Quick Navigation:
| | |
Creating Visual Communication
Introduction to Image Editing
- GIMP (GNU Image Manipulation Program): A Free and Open Source graphics editing tool used for photo editing, collage creation, and freehand drawing.
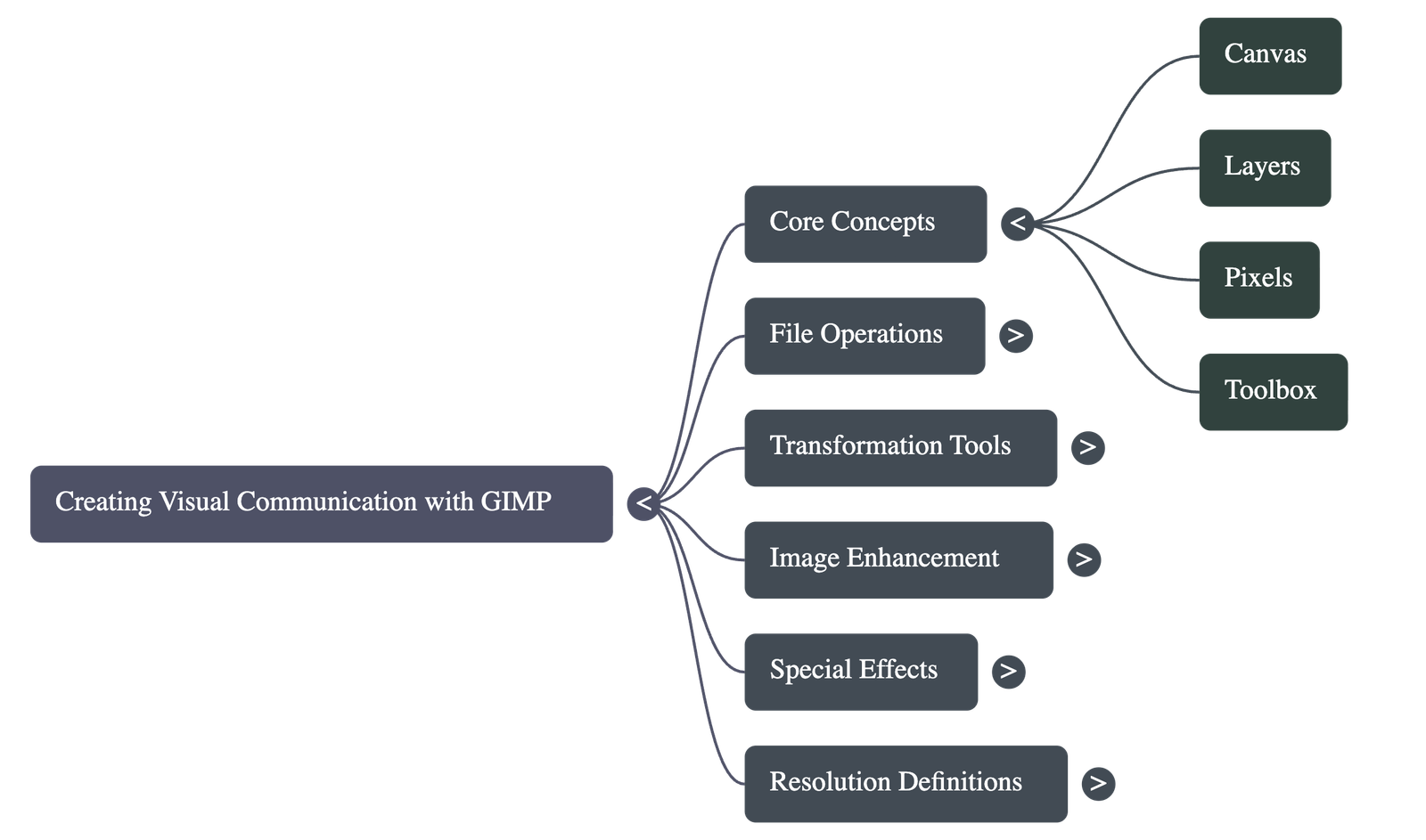
- The Canvas: This is the primary workspace where images are inserted and modified. It can contain multiple layers, each representing a separate image or element.
- Pixels: The smallest illuminated area on a screen. Image size is measured in pixels, and the density of these pixels determines the display resolution (PPI).
- The Toolbox: A dedicated area containing tools for basic tasks. Hovering over a tool displays a "tooltip" with its name, usage, and keyboard shortcut.
Basic Image Transformations
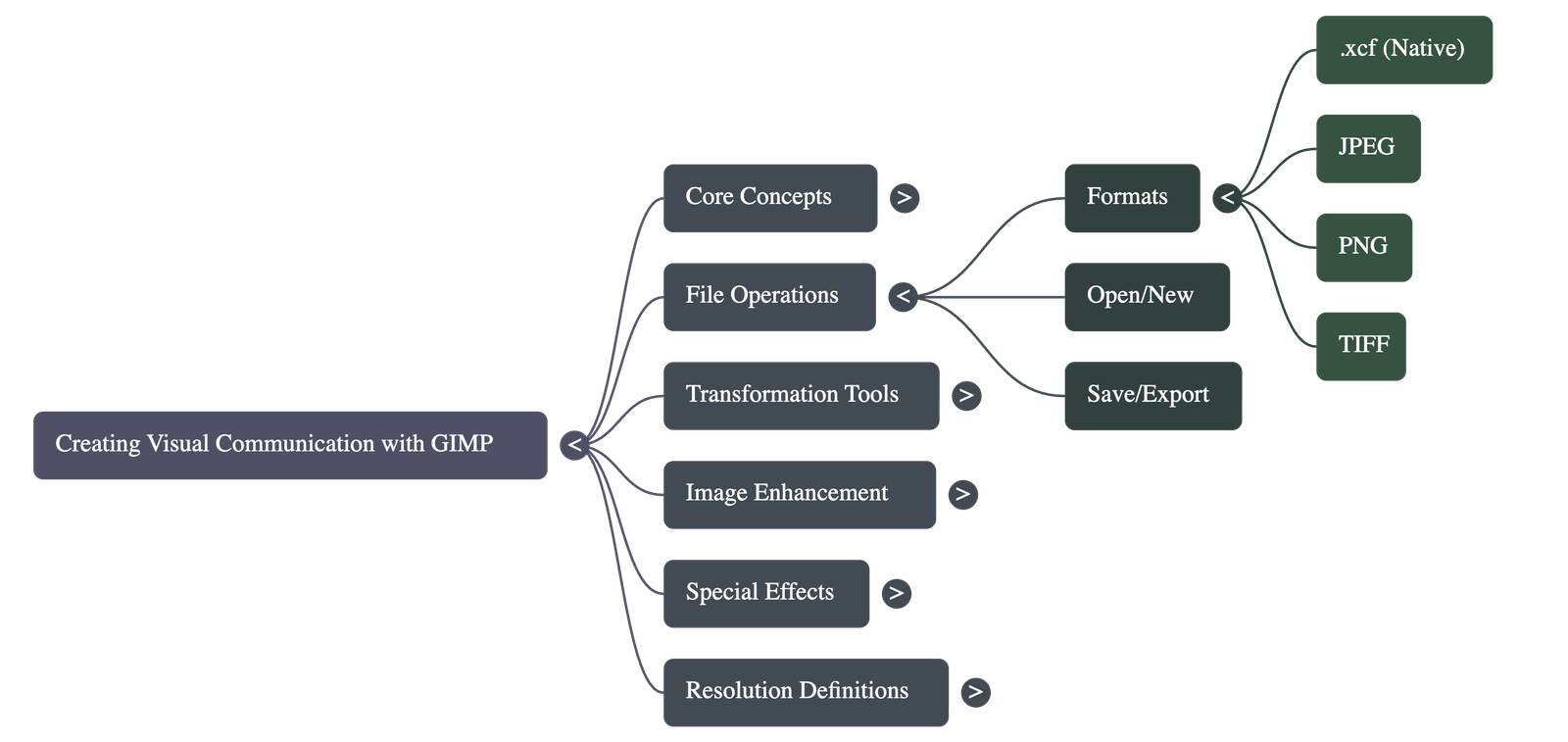
- Opening and Saving: Images are opened via the File menu. GIMP's native format is .xcf, which preserves layers and modification history.
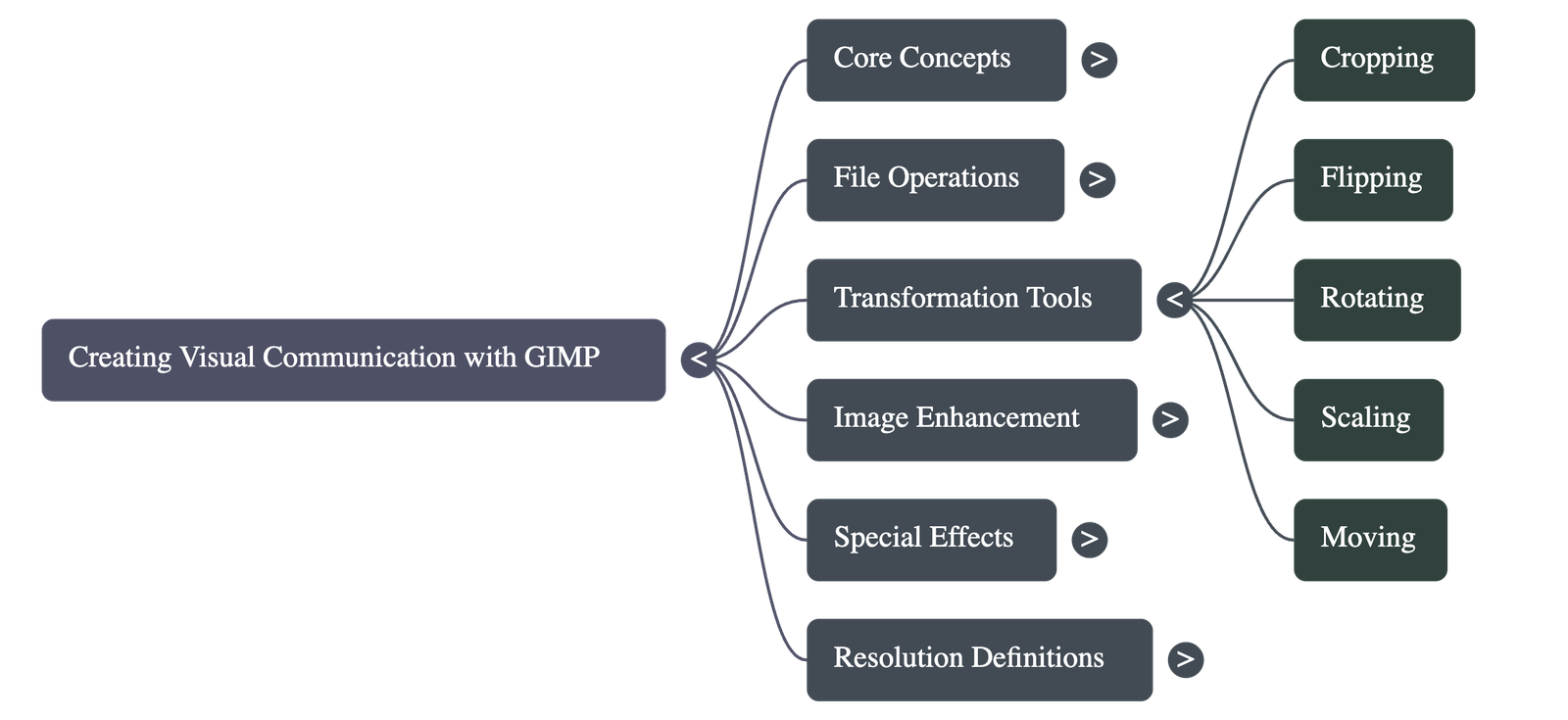
- Cropping: Used to remove unwanted areas of a picture. The Crop Tool (Shift + C) allows users to click and drag to select the desired portion of the image.
- Scaling: The process of reducing or increasing an image's size. Scaling down reduces the number of pixels, which is useful for reducing file size for emailing.
- Flipping and Rotating: Flipping creates a mirror image (Shift + F), while rotating turns the image by a specific angle to change its orientation.
- Moving: The Move Tool is used to reposition images or layers within the canvas, often to the top-left or right corners when organizing layouts.
Advanced Enhancements and Effects
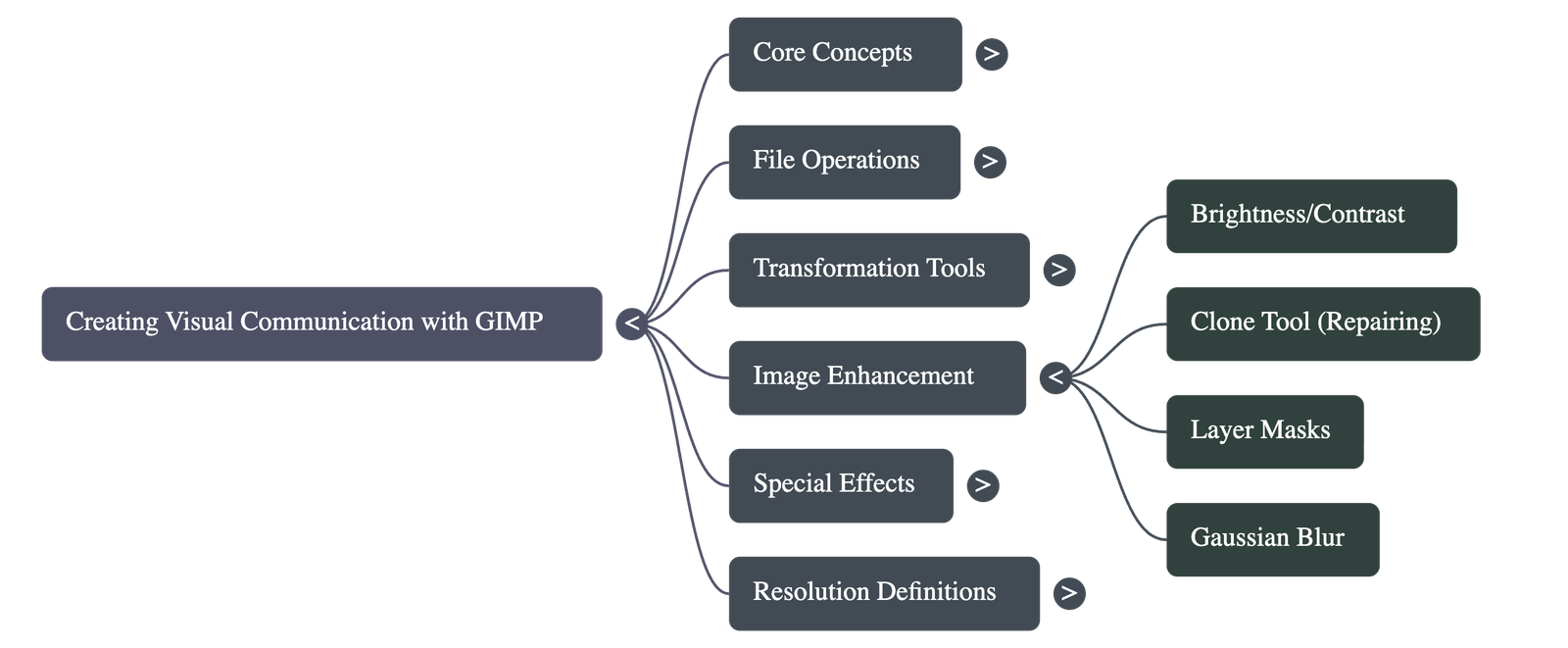
- Brightness and Contrast: Tools used to enhance dull images, making them more vibrant and visually appealing.
- Layer Management: Users can create new layers, duplicate existing ones, and adjust layer opacity to blend images. Layers can be merged down into a single layer once editing is complete.
- Creating Reflections: A complex process involving duplicating a layer, flipping it vertically, adding a white layer mask, and applying a gradient (Blend Tool) to create a realistic mirror effect.
- Text Effects: Text can be added as a new layer. Advanced styling includes applying Gaussian Blur, Plasma effects, and Bump Mapping to create a 3D-like appearance.
- The Clone Tool: Used for repairing images by "painting over" problem areas with pixel data copied from another part of the image. It is activated by holding the Ctrl key to select a source point.
Collage Creation and Exporting
- Creating a Collage: Multiple images can be combined into one canvas by opening them as separate layers, resizing them to fit a grid, and moving them into position.
- Resolution Concepts: PPI (Pixels Per Inch) refers to display resolution, while DPI (Dots Per Inch) refers to printer resolution. Higher resolution generally results in better quality.
- Exporting Files: Since .xcf files are bulky, they should be exported to common formats:
- JPEG: Good quality compressed format accepted worldwide.
- PNG: High quality, bulky format supported by all web browsers.
- TIFF: Bulky, high-quality format used by professional image processing software.
Quick Navigation:
| | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | |