Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
This is a point-wise summary of Chapter 6: The Circulatory System:
1. Overview of the Circulatory System and Body Fluids
- The human circulatory system is a closed vascular system, meaning blood always circulates through blood vessels.
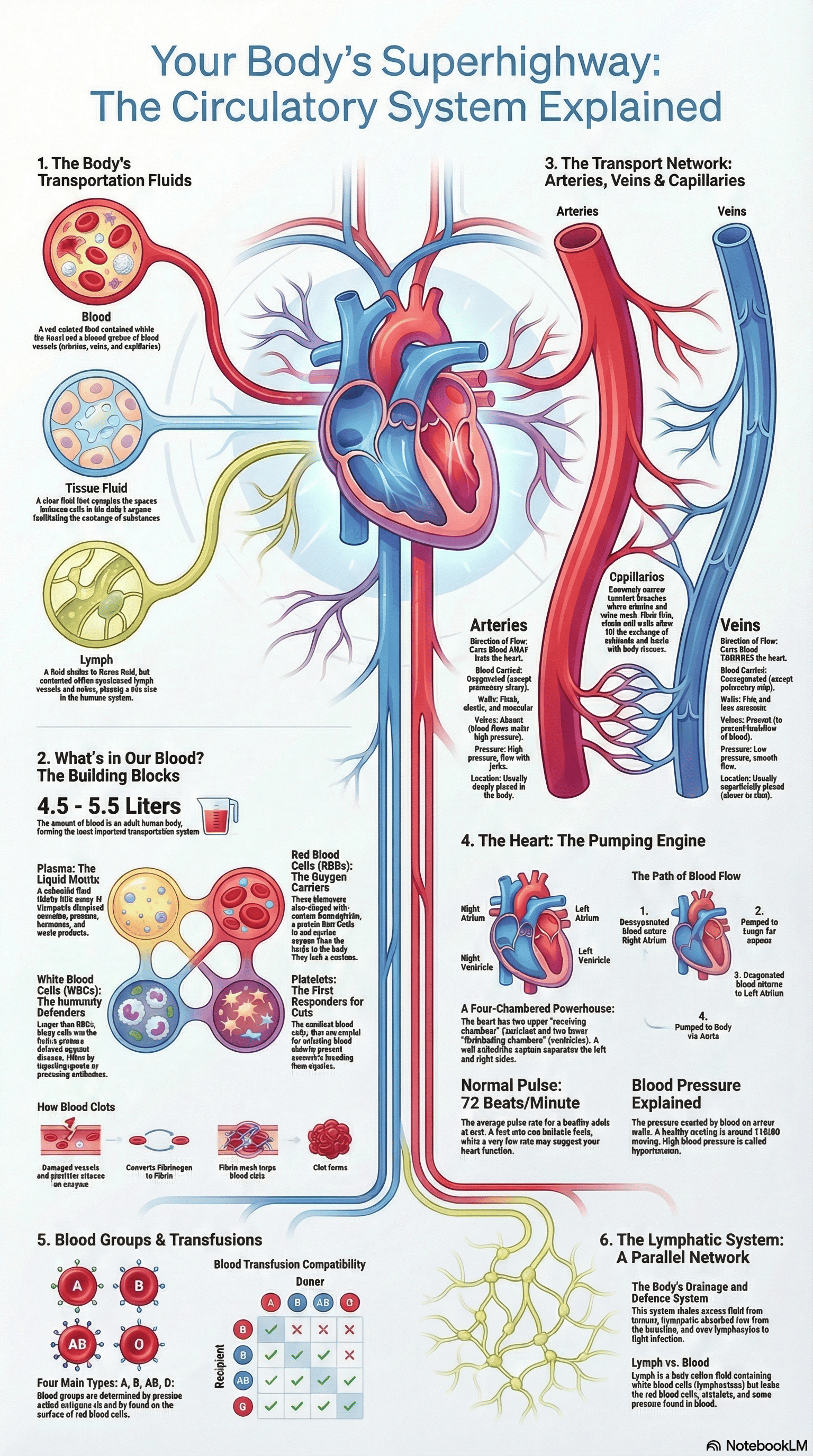
- There are three principal fluids in the body: blood (in the heart and vessels), tissue fluid (between cells), and lymph (within lymph vessels and organs).
- Transportation of substances is carried out by both the blood and the lymph.
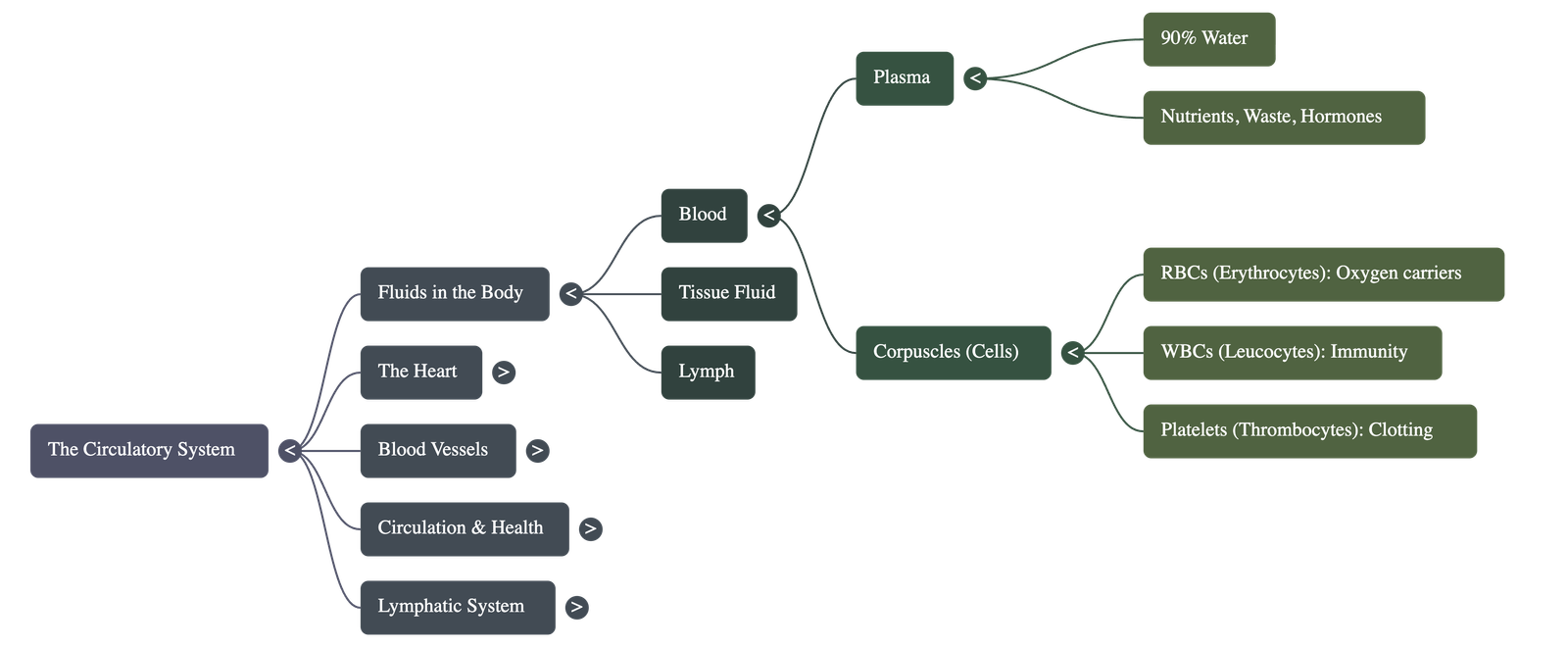
2. Components of Blood
- Blood consists of a liquid part called plasma and a cellular part called corpuscles.
- Plasma: A yellowish fluid made of about 90% water and 10% dissolved nutrients, proteins, waste, and hormones.
- Red Blood Cells (RBCs/Erythrocytes): Disc-shaped cells that lack a nucleus when mature; they contain haemoglobin, which acts as an oxygen carrier.
- White Blood Cells (WBCs/Leucocytes): Larger than RBCs, these cells provide immunity by surrounding and ingesting germs or producing antibodies.
- Platelets (Thrombocytes): The smallest cells, which are essential for blood clotting to prevent excessive blood loss and germ entry.
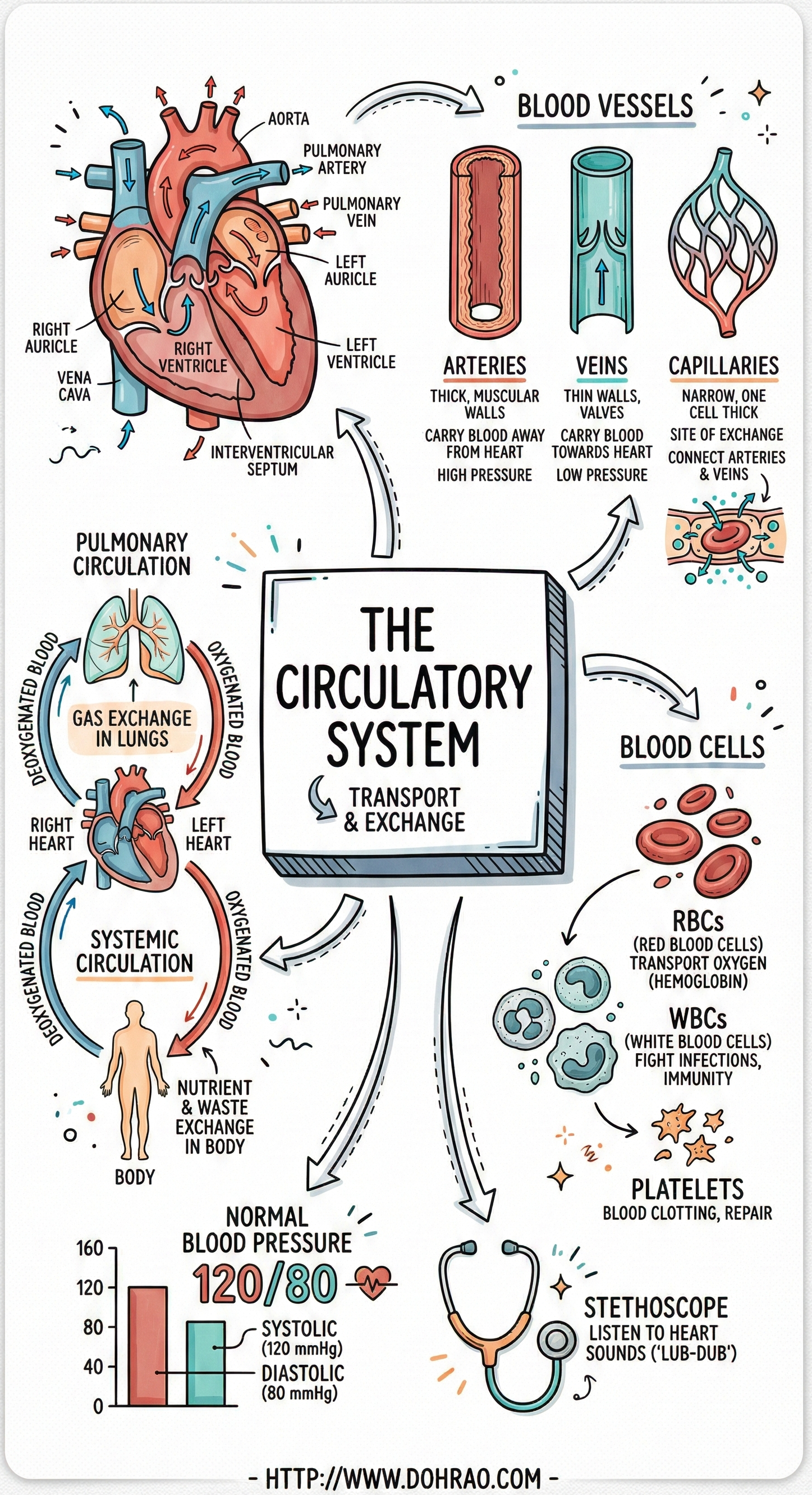
3. Blood Vessels
- Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart; they have thick, elastic walls and lack valves.
- Veins: Take blood toward the heart; they have thin walls and contain valves to prevent the backflow of blood.
- Capillaries: Narrow terminal branches that allow the exchange of nutrients, gases, and wastes between blood and body fluids.
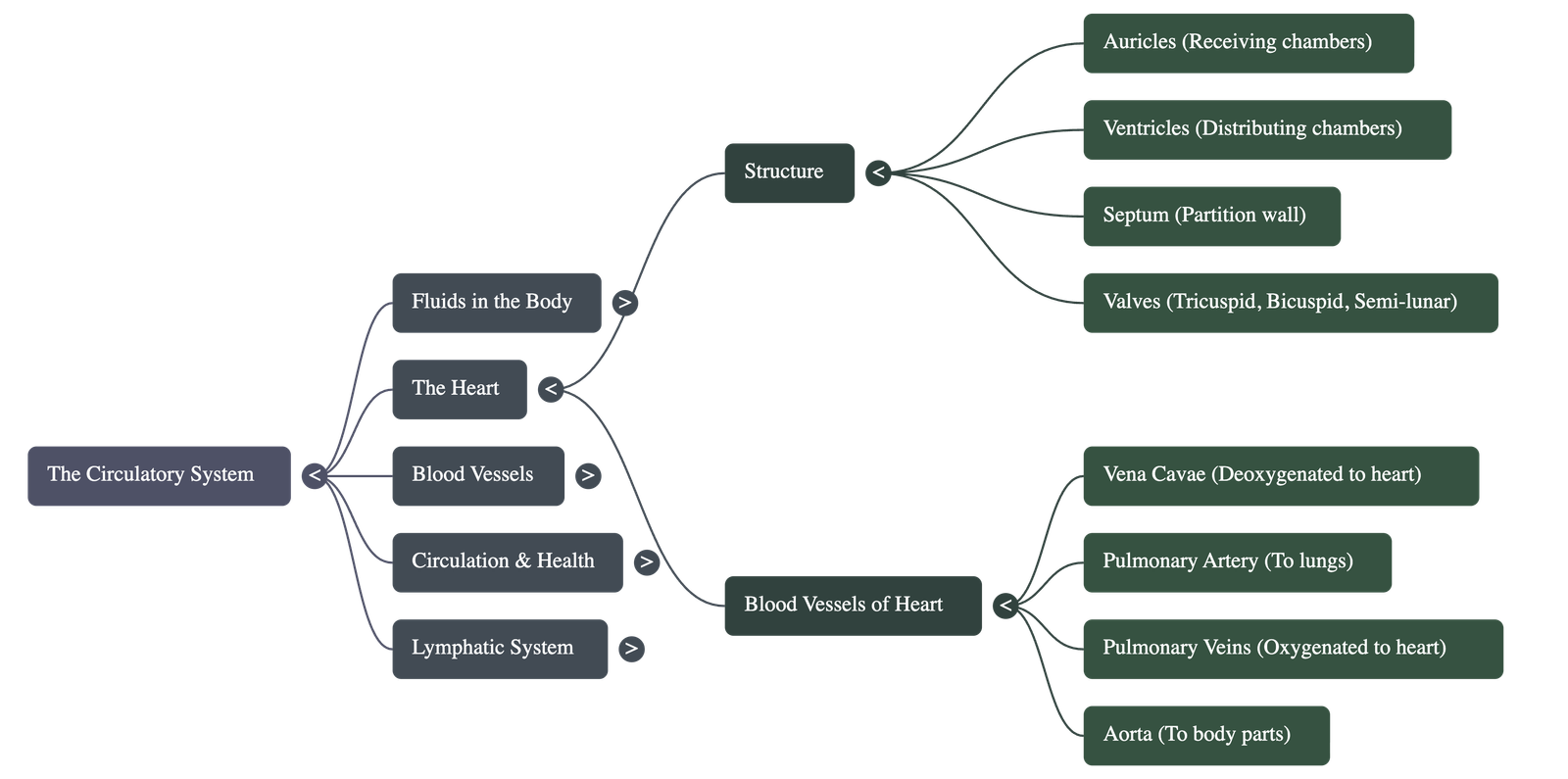
4. Structure and Function of the Heart
- The heart is a pumping organ made of cardiac muscles and is protected by a double membrane containing pericardial fluid.
- It has four chambers: two upper auricles (receiving chambers) and two lower ventricles (distributing chambers).
- A septum prevents the mixing of oxygenated (left side) and deoxygenated (right side) blood.
- Valves (Tricuspid, Bicuspid, and Semi-lunar) ensure blood flows in only one direction.
5. Blood Circulation and Heart Health
- Deoxygenated blood enters the right auricle via the vena cava, while oxygenated blood from the lungs enters the left auricle via pulmonary veins.
- The heartbeat (lub-dub) is produced by the closing of heart valves during contraction.
- Pulse: A throbbing felt in arteries, averaging 72 beats per minute in a normal adult.
- Blood Pressure: Measured with a sphygmomanometer; high blood pressure is called hypertension, while low blood pressure is hypotension.
- Cardiac Arrest: Occurs when the heart suddenly stops pumping; it is different from a heart attack, which is a sudden interruption of blood supply to the heart muscle.
6. Blood Groups and Donation
- Blood groups (A, B, AB, and O) are determined by antigens on the surface of RBCs.
- AB group is the universal recipient, and O group is the universal donor.
- Blood donation is a voluntary procedure where about 420 mL of blood is typically withdrawn to be stored in blood banks.
7. The Lymphatic System
- Tissue fluid leaks out of capillaries to bathe cells; when it enters lymph vessels, it is called lymph.
- Lymph contains only leucocytes (mostly lymphocytes) and lacks RBCs and platelets.
- Its functions include supplying nutrition where blood cannot reach, draining excess fluid, absorbing fats from the intestine, and providing defense against infection.
Analogy for Understanding: Think of the circulatory system as a city’s delivery and waste management network. The heart is the central pumping station, the arteries and veins are the major highways, and the capillaries are the small residential streets where the actual deliveries (oxygen and nutrients) and trash pickups (waste) happen. The lymphatic system acts like a secondary drainage system that catches overflow and helps keep the city clean and safe from "invaders" (germs).
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |