Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
This is a point-wise summary of Chapter 8, "Diseases and First Aid":
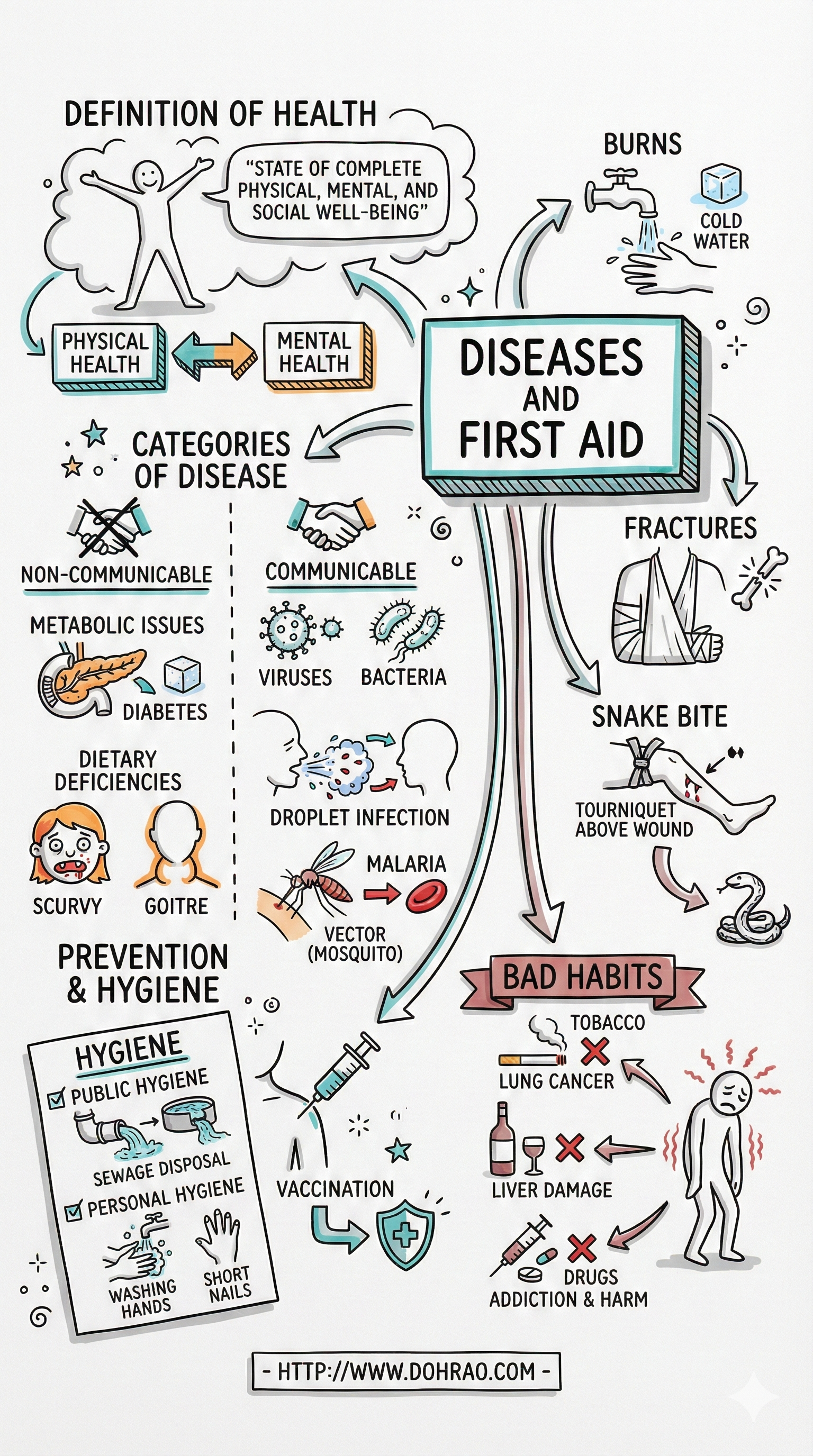
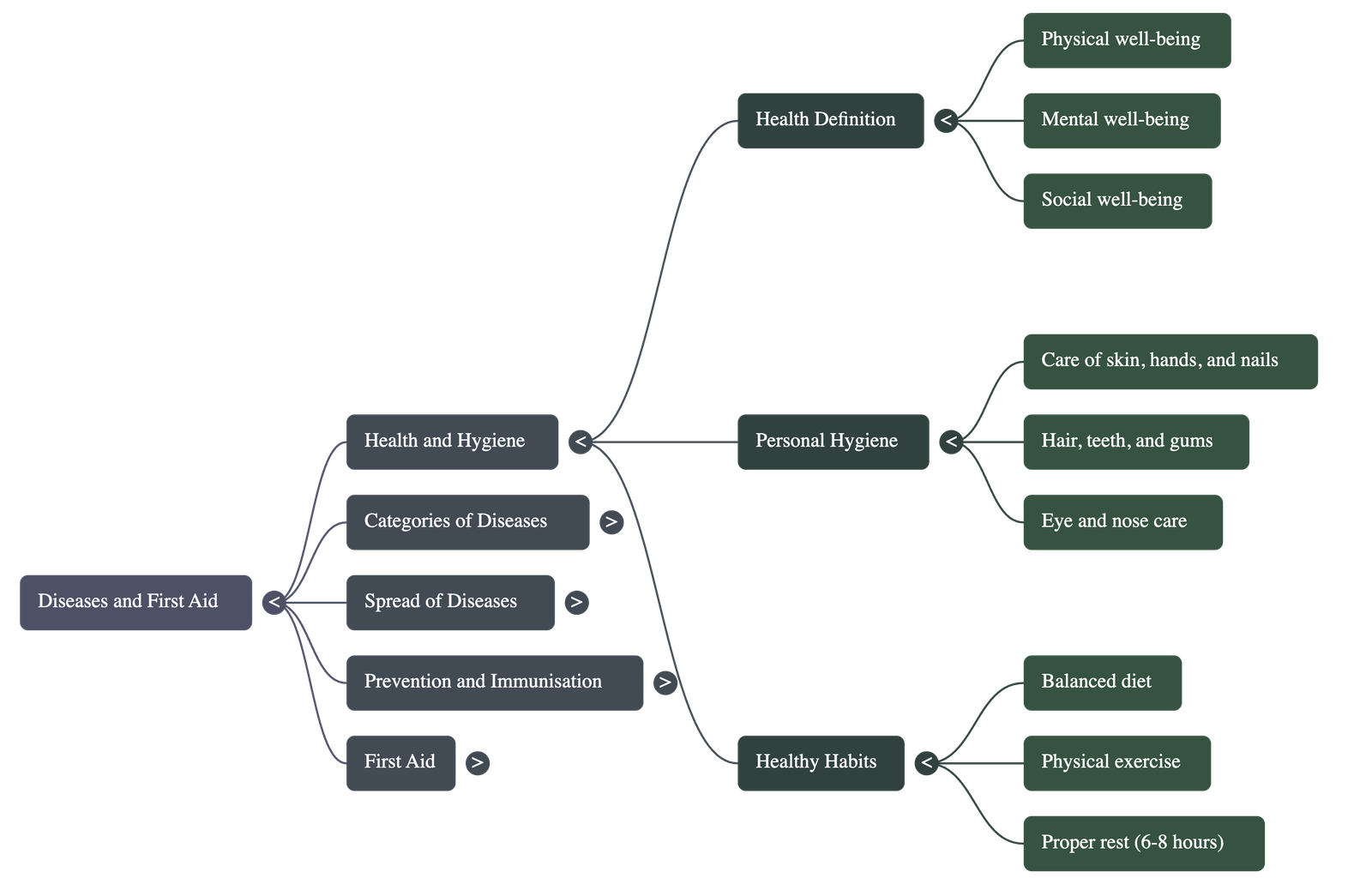
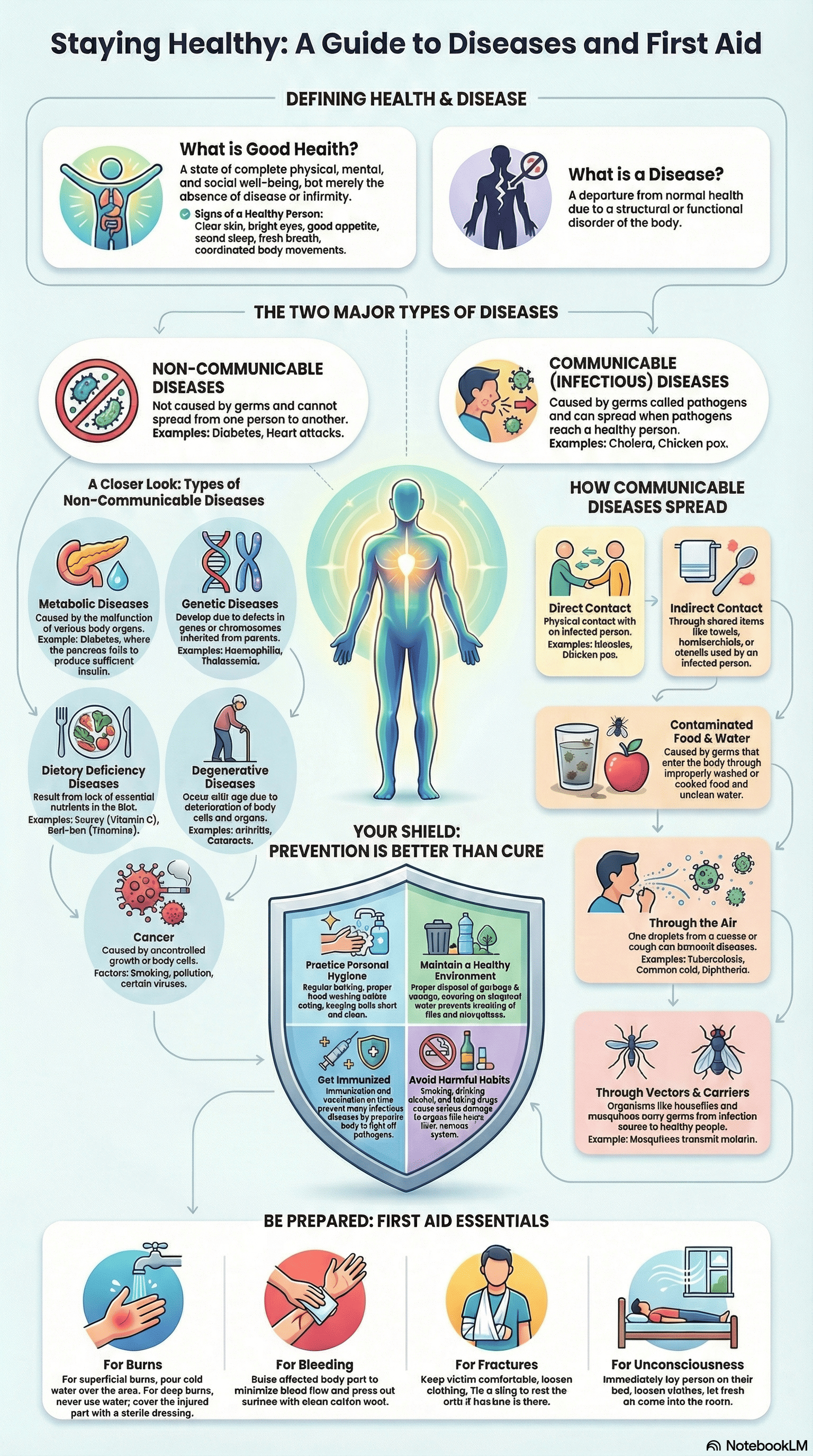
- Understanding Health and Disease: Health is defined as a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being, while disease is a departure from normal health through structural or functional disorders of the body. A healthy person typically exhibits features like clear skin, a balanced body weight, good appetite, and coordinated movements.
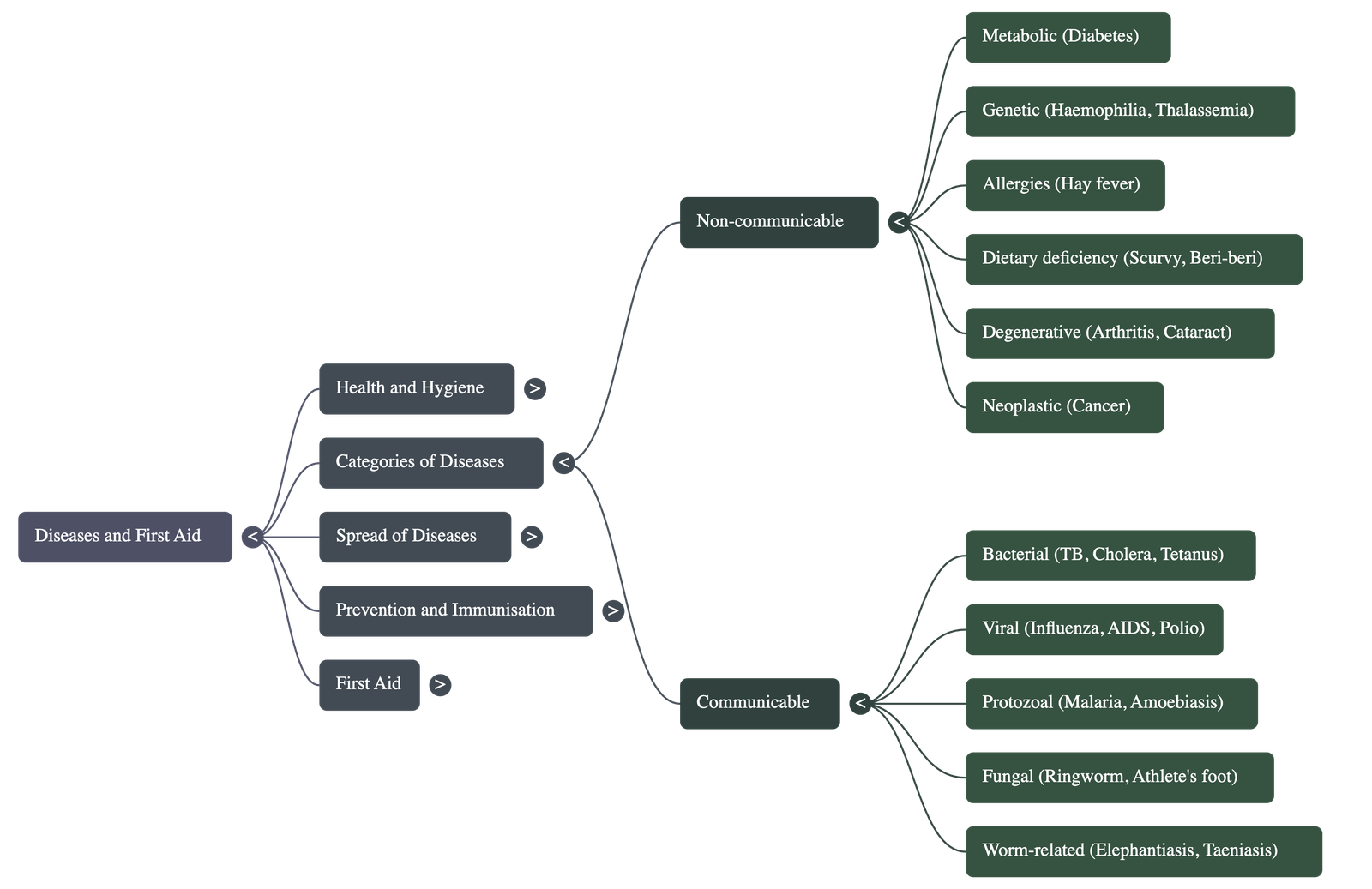
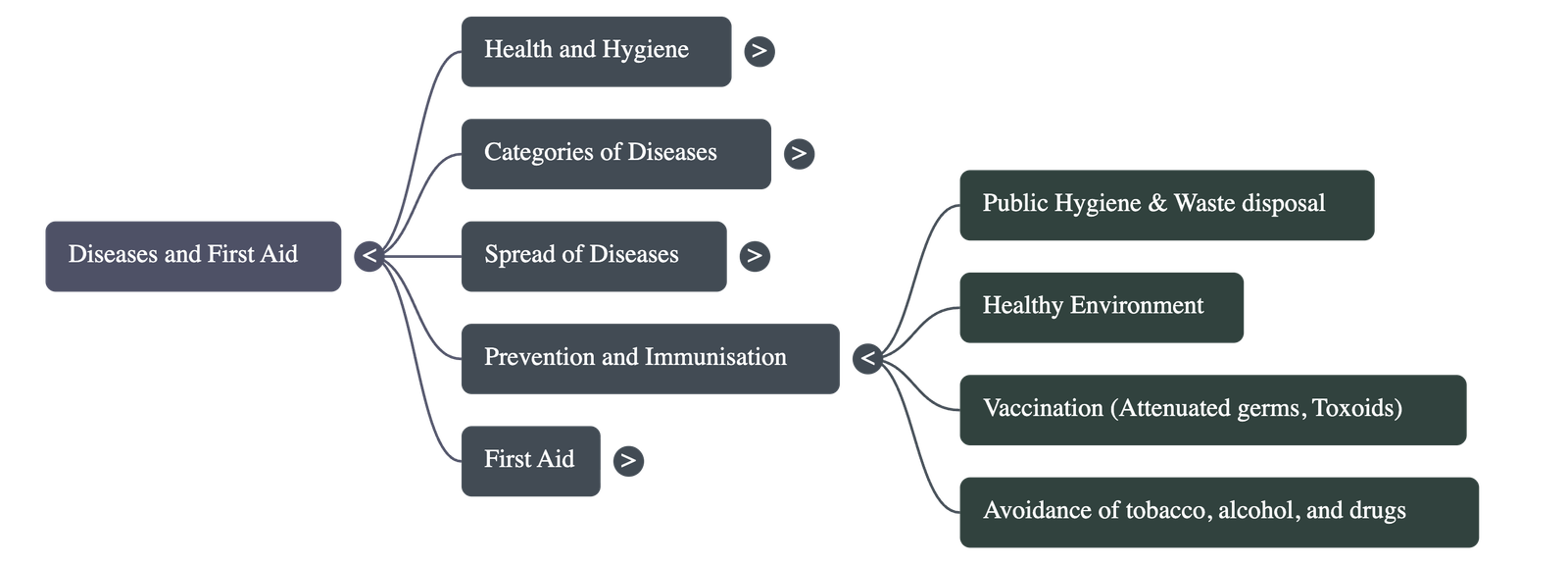
- Categories of Diseases: Diseases are broadly classified into two types: Non-communicable (not caused by germs and non-transmissible) and Communicable (caused by pathogens and spread through agencies like water, air, or insects).
- Types of Non-communicable Diseases:
- Metabolic: Resulting from organ malfunction, such as Diabetes (pancreas failure) or Uraemia (kidney failure).
- Genetic/Congenital: Defects inherited from parents, such as Haemophilia or Thalassemia.
- Allergies: Unpredictable reactions to substances like dust, pollen, or certain medicines.
- Deficiency: Caused by a lack of nutrients, such as Scurvy (Vitamin C) or Goitre (Iodine).
- Neoplastic: Uncontrolled growth of cells leading to Cancer.
- Degenerative: Occurring with age, such as Arthritis or Cataracts.
- Pathogens and Communicable Diseases: These are caused by various organisms, including bacteria (Tuberculosis, Tetanus), fungi (Ringworm), protozoa (Malaria), and worms (Elephantiasis, Taeniasis).
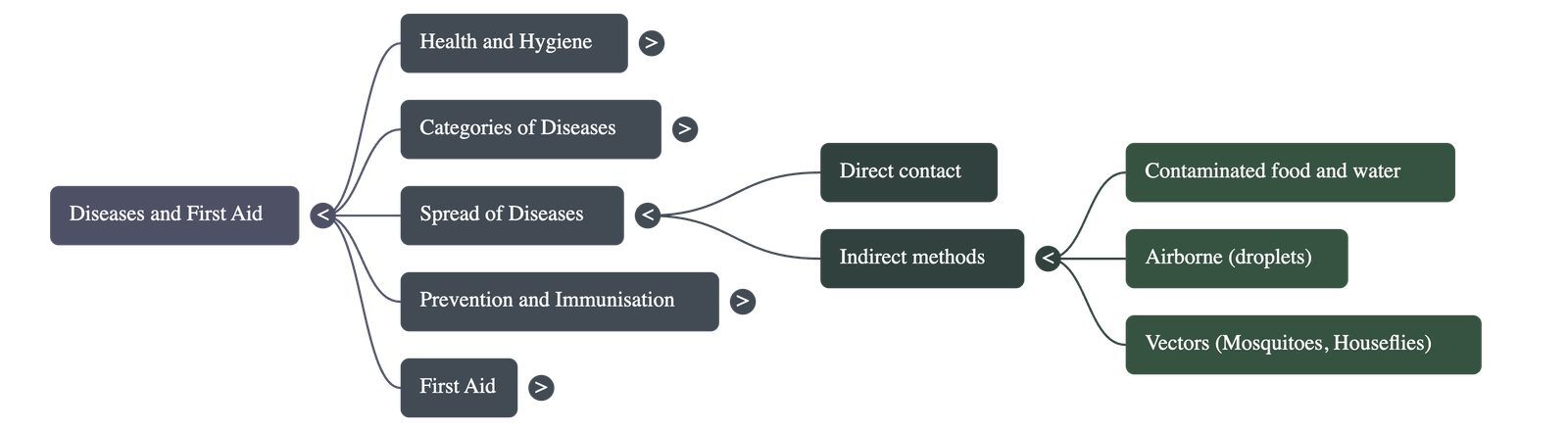
- Transmission of Diseases: Diseases spread through direct contact or indirect methods. Indirect methods include contaminated food and water, air (droplet infection), and vectors—organisms like houseflies and mosquitoes that carry germs without being infected themselves.
- Preventive Measures:
- Hygiene: Maintaining personal hygiene (cleaning skin, hair, teeth) and public hygiene (proper disposal of waste and sewage) is essential.
- Environment: Keeping surroundings clean and preventing water stagnation helps stop the breeding of vectors.
- Immunization: Vaccination provides an artificial way to achieve protection from infections by inducing antibody formation.
- Healthy Habits and Lifestyle: To maintain health, individuals should exercise regularly, get 6–8 hours of sleep, and avoid harmful substances like tobacco, alcohol, and drugs, which can lead to organ damage and addiction.
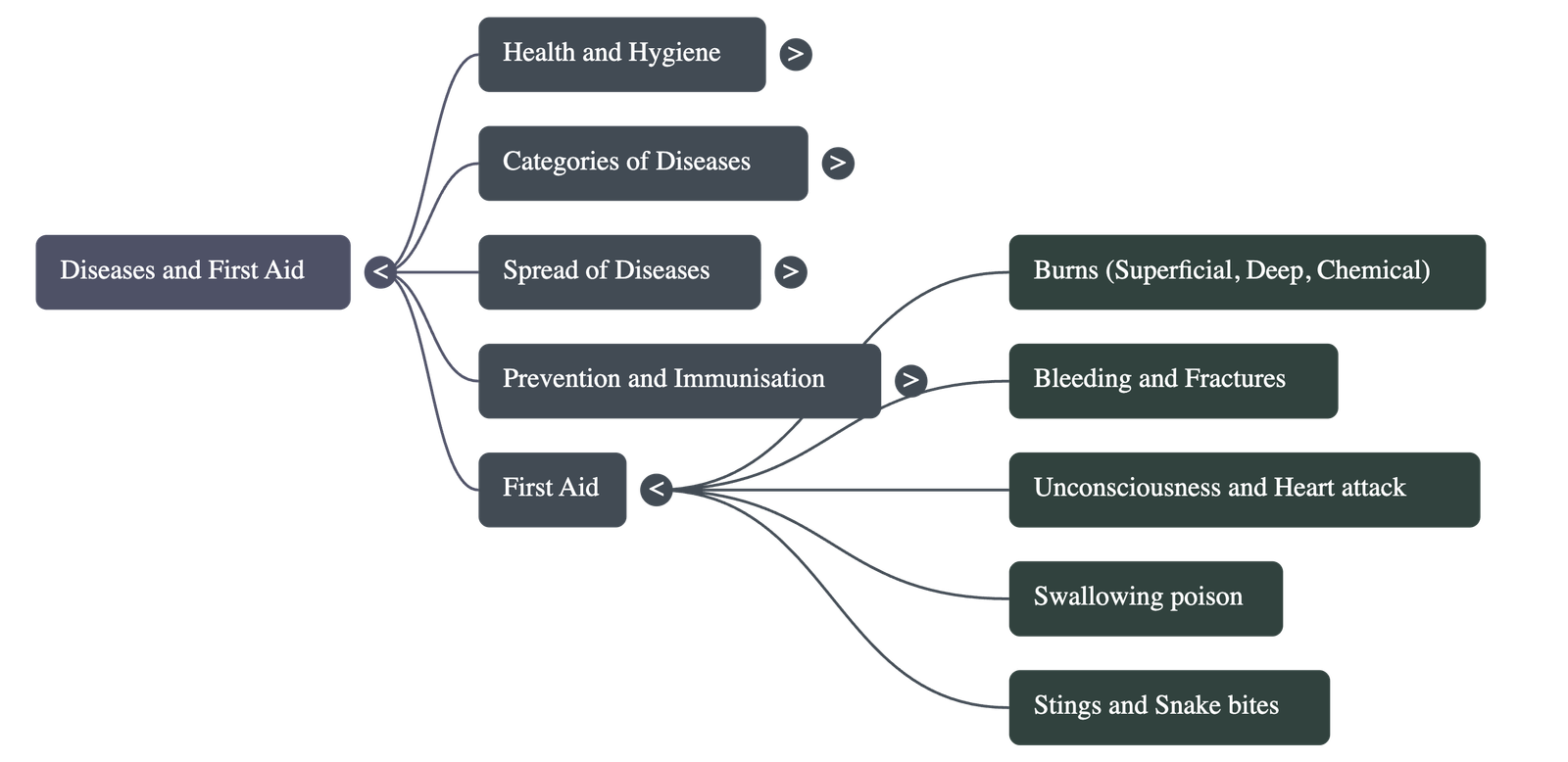
- First Aid: This is the immediate care given to a patient during an emergency before a doctor arrives. The sources detail specific procedures for various situations:
- Burns: Treatment depends on the degree (superficial, deep, or chemical) and often involves cold water and sterile dressings.
- Bleeding: Raising the affected part and applying pressure with clean cotton.
- Other Emergencies: Specific protocols are provided for fractures (using slings), eye injuries (gentle washing), unconsciousness, heart attacks, and swallowing poison.
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |