Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Based on the chapter, here is a point-wise summary of the chapter "Melting Ice in Alaska":
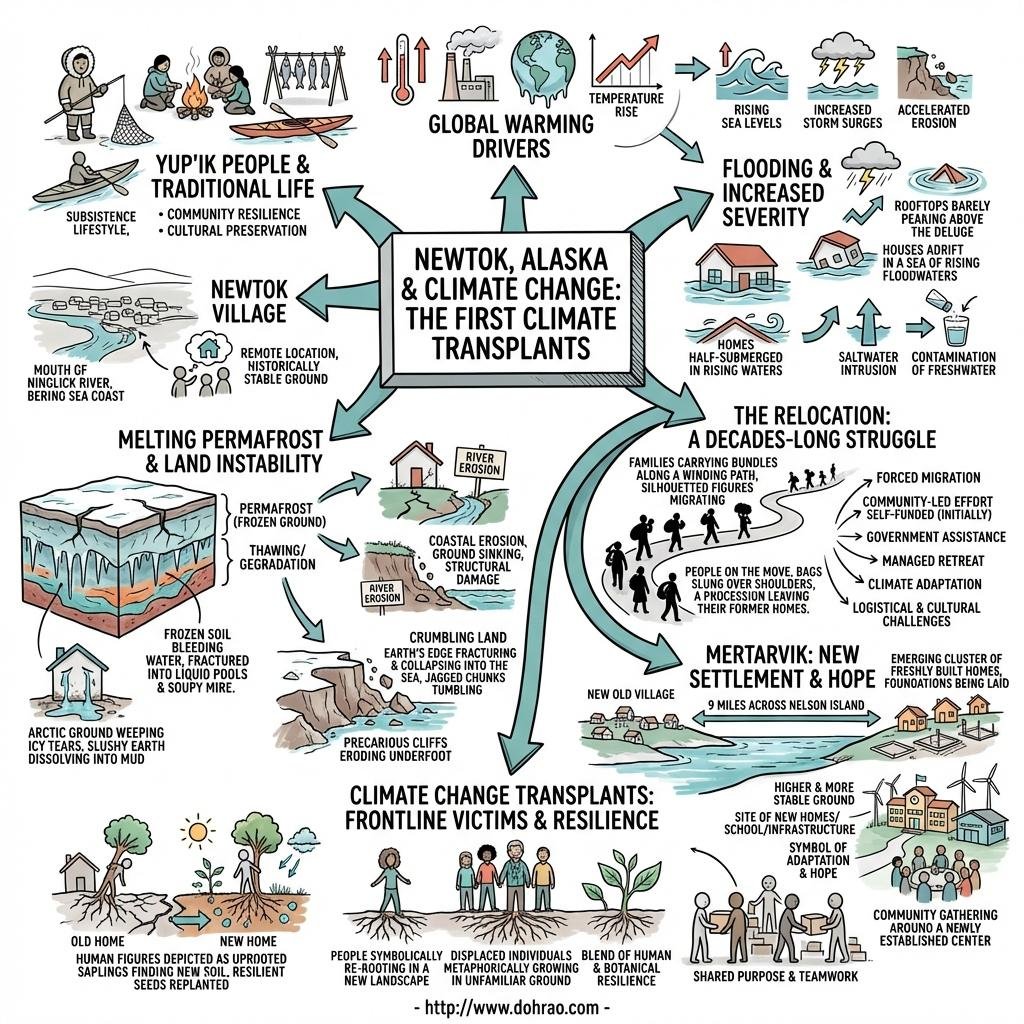
The Environmental Crisis in Newtok
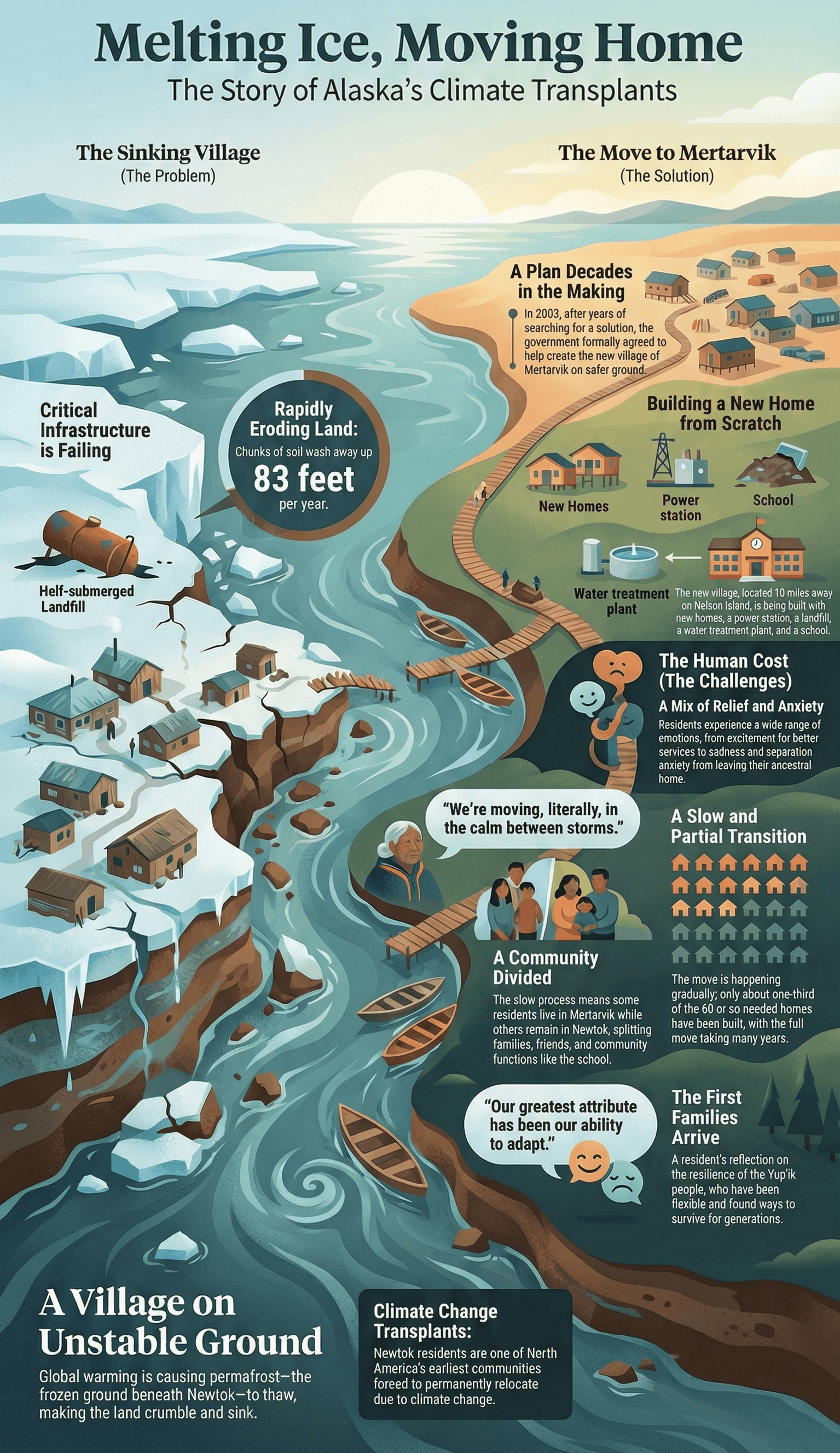
- Climate Change and Erosion: The Yup’ik village of Newtok, situated near the Bering Sea, is facing an existential threat from global warming. Thawing permafrost and riverbank erosion have caused the land to crumble, forcing the community to plan a relocation that has been in the works for over two decades.
- The Impact of Thawing Permafrost: As the frozen ground (permafrost) thaws, it causes roads and building foundations to buckle. This process also releases greenhouse gases, further driving up global temperatures.
- Rising Water Levels: Dwindling sea ice and rising sea levels have led to increased storm surges and flooding. In Newtok, the Ninglick River is "gnawing away" at the banks, with some soil chunks as large as 83 feet disappearing into the water annually.
The Relocation to Mertarvik
- A "Freshly Minted" Village: Residents have begun moving to a new site called Mertarvik, located on higher ground on Nelson Island. These residents are described as some of North America’s earliest "climate change transplants".
- A Slow Transition: The move is a long and difficult process. While some families have moved into new energy-efficient homes, it is expected to take until at least 2023 for enough housing to be built for the entire community.
- Divided Community: For the time being, the community operates from two locations separated by water. This split means families and friends are separated, and essential services like schooling are being split between the two sites.
Living Conditions and Infrastructure
- Lack of Basic Amenities: For decades, Newtok residents lived without indoor plumbing, relying on hauled water, which led to significant health problems.
- Infrastructure Delays: While Mertarvik has electricity, it still lacks public water and sewer systems. Securing the funding for these "pioneering" infrastructure projects remains a major challenge that could take many more years.
The Human and Emotional Element
- Mixed Emotions: Residents feel a complex mix of relief at gaining better services and anxiety or sadness about leaving the only home they have ever known.
- Cultural Resilience: Despite the "unwanted feelings" of moving, the community prides itself on its ability to adapt. Tribal officials emphasize that their people have always been flexible and are finding a way to ensure their story has a "better ending".
Educational and Linguistic Focus
- Grammar and Vocabulary: The chapter utilizes the Newtok story to teach linguistic concepts, such as the use of noun phrases and noun clauses. It also explores the nuances between words like "precarious," "risky," and "dangerous".
- Phonetics and Writing: The text covers the strong and weak forms of words in speech and provides a practical writing task focused on environmental advocacy through email.
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |