Quick Navigation:
| | |
Fun with Logic
The Importance of Logical Sequencing
- • Every task requires a specific sequence of instructions to be completed successfully.
- • Missing a single step, such as forgetting to sign an account opening form, can prevent a task from being accomplished.
- • Interchanging steps or following them out of order often leads to undesired results.
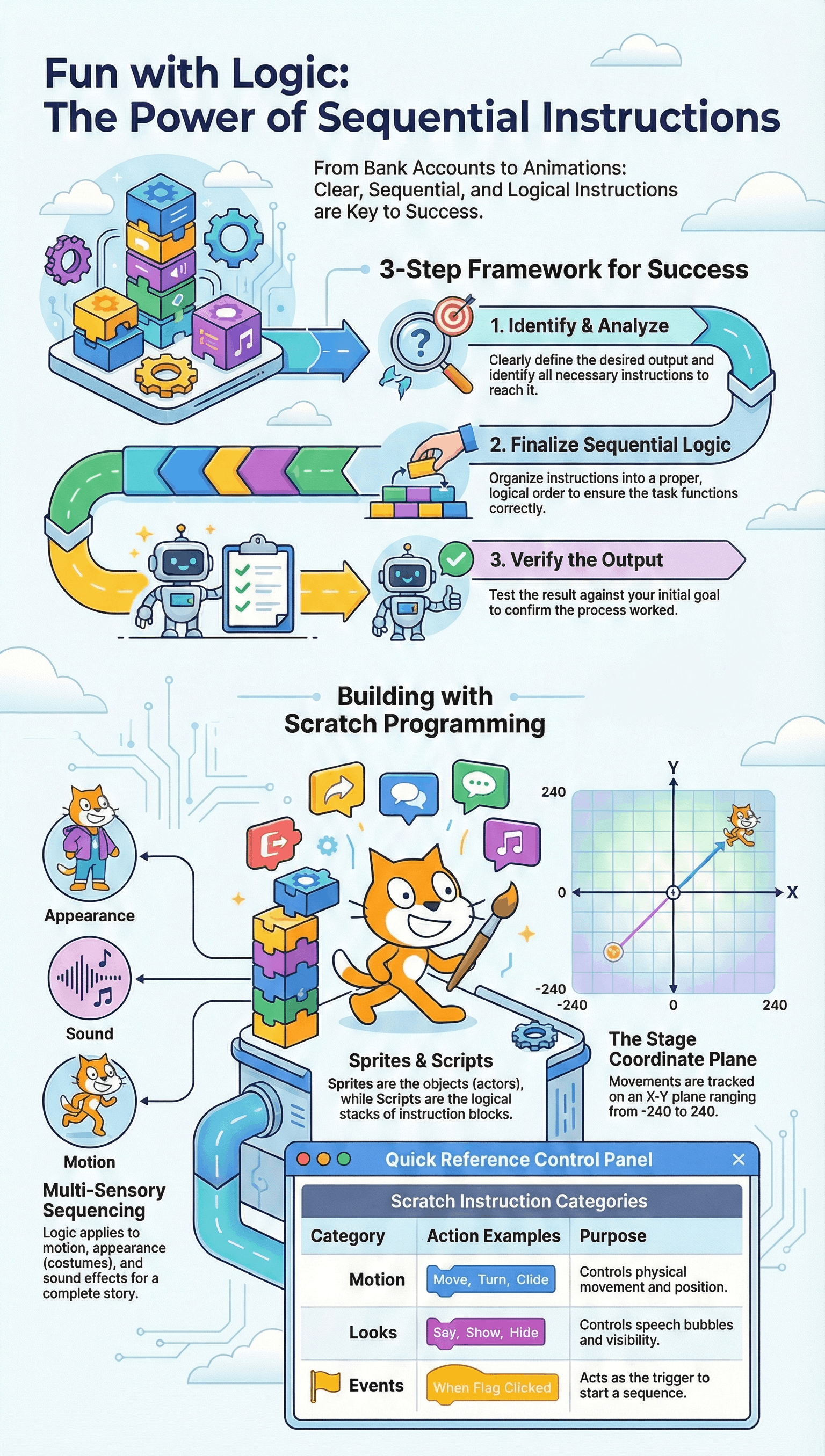
Four Steps to Complete Any Task
- Identify Output: Clearly define the specific result you want to achieve.
- Analyse: Determine the best solution and the correct sequence of instructions required.
- Finalise Instructions: Arrange the instructions in a clear, sequential, and logical order.
- Verify: Check if the produced output matches the goal identified in the first step.
Introduction to Scratch
- • Scratch is a free, open-source programming language developed by MIT in 2005.
- • It allows users to create interactive stories, games, and animations using simple drag-and-drop instruction blocks.
- • It can be used both online through a web browser and offline by downloading the software.
Key Concepts and Vocabulary
- ◆ Sprite: Any object on the Scratch stage, such as a person, animal, or text.
- ◆ Script: A set of instructions stacked together to control the actions of a sprite.
- ◆ Stage: The background area where the animation or story comes to life.
- ◆ Costume: Different visual forms or poses that a sprite can adopt.
- ◆ Backdrop: The background image displayed on the stage.
The X-Y Coordinate System
- • The Scratch stage functions as a coordinate plane to specify positions.
- • The center of the stage is the origin point with coordinates (0,0).
- • X-coordinates range from -240 to 240, and Y-coordinates range from -180 to 180.
Core Instruction Categories
| Category | Function |
|---|---|
| Motion | Controls movement (moving steps, turning, gliding to coordinates). |
| Looks | Manages visibility, speech bubbles, and costume changes. |
| Sound | Plays audio clips and controls sound playback. |
| Events | Triggers the start of a script (e.g., "When Green Flag Clicked"). |
| Control | Manages timing, such as making a sprite wait for a few seconds. |
Building an Animation
- • Users start by choosing backdrops and sprites from the built-in library or creating their own.
- • Scripts are built by dragging blocks into the script area and snapping them together in a logical sequence.
- • Animations can be tested by clicking the Green Flag and viewed in full-screen mode to verify the output.
Quick Navigation:
| | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | |