Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Articles
A comprehensive overview of how articles are used in English grammar. Below is a point-wise summary of the chapter:
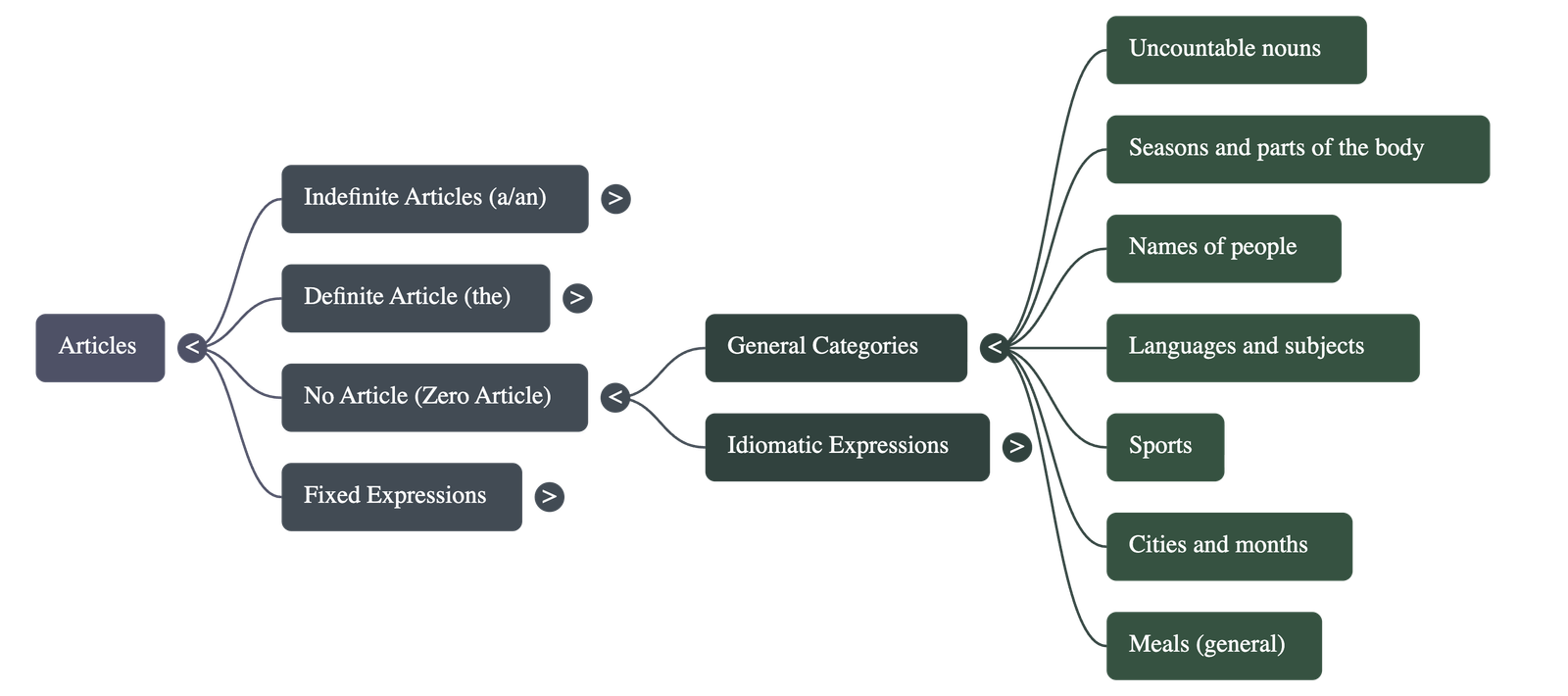
Overview of Articles
- Articles are a type of determiner used to clarify nouns.
- There are two types: the indefinite article (a/an) and the definite article (the).
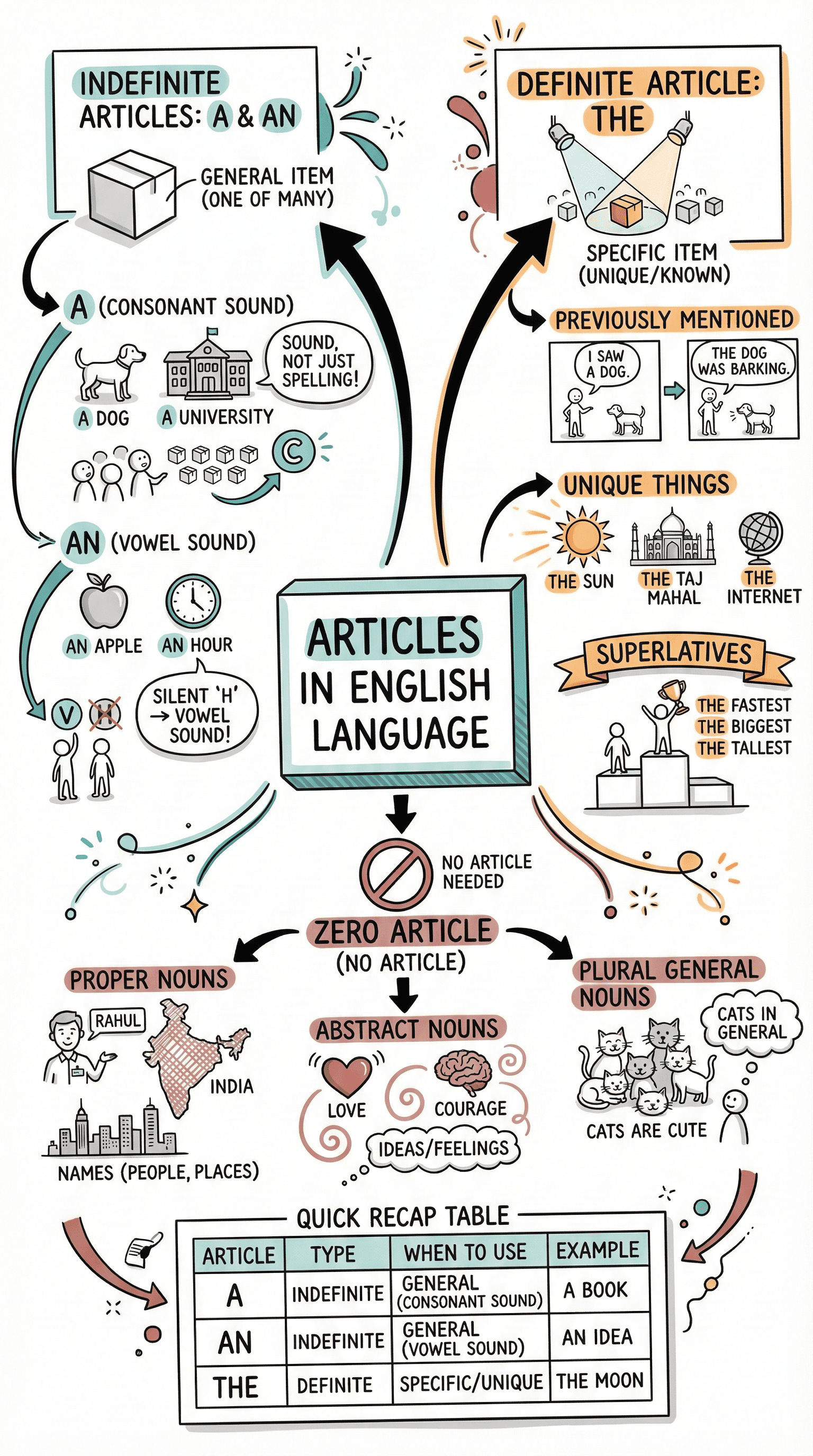
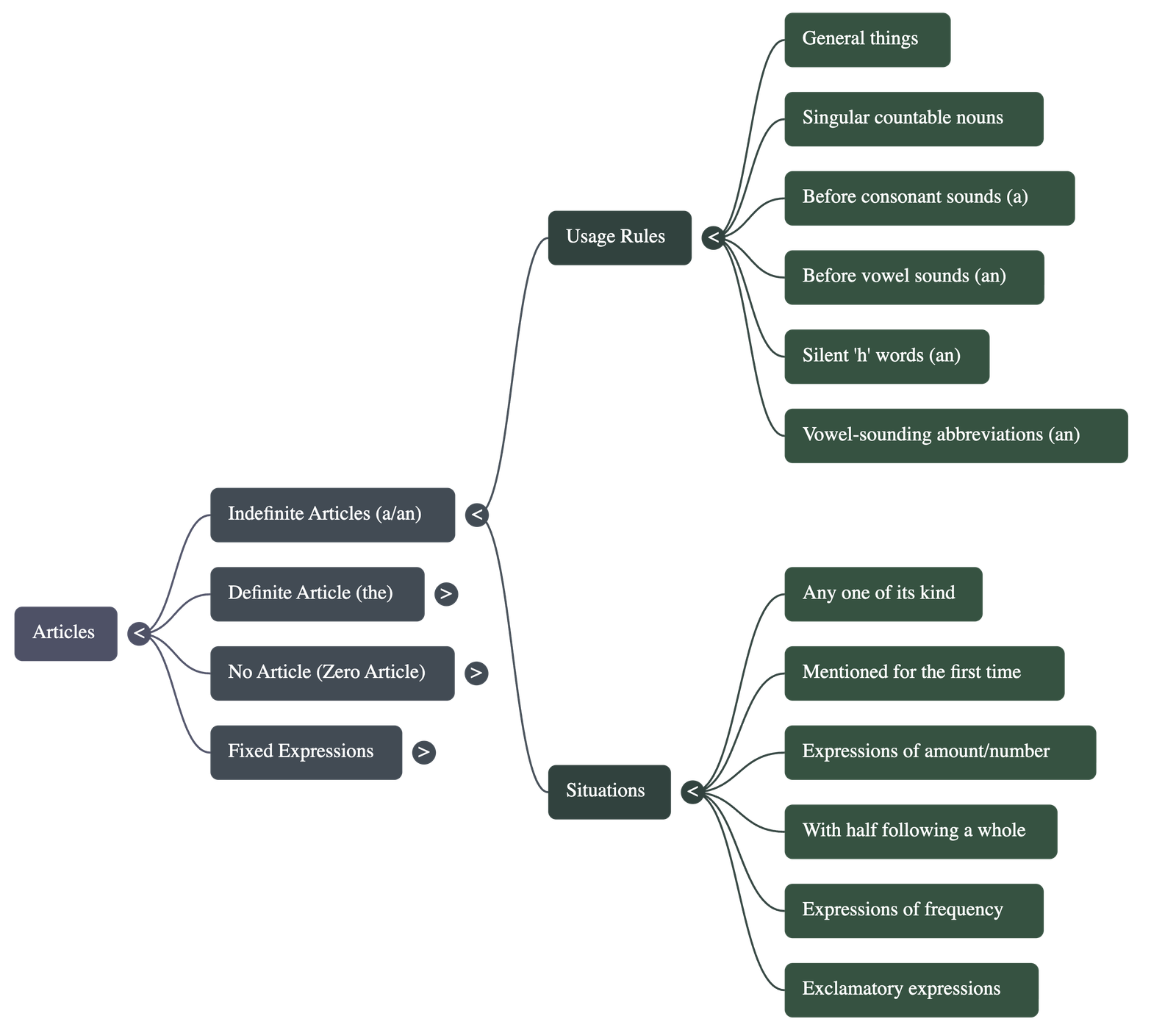
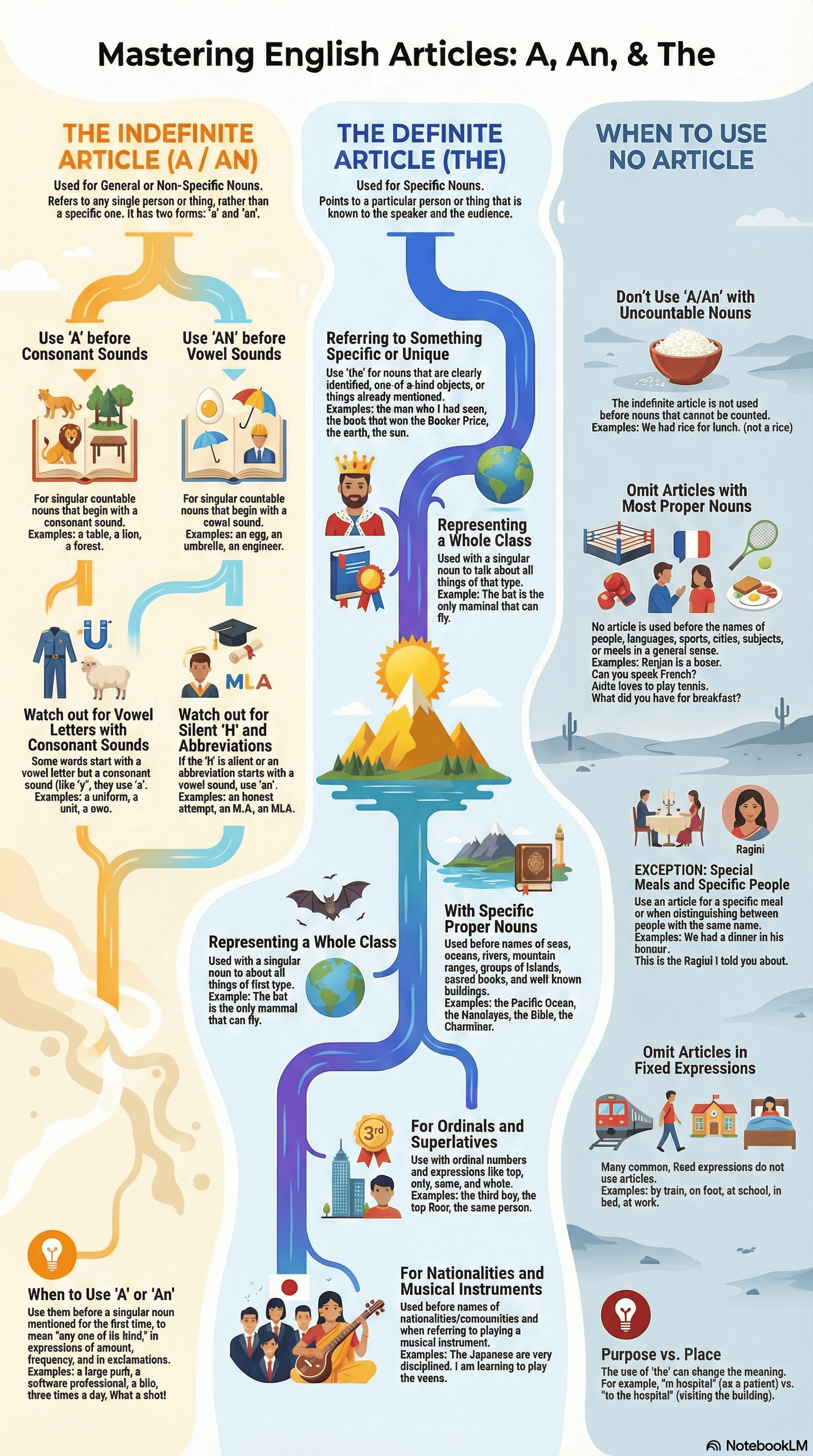
Indefinite Articles (a and an)
- Definition: These talk about things in general or non-specific items rather than a particular person or thing.
- Usage Rule: They are used before singular countable nouns.
- Distinction by Sound:
- a is used before words beginning with a consonant sound (e.g., a forest, a unit).
- an is used before words beginning with a vowel sound (e.g., an egg, an honest attempt, an M.A.).
- Specific Situations for Use:
- To mean "any one of its kind" or when mentioning a noun for the first time.
- In expressions of amount, number, frequency, or within certain exclamatory expressions (e.g., a kilo, once a month, What a shot!).
- With the word half when it follows a whole number (e.g., one and a half).
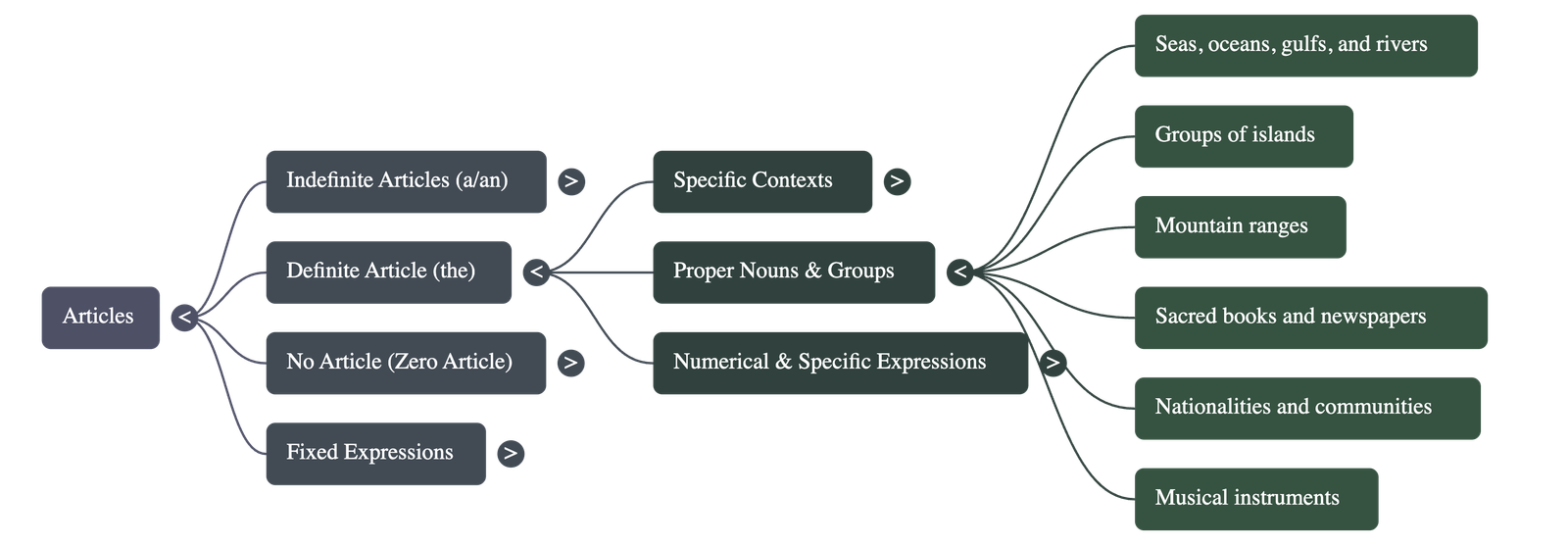
The Definite Article (the)
- Definition: Points to a particular or specific person, thing, or someone already mentioned in the conversation.
- General Rules:
- Used when both the speaker and audience know what is being referred to (e.g., the bank).
- Used when a singular noun represents a whole class (e.g., The butterfly has beautiful wings), though this does not apply to "man" when referring to humanity.
- Geographical and Specific Proper Nouns:
- Included: Names of seas, oceans, rivers, groups of islands, and mountain ranges.
- Excluded: Individual lakes and specific mountain peaks (e.g., Mount Everest).
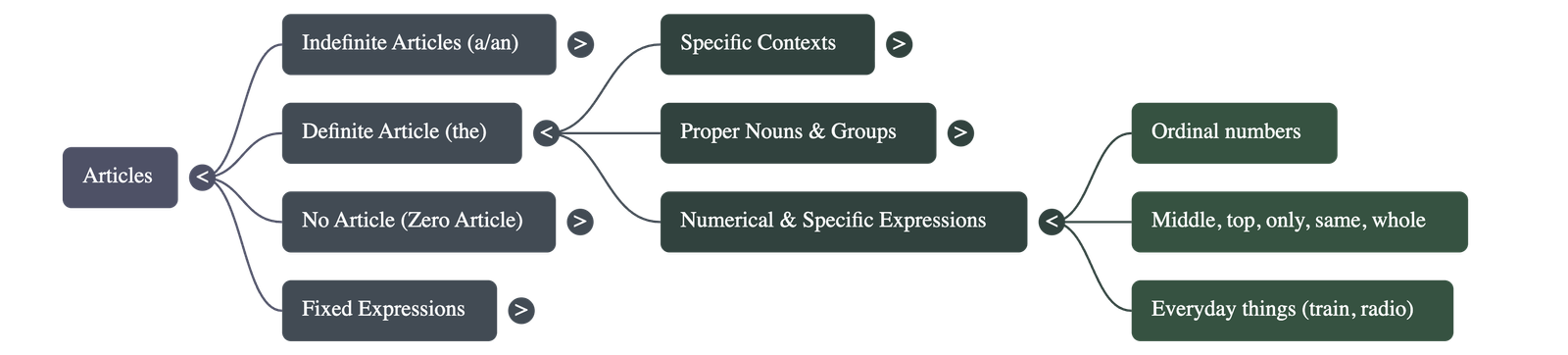
- Used for sacred books, newspapers, well-known buildings, unique objects (the sun), and musical instruments.
- Specific Expressions: Used with ordinal numbers (e.g., the third boy) and words like middle, top, same, and whole.
When to Omit Articles
- General Omissions: Articles are usually not used before uncountable nouns, names of seasons, parts of the body, languages, sports, cities, subjects, or most meals.
- People’s Names: Generally, no article is used before names, except when referring to one specific person among others of the same name or expressing uncertainty about someone's identity.
- Contextual Omission: No article is used for idiomatic phrases like by train or on foot.
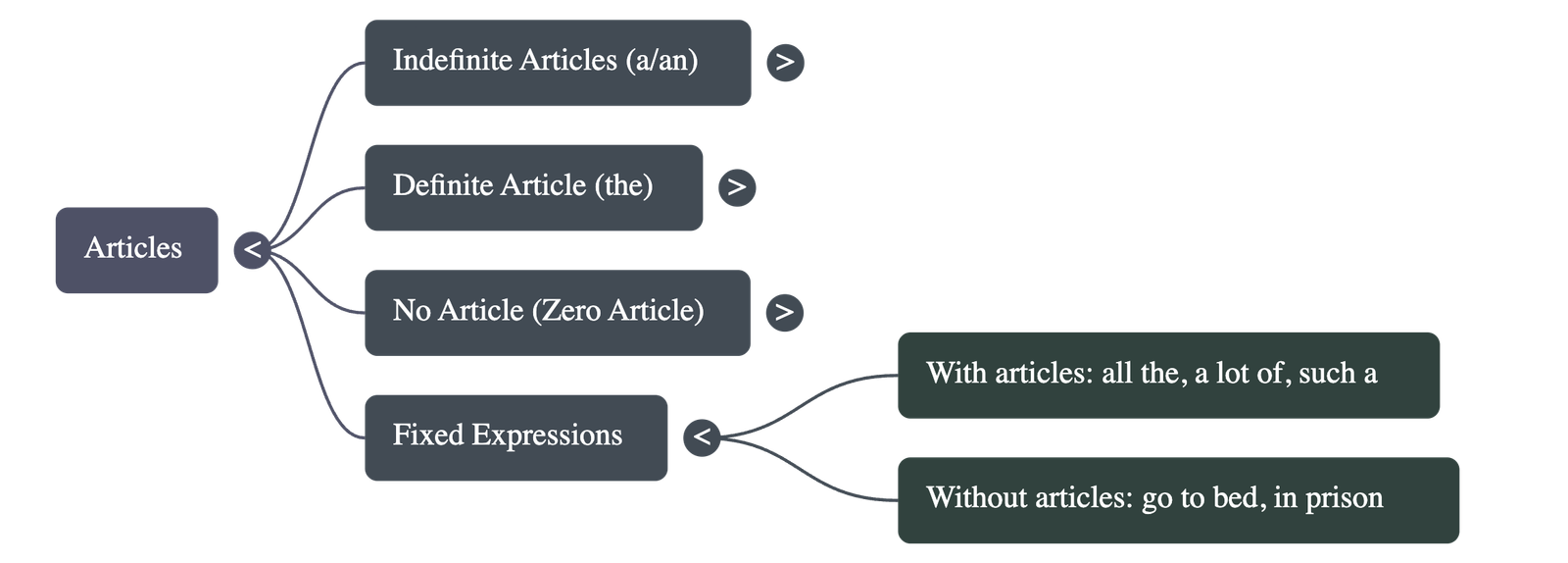
Fixed Expressions and Subtle Distinctions
- Fixed Phrases: Some phrases always require articles (e.g., a lot of, all the), while others do not (e.g., at work, go to bed).
- Purpose vs. Place:
- The article is omitted when referring to the primary purpose or activity of a place (e.g., in school for studying, in hospital for treatment).
- The is used when referring specifically to the building itself (e.g., The school will remain closed).
Analogy for Understanding: Think of articles like camera lenses. Using "a" or "an" is like a wide-angle lens; it captures a general scene where no single object stands out. Using "the" is like a zoom lens; it focuses sharply on one specific subject that you want everyone to notice.
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |