Quick Navigation:
| | |
Lifelines of National Economy
Introduction
- The development of a country depends on the production of goods and services and their movement over space.
- Transport plays a key role in moving goods from supply locations to demand locations.
- Transport, communication, and trade are complementary to each other and are prerequisites for local, national, and global trade.
- India is well-linked with the rest of the world despite its vast size and diversity due to efficient transport and communication systems.
- Transport is classified into three domains: Land, Water, and Air.
Transport: Roadways
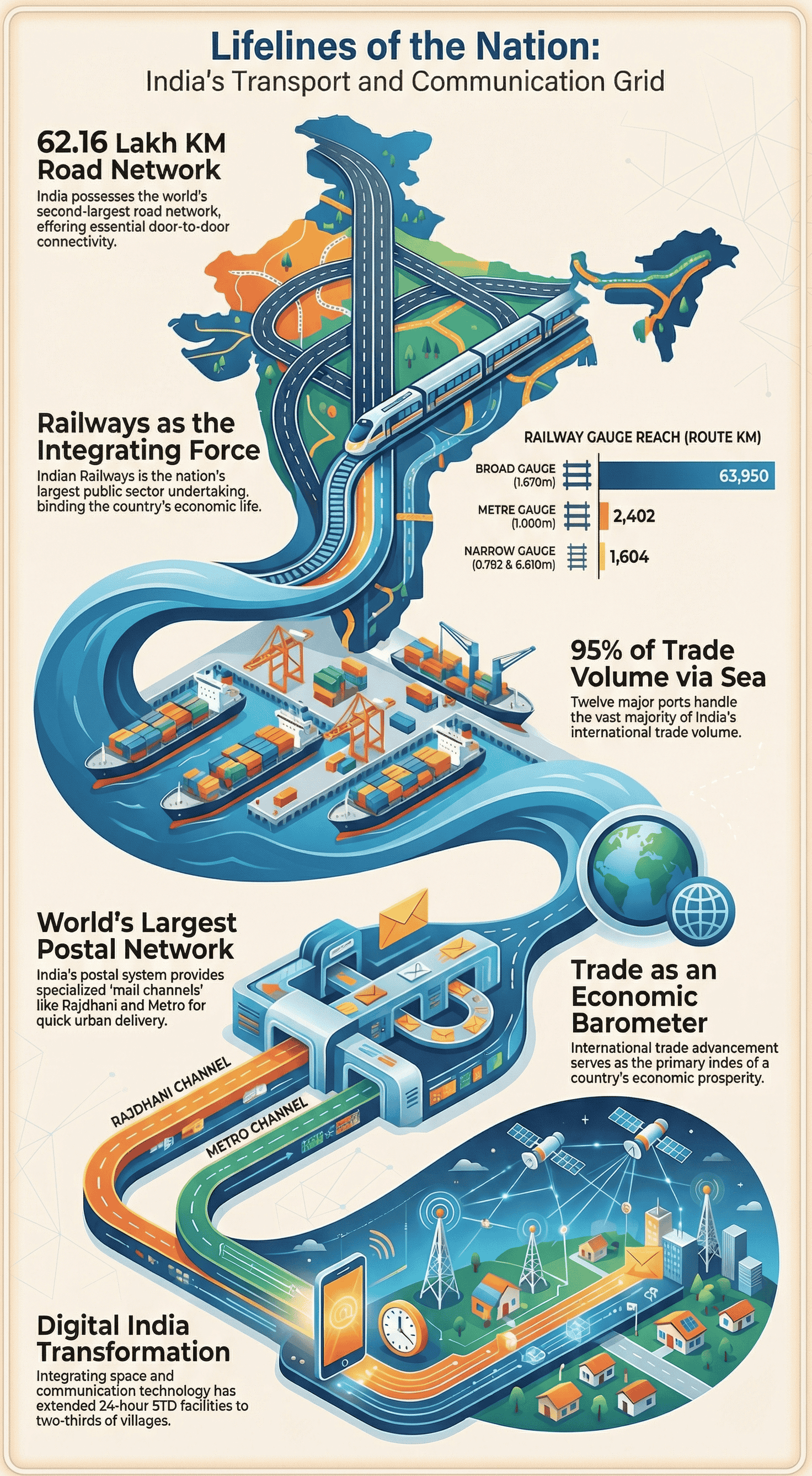
India has one of the largest road networks in the world (approx. 62.16 lakh km). Roadways have an edge over railways for several reasons:
- Lower construction cost compared to railways.
- Ability to traverse dissected and undulating topography and higher gradients (e.g., Himalayas).
- Economical for transporting few people and smaller amounts of goods over short distances.
- Provides door-to-door service, reducing loading/unloading costs.
- Acts as a feeder to other modes of transport (links to railway stations, airports, and sea ports).
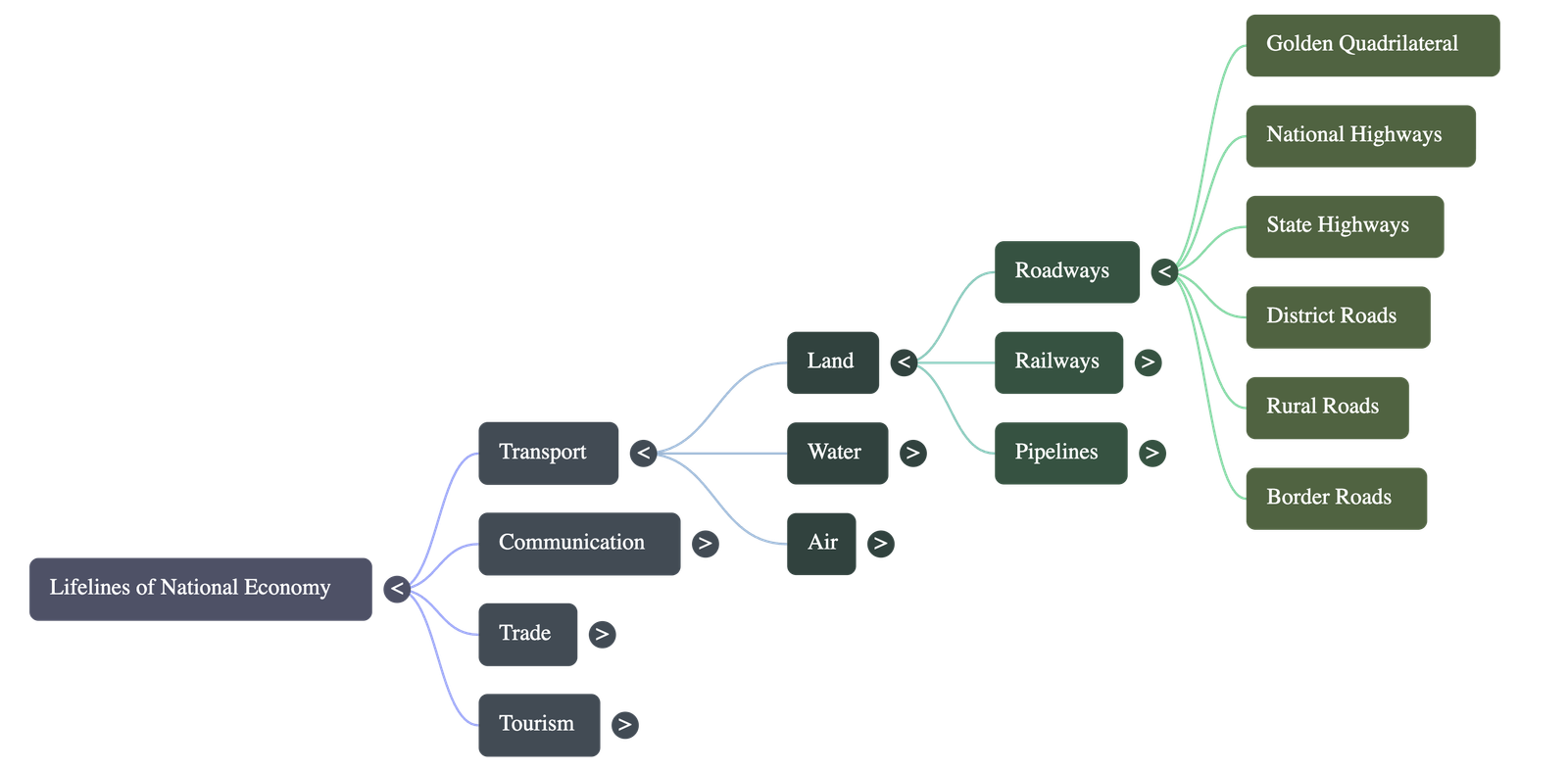
Classification of Roads
- Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways: A major project linking Delhi-Kolkata-Chennai-Mumbai-Delhi by six-lane super highways. Includes North-South corridors (Srinagar to Kanniyakumari) and East-West corridors (Silchar to Porbandar). Implemented by NHAI.
- National Highways: Primary road systems linking extreme parts of the country, maintained by the Central Public Works Department (CPWD).
- State Highways: Link state capitals with district headquarters, constructed and maintained by State Public Works Departments (PWD).
- District Roads: Connect district headquarters with other places in the district, maintained by the Zila Parishad.
- Other Roads: Rural roads linking villages to towns. Received impetus under the Pradhan Mantri Grameen Sadak Yojana to provide all-weather motorable connectivity to every village.
- Border Roads: Constructed and maintained by the Border Roads Organisation (BRO) in strategic border areas (North and North-Eastern border). These roads improve accessibility in difficult terrain and aid economic development.
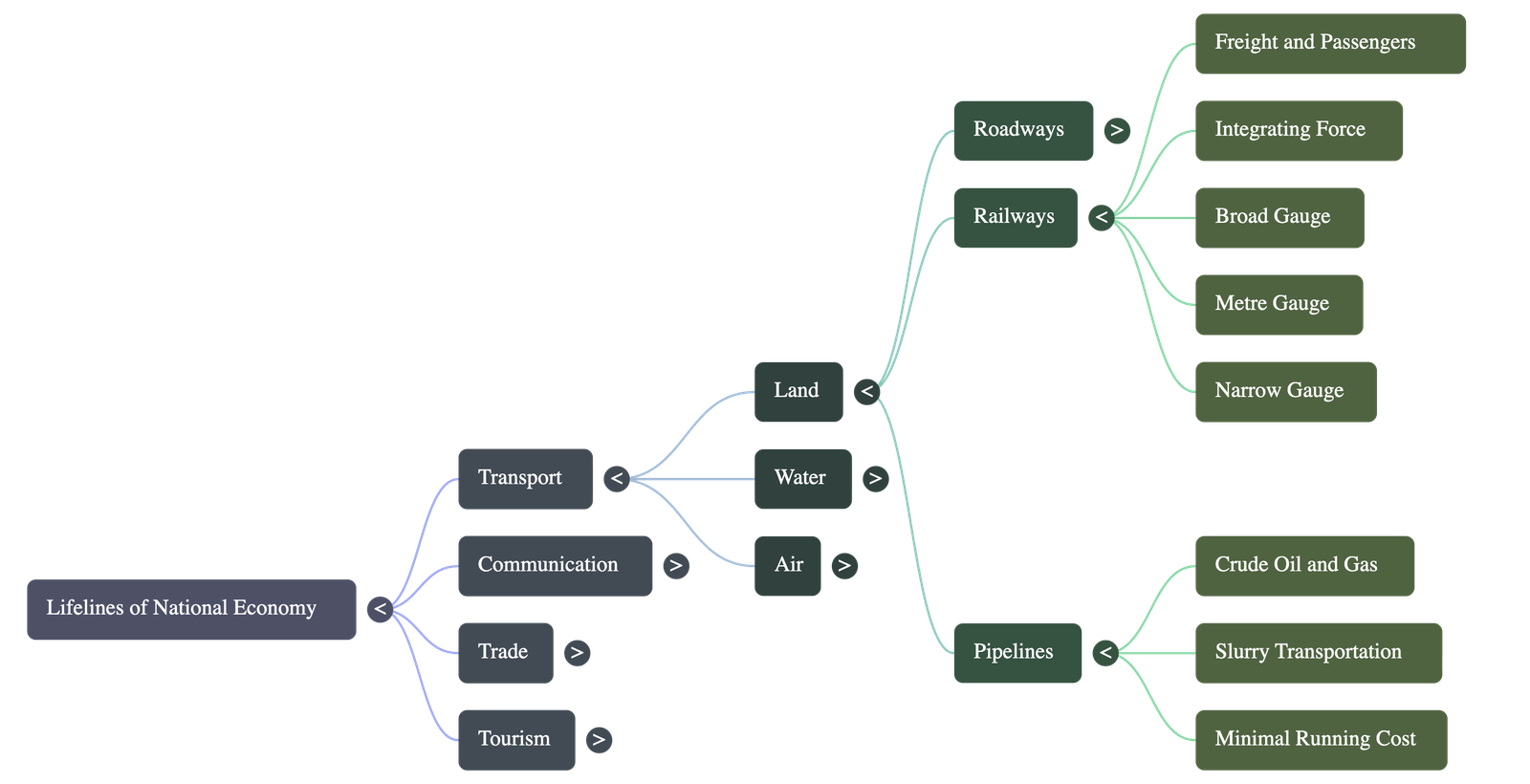
Transport: Railways
- Railways are the principal mode of transportation for freight and passengers in India.
- They facilitate multifarious activities like business, sightseeing, and pilgrimage over long distances.
- The Indian Railways have been a great integrating force for over 150 years, accelerating the development of industry and agriculture.
- Network Distribution Factors:
- Northern Plains: Favorable due to vast level land, high population density, and rich agricultural resources.
- Hilly/Mountainous Regions: Unfavorable due to high relief, sparse population, and lack of economic opportunities (e.g., Himalayas).
- Deserts/Swamps: Difficult to lay tracks in sandy plains of Rajasthan or swamps of Gujarat.
- Peninsular Region: Tracks are laid through low hills, gaps, or tunnels. The Konkan Railway has facilitated movement along the west coast but faces challenges like landslides.
- Problems: Ticketless travel, theft, damaging of railway property, and unnecessary chain pulling causing delays.
Transport: Pipelines
- Used to transport crude oil, petroleum products, and natural gas from fields to refineries, fertilizer factories, and thermal power plants.
- Solids can be transported as slurry.
- Allows refineries to be located far inland (e.g., Barauni, Mathura, Panipat).
- Initial laying costs are high, but running costs are minimal. It rules out trans-shipment losses and delays.
- Important Networks:
- Upper Assam to Kanpur (via Guwahati, Barauni, Prayagraj).
- Salaya (Gujarat) to Jalandhar (Punjab).
- Hazira-Vijaipur-Jagdishpur (HVJ) gas pipeline linking Mumbai High to northern India.
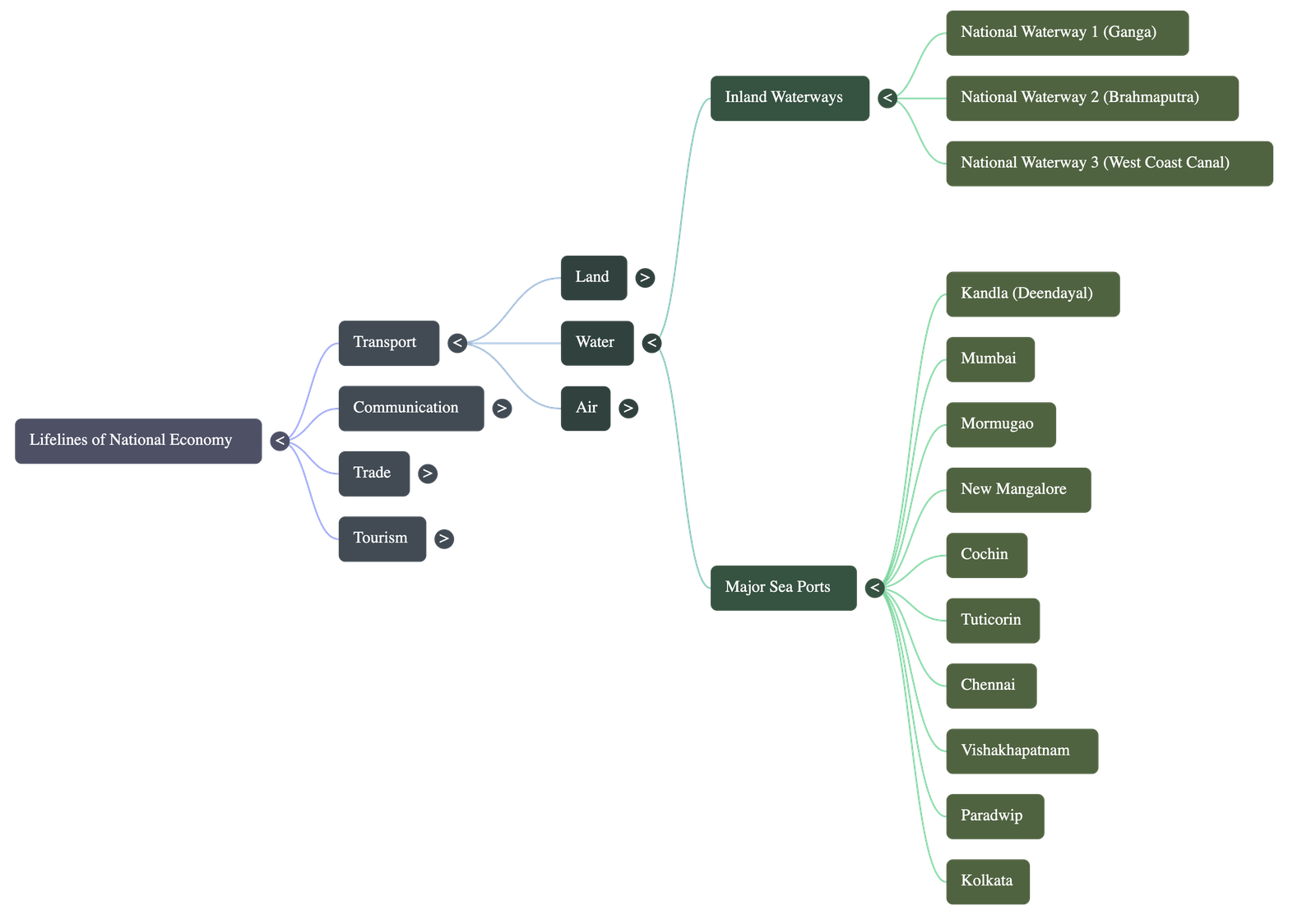
Transport: Waterways
- Cheapest means of transport, fuel-efficient, and eco-friendly.
- Most suitable for carrying heavy and bulky goods.
- Inland Waterways: India has 14,500 km of navigable waterways. Major National Waterways (NW) include:
- NW-1: Ganga river (Prayagraj to Haldia).
- NW-2: Brahmaputra river (Sadiya to Dhubri).
- NW-3: West-Coast Canal in Kerala.
- NW-4: Godavari and Krishna rivers stretches.
- NW-5: Brahmani river and East Coast Canal.
- Overseas Trade: 95% of the country's trade volume is moved by sea through ports.
- Major Sea Ports: India has 12 major ports and roughly 200 minor ports.
- Kandla (Deendayal Port): Tidal port, developed to ease pressure on Mumbai after partition.
- Mumbai: Biggest port with a spacious natural harbour.
- Jawaharlal Nehru Port: Planned to decongest Mumbai port.
- Mormugao (Goa): Premier iron ore exporting port.
- New Mangalore: Exports iron ore from Kudremukh.
- Cochin: Natural harbour at a lagoon entrance.
- Tuticorin: Natural harbour, rich hinterland.
- Chennai: One of the oldest artificial ports.
- Vishakhapatnam: Deepest landlocked and well-protected port.
- Paradwip: Specializes in iron ore export.
- Kolkata: Inland riverine port (tidal), requires constant dredging.
- Haldia: Subsidiary port to relieve pressure on Kolkata.
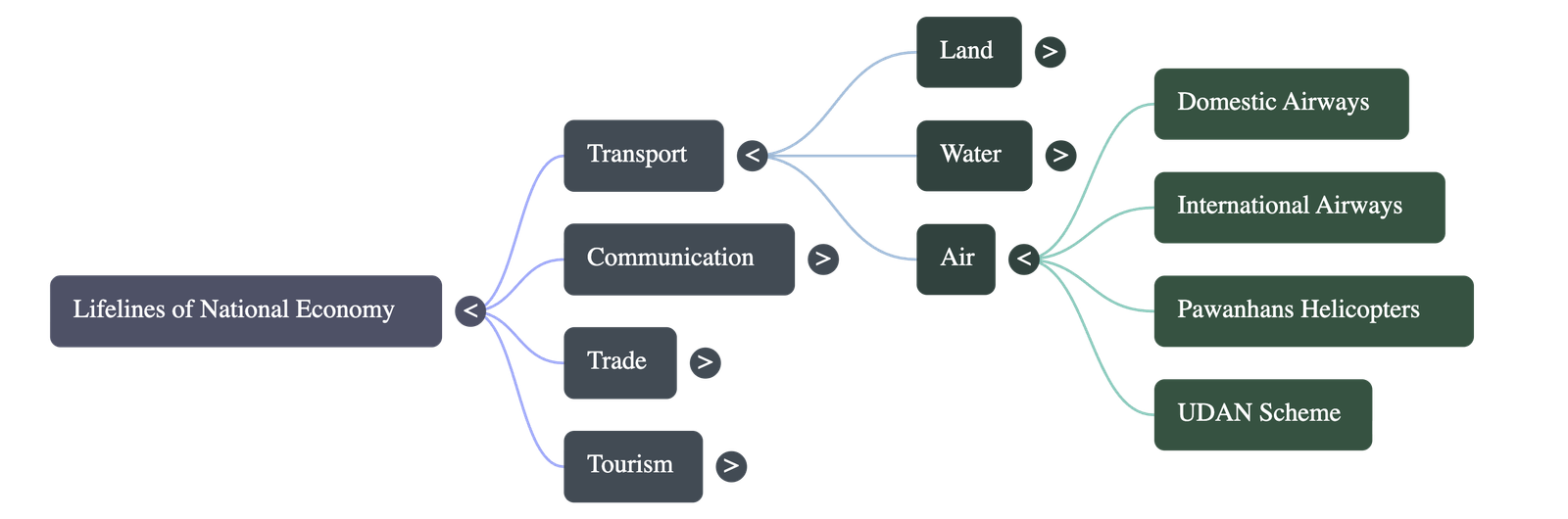
Transport: Airways
- Fastest, most comfortable, and prestigious mode of transport.
- Crucial for accessing difficult terrains like high mountains, dreary deserts, dense forests, and oceanic stretches.
- Vital for the North-Eastern states due to difficult relief, big rivers, forests, and international frontiers.
- Services:
- Air India provides domestic and international air services.
- Pawanhans Helicopters Ltd. provides services to ONGC and inaccessible areas (J&K, Himachal, North-East).
- UDAN Scheme: "Ude Desh ka Aam Nagrik" aims to make regional air travel affordable for common citizens.
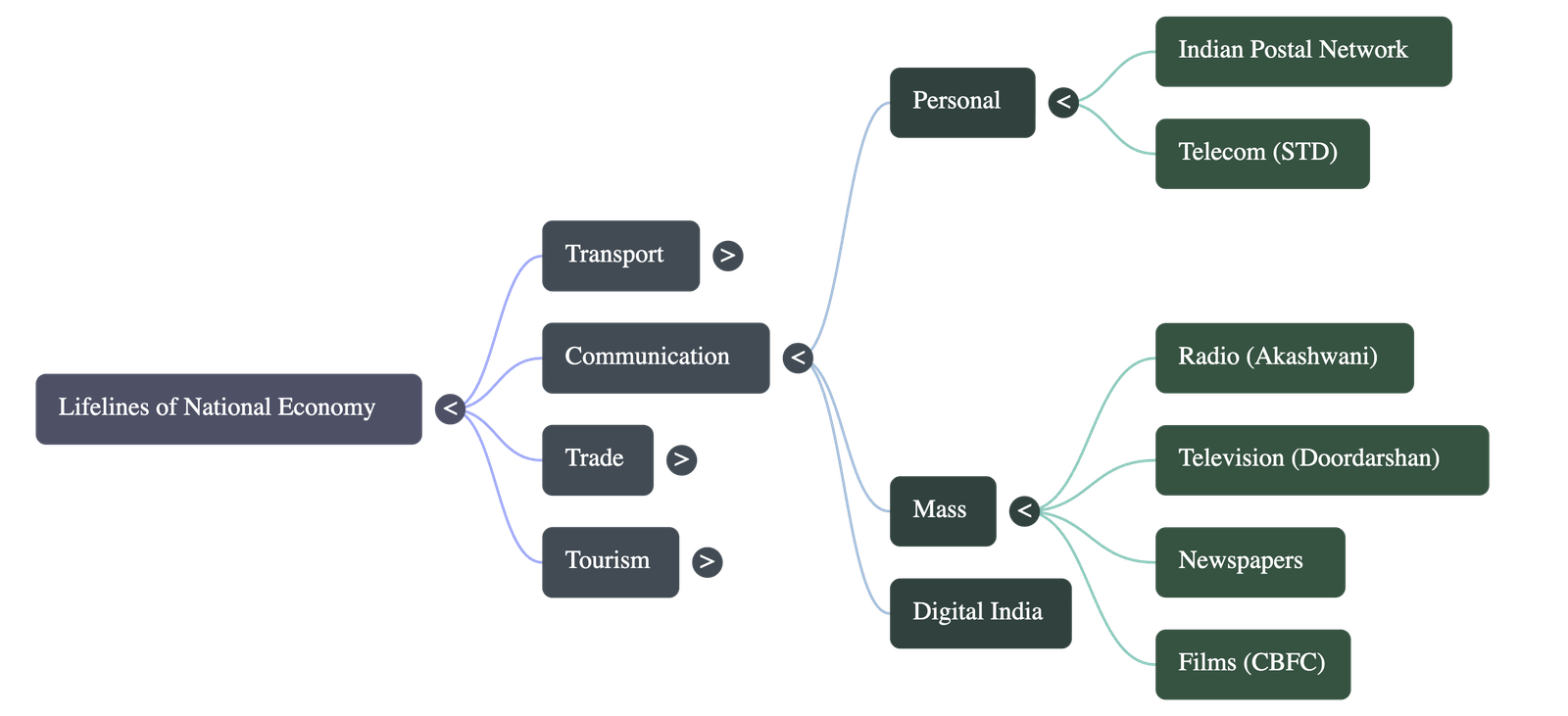
Communication
- Personal vs. Mass Communication: Includes post, telegraph, telephone, wireless, films, radio, TV, etc.
- Indian Postal Network: Largest in the world.
- First-class mail: Cards and envelopes (airlifted).
- Second-class mail: Book packets, newspapers, periodicals (surface mail).
- Mail Channels: Six channels introduced for quick delivery in large cities (Rajdhani, Metro, Green, Business, Bulk Mail, Periodical).
- Telecom Network: India has one of the largest telecom networks in Asia. STD facilities extend to most villages with uniform rates. Digital India programme focuses on knowledge-based transformation.
- Mass Communication:
- All India Radio (Akashwani): Broadcasts in national, regional, and local languages.
- Doordarshan: National TV channel, one of the largest terrestrial networks.
- Press: Newspapers published in about 100 languages/dialects (largest numbers in Hindi, English, Urdu).
- Films: India is the largest producer of feature films. Certified by the Central Board of Film Certification.
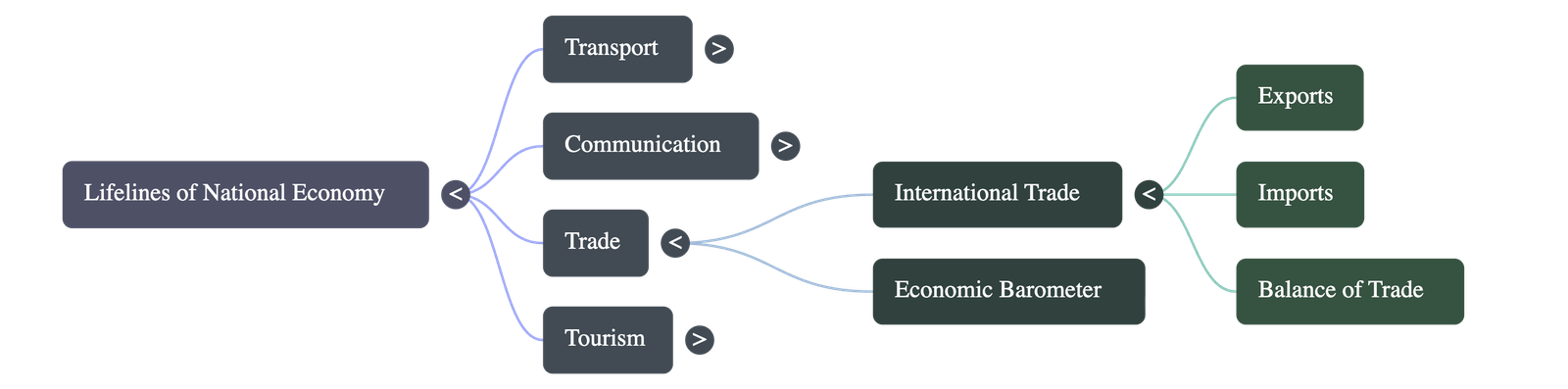
International Trade
- Trade: The exchange of goods among people, states, and countries.
- International Trade: Trade between two countries. Considered the economic barometer of a country.
- Balance of Trade: The difference between exports and imports.
- Favourable Balance: Value of exports exceeds value of imports.
- Unfavourable Balance: Value of imports exceeds value of exports.
- Exports: Gems and jewelry, chemicals, agriculture and allied products, and software (information technology). India is a software giant earning large foreign exchange.
- Imports: Crude petroleum, gems and jewelry, chemicals, base metals, electronics, and machinery.
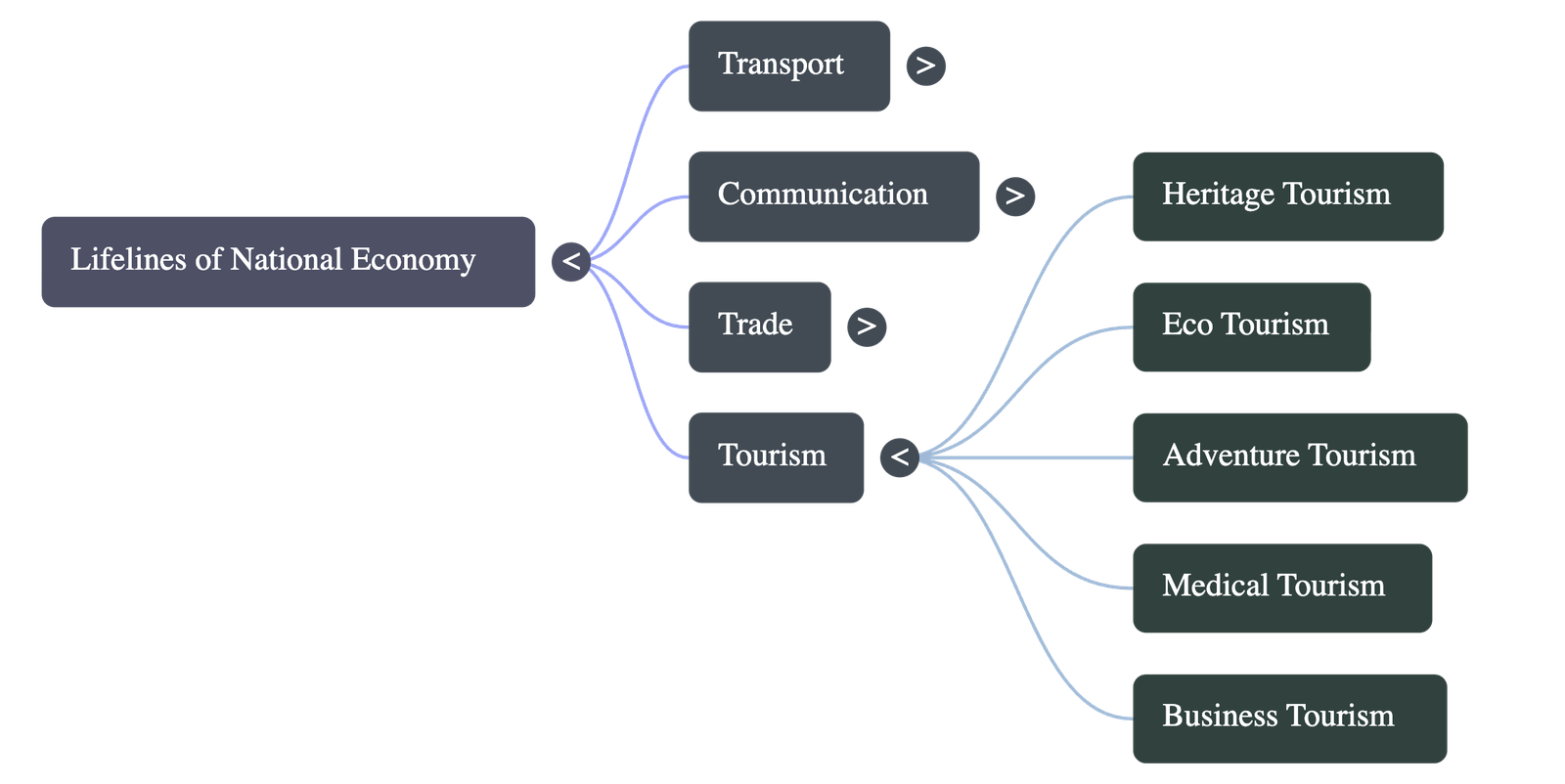
Tourism as a Trade
- Tourism has grown significantly over the last few decades.
- Benefits:
- Promotes national integration.
- Supports local handicrafts and cultural pursuits.
- Develops international understanding of Indian culture and heritage.
- Earns huge foreign exchange.
- Types of Tourism: Heritage, eco-tourism, adventure, cultural, medical, and business tourism.
- Government Initiatives: Swadesh Darshan 2.0, Vibrant Village Programme, PRASHAD to boost tourism infrastructure.
Quick Navigation:
| | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | |