Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
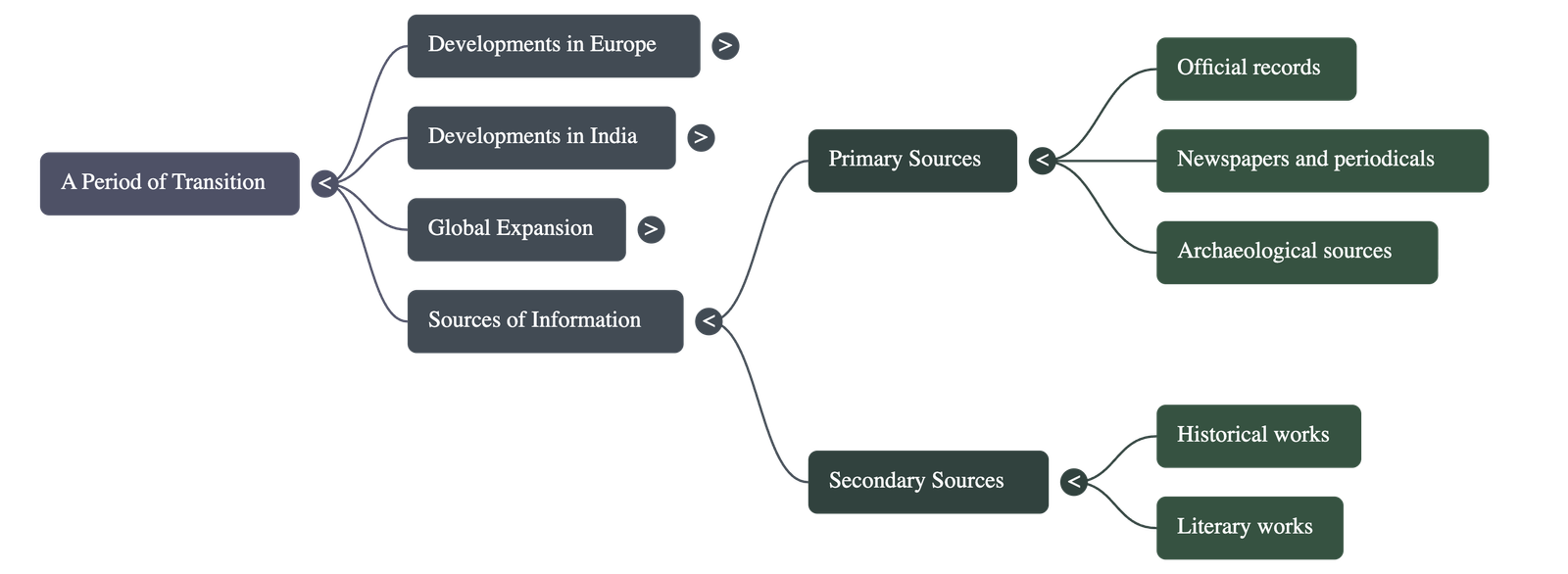
A Period of Transition
A point-wise summary:
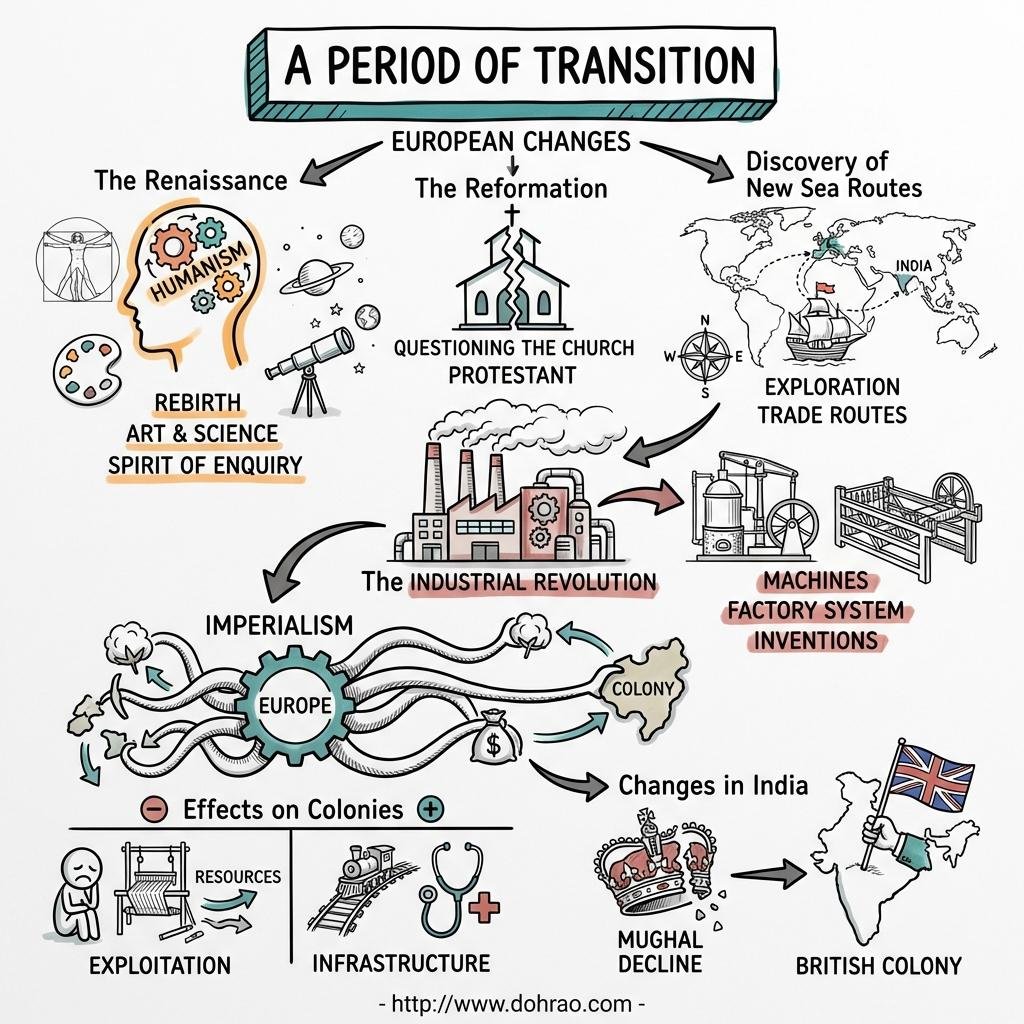
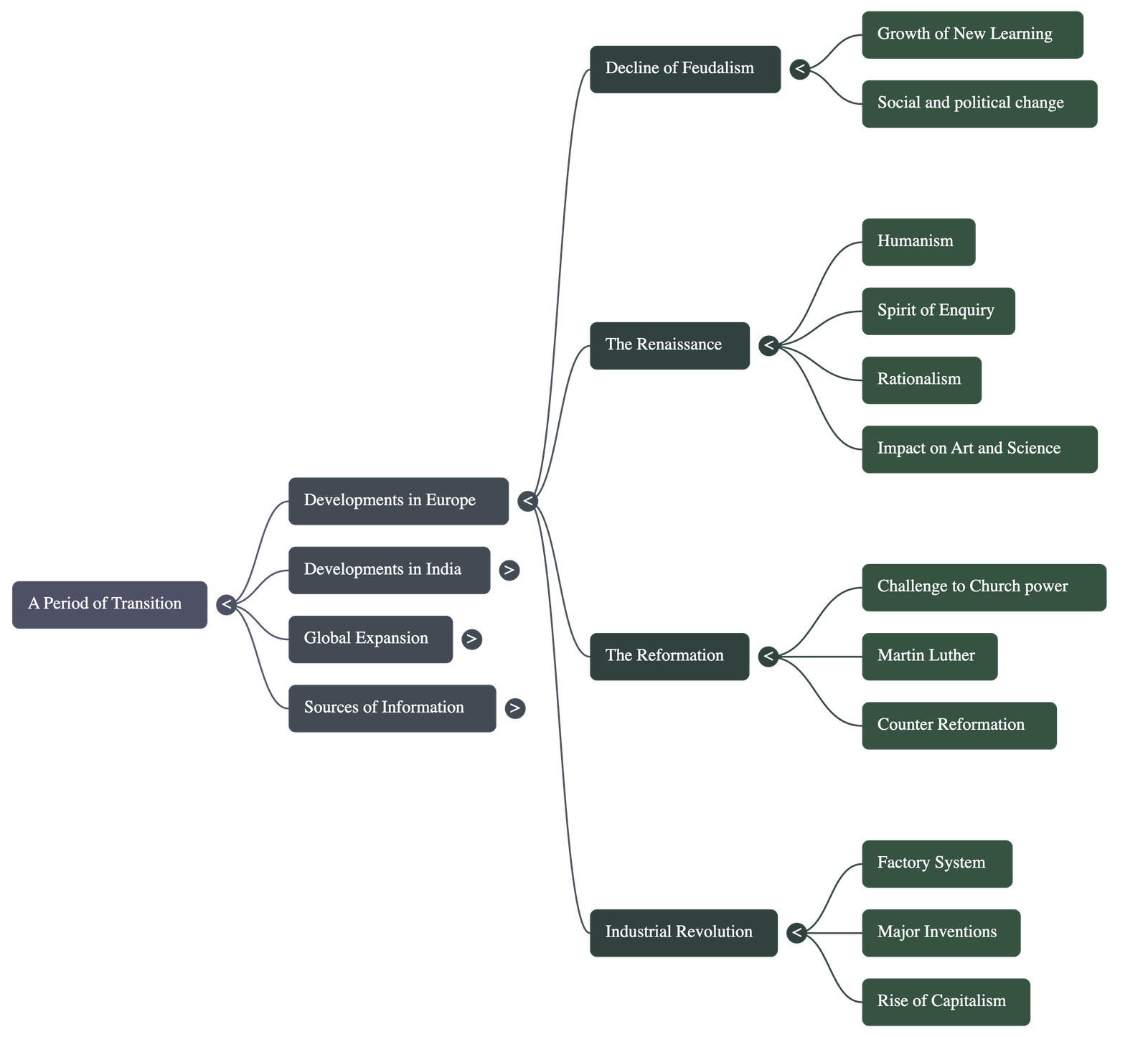
- Defining the Period of Transition
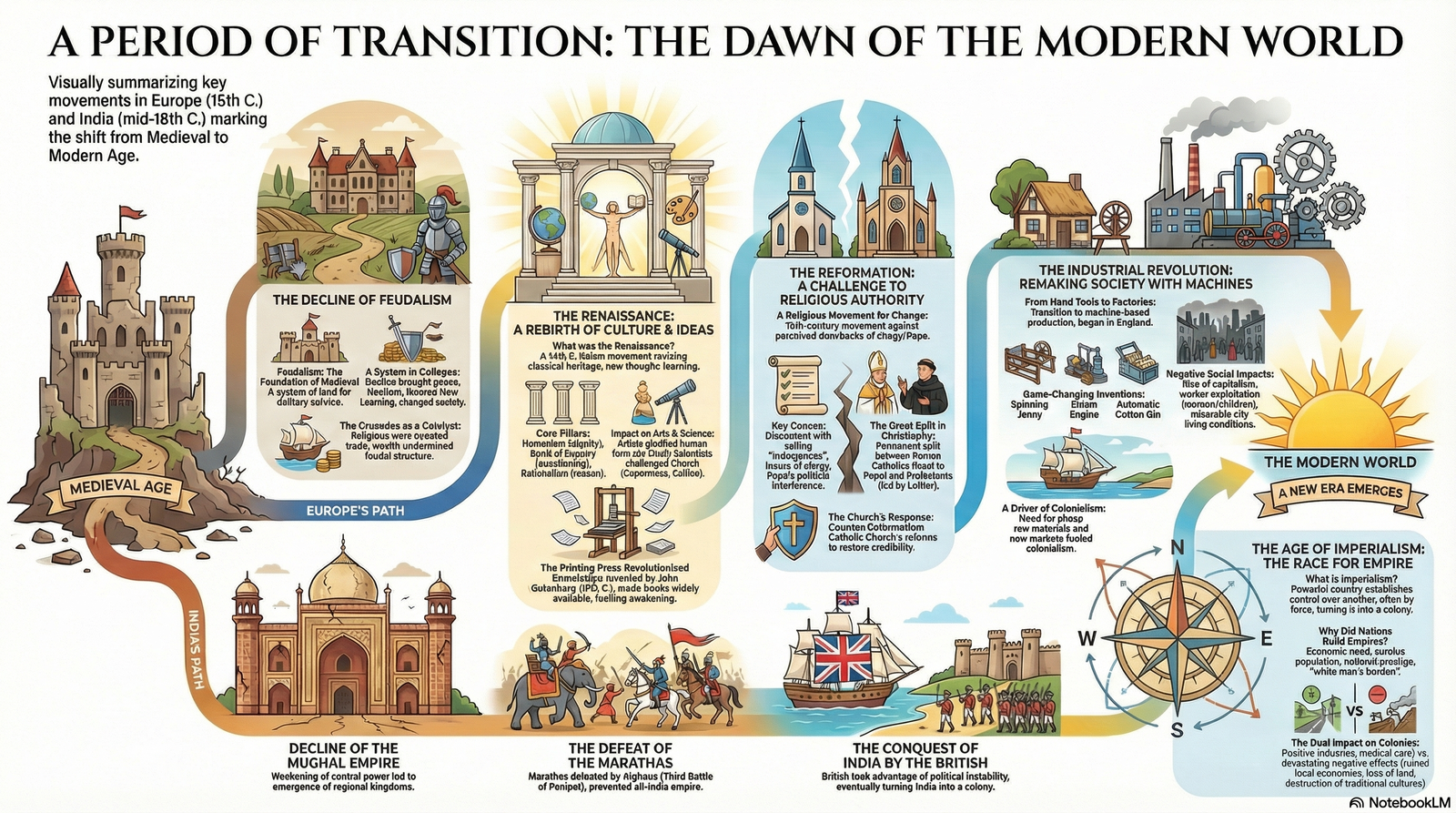
- This period marks the movement from the Medieval Age to the Modern Age.
- In Europe, this transition began in the 15th century, while in India, it began in the mid-18th century.
- Key factors facilitating this shift in Europe included the decline of feudalism, the rise of "New Learning" sparked by the Crusades, and the discovery of new sea routes to the East.
- The Renaissance (Rebirth)
- The term Renaissance refers to the 14th-century movement originating in Italy that aimed to revive the classical Greek and Roman heritage.
- Key Principles:
- Humanism: Shifting the focus from spiritual/divine matters to human problems and reason.
- Spirit of Enquiry and Rationalism: Encouraging curiosity, scientific experimentation, and the rejection of blind faith or superstition.
- Impact on Arts and Science:
- Arts: Artists like Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo focused on realism and human anatomy.
- Science: Major breakthroughs included the heliocentric theory (Copernicus/Kepler), the telescope (Galileo), the laws of gravitation (Newton), and the discovery of blood circulation (William Harvey).
- Communication: John Gutenberg’s printing press made books accessible to the masses, spreading new ideas rapidly.
- The Reformation
- This was a 16th-century religious movement against the drawbacks and "objectionable practices" of the Catholic Church, such as selling pardon certificates (Indulgences) and interference in political affairs.
- Led by figures like Martin Luther, it resulted in a split in Christianity between Roman Catholics and Protestants.
- In response, the Catholic Church launched the Counter-Reformation to regain its credibility and reform its own practices.
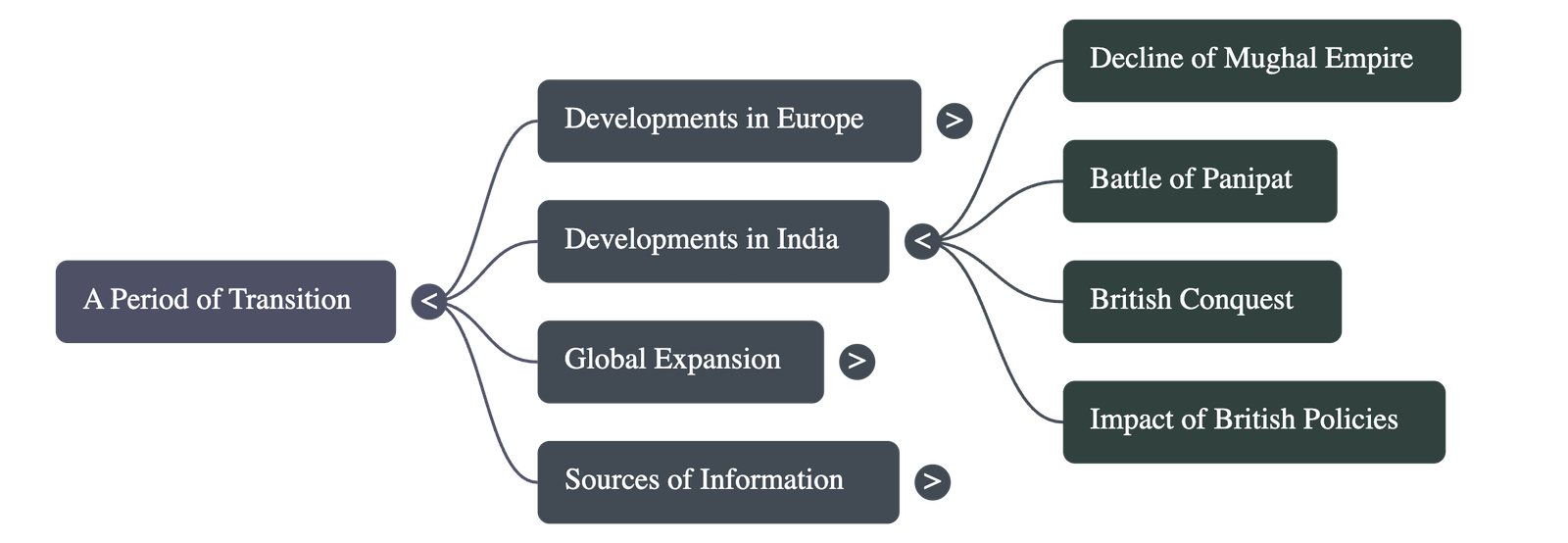
- Developments in India
- The transition in India was characterized by the decline of the Mughal Empire, the defeat of the Marathas at Panipat, and the eventual British conquest.
- Sources of Information: Historians reconstruct this period using Primary Sources (government records, diaries, and official papers of the British Crown and East India Company) and Secondary Sources (biographies, newspapers, and historical works).
- The Industrial Revolution
- This refers to the transition from handwork to machines and from the domestic system to the factory system of production, starting in England.
- Key Inventions: The steam engine (James Watt), the spinning jenny, the cotton gin, and the telegraph/telephone.
- Impact:
- Positive: Increased national wealth, urbanization, and improved transportation/communication.
- Negative: Rise of capitalism, ruthless exploitation of workers (including women and children), and miserable living conditions in slums.
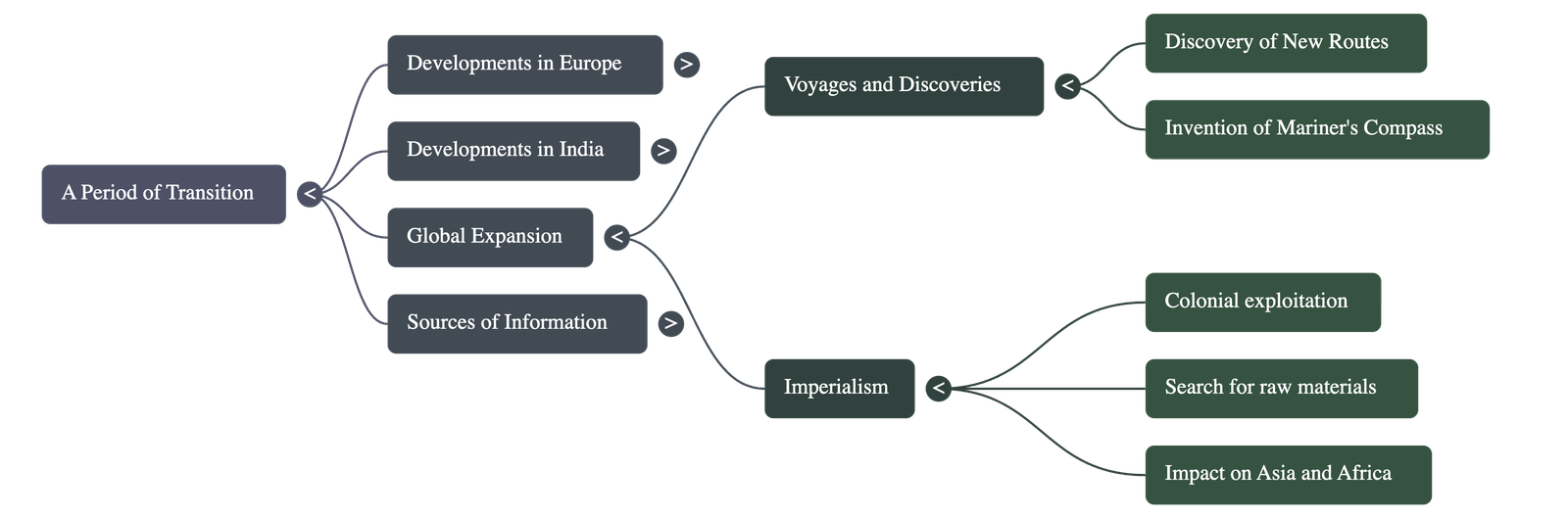
- Imperialism and Colonialism
- The need for raw materials and new markets for industrial goods drove European nations to establish control over other countries, a system known as Imperialism.
- Consequences:
- While it introduced new technology, infrastructure (roads/railways), and sanitation to colonies, it also destroyed local economies, ruined traditional handicrafts, and forced western culture upon colonized societies.
- Intense rivalries between European powers for colonies eventually led to the First World War.
Analogy for Understanding: Think of the Period of Transition like a house renovation. The Renaissance was the "design phase" where people decided to use new tools (reason/science) instead of old blueprints (superstition). The Industrial Revolution was the "power tool phase," where manual labor was replaced by heavy machinery to build faster. However, this renovation also led to "neighbor disputes" (Imperialism), as those with the best tools tried to take over their neighbors' yards to get more supplies and space.
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |