Quick Navigation:
| | |
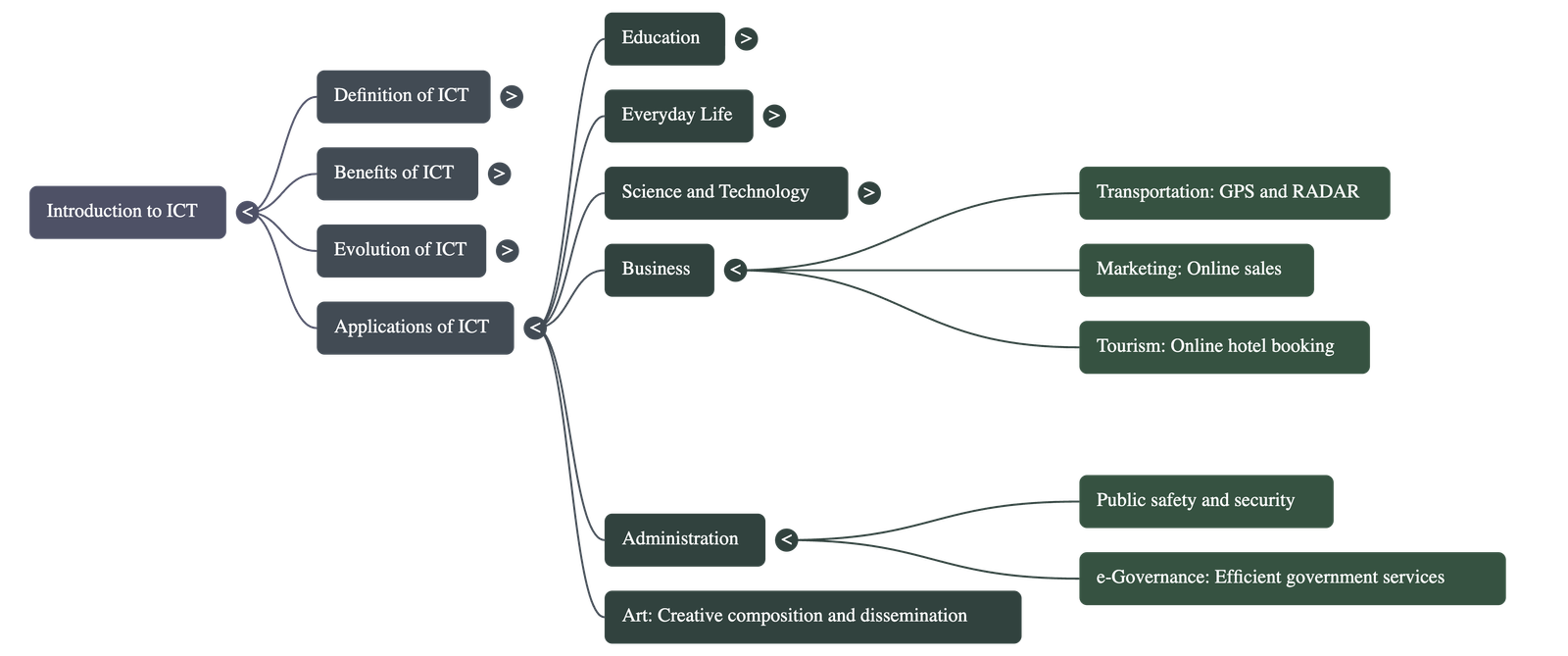
Introduction to ICT
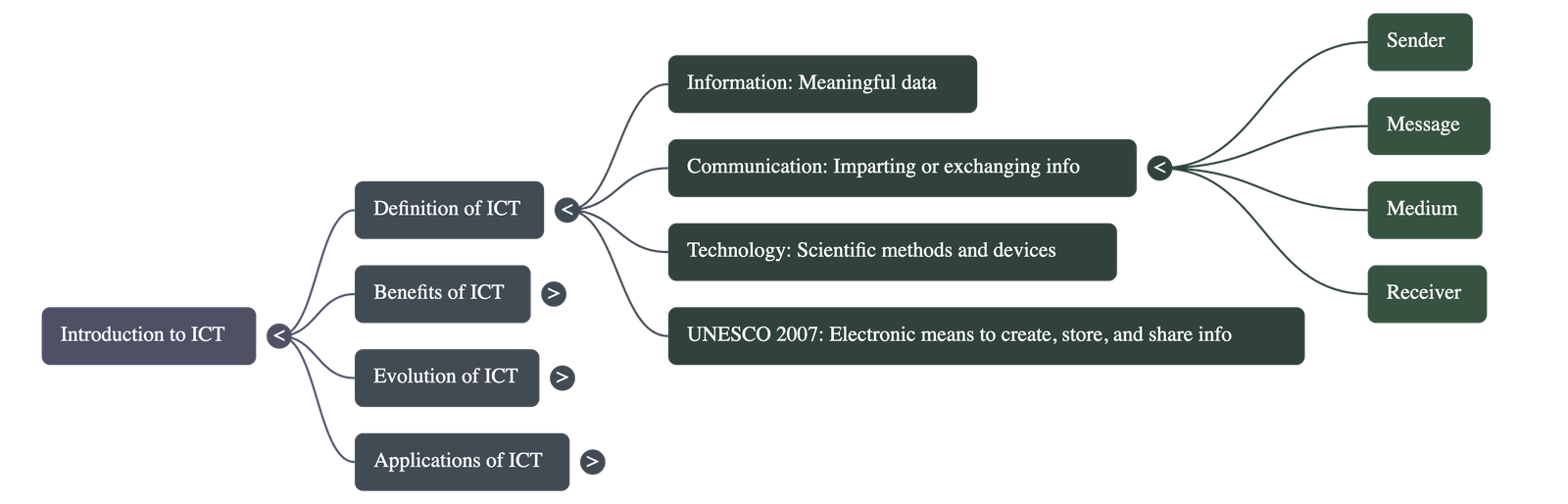
Defining ICT
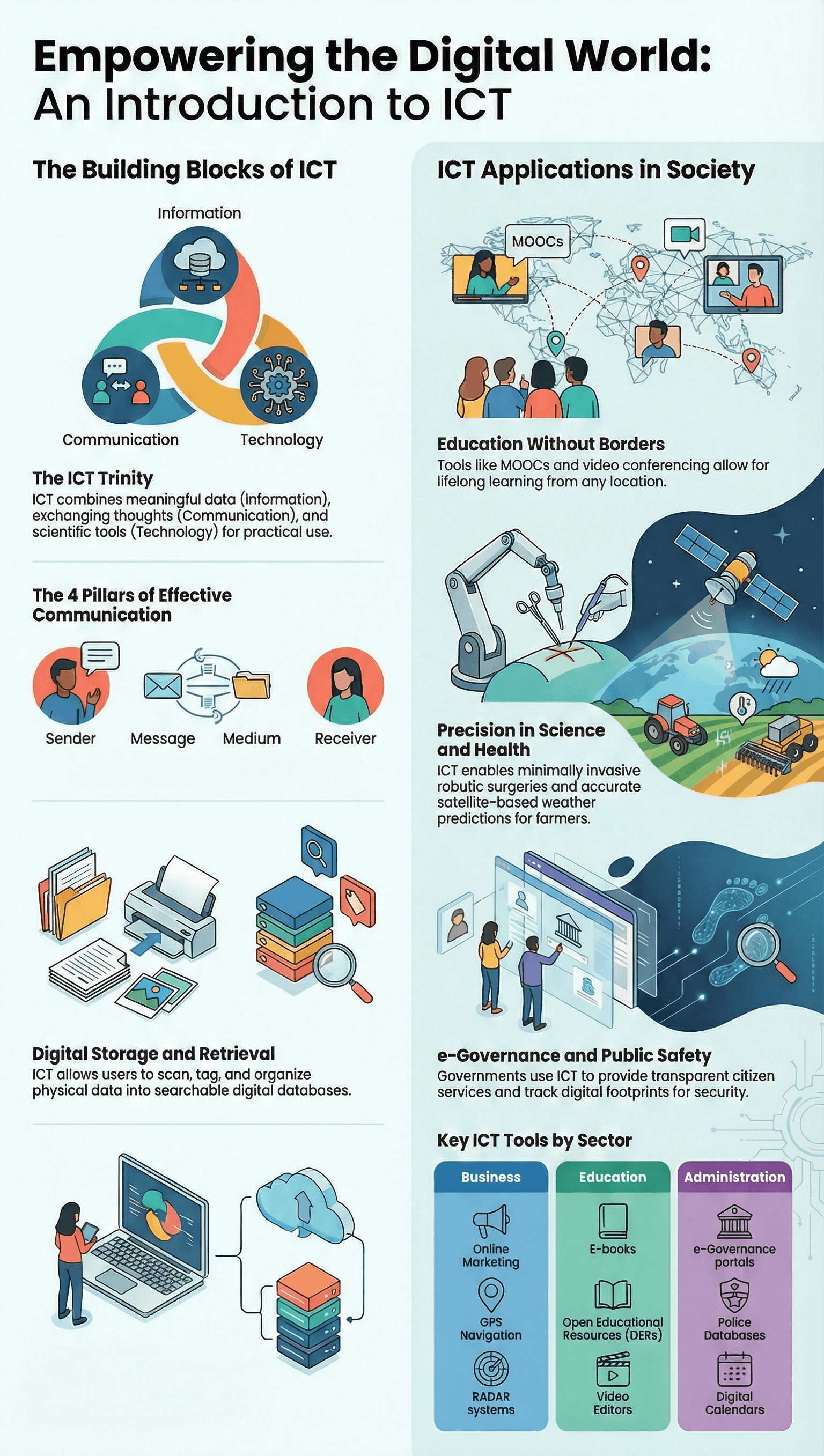
- Information: Refers to data represented in a meaningful way that helps in decision-making.
- Communication: The process of exchanging information, feelings, or thoughts through various mediums. It requires four essential elements: a sender, a message, a medium, and a receiver.
- Technology: The use of scientific knowledge to create methods, systems, and devices for practical purposes.
- ICT: A discipline that includes diverse technological tools used to create, store, process, transmit, and exchange information electronically.
Evolution and Advantages
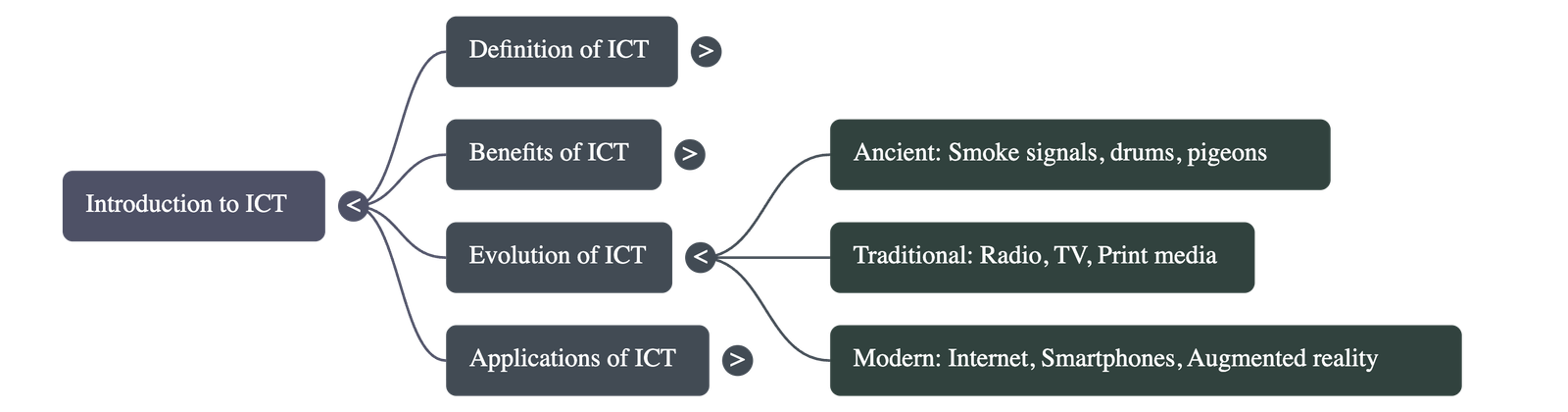
- Rapid Progression: Communication has evolved from ancient smoke signals and drum sounds to digital television, online radio, and global internet connectivity.
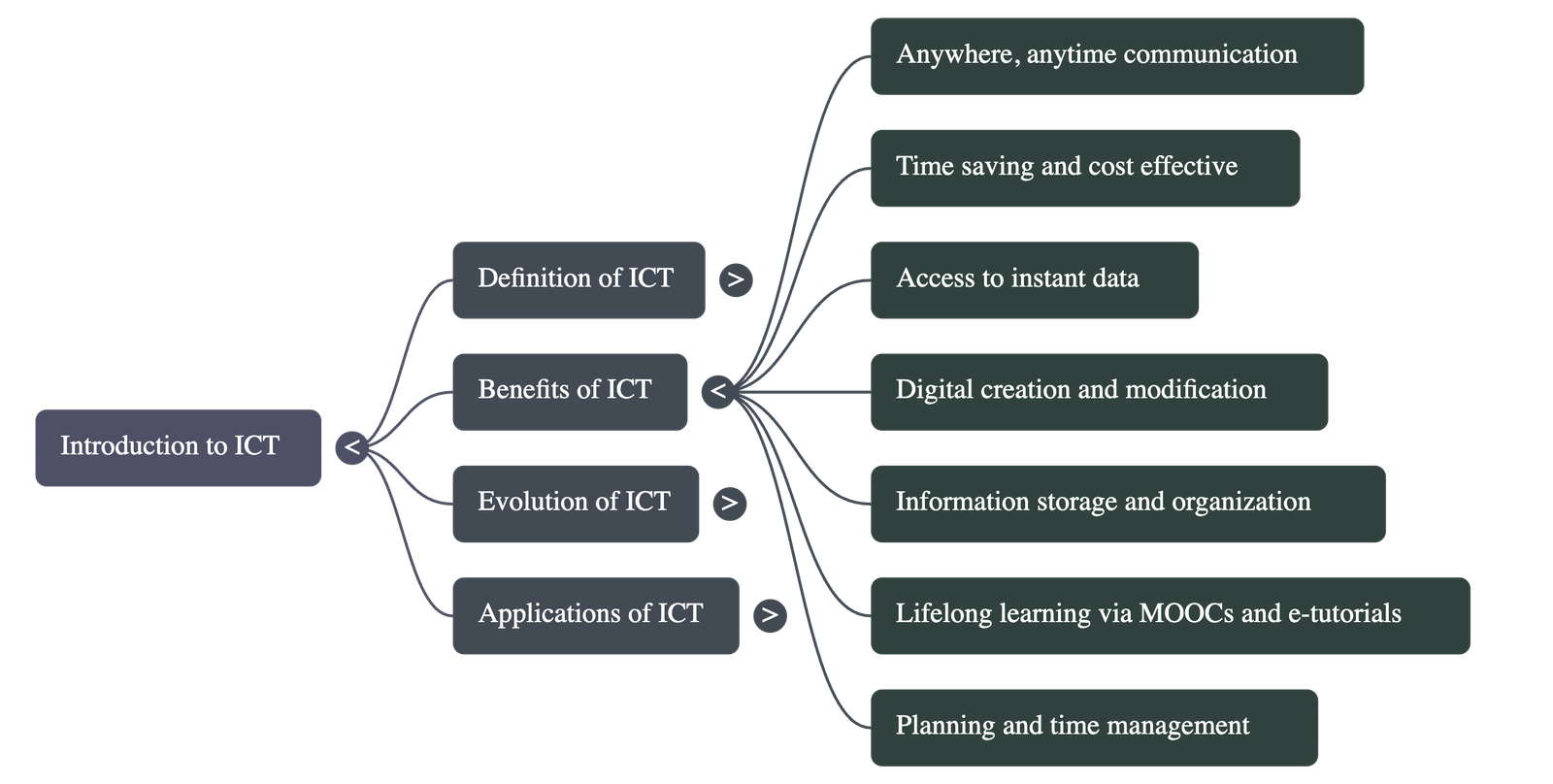
- Cost and Time Efficiency: Modern ICT tools like video calling (e.g., Skype, Google Meet) are significantly more affordable and faster than traditional methods.
- Instant Data Access: Real-time information, such as weather updates or digital archives, aids in better preparedness and knowledge acquisition.
Key Functions of ICT
- Creation and Modification: Digital information is easy to create, edit, and share across multiple platforms.
- Storage and Organization: ICT helps organize vast amounts of data (like library databases or stamp collections) for easy retrieval and preservation.
- Lifelong Learning: Tools like Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) allow individuals to learn new skills from anywhere at any time.
- Planning and Management: Digital calendars and mobile apps help users manage deadlines, schedule exams, and set alerts.
Applications Across Sectors
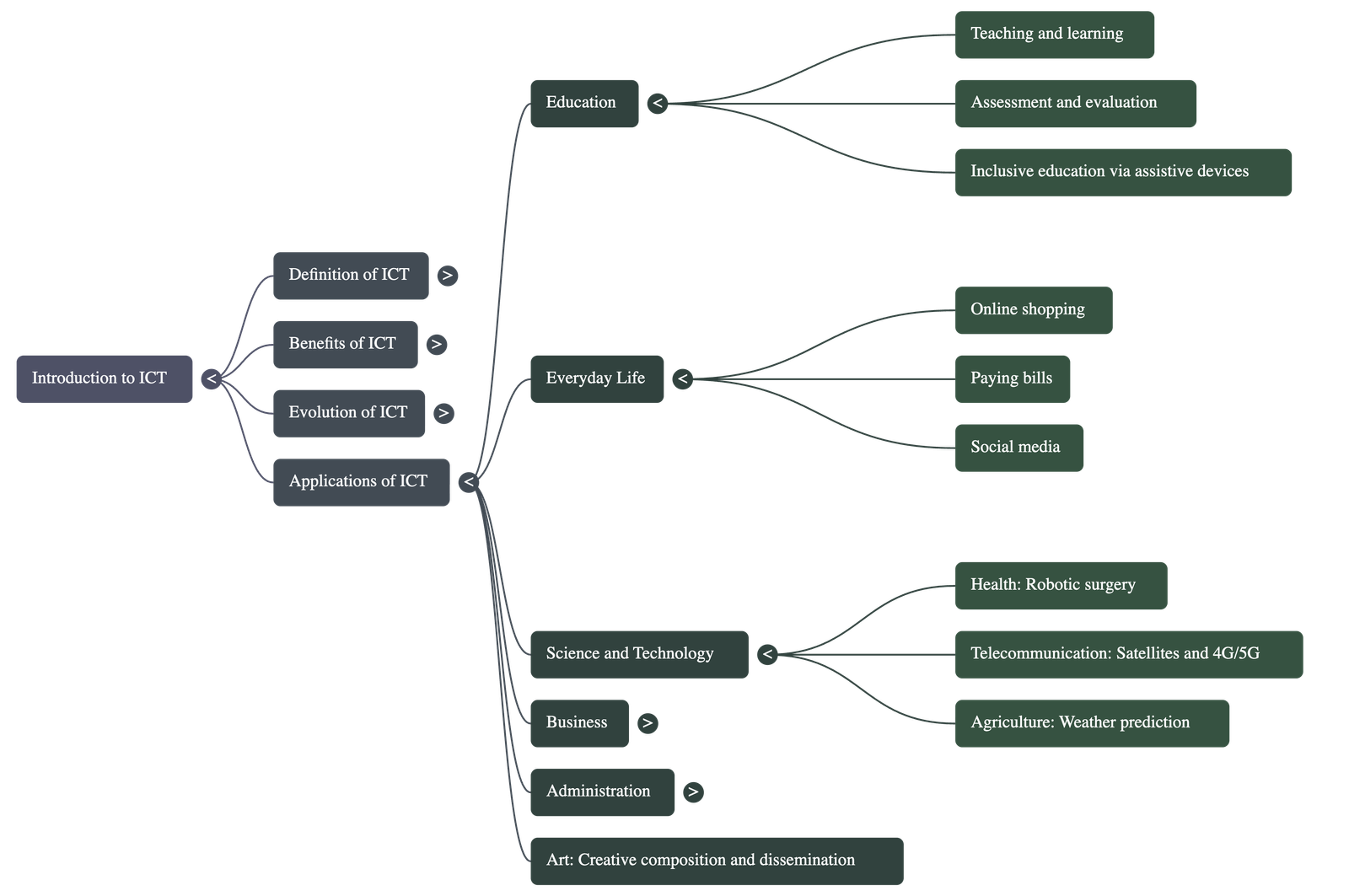
- Education: Used for school administration, interactive teaching, and inclusive education through assistive devices like talking books for students with special needs.
- Science and Health: Facilitates precise robotic surgeries, remote medical consultations, and satellite-based weather predictions for agriculture.
- Business and Transport: Enables online marketing, GPS navigation, and hassle-free flight or hotel reservations.
- Administration: Powers e-Governance, providing transparent and efficient government services to citizens while enhancing public safety through digital record-keeping.
- Art and Culture: Allows for the creative composition and wide dissemination of art forms to global audiences.
Quick Navigation:
| | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | |