Quick Navigation:
| | |
Getting Connected Internet
Introduction to the Internet
- The Internet is a global network used to search for information, gather resources, and enhance knowledge.
- It has largely replaced traditional libraries as the primary source for multimedia resources like images, videos, and text.
- Common uses include sharing videos via messenger apps, blogging, making video calls (e.g., Skype), and joining online courses.
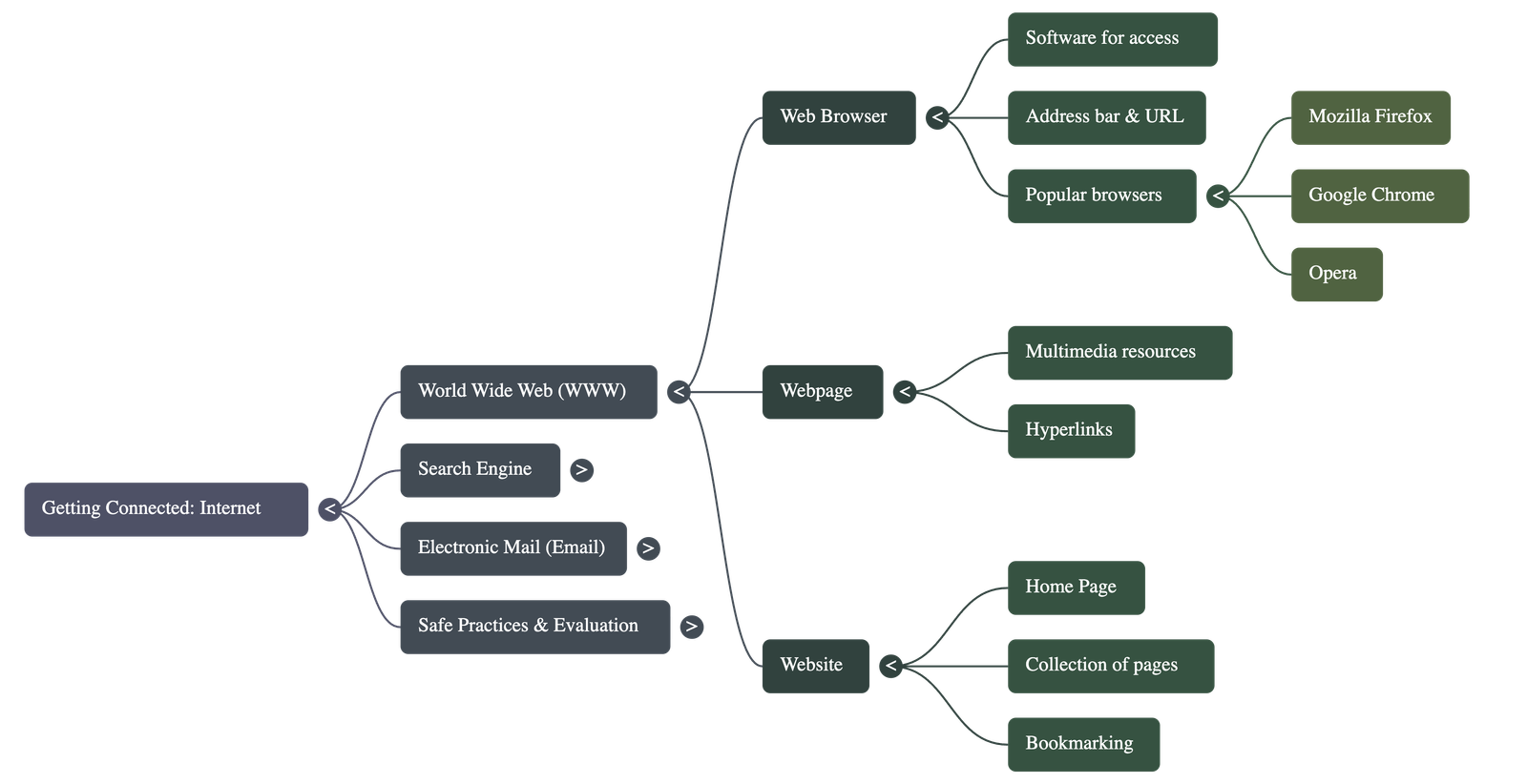
Web Browsers and Navigation
- A Web Browser is the software required to access information on the World Wide Web (WWW).
- Popular examples include Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, and Opera.
- The Address Bar allows users to type the specific URL (Uniform Resource Locator) of a webpage to access it directly.
- A Website is a collection of webpages, and the Home Page is the first page encountered when opening a website.
- Hyperlinks are clickable text or images that connect to other webpages; the mouse cursor typically changes to a hand symbol when hovering over them.
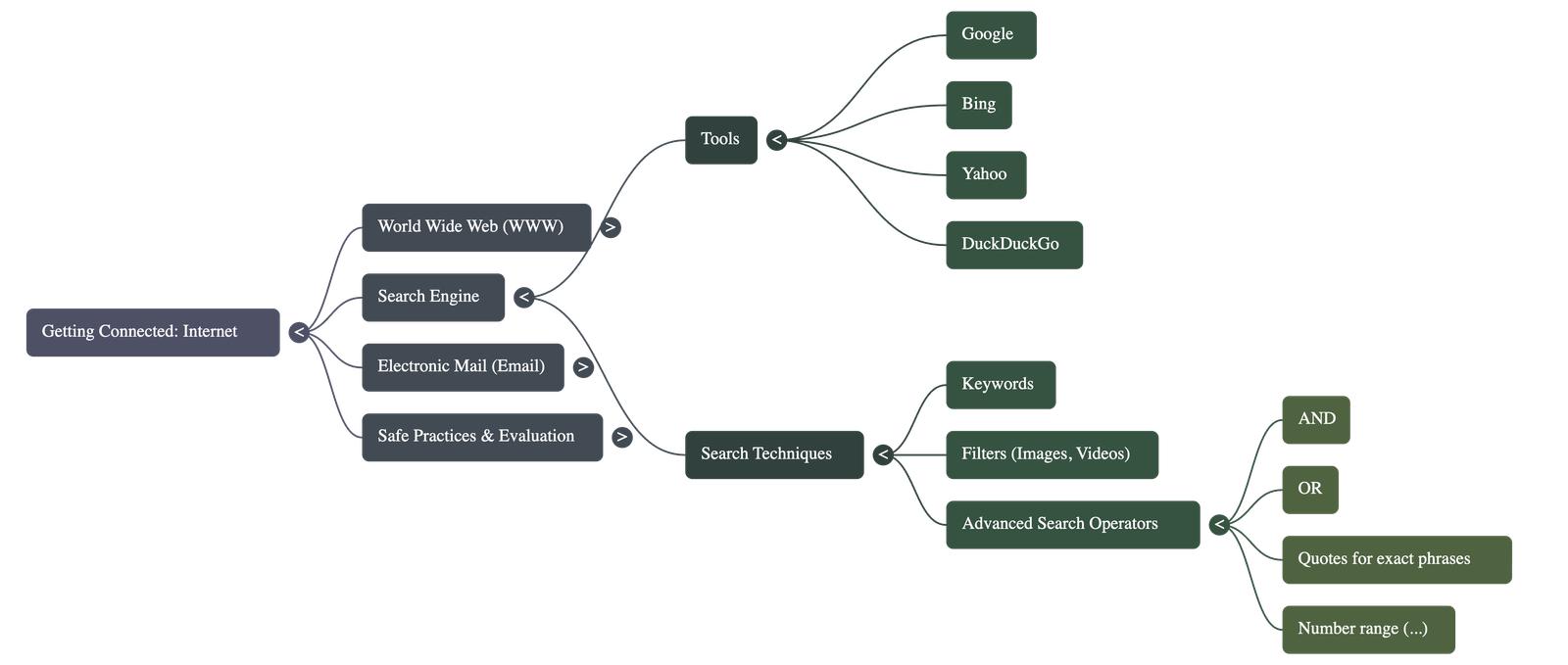
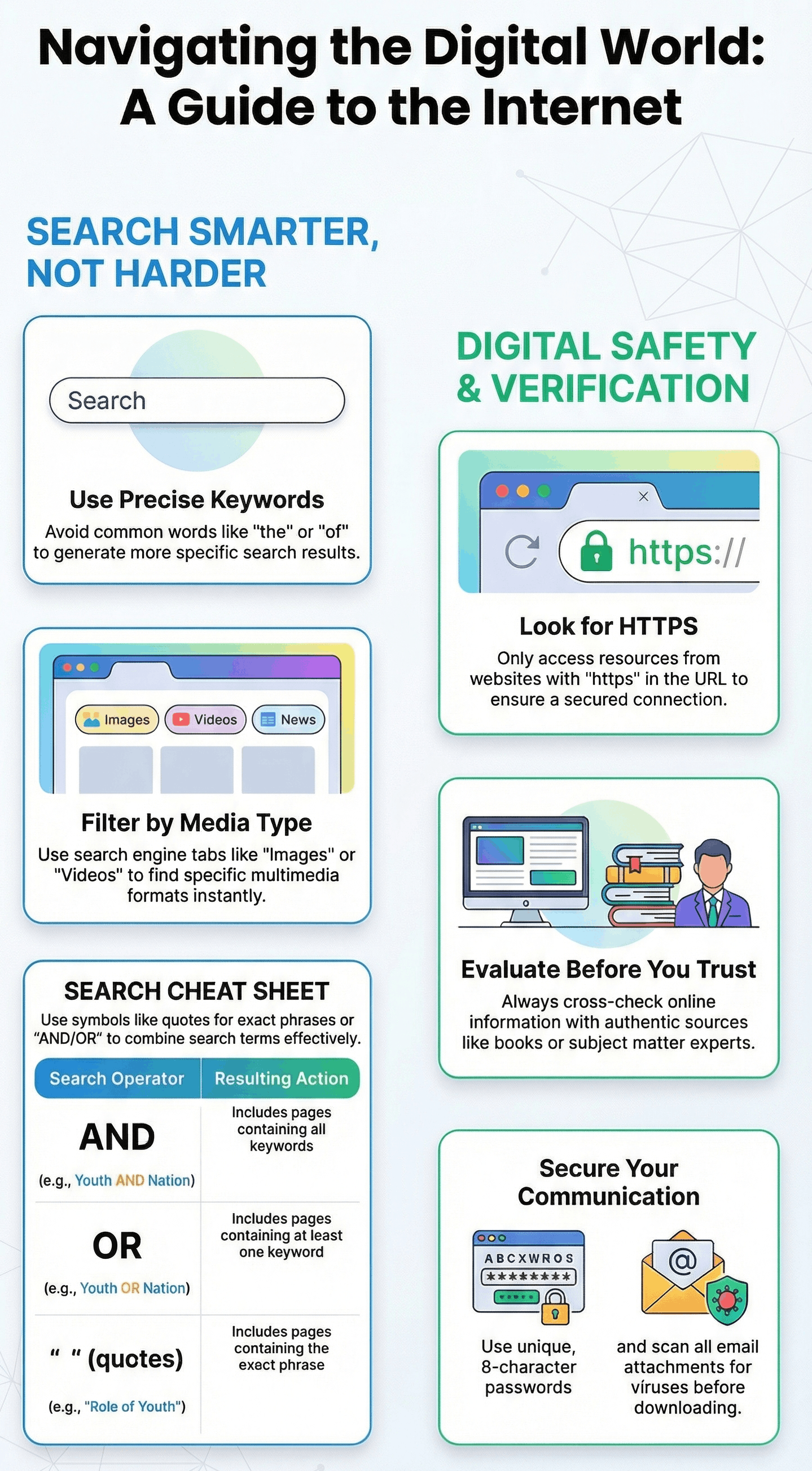
Search Engines and Effective Searching
- Search Engines (like Google, Bing, Yahoo) are tools used to find information when the specific URL is unknown.
- Users enter Keywords into a search box to find relevant resources.
- Search results can be filtered by type, such as "All," "Images," or "Videos," to narrow down the information.
- Advanced Search Operators can be used to refine results:
- AND: Includes pages containing all specified keywords.
- OR: Includes pages containing at least one of the keywords.
- " " (Quotes): Finds the exact phrase within the quotes.
- ... (Ellipsis): Finds results within a specific number range (e.g., years).
Managing and Evaluating Resources
- Bookmarking: Saving the URL of a webpage for future reference using the "star" icon in the browser.
- Plug-ins: Additional software that enables the browser to display specific types of multimedia content.
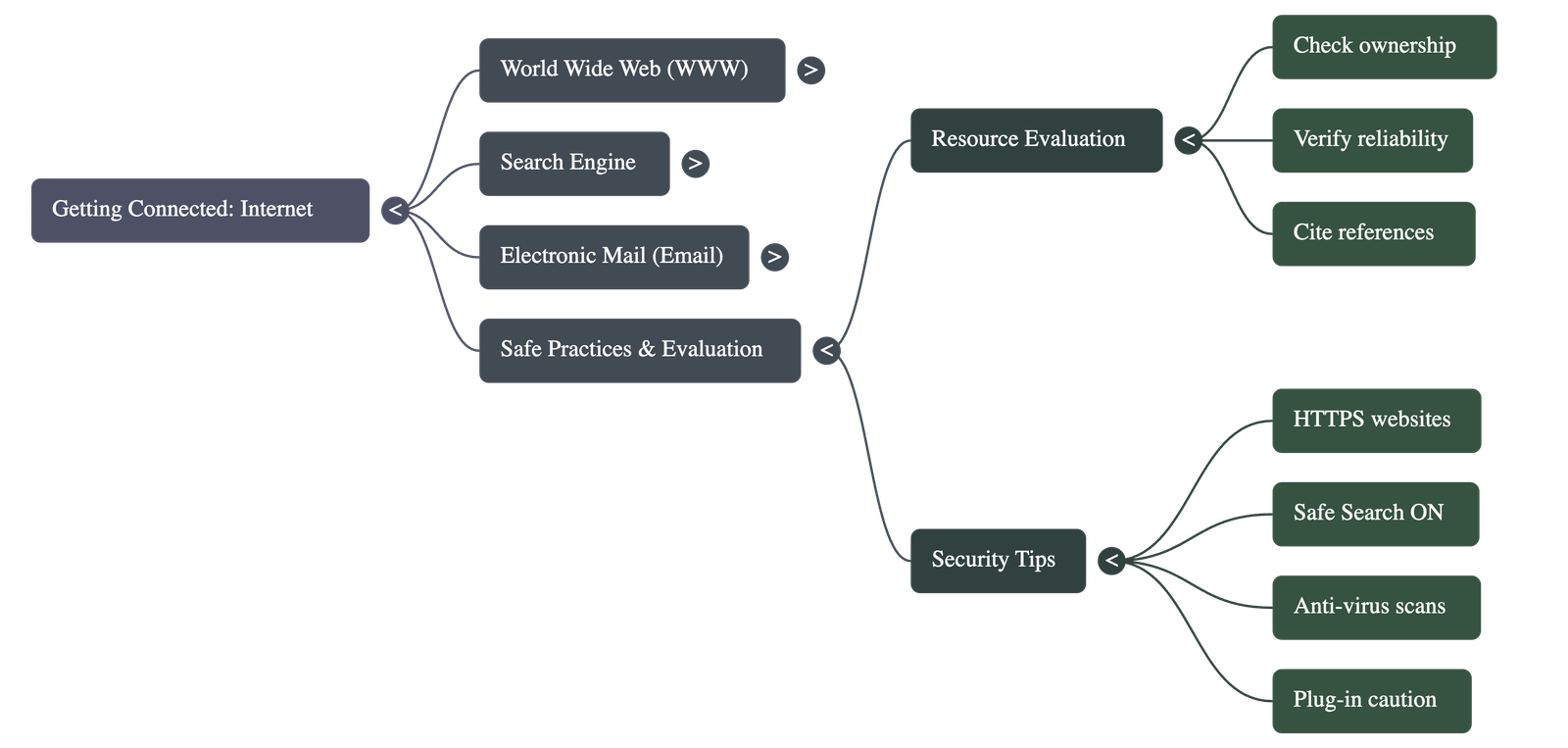
- Evaluation: Not all information on the web is accurate. Users must check the website’s ownership, reliability, purpose (commercial vs. educational), and cross-check facts with authentic sources.
- Citation: Always give credit to the original owner of a resource when using it.
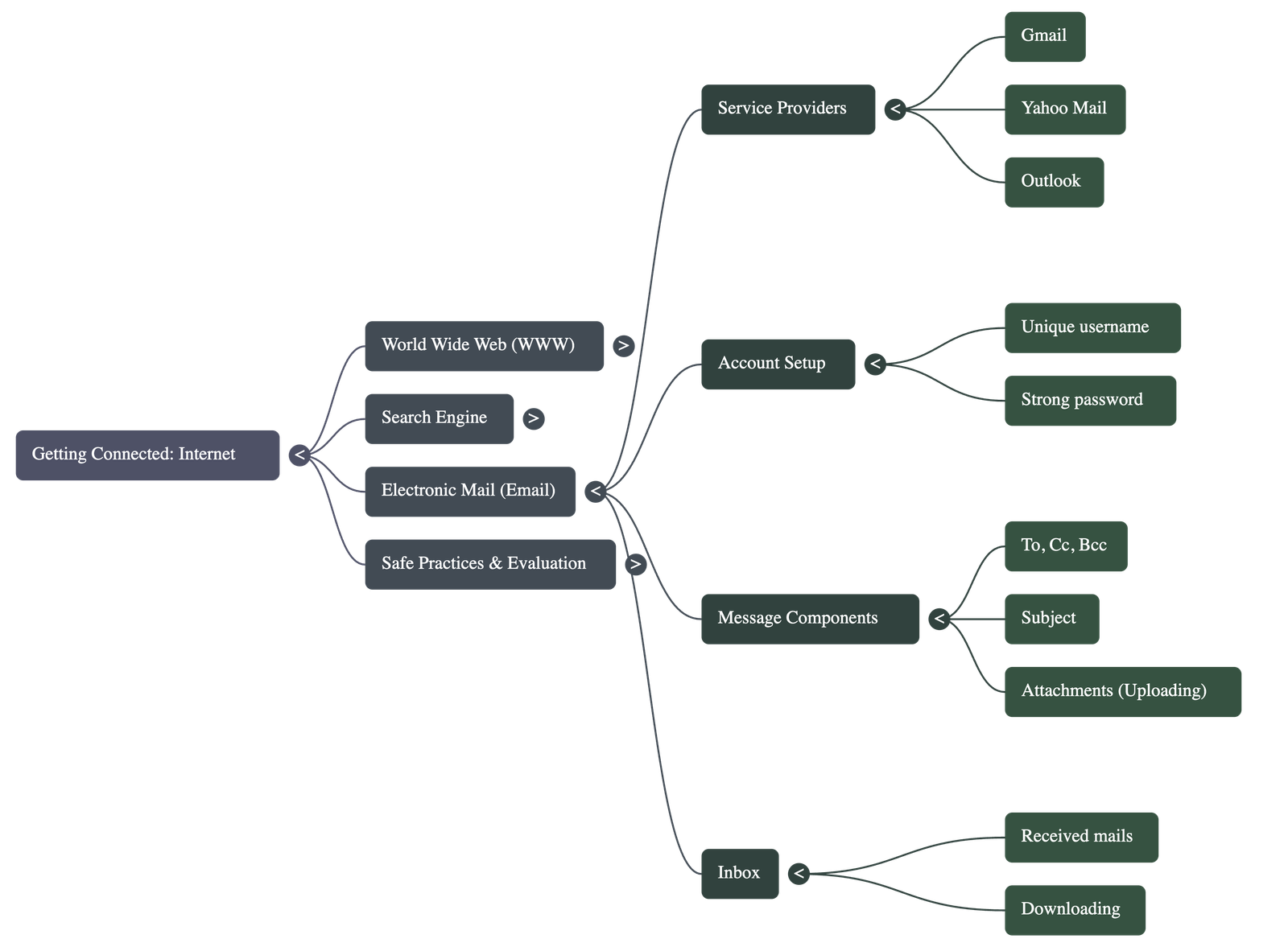
Electronic Mail (Email)
- Email allows users to communicate and share files (attachments) globally via internet-enabled devices.
- Common service providers include Gmail, Yahoo Mail, and Outlook.
- Key Components of an Email:
- To: The recipient's email address.
- Cc (Carbon Copy): Sends a copy to others; all recipients can see these addresses.
- Bcc (Blind Carbon Copy): Sends a copy privately; other recipients cannot see these addresses.
- Subject: A brief description of the email's content.
- Attachments: Files (images, documents) sent along with the message.
- Uploading refers to attaching a document to an email, while Downloading refers to saving a file from the internet to a local computer.
Internet Safety and Security
- Passwords: Should be strong, using a combination of uppercase/lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols, and changed frequently.
- Secure Websites: Look for "https" in the URL, indicating a secure connection.
- Safe Search: Ensure browser safety settings are turned ON.
- Malware and Viruses: Harmful programs that can destroy data or affect performance. Users should use anti-virus software (e.g., Norton, Kaspersky) and scan all downloads.
- Responsible Behavior: Users should exercise caution and set an example for others in the "cyber world."
Quick Navigation:
| | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | |