Quick Navigation:
| | |
Chapter 11: Areas Related to Circles
1. Fundamental Definitions
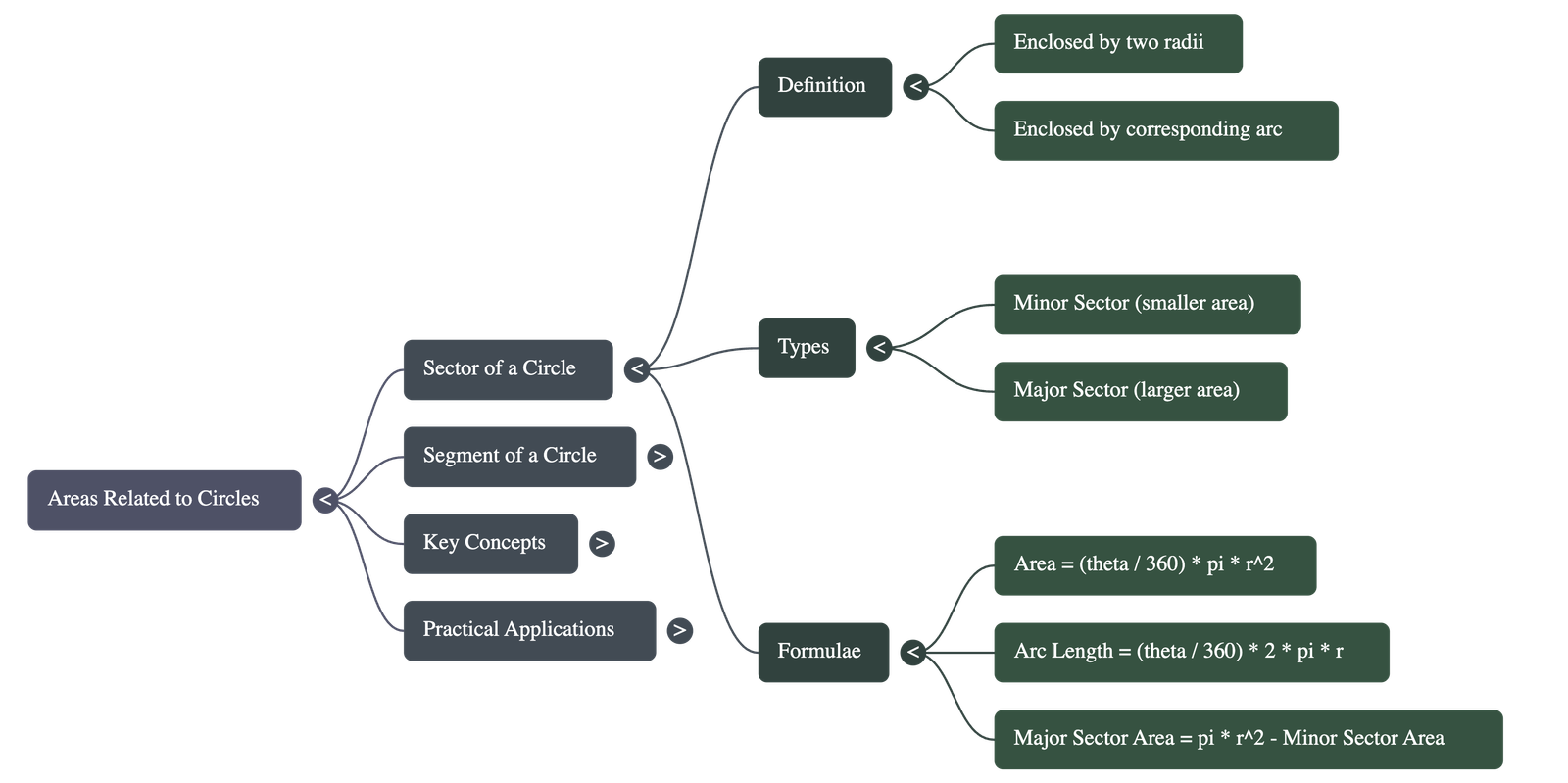
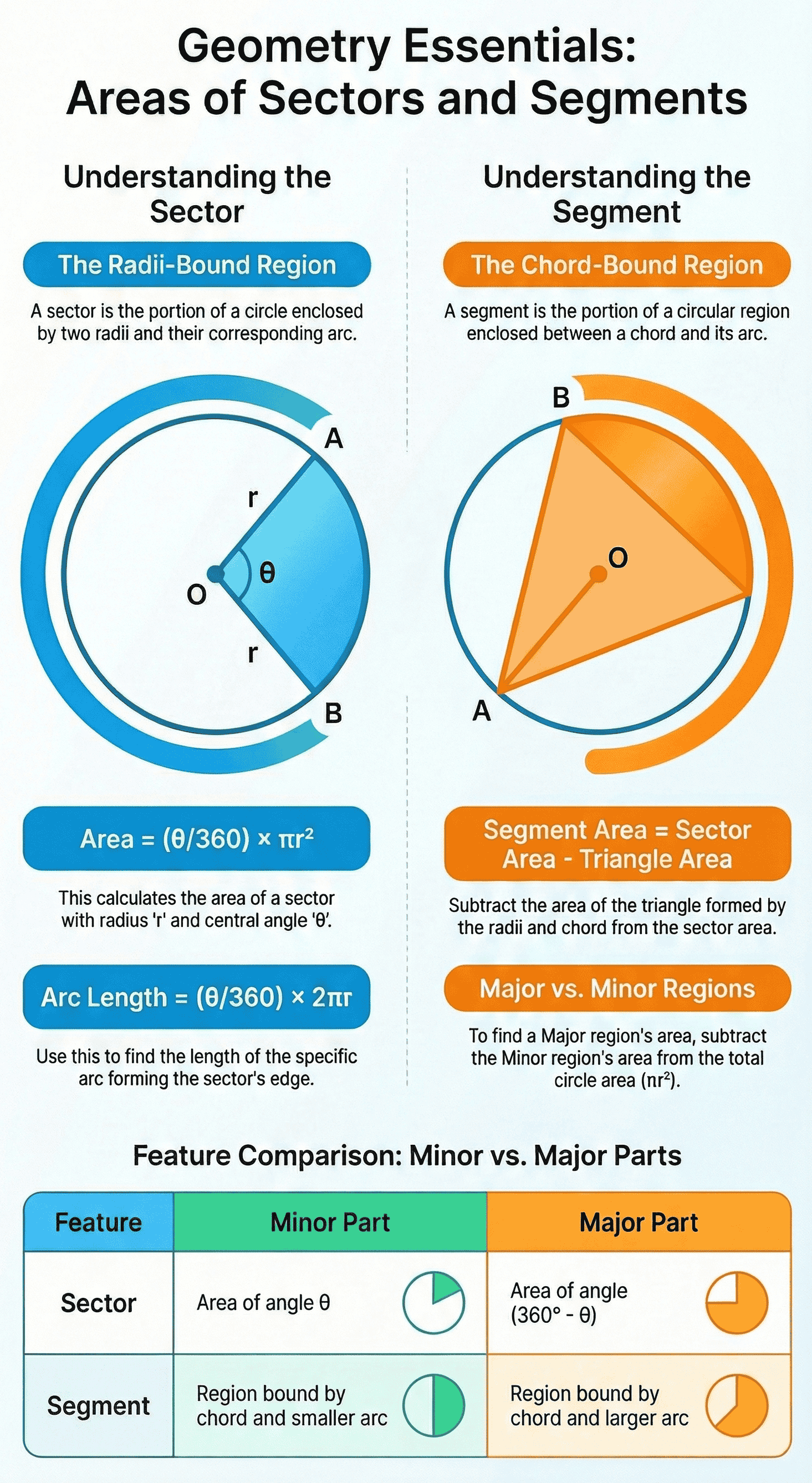
- Sector of a Circle: The portion of the circular region enclosed by two radii and the corresponding arc. The angle formed by the two radii at the center is called the angle of the sector.
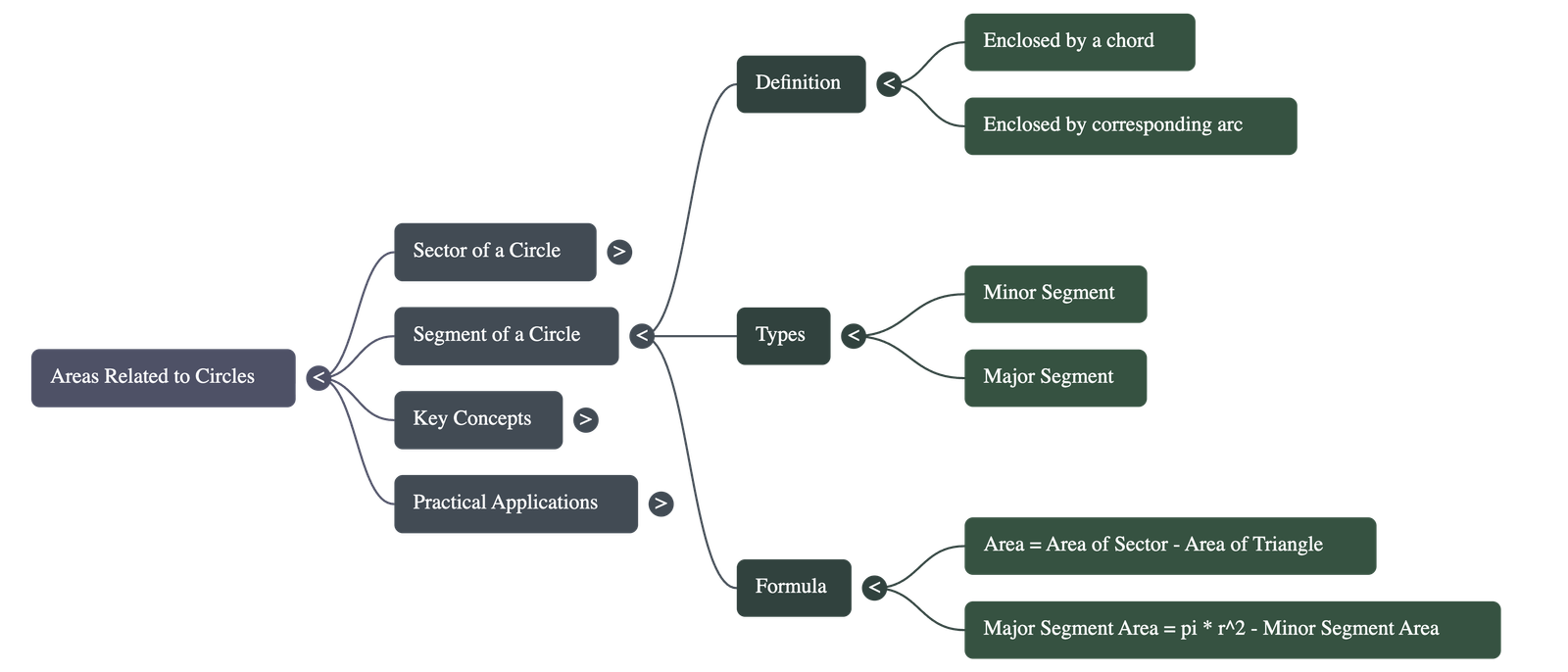
- Segment of a Circle: The portion of the circular region enclosed between a chord and the corresponding arc.
-
Minor vs. Major: Both sectors and segments are divided into minor (smaller area) and major (larger area) parts.
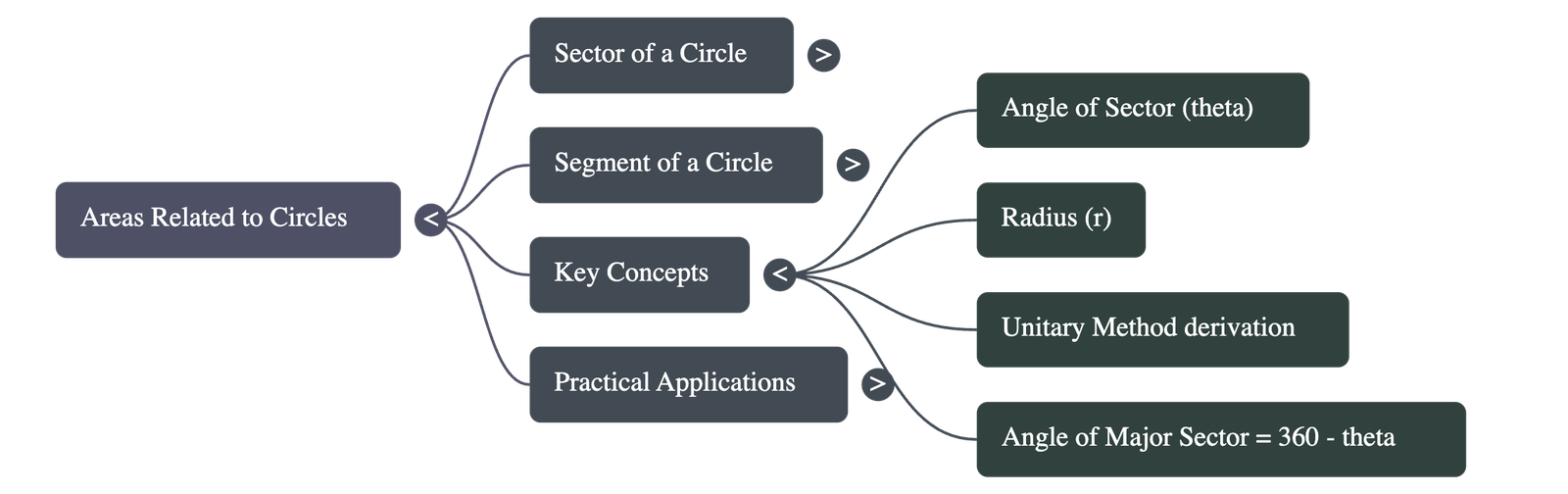
- The angle of the major sector is calculated as 360° – angle of the minor sector.
- Unless explicitly stated otherwise, the terms "sector" and "segment" refer to the minor sector and minor segment, respectively.
2. Calculating the Area of a Sector
The area of a sector can be derived by considering the circular region as a sector forming an angle of 360° at the center.
-
Unitary Method Logic:
- If the angle at the center is 360°, the area is πr².
- If the angle at the center is 1°, the area is πr² / 360.
- Therefore, if the angle at the center is θ, the area is (πr² / 360) × θ.
- Formula: Area of the sector of angle θ = (θ / 360) × πr²
- Area of Major Sector: This can be calculated by subtracting the area of the minor sector from the total area of the circle (πr²).
3. Calculating the Length of an Arc
Similar to the area, the length of an arc corresponding to a sector can be found by relating it to the circumference of the circle.
-
Unitary Method Logic:
- If the angle at the center is 360°, the length of the arc (circumference) is 2πr.
- Therefore, for an angle θ, the arc length is a fraction of the total circumference.
- Formula: Length of an arc of a sector of angle θ = (θ / 360) × 2πr
4. Calculating the Area of a Segment
The area of a segment is derived by combining the area of the sector and the area of the triangle formed by the radii and the chord.
- Formula: Area of Segment = Area of the corresponding Sector – Area of the corresponding Triangle
- To find the area of the triangle, trigonometric ratios (like sin and cos) or standard geometric formulas may be required depending on the given angle θ (e.g., 60°, 90°, 120°).
- Area of Major Segment: This is calculated by subtracting the area of the minor segment from the total area of the circle (πr²).
5. Chapter Summary Recap
- The circumference of a circle is 2πr and the area is πr².
- Length of an arc of a sector of angle θ = (θ/360) × 2πr.
- Area of a sector of angle θ = (θ/360) × πr².
- Area of a segment = Area of the corresponding sector – Area of the corresponding triangle.
Quick Navigation:
| | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | |