Quick Navigation:
| | |
Manufacturing Industries
Introduction to Manufacturing
- Definition: Manufacturing is the production of goods in large quantities after processing raw materials into more valuable products.
- Sector: It falls under the secondary sector.
- Economic Strength: The economic strength of a country is measured by the development of its manufacturing industries.
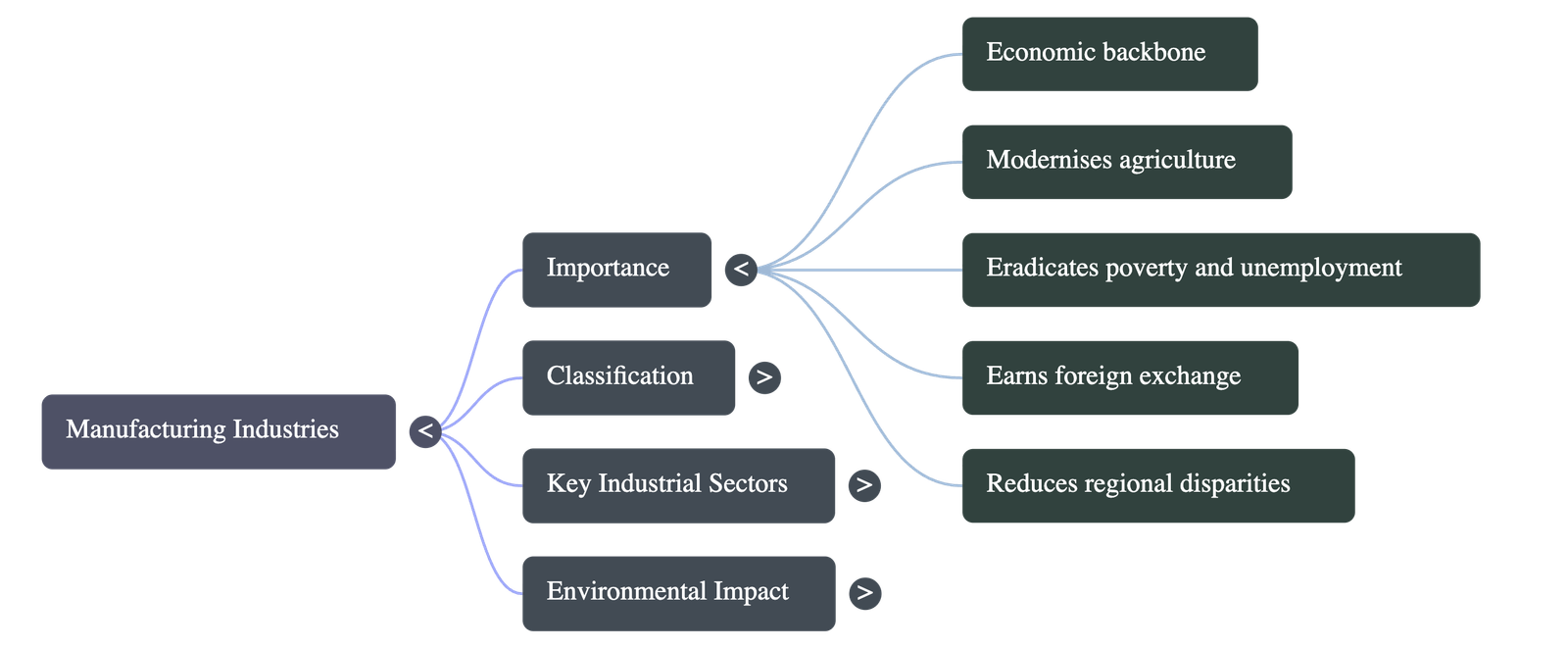
Importance of Manufacturing
- Modernizing Agriculture: Helps in modernizing agriculture, which is the backbone of the economy.
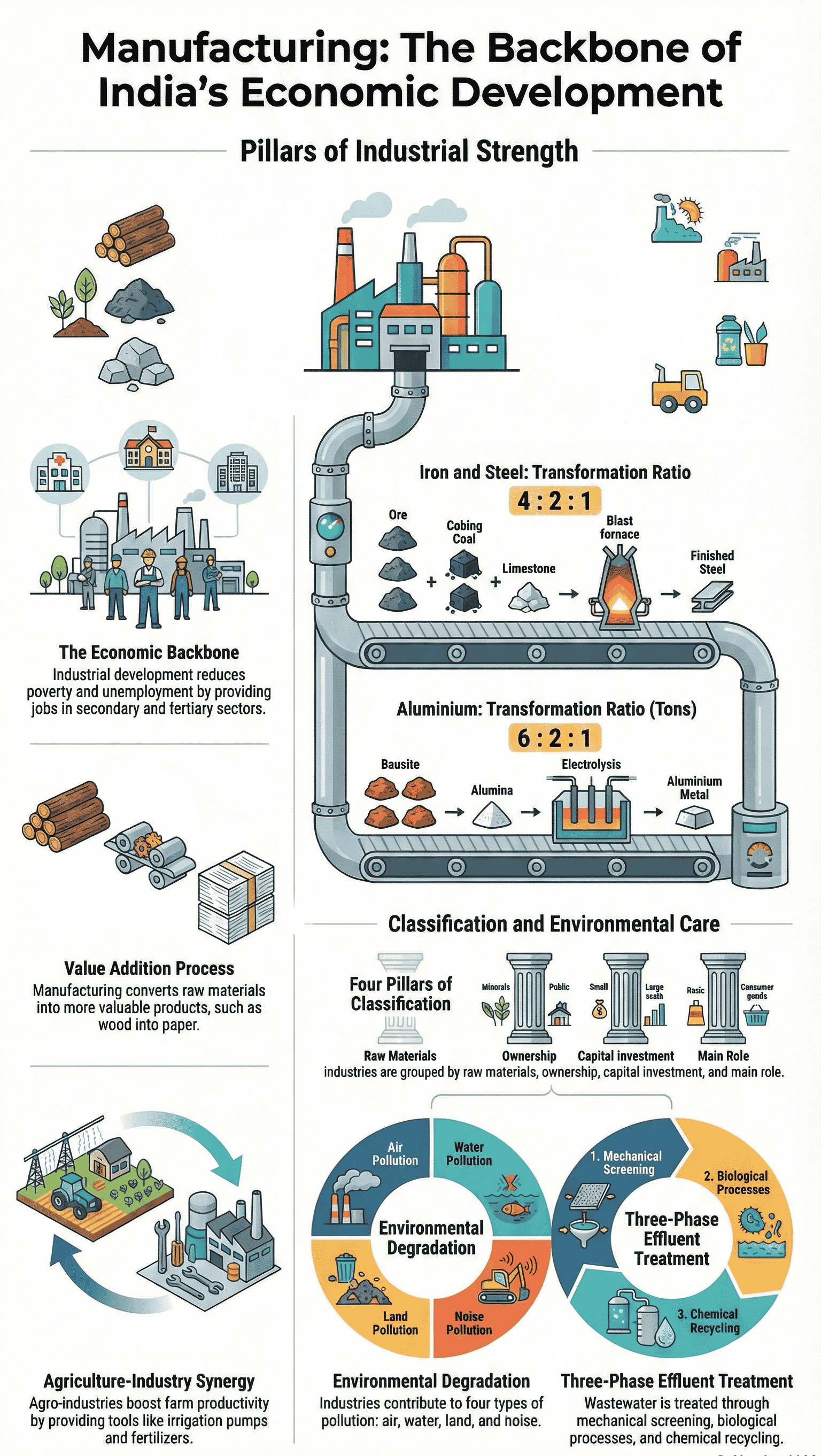
- Job Creation: Reduces dependence on agricultural income by providing jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors.
- Poverty Eradication: Industrial development is a precondition for eradicating unemployment and poverty. It aims to bring down regional disparities by establishing industries in backward areas.
- Foreign Exchange: Export of manufactured goods expands trade and brings in foreign exchange.
- Prosperity: Countries that transform raw materials into high-value finished goods are prosperous.
- Agriculture and Industry Link: They are not exclusive but move hand in hand. Agro-industries boost agriculture by raising productivity, and agriculture provides raw materials to industries.
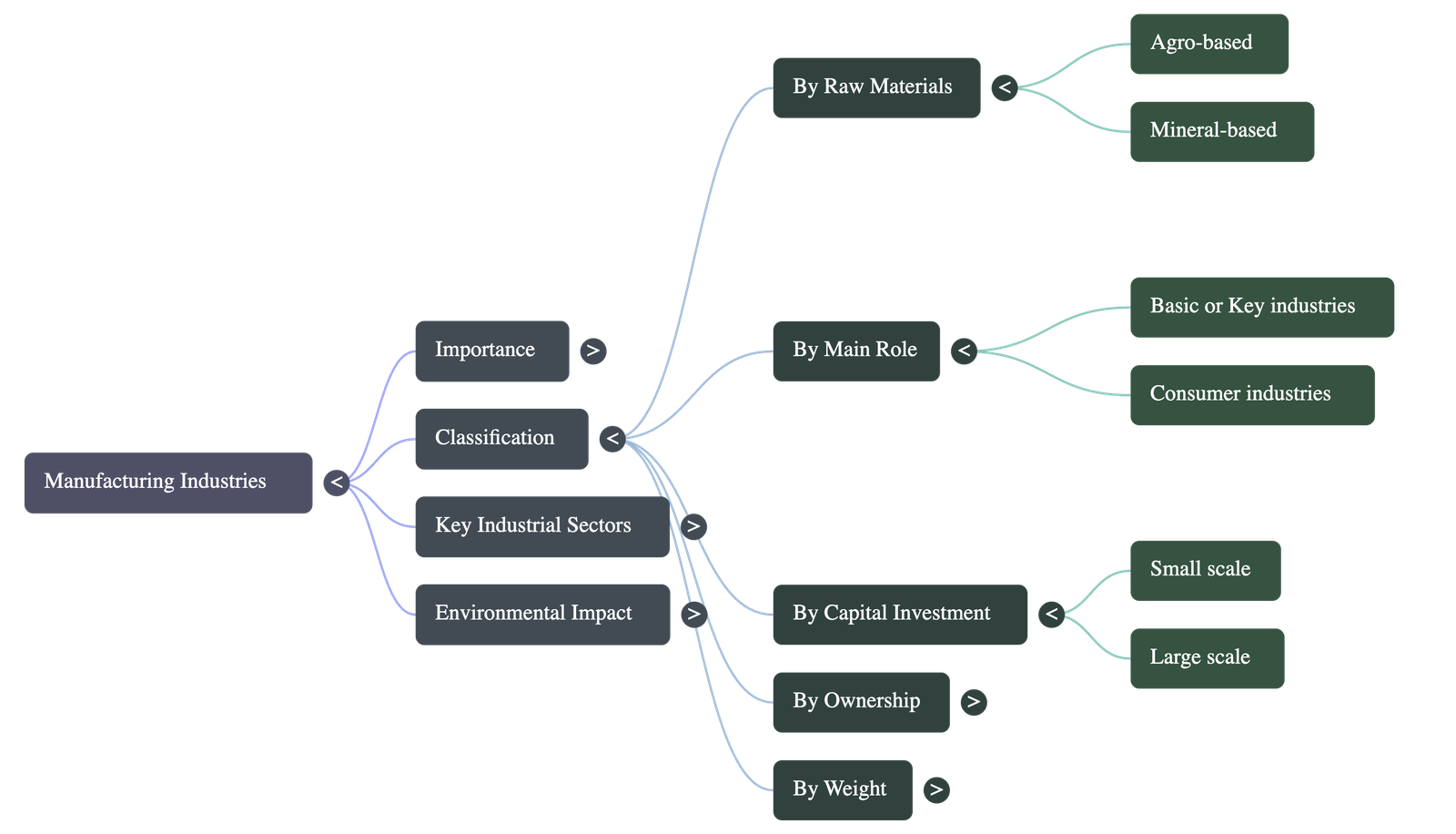
Classification of Industries
1. On the basis of Raw Materials
- Agro-based: Cotton, woollen, jute, silk textile, rubber, sugar, tea, coffee, edible oil.
- Mineral-based: Iron and steel, cement, aluminium, machine tools, petrochemicals.
2. On the basis of Main Role
- Basic/Key Industries: Supply their products as raw materials to manufacture other goods (e.g., iron and steel, copper smelting).
- Consumer Industries: Produce goods for direct use by consumers (e.g., sugar, toothpaste, paper, fans).
3. On the basis of Capital Investment
- Small Scale Industry: Defined by the maximum investment allowed on the assets of a unit (currently rupees one crore).
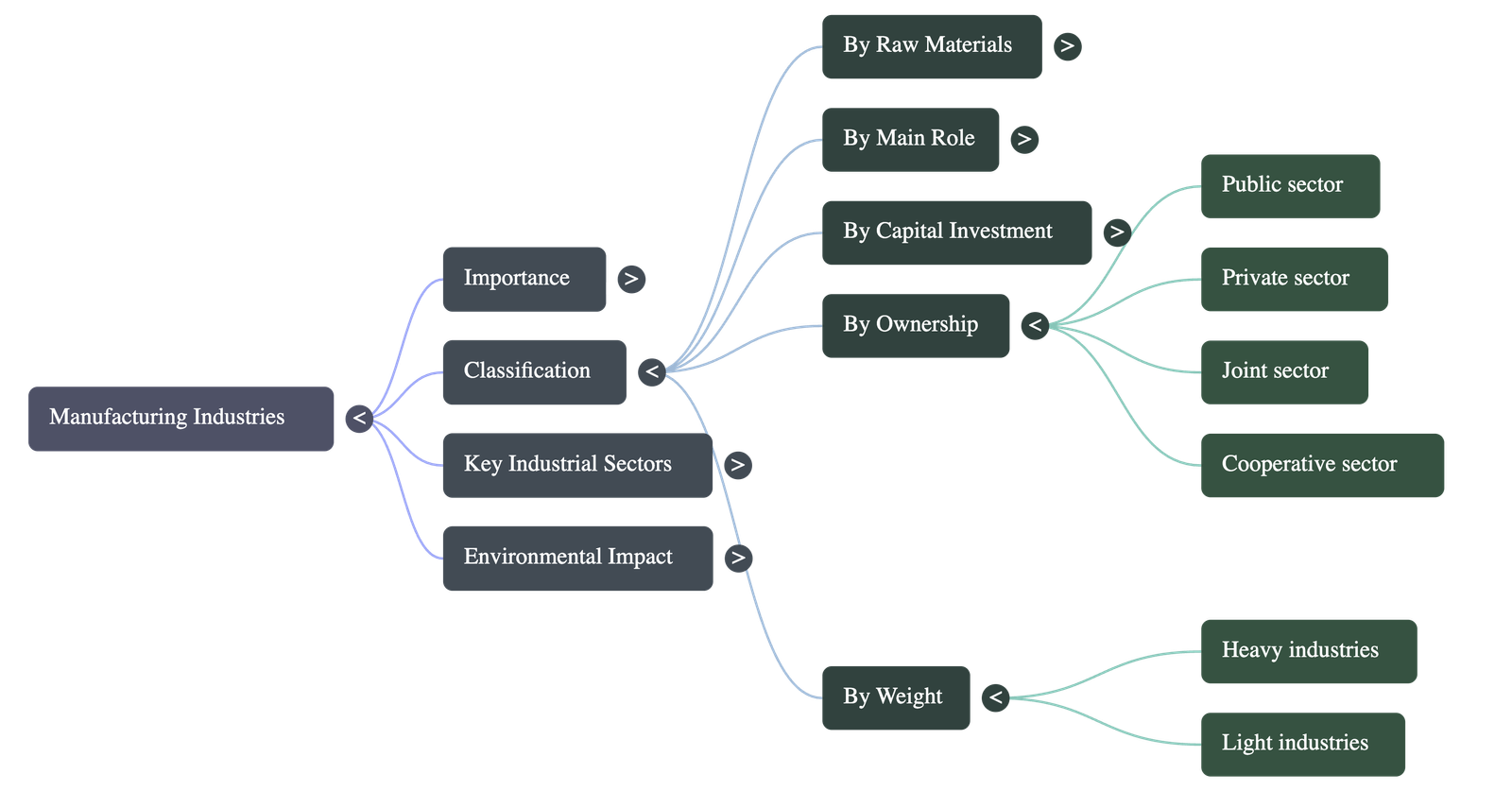
4. On the basis of Ownership
- Public Sector: Owned and operated by government agencies (e.g., BHEL, SAIL).
- Private Sector: Owned and operated by individuals or groups (e.g., TISCO, Bajaj Auto Ltd.).
- Joint Sector: Jointly run by the state and individuals (e.g., Oil India Ltd).
- Cooperative Sector: Owned and operated by producers/suppliers of raw materials or workers. They pool resources and share profits (e.g., Sugar industry in Maharashtra, Coir industry in Kerala).
5. On the basis of Bulk and Weight
- Heavy Industries: e.g., Iron and steel.
- Light Industries: Use light raw materials and produce light goods (e.g., electrical goods).
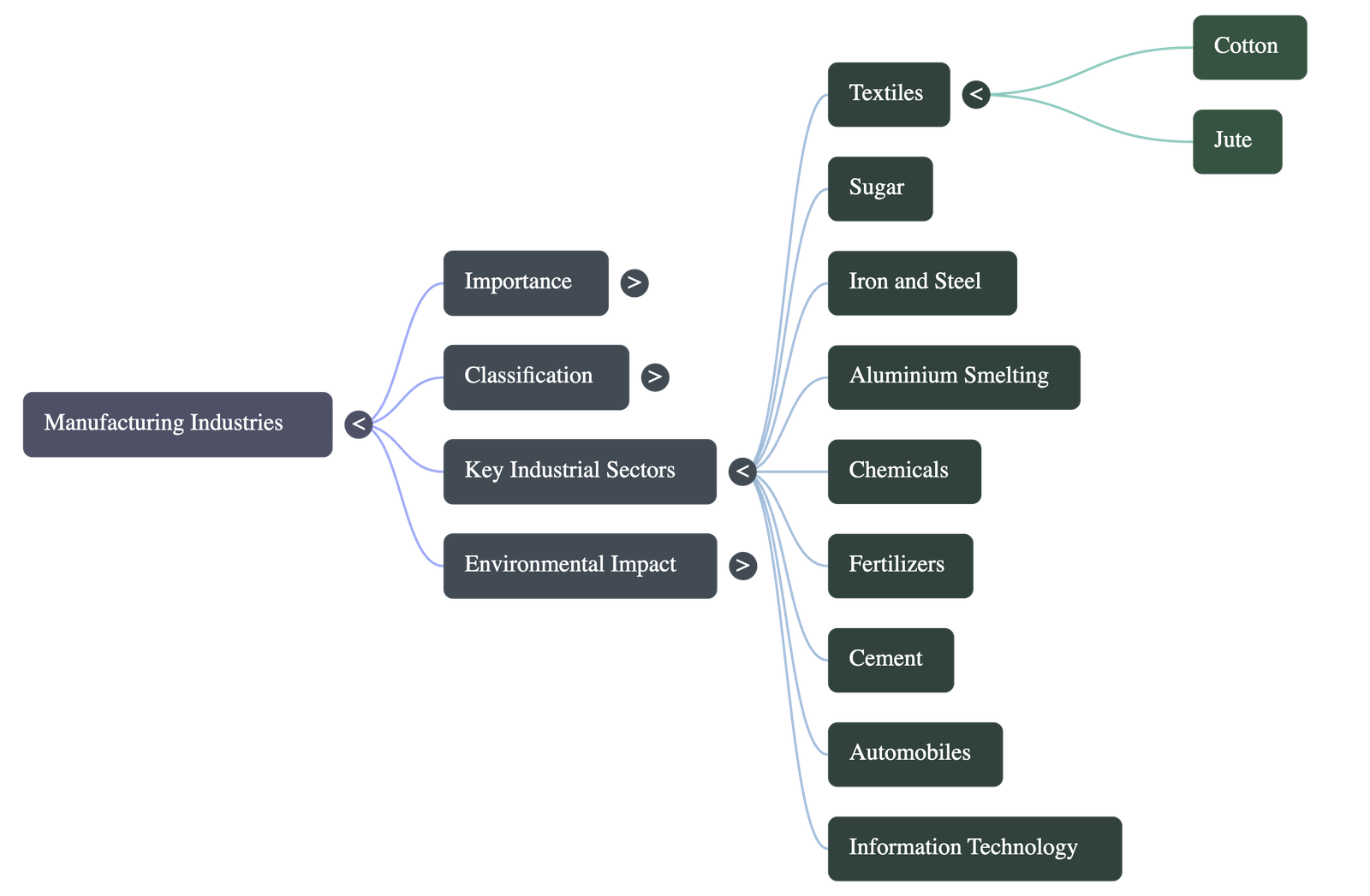
Major Agro-Based Industries
Textile Industry
- Unique position in the Indian economy.
- Contributes significantly to industrial production, employment, and foreign exchange.
- Self-reliant and complete in the value chain (from raw material to value-added products).
Cotton Textiles
- Historically produced with hand spinning and handloom weaving.
- Location Factors: Availability of raw cotton, market, transport, moist climate, and cheap labor. Originally concentrated in Maharashtra and Gujarat.
- Current Status: Spinning is centralized (Maharashtra, Gujarat, TN), but weaving is highly decentralized to incorporate traditional skills.
- Challenges: Erratic power supply, outdated machinery, low labor output, and stiff competition from synthetic fiber.
Jute Textiles
- India is the largest producer of raw jute and the second-largest exporter of jute goods.
- Location: Most mills are in West Bengal along the Hugli river.
- Factors for Location: Proximity to jute producing areas, inexpensive water transport, abundant water for processing, and cheap labor from nearby states.
Sugar Industry
- India is the second-largest producer of sugar in the world and first in gur and khandsari.
- Nature: Seasonal industry, ideally suited to the cooperative sector.
- Shifting Trends: Mills are shifting to southern and western states (especially Maharashtra) due to higher sucrose content in cane, cooler climate ensuring longer crushing seasons, and successful cooperatives.
Major Mineral-Based Industries
Iron and Steel Industry
- Basic Industry: All other industries depend on it for machinery.
- Heavy Industry: Raw materials and finished goods are bulky.
- Raw Materials: Iron ore, coking coal, and limestone are required in a ratio of approximately 4:2:1. Manganese is used to harden steel.
- Location: Maximum concentration in the Chhotanagpur plateau region due to low cost of iron ore, high-grade raw materials, and cheap labor.
Aluminium Smelting
- Second most important metallurgical industry in India.
- Properties: Light, corrosion-resistant, good conductor of heat, malleable.
- Raw Material: Bauxite (bulky, dark reddish rock).
- Key Location Factors: Regular supply of electricity and assured source of raw material at minimum cost.
Chemical Industries
- Fast-growing and diversifying.
- Inorganic: Sulphuric acid, nitric acid, alkalies, soda ash, caustic soda.
- Organic: Petrochemicals used for synthetic fibers, rubber, plastics, drugs, and pharmaceuticals. often located near oil refineries.
Fertilizer Industry
- Centered around nitrogenous fertilizers (Urea), phosphatic fertilizers (DAP), and complex fertilizers.
- Potash is entirely imported.
- Expanded significantly after the Green Revolution.
Cement Industry
- Essential for construction (houses, factories, roads, dams).
- Raw Materials: Bulky and heavy materials like limestone, silica, and gypsum.
- Plants in Gujarat have a strategic advantage for export to Gulf countries.
Automobile Industry
- Provides vehicles for quick transport of goods and passengers.
- Liberalization and new models stimulated demand.
- Concentrated around Delhi, Gurugram, Mumbai, Pune, Chennai, etc.
Information Technology and Electronics Industry
- Covers products from transistor sets to computers and telecom equipment.
- Bengaluru: Emerged as the "Electronic Capital of India".
- Major impact on employment generation.
- Success depends on the continuing growth of hardware and software.
Industrial Pollution and Environmental Degradation
- Air Pollution: Caused by high proportions of sulphur dioxide and carbon monoxide. Smoke from factories, brick kilns, and refineries contains particulate matter. Toxic gas leaks can be hazardous.
- Water Pollution: Caused by organic and inorganic industrial wastes discharged into rivers. Major culprits include paper, chemical, textile, and tannery industries.
- Thermal Pollution: Occurs when hot water from factories and thermal plants is drained into rivers before cooling, affecting aquatic life.
- Noise Pollution: Results in irritation, anger, hearing impairment, increased heart rate, and blood pressure. Caused by industrial and construction activities.
- Land Degradation: Dumping of wastes (glass, chemicals, salts) renders soil useless and contaminates groundwater.
Control of Environmental Degradation
Sustainable development requires integrating economic growth with environmental concerns:
- Water Management: Minimizing water use by reusing and recycling in successive stages. Harvesting rainwater.
- Effluent Treatment: Treating hot water and effluents before release (Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary treatment).
- Air Pollution Control: Using smoke stacks with electrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers, and inertial separators. Using oil or gas instead of coal to reduce smoke.
- Noise Control: Fitting generators with silencers, redesigning machinery to increase efficiency, and using noise-absorbing materials.
NTPC Example (National Thermal Power Corporation)
NTPC has ISO certification for EMS 14001 and follows a proactive approach:
- Optimum utilization of equipment and upgrading technology.
- Minimizing waste generation by maximizing ash utilization.
- Creating green belts for ecological balance.
- Ash pond management and water recycling.
- Ecological monitoring and online database management.
Quick Navigation:
| | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | |