Quick Navigation:
| | |
QUADRILATERALS
Basic Concepts
- A quadrilateral is a polygon with four sides, four angles, and four vertices.
- A parallelogram is a specific type of quadrilateral where both pairs of opposite sides are parallel.
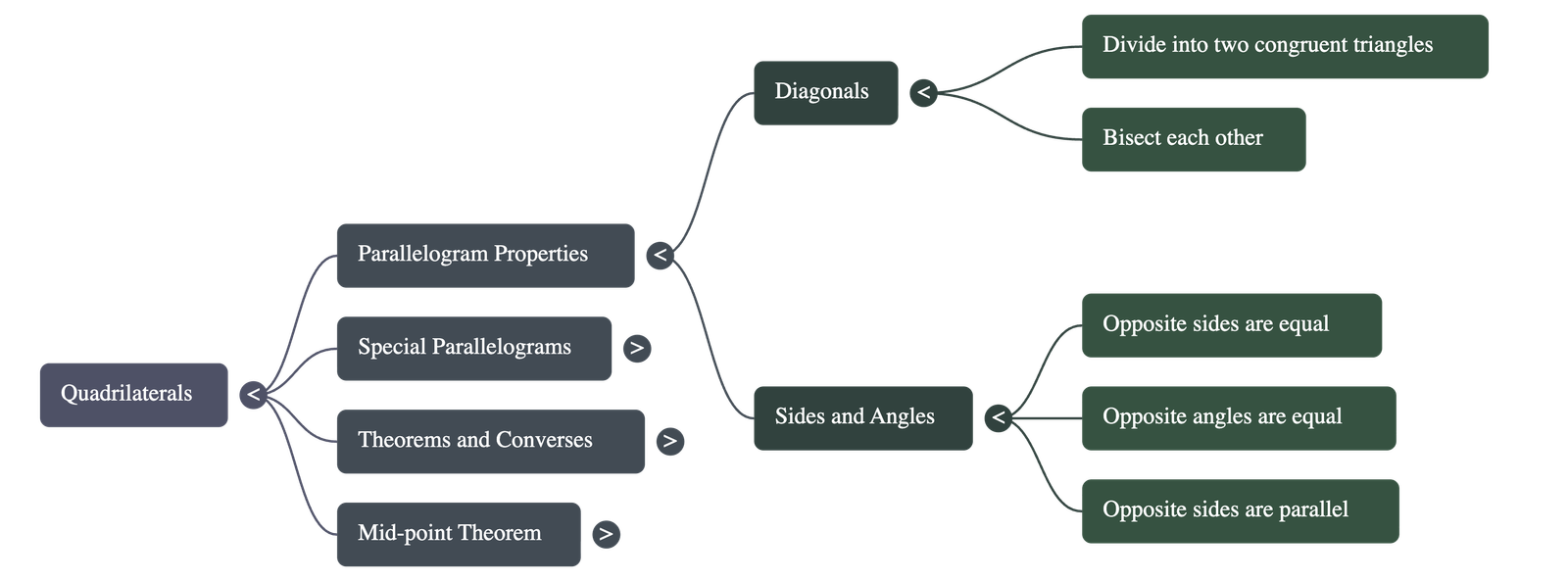
Properties of a Parallelogram
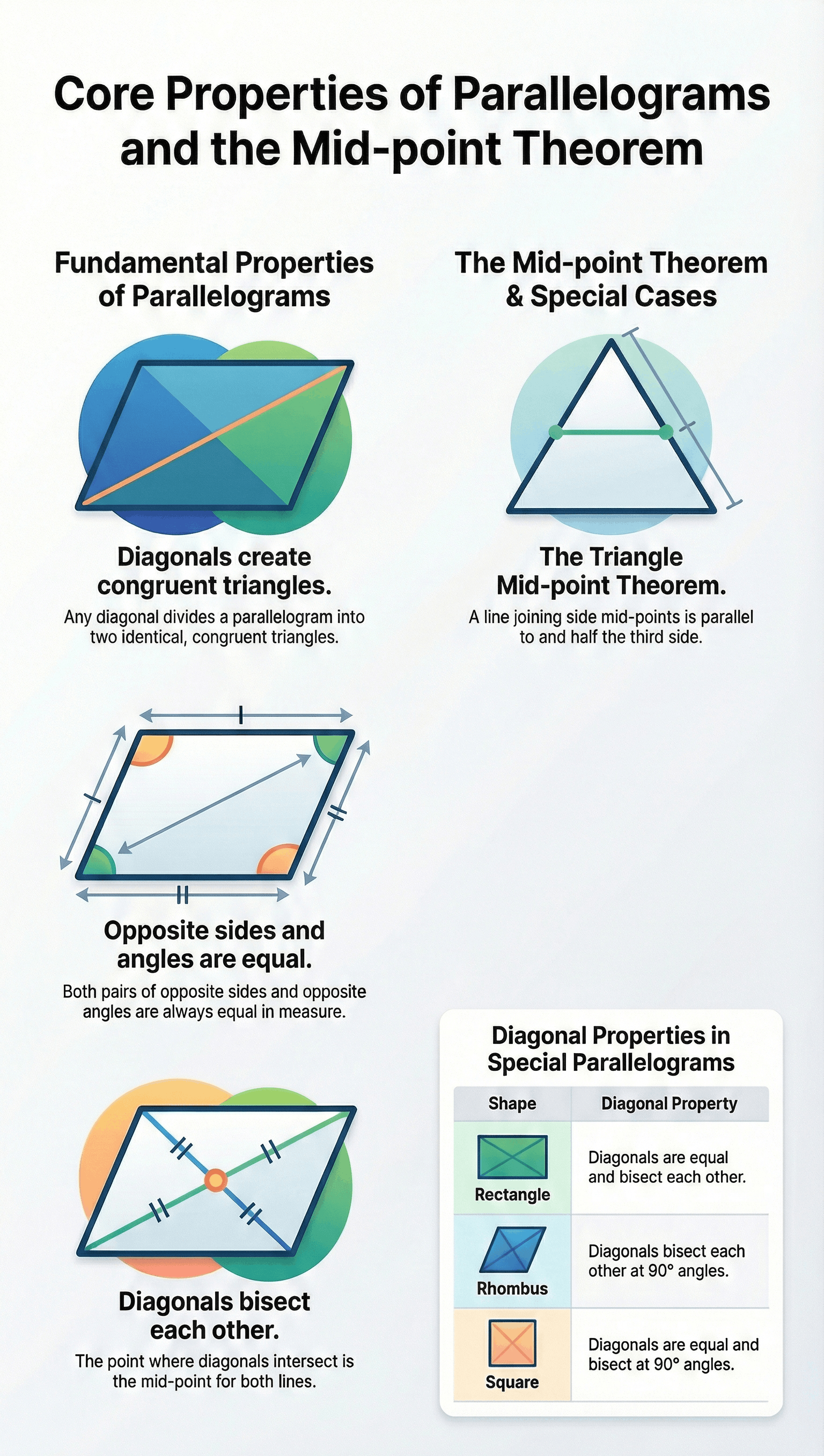
- Congruent Triangles: A diagonal of a parallelogram divides the shape into two congruent triangles.
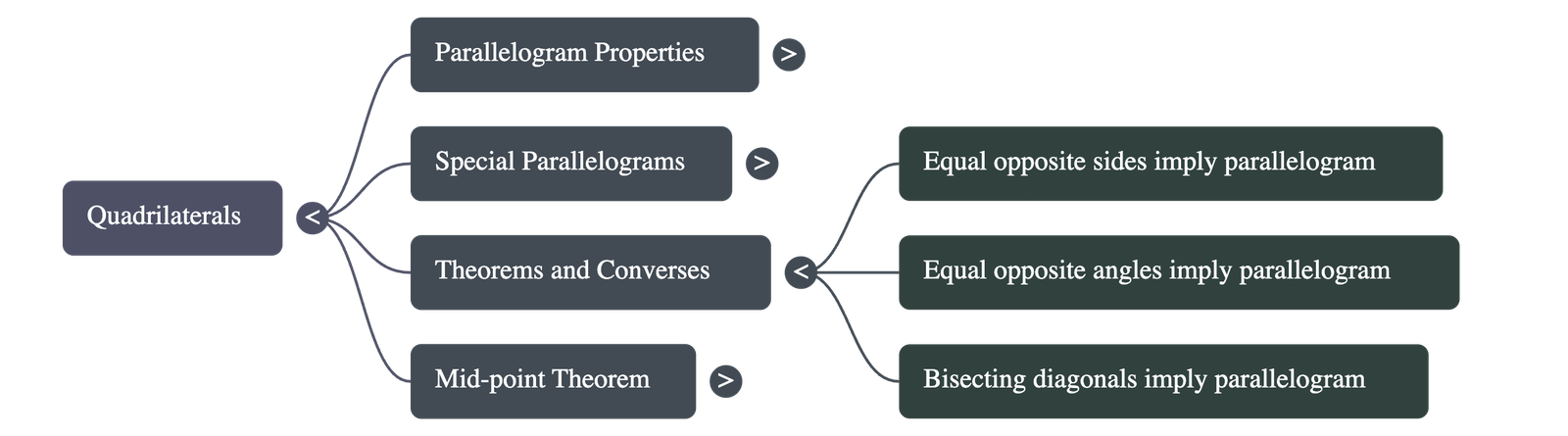
- Opposite Sides: In any parallelogram, the opposite sides are equal in length. Conversely, if each pair of opposite sides of a quadrilateral is equal, it is a parallelogram.
- Opposite Angles: The opposite angles in a parallelogram are equal. Conversely, if each pair of opposite angles in a quadrilateral is equal, it is a parallelogram.
- Diagonal Bisectors: The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other. Conversely, if the diagonals of a quadrilateral bisect each other, the shape is a parallelogram.
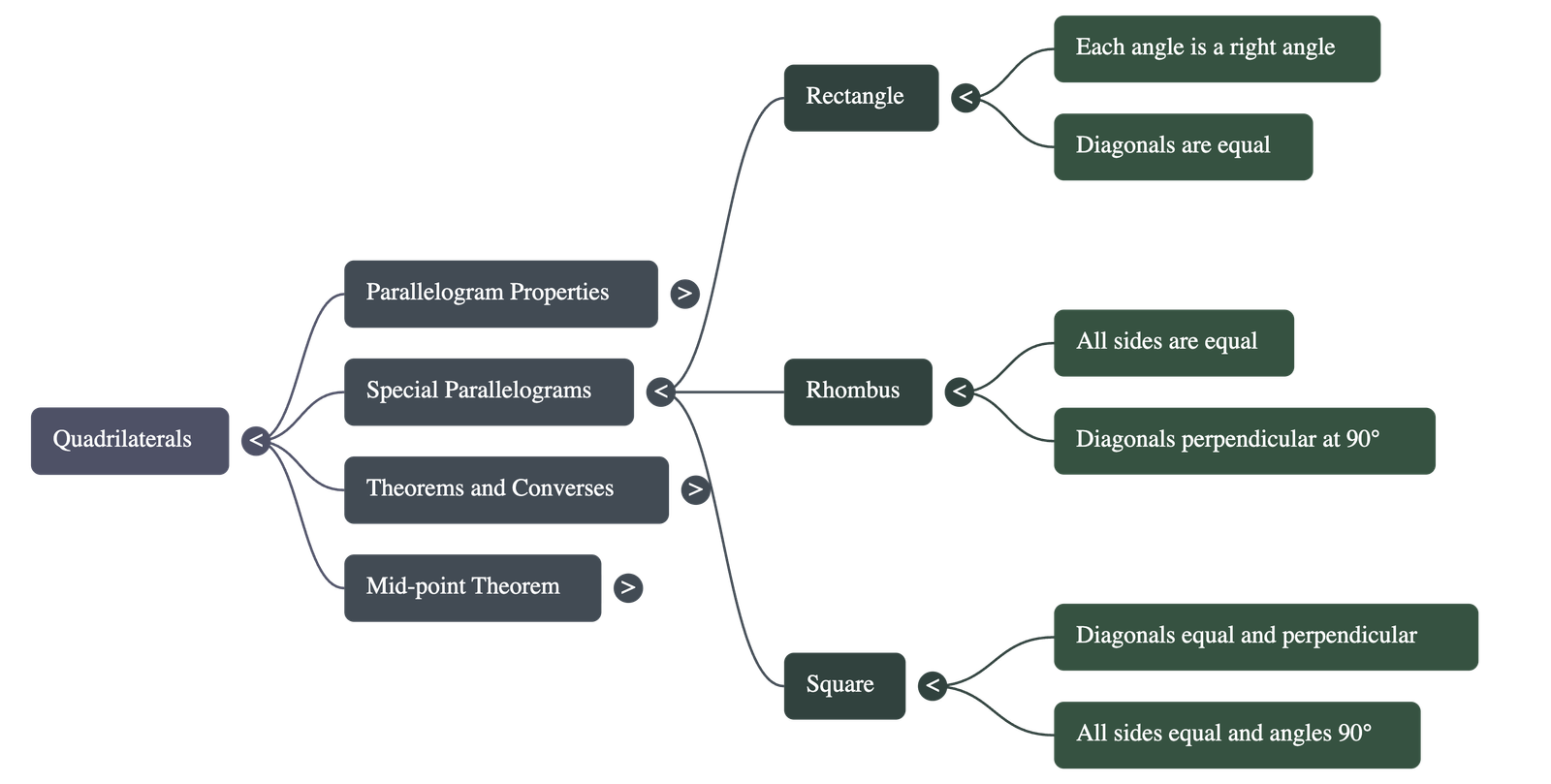
Special Quadrilaterals
- Rectangle: A rectangle is a parallelogram where one angle is a right angle. Consequently, all angles in a rectangle are right angles. Its diagonals bisect each other and are equal in length.
- Rhombus: A rhombus is a quadrilateral with all sides of equal length. Its diagonals are perpendicular to each other and bisect each other at right angles.
- Square: A square is a parallelogram with all sides equal and all angles equal to 90 degrees. Its diagonals are equal and bisect each other at right angles.
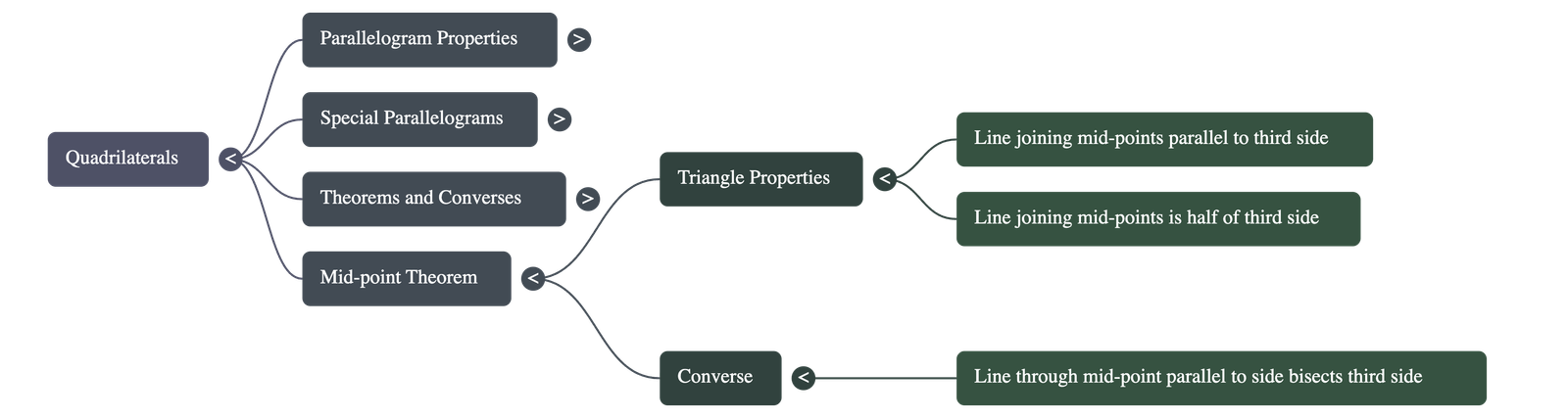
The Mid-point Theorem
- Theorem: The line segment joining the mid-points of any two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side and is equal to half of it.
- Converse: A line drawn through the mid-point of one side of a triangle, parallel to another side, will bisect the third side.
Key Summary Points
- Opposite sides and angles of a parallelogram are always equal.
- A quadrilateral is a parallelogram if its diagonals bisect each other or if one pair of opposite sides is both parallel and equal.
- Diagonals of a rectangle are equal and bisect each other.
- Diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at 90°.
- Diagonals of a square are equal and bisect each other at 90°.
- The mid-point theorem is a critical tool for proving properties involving triangles and parallel lines.
Quick Navigation:
| | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | |