Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Carbon & Its Compounds
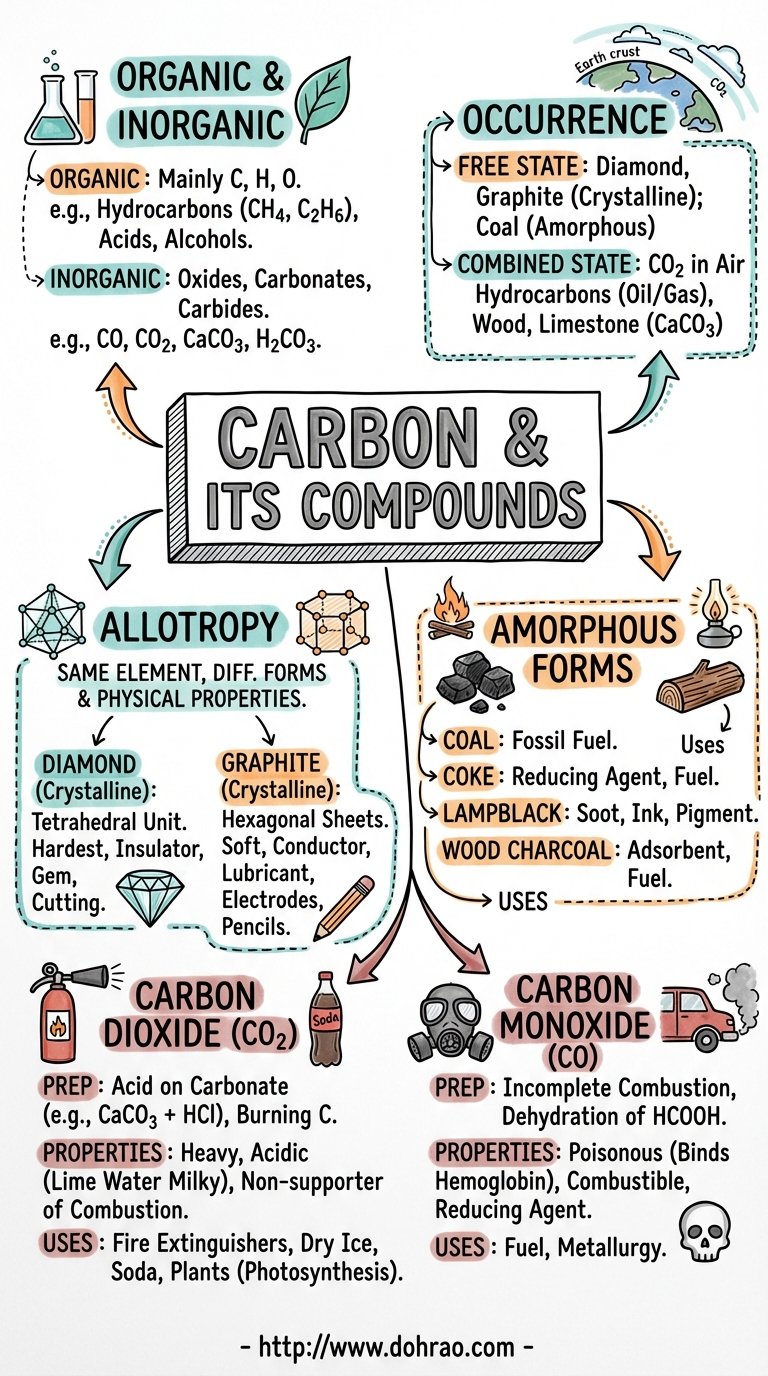
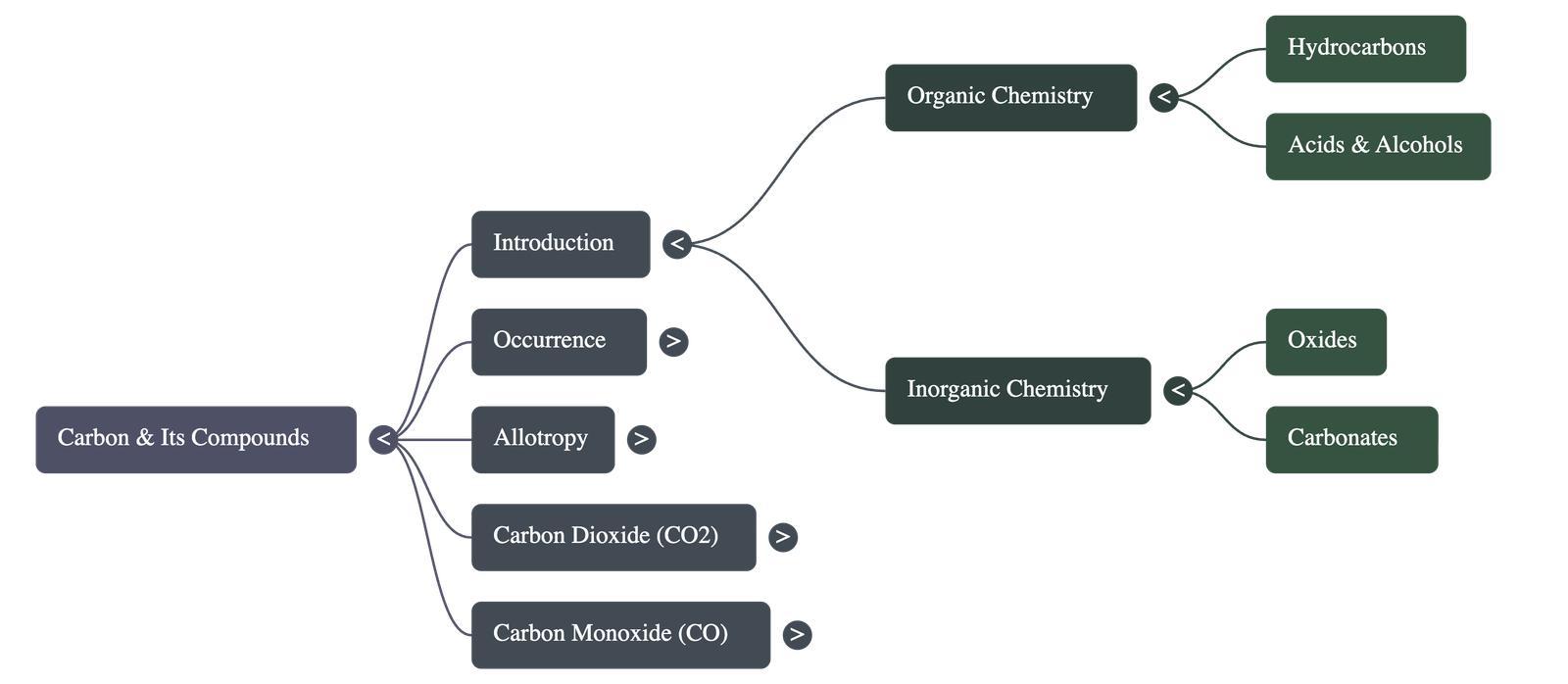
1. Introduction to Carbon
- Organic Chemistry: The study of specific carbon compounds mainly containing carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, such as hydrocarbons (methane, ethane), acids (acetic acid), and alcohols.
- Inorganic Chemistry: Includes the study of carbon oxides, carbonates, bicarbonates, and metallic carbides.
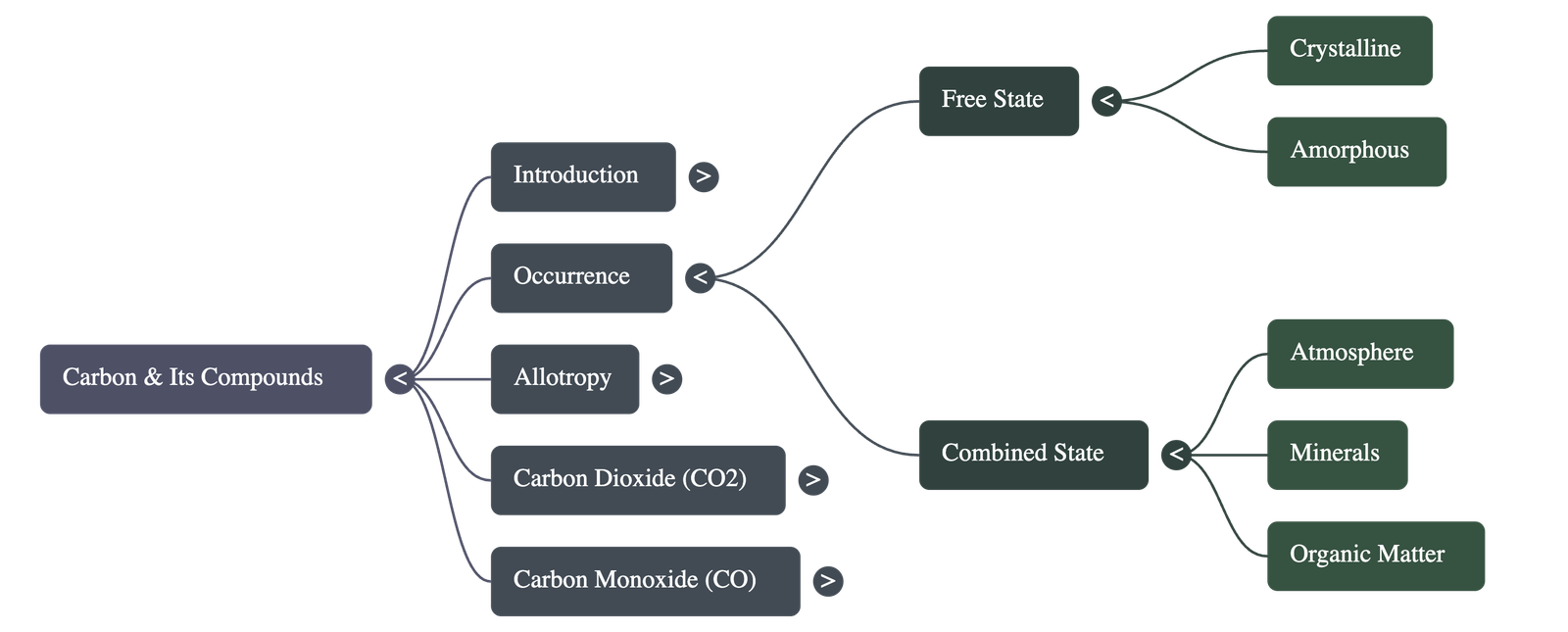
- Occurrence: Carbon occurs in the free state (diamond, graphite, and coal) and the combined state (carbon dioxide, hydrocarbons, limestone, and cellular wood).
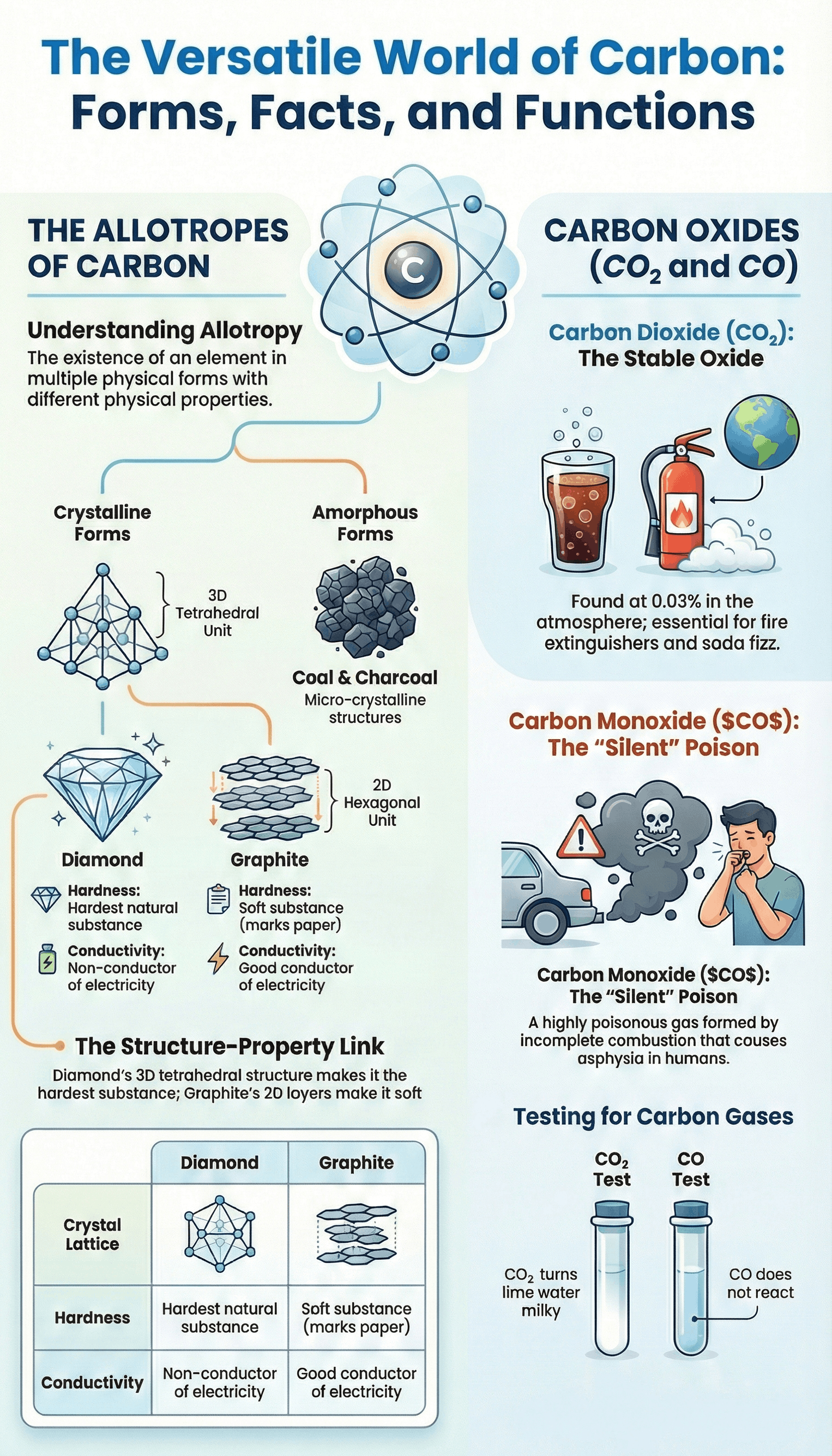
2. Allotropy of Carbon
- Definition: The existence of an element in more than one physical form having different physical properties but similar chemical properties.
- Cause: It results from differences in the atomic arrangement in the crystal structure of the element.
- Classification: Allotropes are divided into Crystalline forms (Diamond, Graphite, Fullerene) and Amorphous forms (Coal, Coke, Lampblack, Charcoal).
3. Crystalline Allotropes
Diamond
- Structure: A three-dimensional octahedral crystal where each carbon atom is linked to four others by strong covalent bonds in a tetrahedral unit.
- Properties: The hardest natural substance, high density, and a non-conductor of electricity due to the absence of free electrons.
- Uses: Industrial applications for drilling and cutting glass; used as a precious gem due to its high refractive index and brilliance.
Graphite
- Structure: A two-dimensional layered structure with hexagonal units. Layers are held by weak Van der Waals forces, allowing them to slide over each other.
- Properties: Soft and greasy to touch, leaves a mark on paper, and a good conductor of electricity due to the presence of mobile electrons.
- Uses: Used as "lead" in pencils, a dry lubricant for high-temperature machinery, and as electrodes in dry cells.
4. Amorphous Allotropes
- Coal: Formed by the slow bacterial decomposition of vegetable matter over millions of years; types include Peat, Lignite, Bituminous, and Anthracite.
- Coke: Prepared by the destructive distillation of coal; used as a fuel and a vital reducing agent in the extraction of iron and steel.
- Lampblack (Soot): Produced by burning carbon-rich substances like kerosene in limited air; used in making printer's ink and black paints.
- Wood Charcoal: Obtained by the destructive distillation of wood. It is highly porous and used as an adsorbent for gases and a decolourising agent for organic matter.
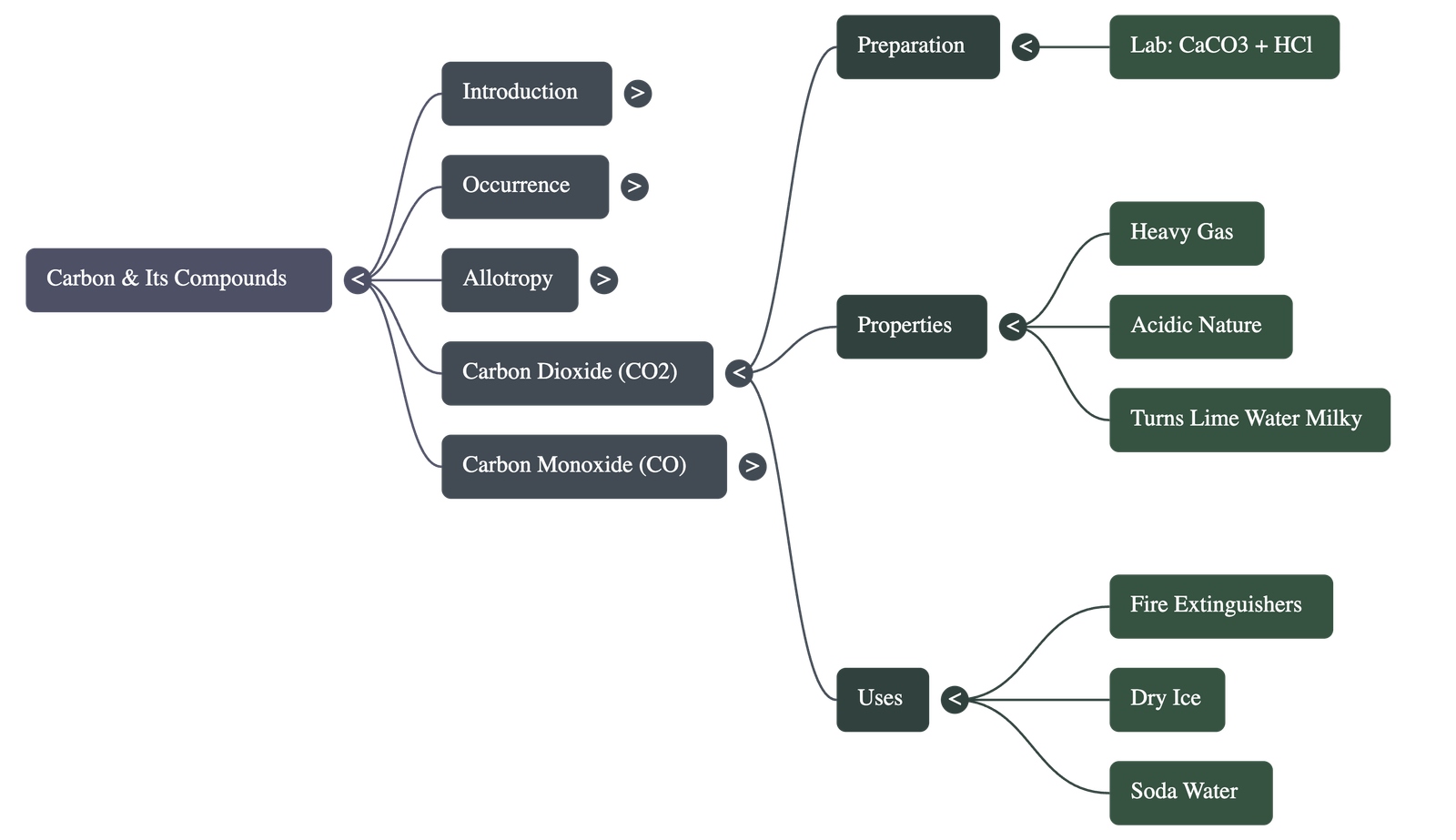
5. Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
- Laboratory Preparation: Produced by the action of dilute hydrochloric acid on marble chips (calcium carbonate). It is collected by the upward displacement of air because it is heavier than air.
- Physical Properties: Colourless, odourless, and has a slightly sour taste. It solidifies at -78°C to form Dry Ice.
- Chemical Properties: Non-combustible and does not support combustion. It is slightly acidic, turning blue litmus pink.
- Key Reaction: When bubbled through lime water, it turns the solution milky due to the formation of insoluble calcium carbonate. The milkiness disappears if excess gas is passed.
- Uses: Used in the manufacture of aerated soda water, as a refrigerant (dry ice), and in fire extinguishers.
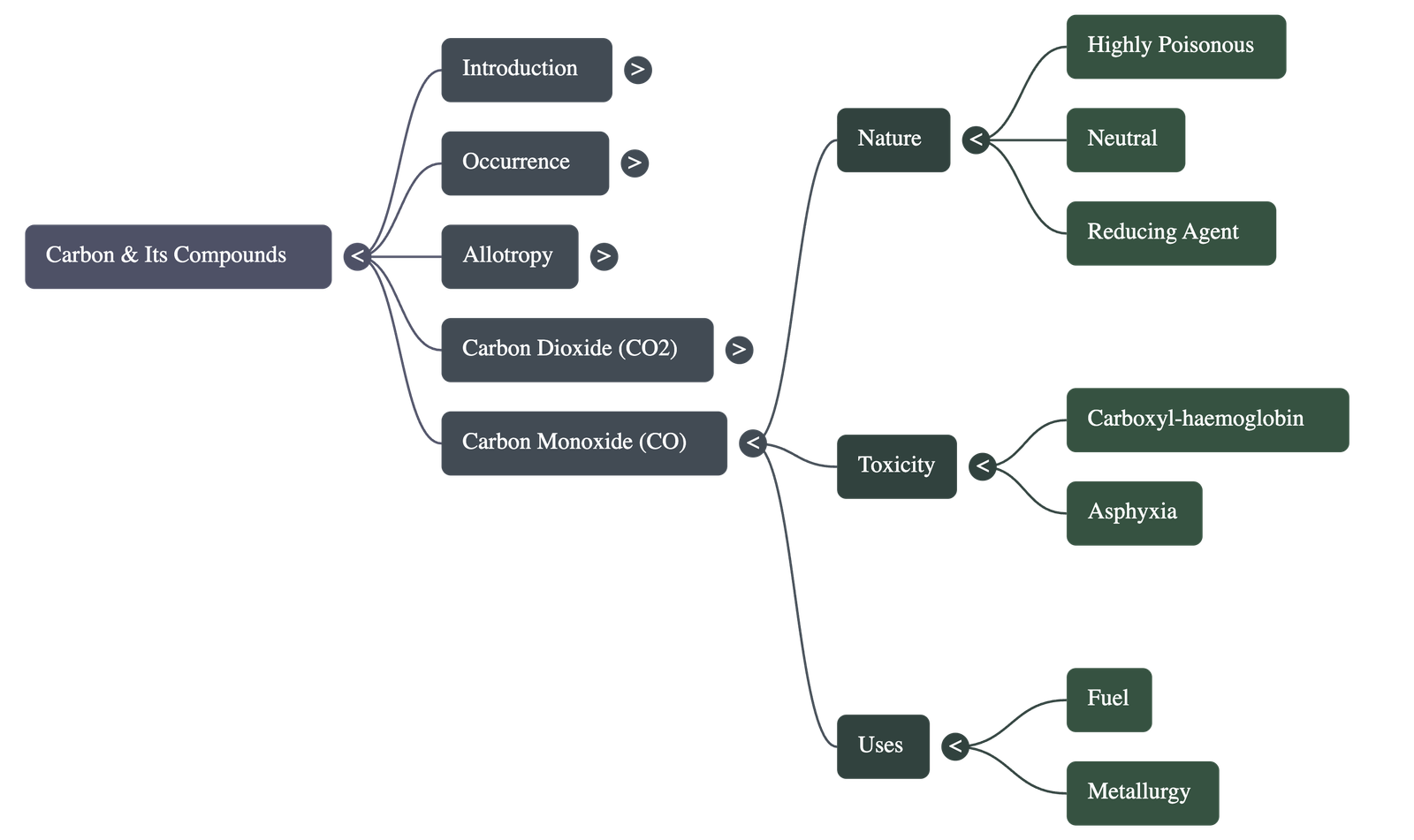
6. Carbon Monoxide (CO)
- Preparation: Formed by the incomplete combustion of fuels or by heating formic acid with concentrated sulphuric acid, which acts as a dehydrating agent.
- Poisonous Nature: Highly dangerous because it combines with haemoglobin in the blood to form carboxyl-haemoglobin, which prevents the blood from carrying oxygen, leading to asphyxia.
- Chemical Properties: Highly combustible, burning with a pale blue flame. It is a powerful reducing agent used in metallurgy to reduce metallic oxides to metals.
- Precautions: It is dangerous to sleep in a closed room with a coal fire or stand behind a running automobile engine due to CO presence in exhaust fumes.
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |