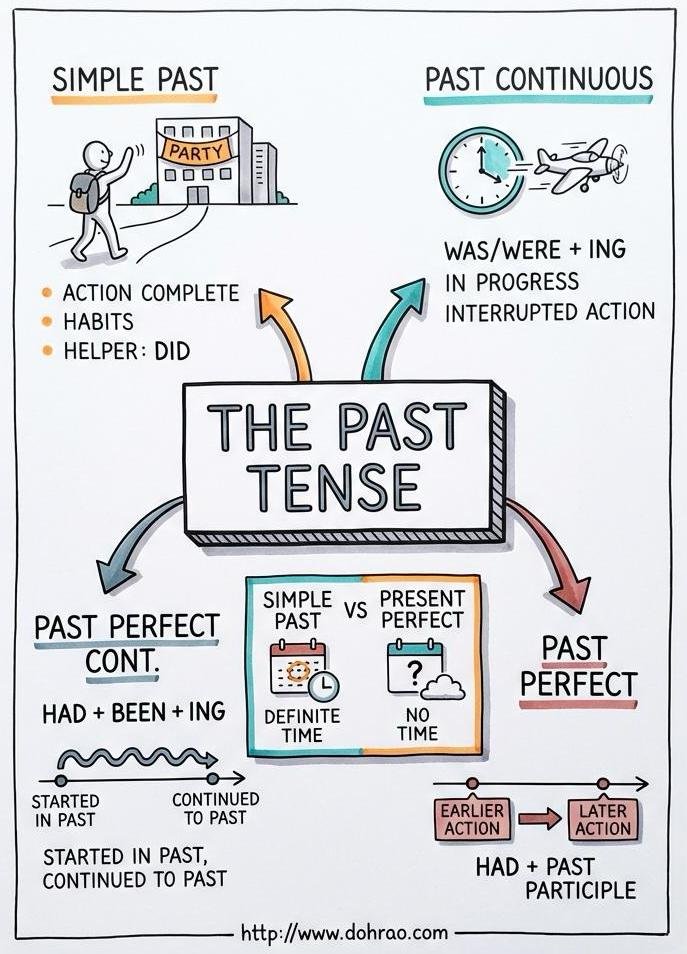
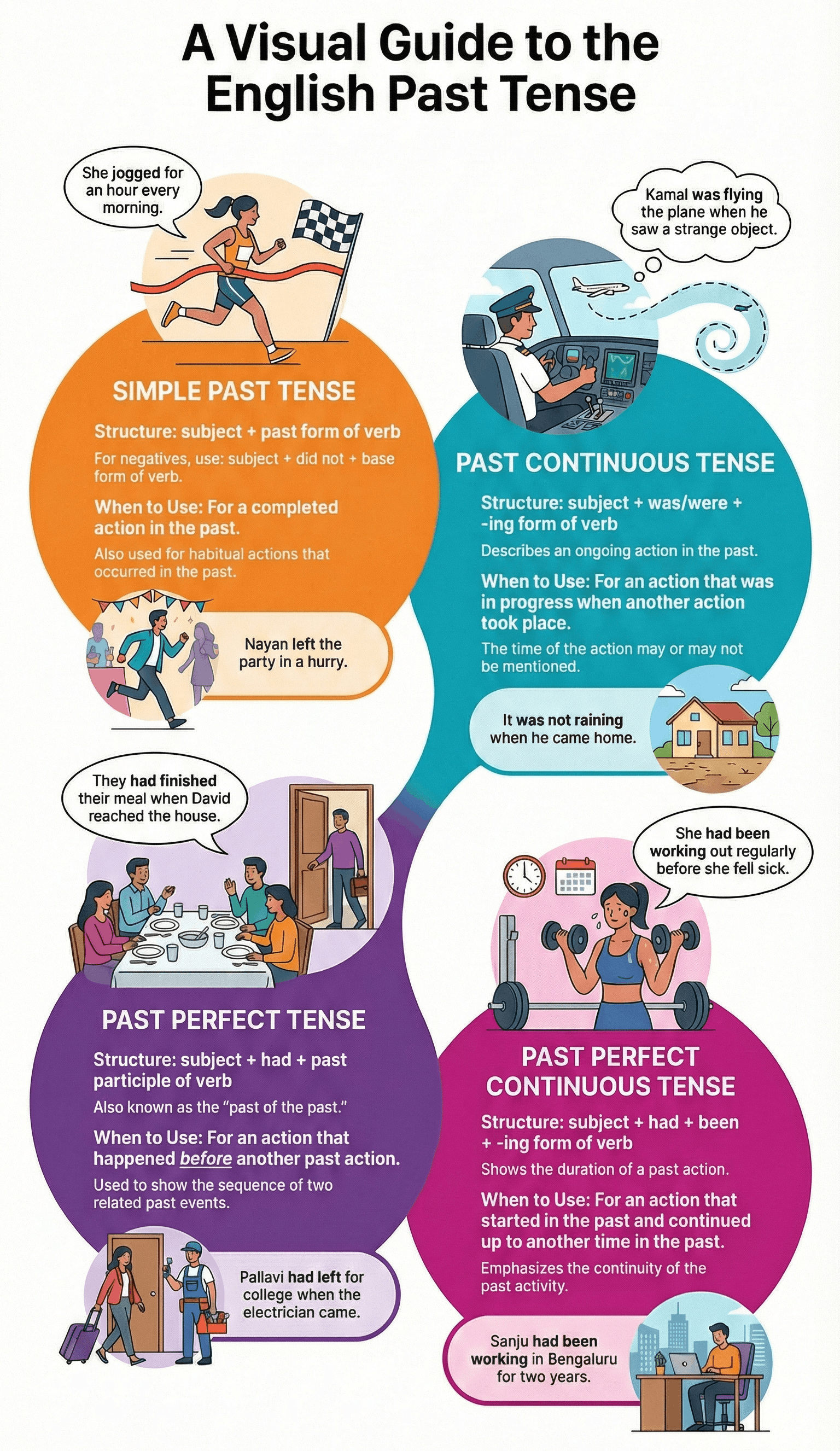
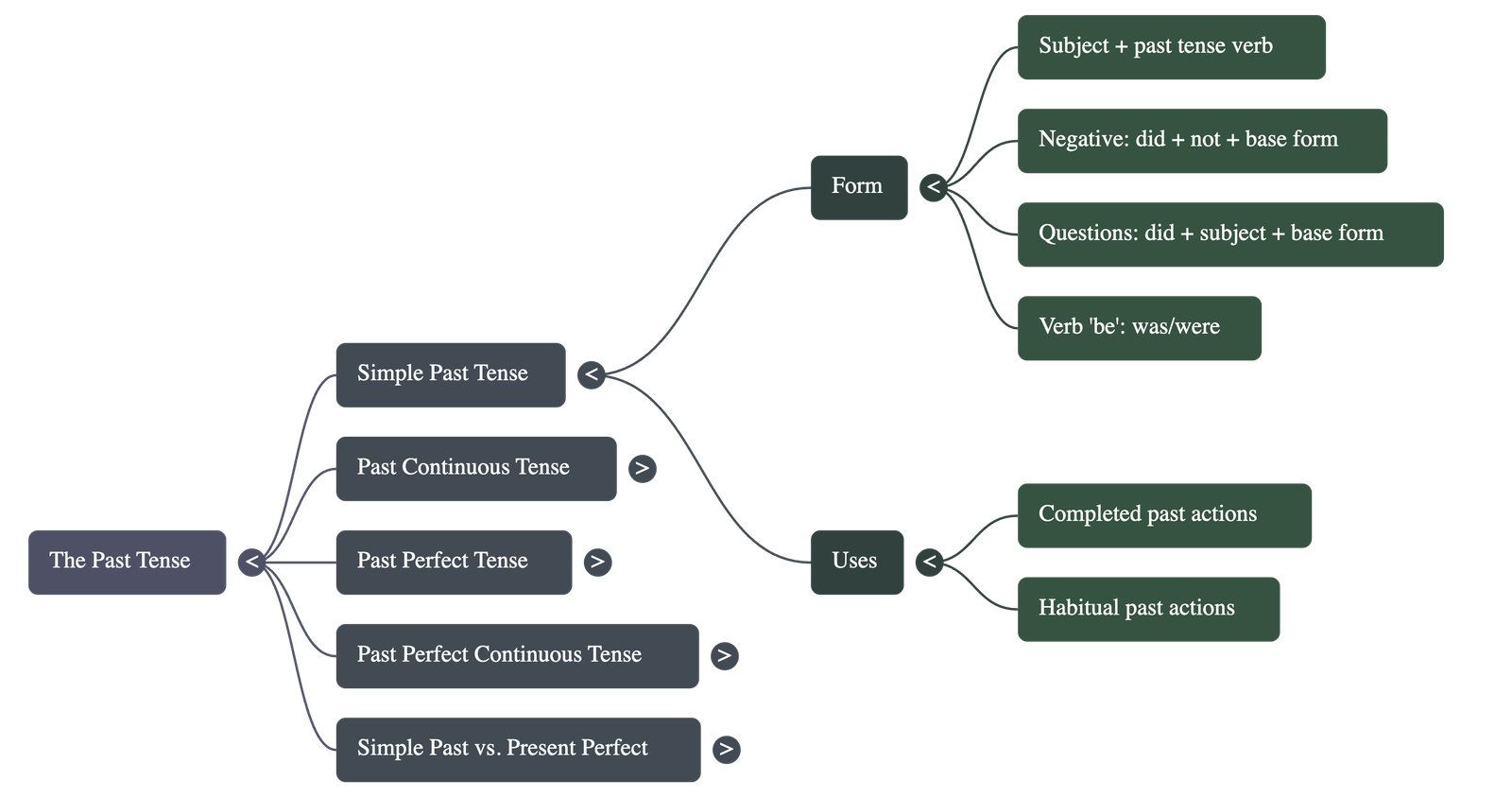
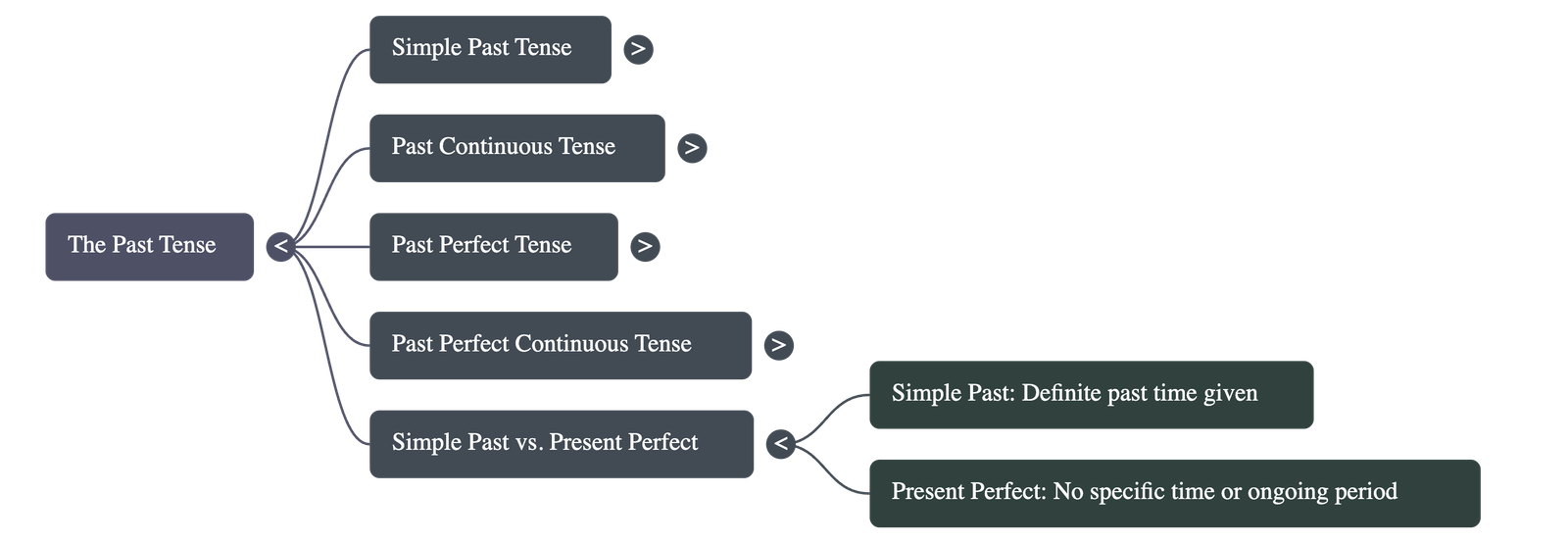
The simple past is used to describe completed actions or habitual behaviours in the past.
- Forms:
- Positive: Subject + past tense form of verb (e.g., Nayan left the party).
- Negative: Subject + did + not + base form of verb (e.g., They did not go).
- Questions: Did + subject + base form of verb? (e.g., Did you meet Sudhir?).
- Key Uses:
- Actions finished at a specific time in the past.
- Habitual past actions (e.g., She jogged every morning).