Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Point-wise summary of Chapter 5, "Agencies of The UN":
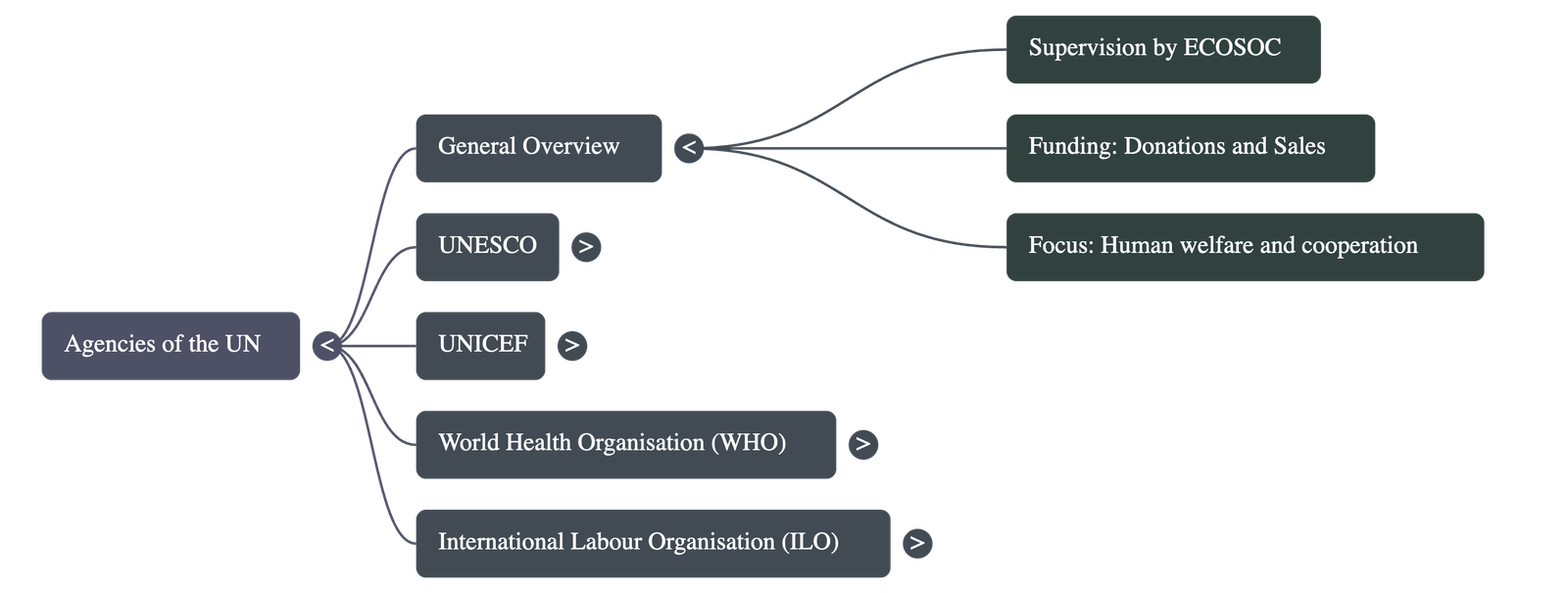
Overview of UN Specialized Agencies
- The United Nations operates through several specialised agencies that work for human welfare and international cooperation.
- These agencies operate under the supervision of the UN Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC).
- Each agency has its own specific agenda, membership, budget, and headquarters.
- Funding is obtained through donations from various governments, Non-Governmental Organisations (NGOs), individuals, and the sale of items like greeting cards, posters, and books.
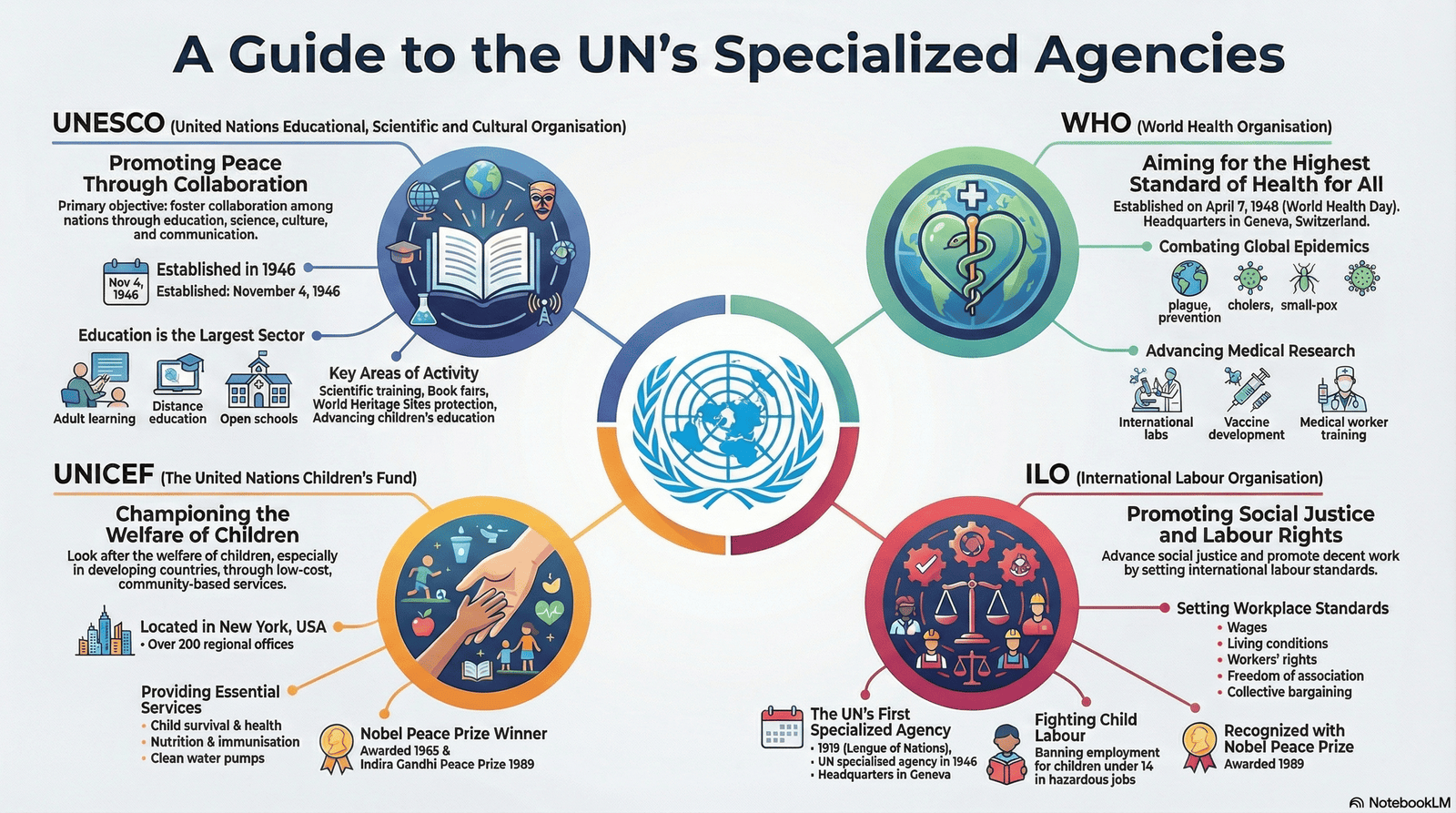
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO)
- Established: November 4, 1946, with headquarters in Paris, France.
- Primary Objective: To contribute to peace and security by promoting collaboration among nations through education, science, culture, and communication.
- Key Functions:
- Education: Focuses on removing illiteracy through adult education, open school systems, and distance education.
- Culture: Aims at preserving the cultural heritage of various countries.
United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF)
- Headquarters: Located in New York, USA.
- Primary Objective: To look after children’s welfare, particularly in developing countries, by focusing on health, nutrition, and maternal care.
- Key Functions:
- Provides training for health personnel and teachers.
- Supplies technical aids like pipes and pumps for clean water in rural areas.
- Works to prevent diseases, suppress trafficking in children and women, and assist during emergencies.
- Recognition: Awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1965 and the Indira Gandhi Peace Prize in 1989.
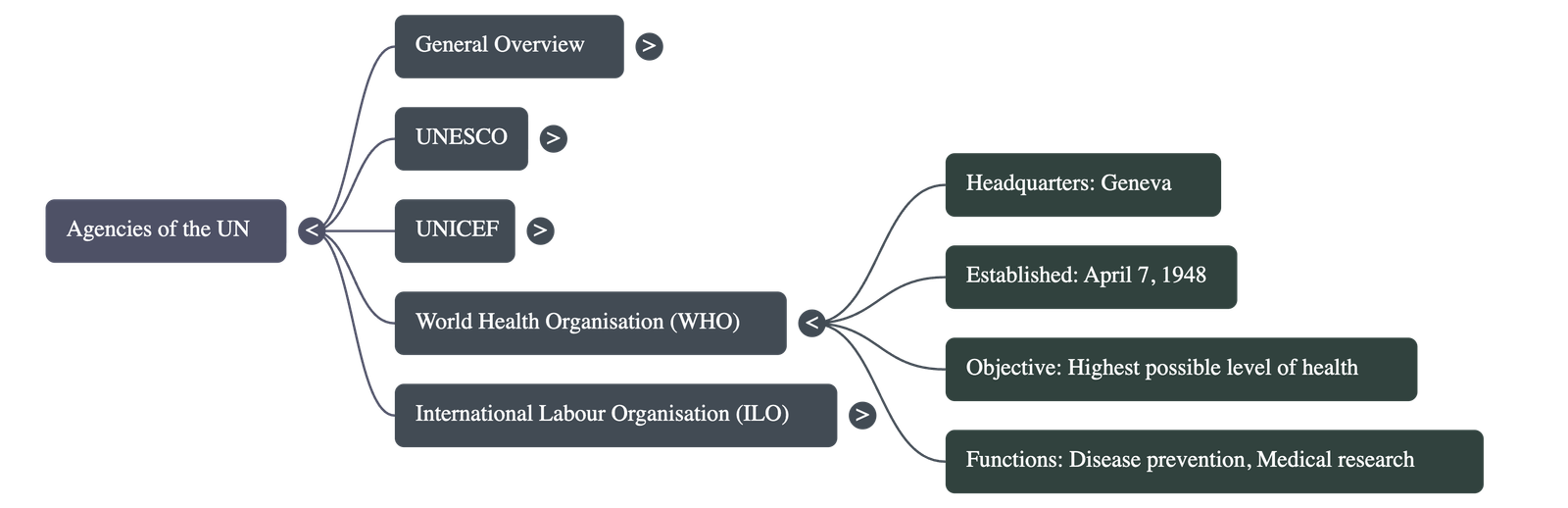
World Health Organisation (WHO)
- Established: April 7, 1948 (celebrated annually as World Health Day), with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland.
- Primary Objective: To help all people attain the "highest possible level of health".
- Key Functions:
- Combats epidemics and diseases like malaria, cholera, and tuberculosis.
- Encourages medical research and trains research workers.
- Works to provide pure water supplies and sanitation systems in remote areas.
International Labour Organisation (ILO)
- History: Founded in 1919 (as part of the League of Nations) and became the first specialised agency of the UN in 1946.
- Headquarters: Located in Geneva, Switzerland.
- Primary Objective: To promote social justice and labour rights.
- Key Functions:
- Establishes international labour standards for wages, living conditions, and freedom of association.
- Bans the employment of children under 14 years of age in hazardous jobs like mines and factories.
- Offers training opportunities for economic development.
- Recognition: Awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1969.
To better understand these agencies, you can think of the United Nations as a large city government. While the main office manages overall policy, specialized agencies are like dedicated departments: the Education Department (UNESCO) builds schools, the Health Department (WHO) runs hospitals, the Social Services Department (UNICEF) protects children, and the Labor Board (ILO) ensures workers are treated fairly. Together, they ensure the city—or in this case, the world—functions smoothly and safely.
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |