Quick Navigation:
| | |
CHAPTER 10: HERON’S FORMULA
Introduction to Triangle Area
- The traditional method for calculating the area of a triangle is 1/2 × base × height. However, this formula is difficult to use when the height of the triangle is not known.
- The chapter introduces a method to calculate the area of a triangle using only the lengths of its three sides, which is particularly useful for scalene triangles where height is not easily determined.
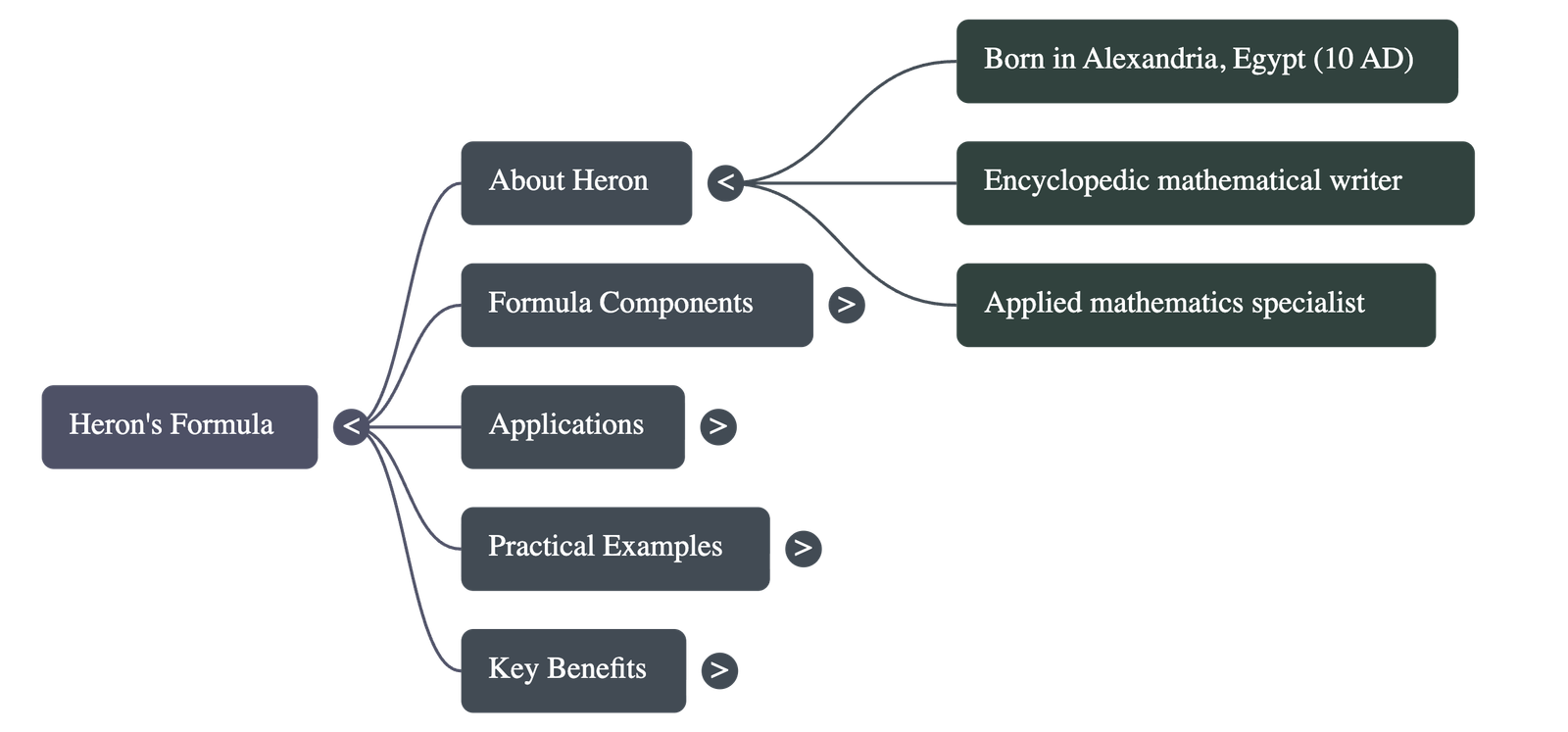
About Heron of Alexandria
- Heron (also known as Hero) was a mathematician born around 10 C.E. in Alexandria, Egypt, who worked extensively in applied mathematics.
- His work, specifically Book I of his geometrical writings, contains the derivation of the famous formula for the area of a triangle in terms of its three sides.
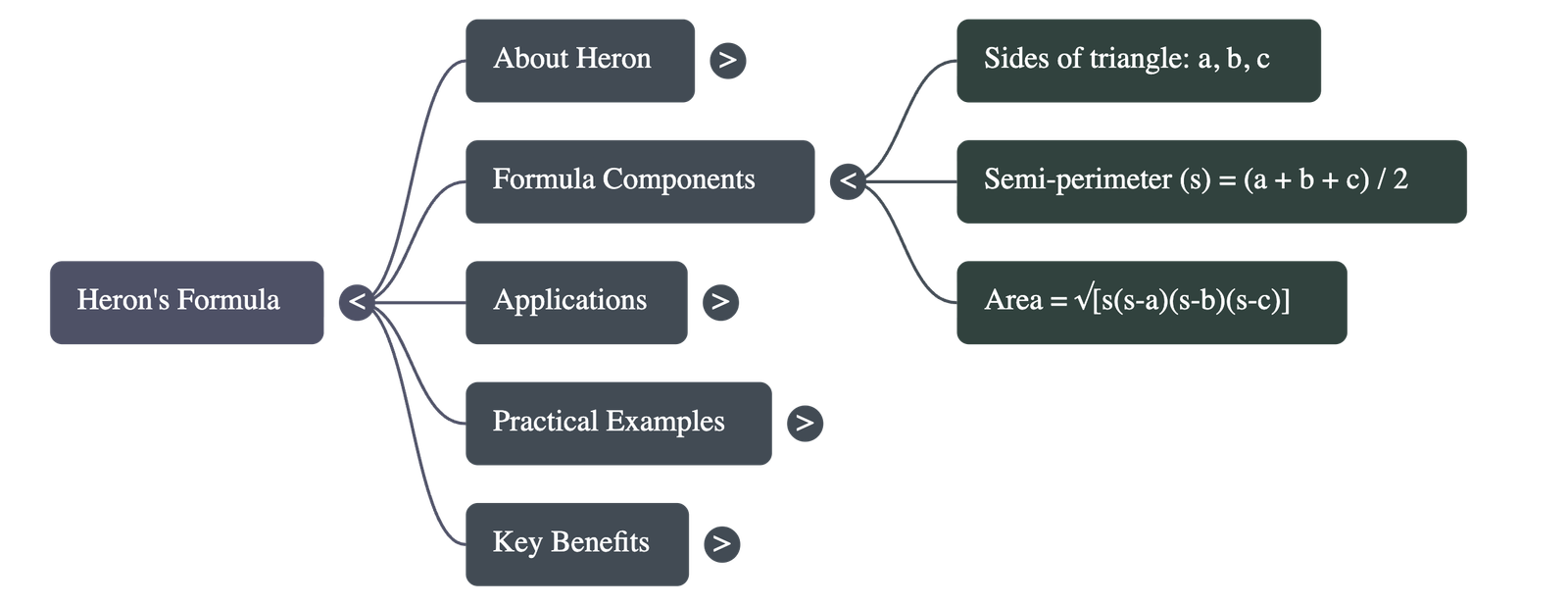
The Formula
The area of a triangle with sides a, b, and c is given by:
Area = √[s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)]
Where s is the semi-perimeter of the triangle, calculated as:
s = (a + b + c) / 2
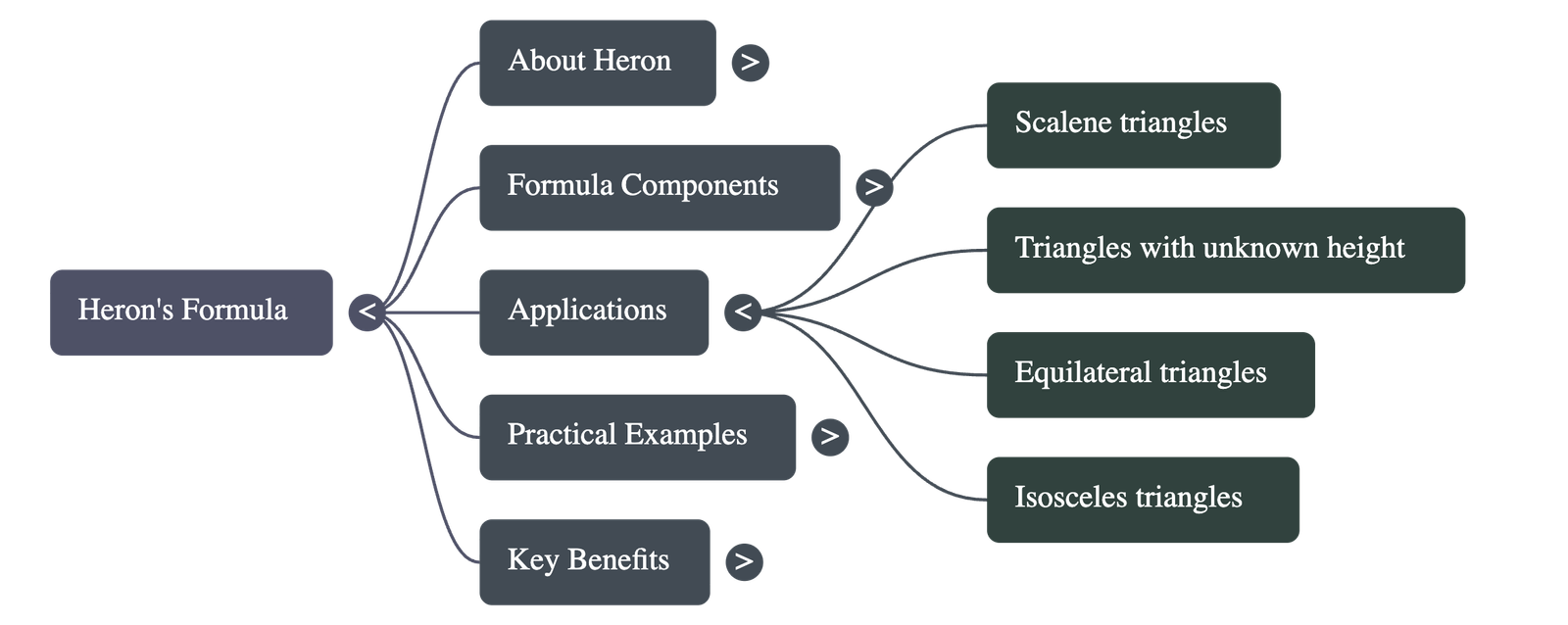
Key Application Scenarios
- Triangles with known sides: Directly plug the side lengths into the formula to find the area.
- Triangles with perimeter and two sides: First, find the third side by subtracting the sum of the known sides from the perimeter, then apply the formula.
- Side Ratios: If sides are given as a ratio (e.g., 3:5:7) along with the perimeter, use a variable (like x) to determine the actual side lengths before calculating the area.
- Equilateral and Isosceles Triangles: The formula can also be used to verify areas for triangles with equal sides, providing the same result as standard geometric height-based formulas.
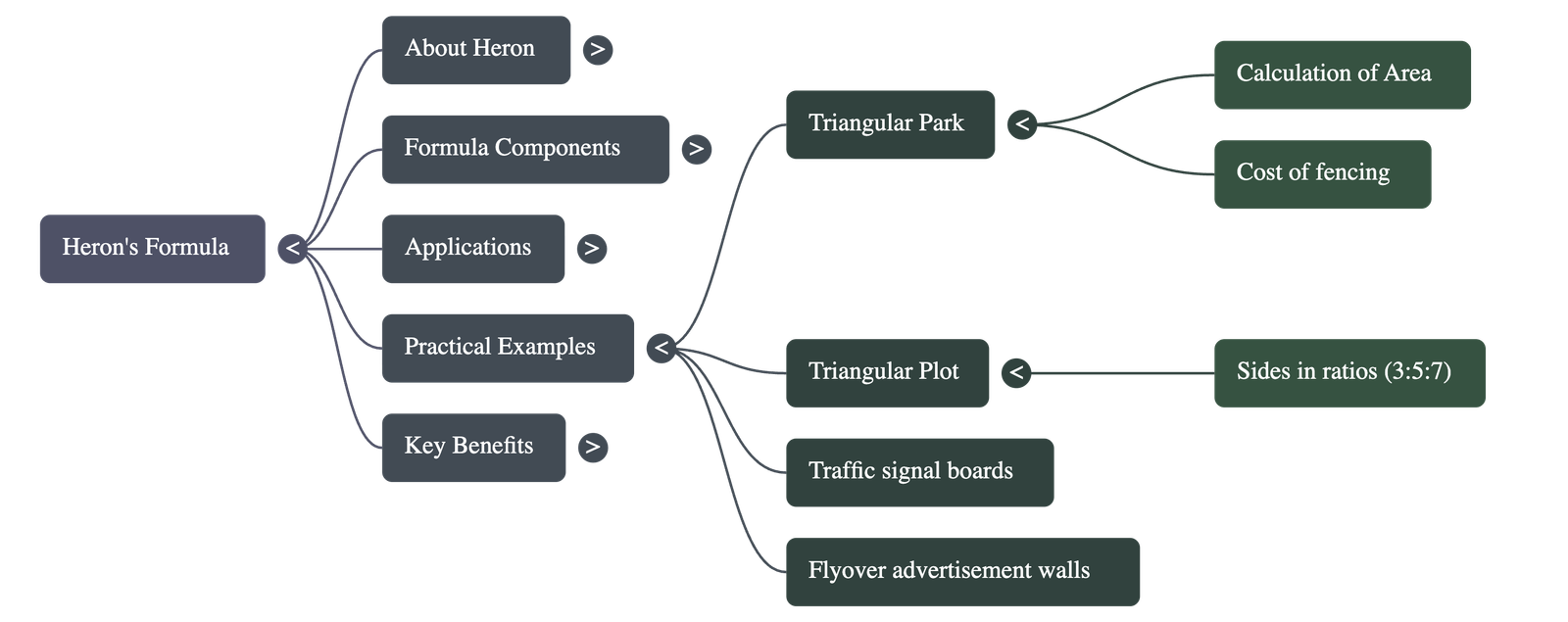
Real-World Utility
- The chapter demonstrates practical uses, such as calculating the area of triangular parks for grass planting and determining the cost of fencing based on the perimeter.
- It is also applied to industrial problems, such as calculating rent for advertising space on triangular flyover walls based on their surface area.
Summary of Core Concepts
- Heron's Formula is defined as √[s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)].
- The semi-perimeter s is half of the total perimeter (a + b + c).
- The formula is a versatile tool for any triangle where all three side lengths are available, regardless of whether it is a right-angled triangle or not.
Quick Navigation:
| | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | |