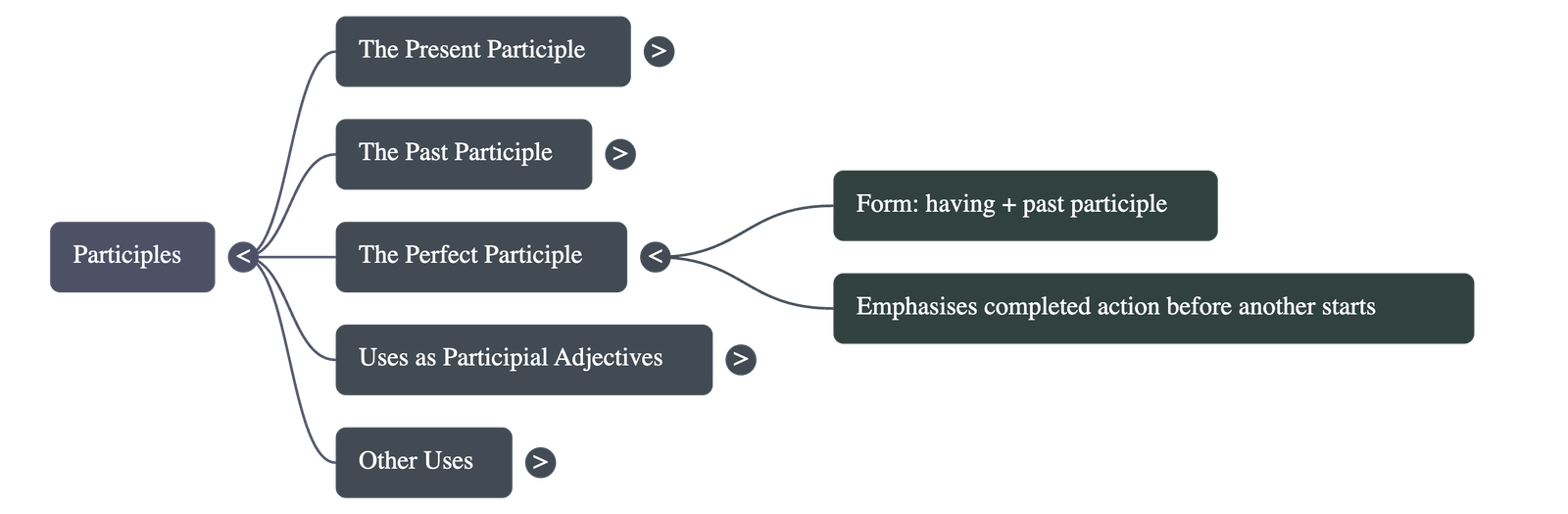
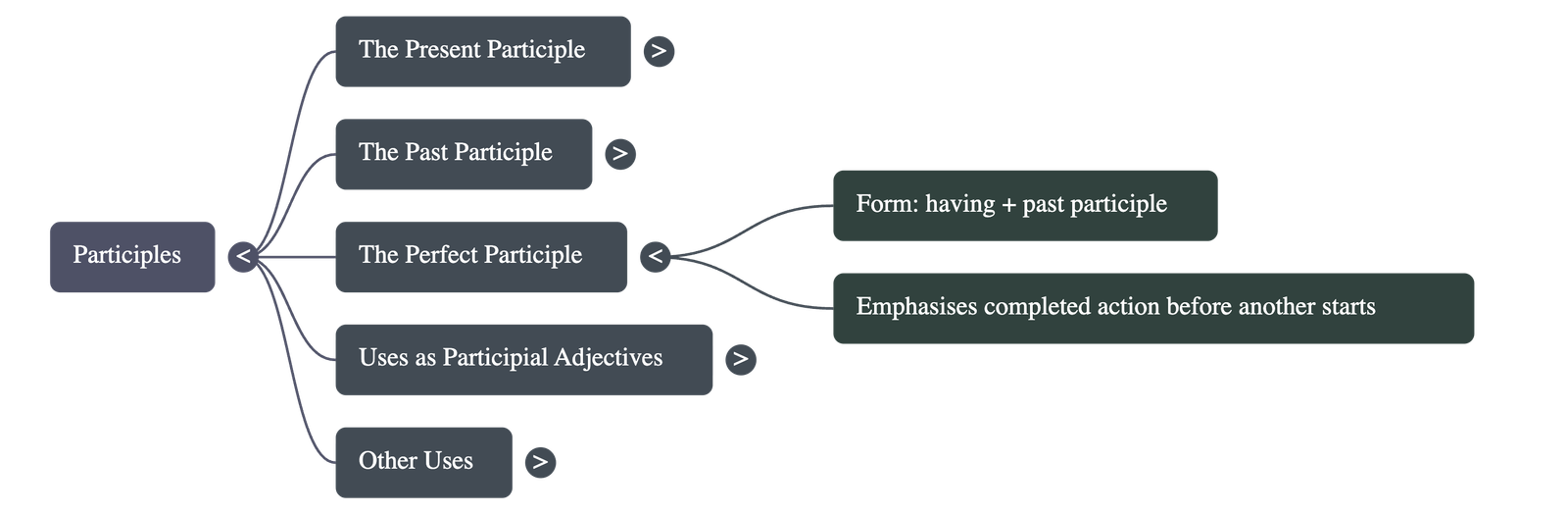
4. The Perfect Participle
- Form: Created by placing the word "having" before a past participle (e.g., having watched, having cooked).
- Function: Used to emphasize that one action was completely finished before a second action began.
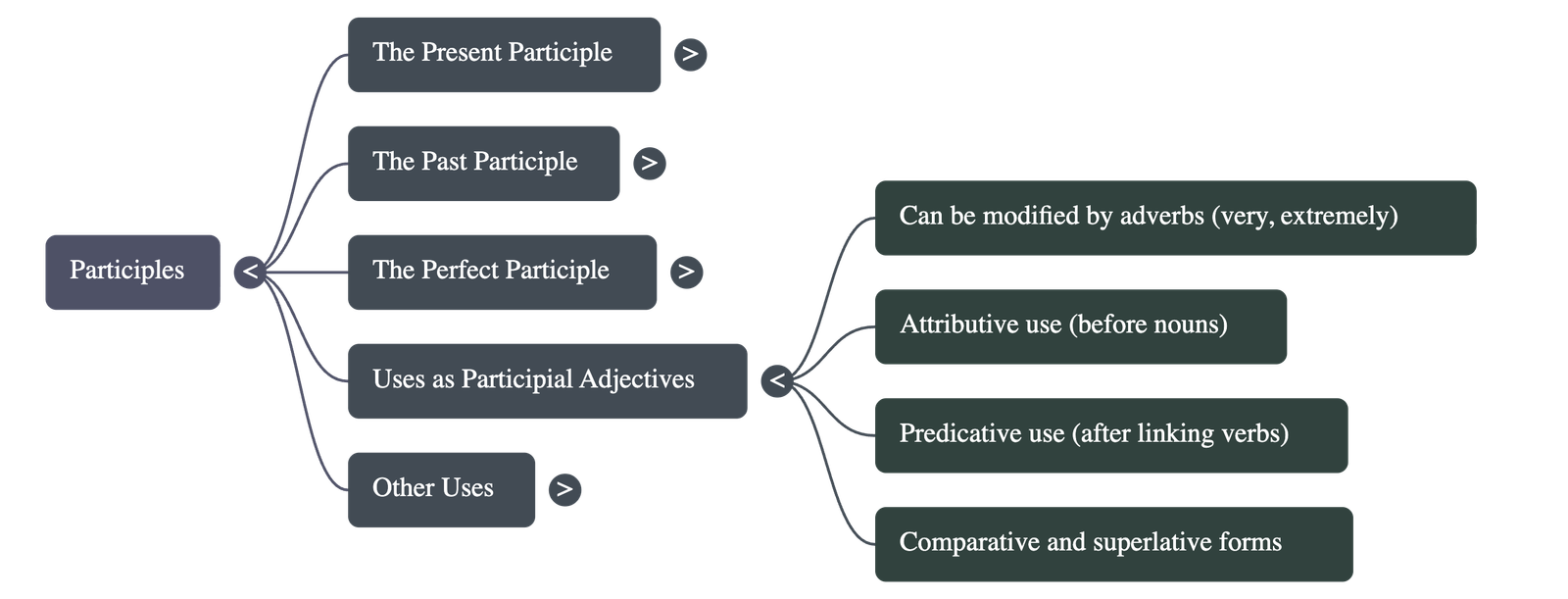
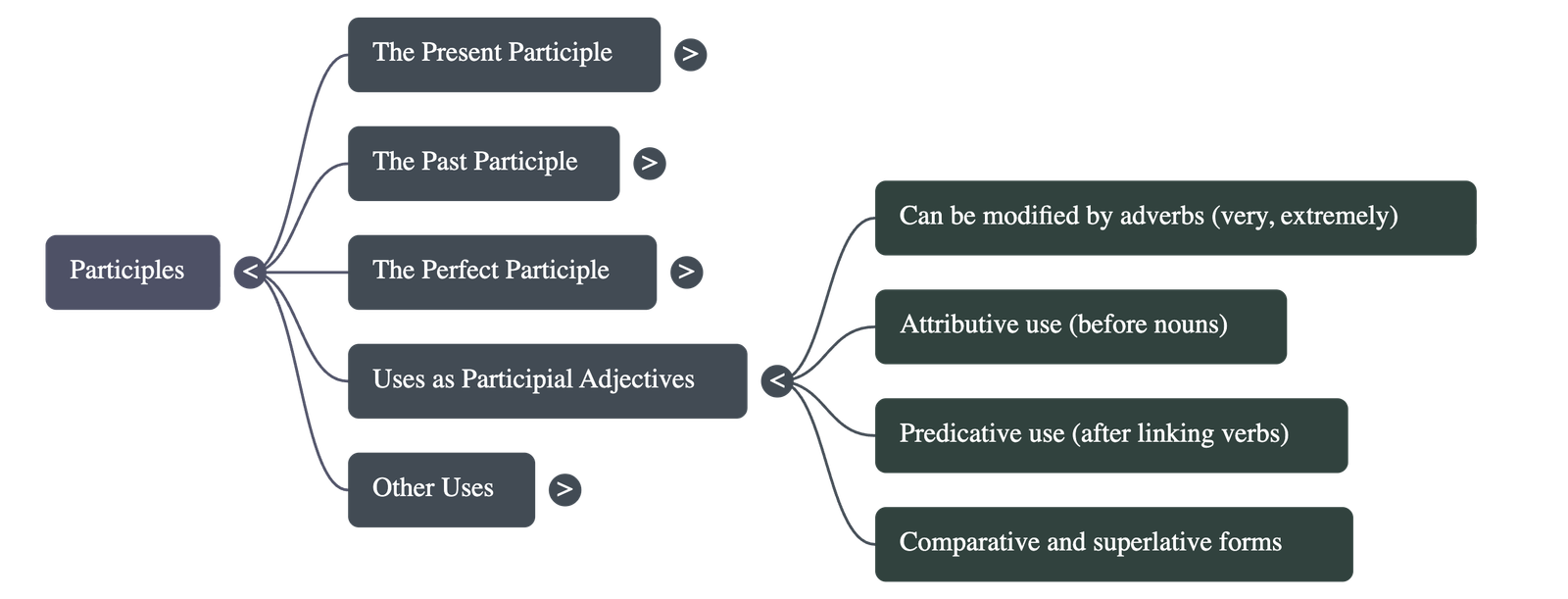
5. Usage as Participial Adjectives
- Adverb Modification: Can be modified by adverbs like very or extremely.
- Attributive Use: Placed directly before the noun they qualify (e.g., "a working condition").
- Predicative Use: Used as a subject complement after linking verbs like be, look, sound, or seem (e.g., "The idea sounds interesting").
- Comparison: Like standard adjectives, they can have comparative and superlative forms (e.g., "more exciting," "least surprised").
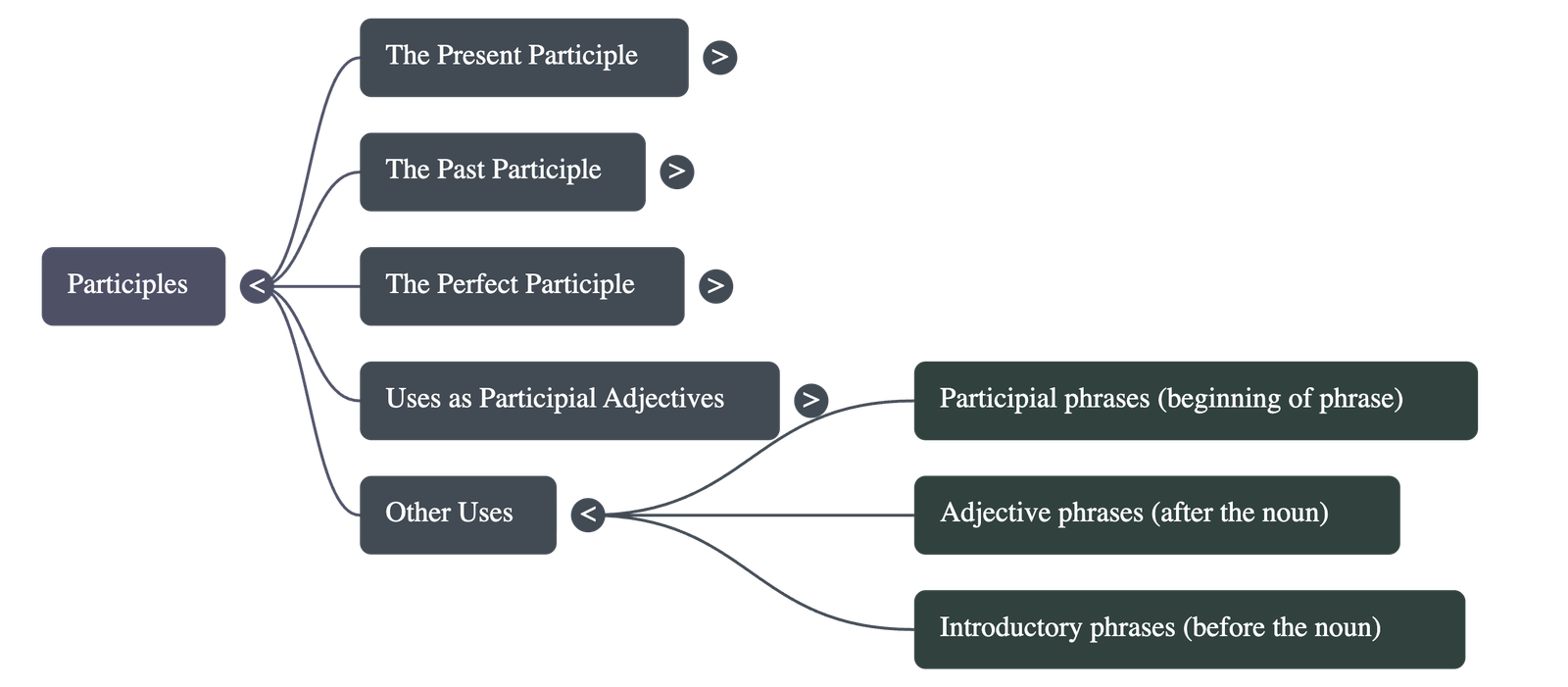
6. Participial Phrases
- Structure: A phrase beginning with a participle along with its modifiers or objects.
- Placement:
- Can follow the noun it describes (e.g., "The woman dressed in red...").
- Can precede the noun, often to indicate an action that happened earlier (e.g., "Hearing the phone ring, Sapna rushed...").
- Sentence Combination: Participles are useful tools for merging two short sentences into a single, more fluid sentence.
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |