Quick Navigation:
| | |
Arithmetic Progressions
1. Introduction to Patterns
- Many occurrences in nature follow certain patterns, such as the petals of a sunflower, holes of a honeycomb, or spirals on a pine cone.
- Patterns also exist in daily life, such as fixed annual salary increments or the decreasing lengths of rungs on a ladder.
- In mathematics, we study specific patterns where succeeding terms are obtained by adding a fixed number to preceding terms.
2. Arithmetic Progressions (AP)
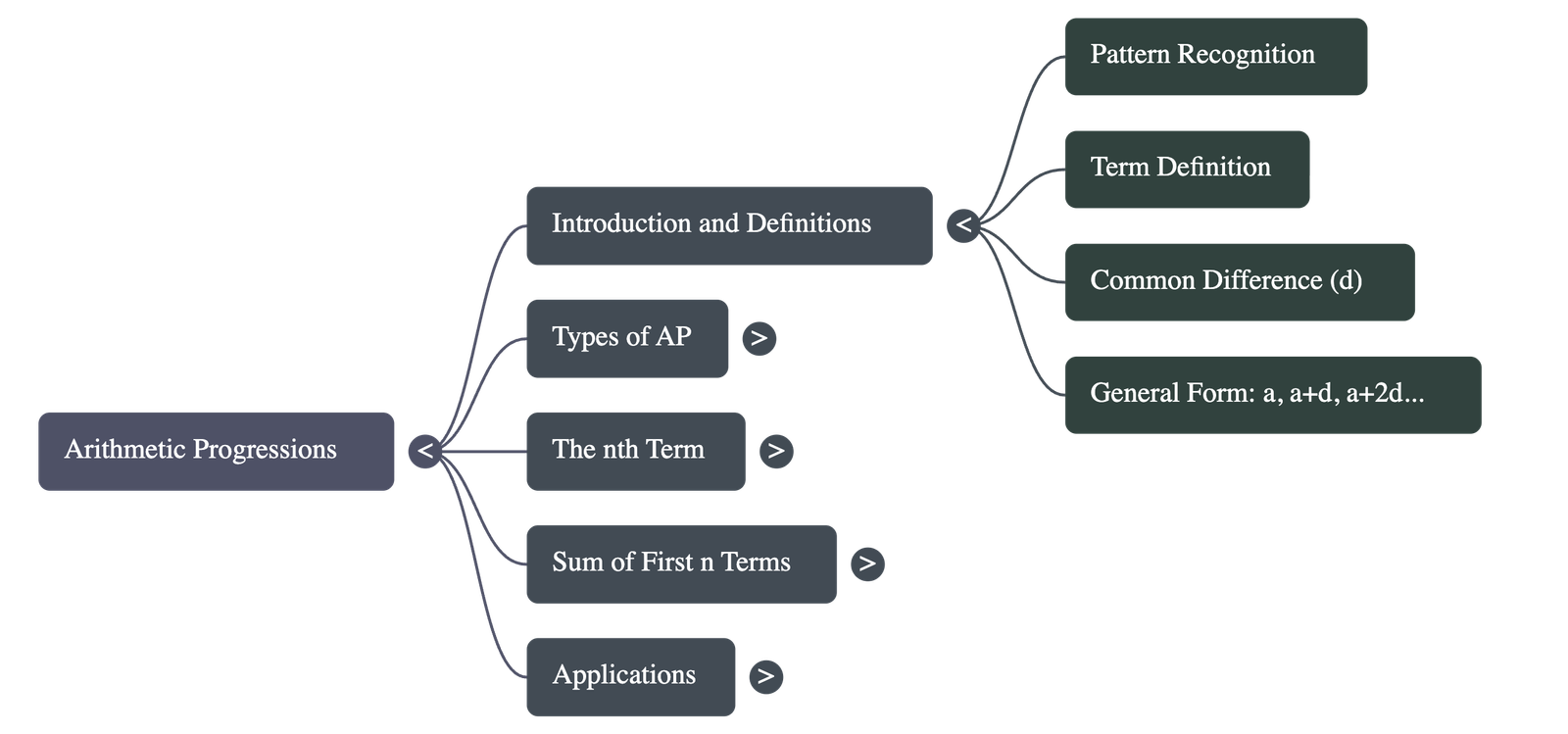
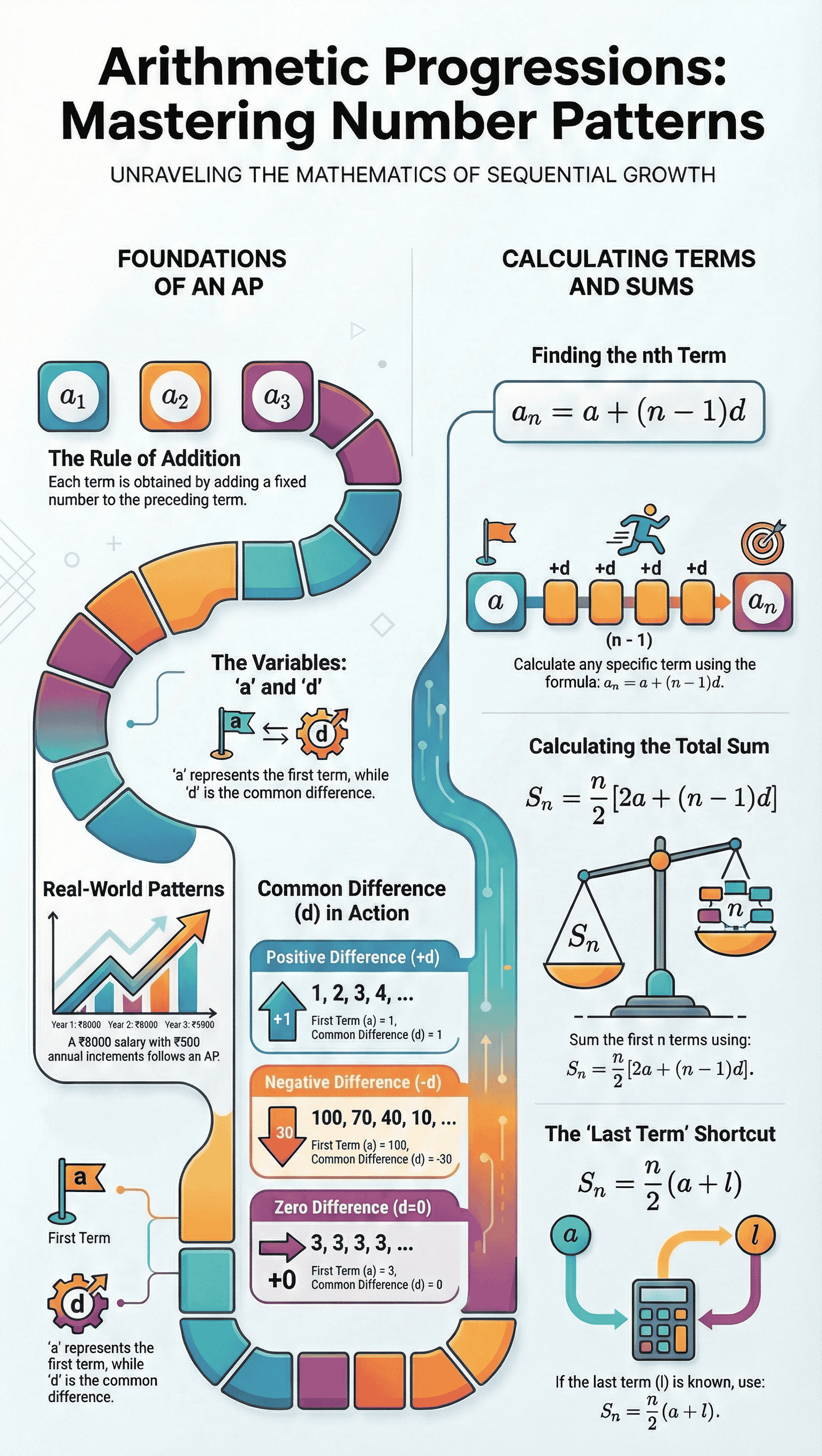
An Arithmetic Progression is a list of numbers in which each term is obtained by adding a fixed number to the preceding term, except for the first term.
Key Components:
- Terms: Each number in the list is called a term.
- Common Difference (d): The fixed number added to get the next term. It can be positive, negative, or zero.
- First Term (a): The starting number of the progression.
- General Form: An AP can be represented as:
a, a + d, a + 2d, a + 3d, ...
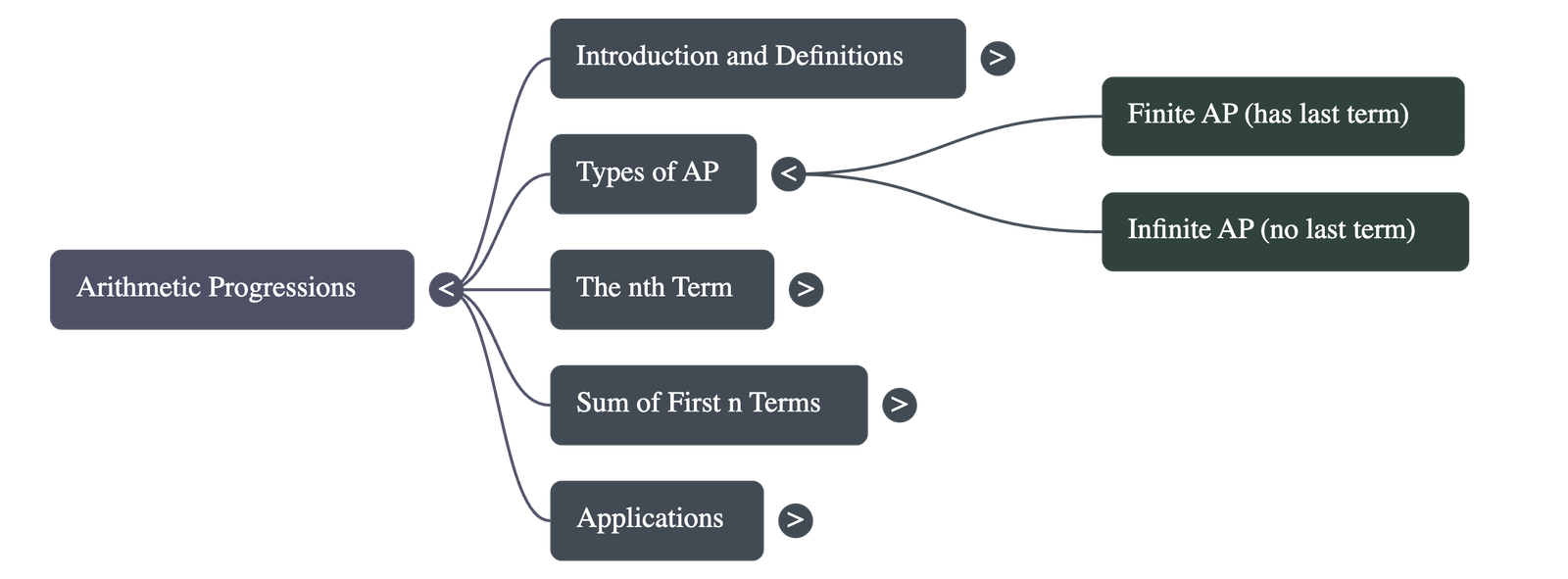
Types of APs:
- Finite AP: Contains a finite number of terms and has a specific last term.
- Infinite AP: Contains an infinite number of terms and has no last term.
Checking for an AP:
- A list of numbers is an AP if the difference between any two consecutive terms is the same.
- Formula check: ak+1 – ak is constant for all values of k.
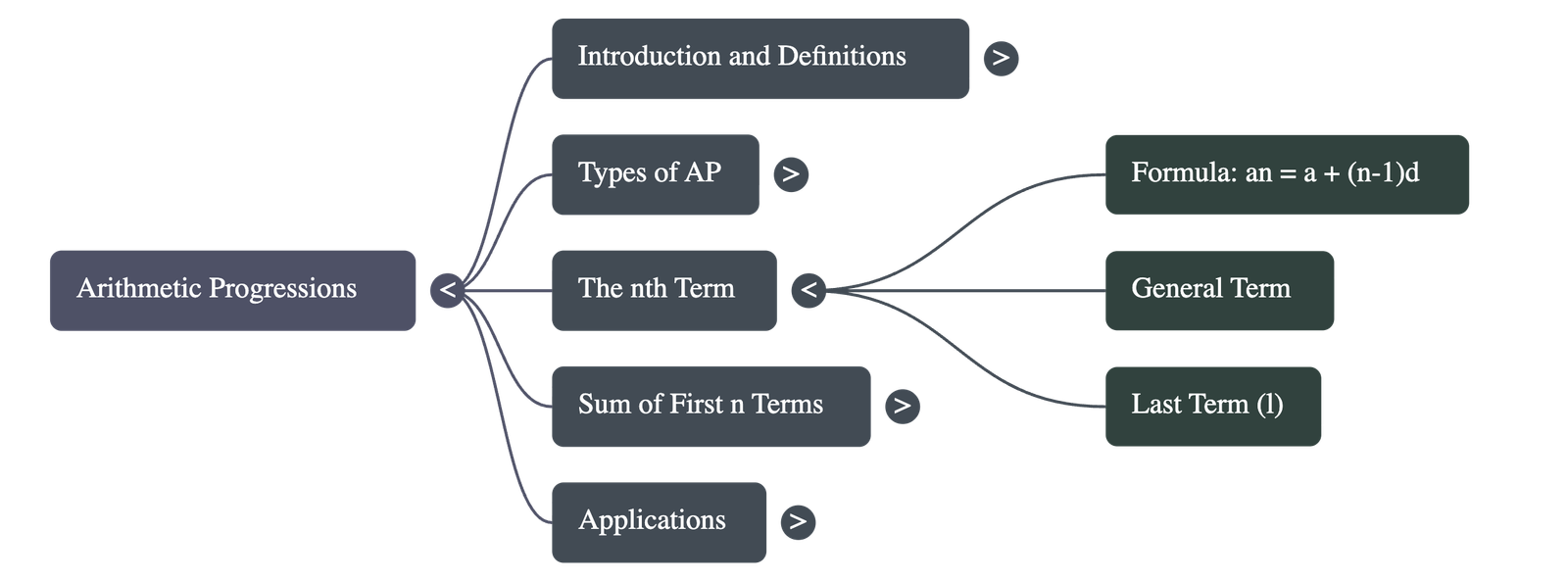
3. The nth Term of an AP
To find a specific term in a progression without listing all previous numbers, we use the general term formula.
an = a + (n – 1)d
- an: The nth term (or general term).
- a: The first term.
- d: The common difference.
- n: The position of the term.
- If an AP has m terms, am represents the last term, often denoted by l.
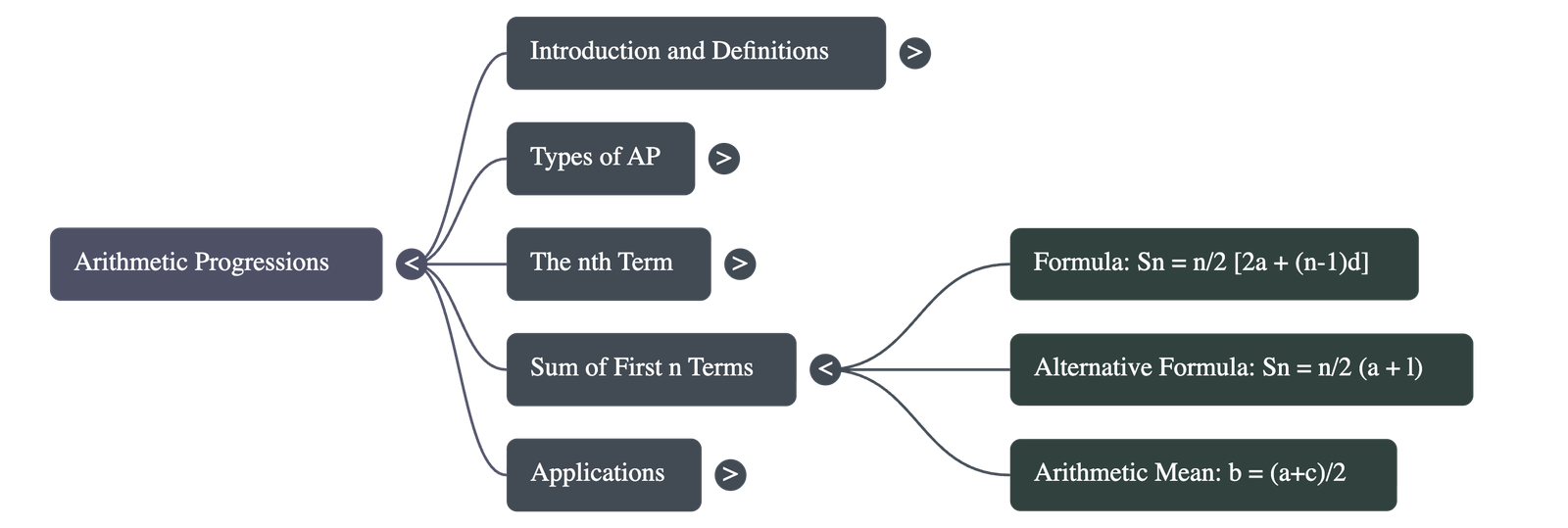
4. Sum of First n Terms of an AP
Instead of adding terms manually, specific formulas can be used to calculate the sum of the first n terms (denoted as S).
Primary Formula:
S = n⁄2 [ 2a + (n – 1)d ]
Alternative Formula (using last term):
If the first term (a) and the last term (l) are known:
S = n⁄2 ( a + l )
Important Properties:
- Sum of first n positive integers:
Sn = n(n + 1)⁄2 - Finding the nth term from the Sum:
The nth term is the difference between the sum of the first n terms and the sum of the first n-1 terms:
an = Sn – Sn-1
5. Arithmetic Mean
A useful property for three numbers in an Arithmetic Progression:
-
If a, b, c are in AP, then b is the arithmetic mean of a and c, given by:
b = (a + c)⁄2
Quick Navigation:
| | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | |