Urbanisation
Point-wise summary of the chapter on Urbanisation:
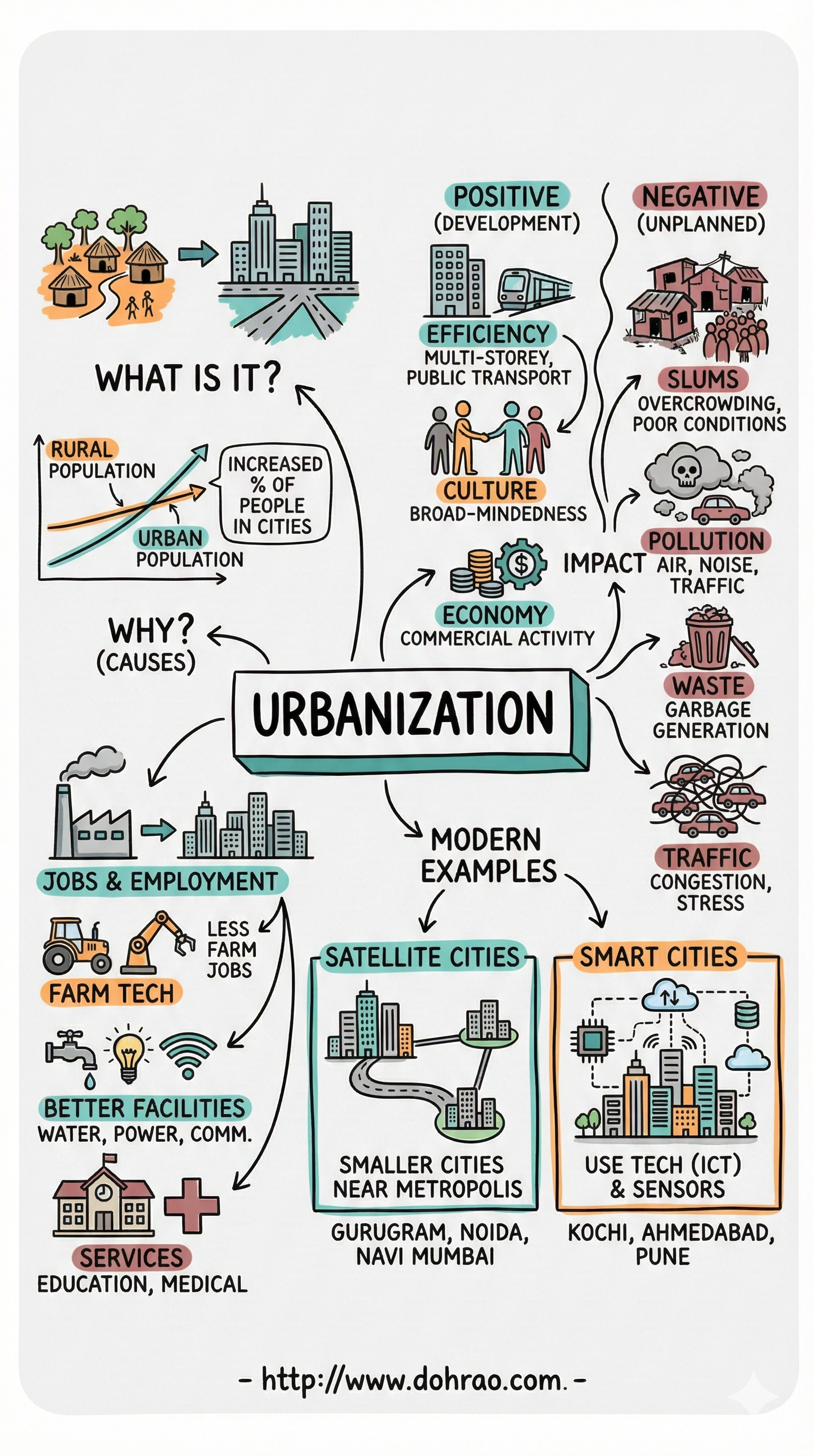
Understanding Urbanisation and its Causes
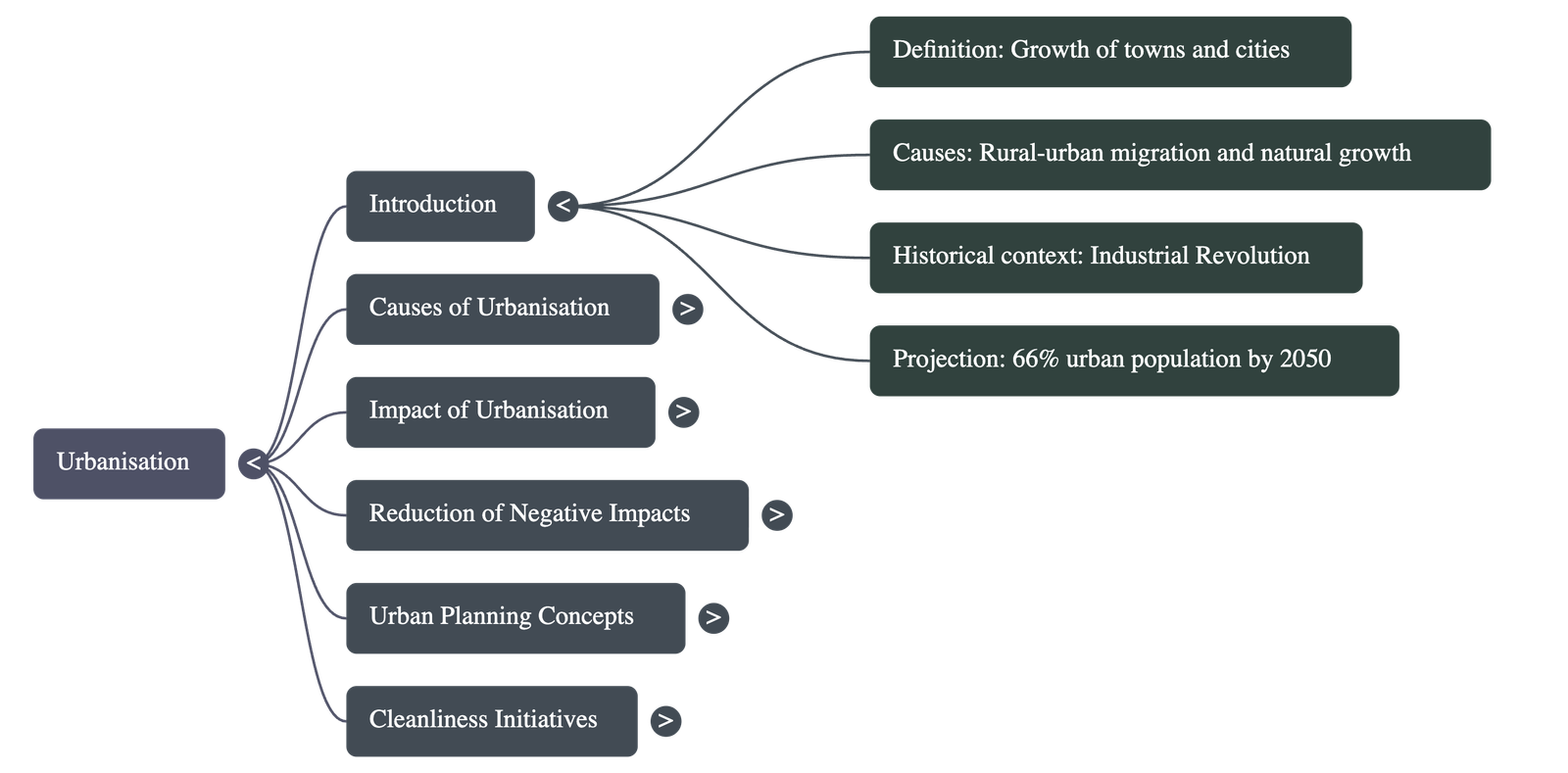
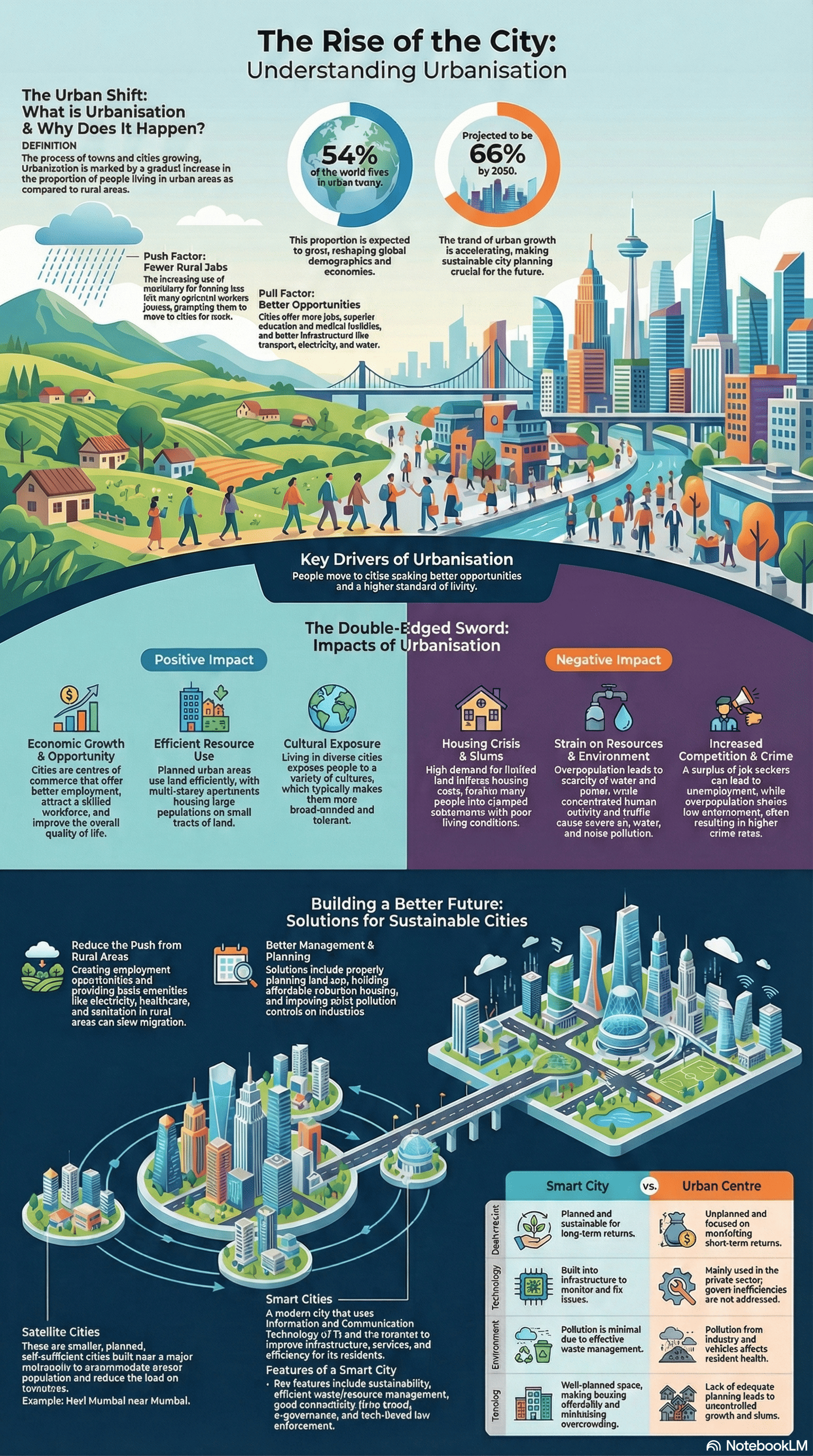
- Definition: Urbanisation is the process by which towns and cities grow, resulting in a gradual increase in the proportion of people living in urban areas compared to rural areas.
- Historical Context: A major surge in urbanisation began in the 18th century due to the Industrial Revolution, as workers migrated to urban centers for factory jobs.
- Primary Causes:
- Agricultural Mechanization: The use of machines in farming left many rural workers jobless, pushing them toward cities for work.
- Better Facilities: People are attracted to cities by better access to piped drinking water, electricity, advanced medical care, and efficient transport.
- Opportunities: Cities offer greater employment prospects, better educational facilities, and more opportunities for trade and commerce.
Impact of Urbanisation
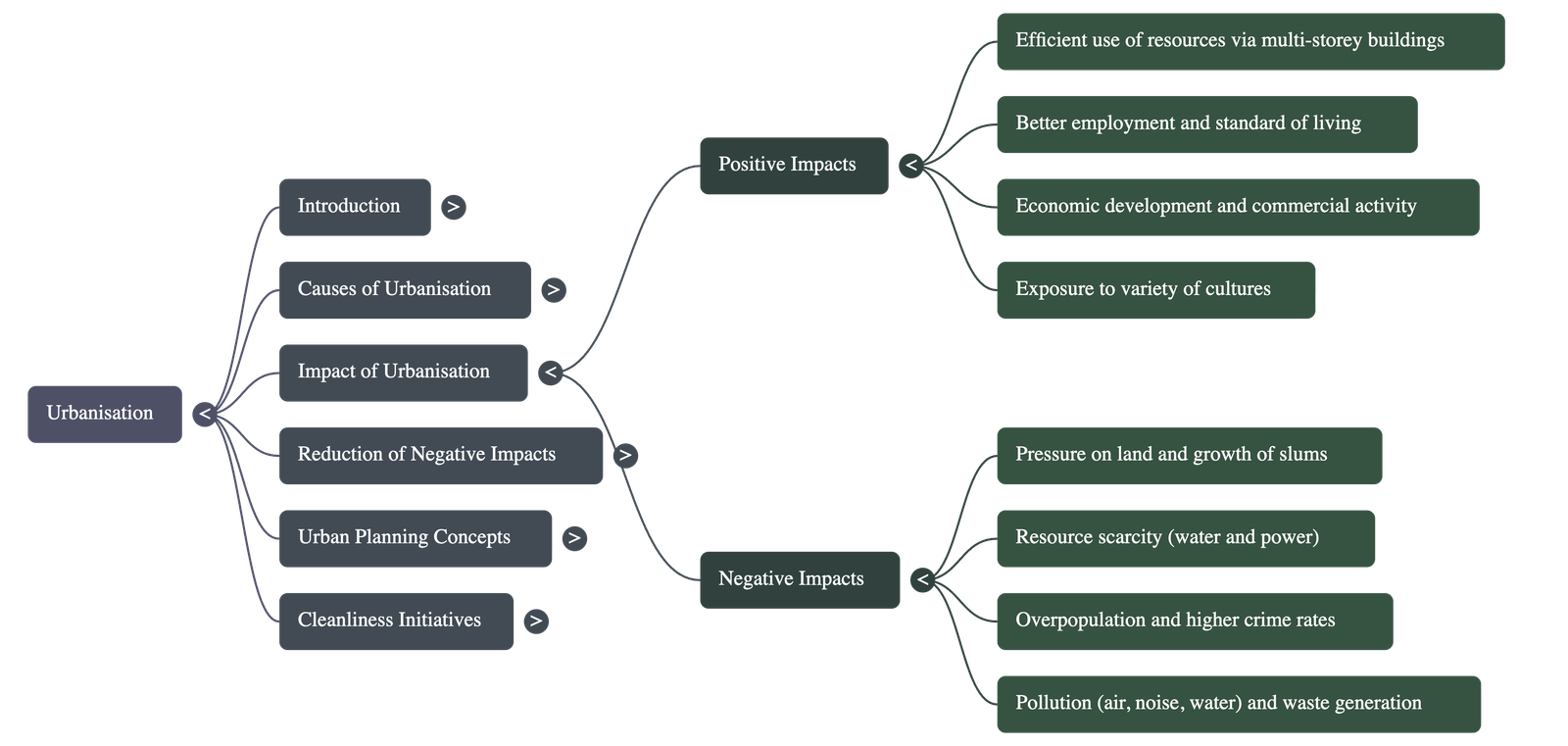
- Positive Impacts:
- Resource Efficiency: High-density living and public transport systems like Metro rails help save fuel and land.
- Economic & Social Growth: Cities act as centers for commercial activity and expose residents to diverse cultures, often making them more tolerant.
- Negative Impacts:
- Overcrowding and Slums: High demand for housing leads to expensive land and the growth of slums, which are settlements with very poor living conditions.
- Resource Scarcity: Increased population leads to the scarcity of water and power.
- Environmental Degradation: Rapid expansion encroaches on forests and agricultural land, while high activity levels cause air, noise, water, and land pollution.
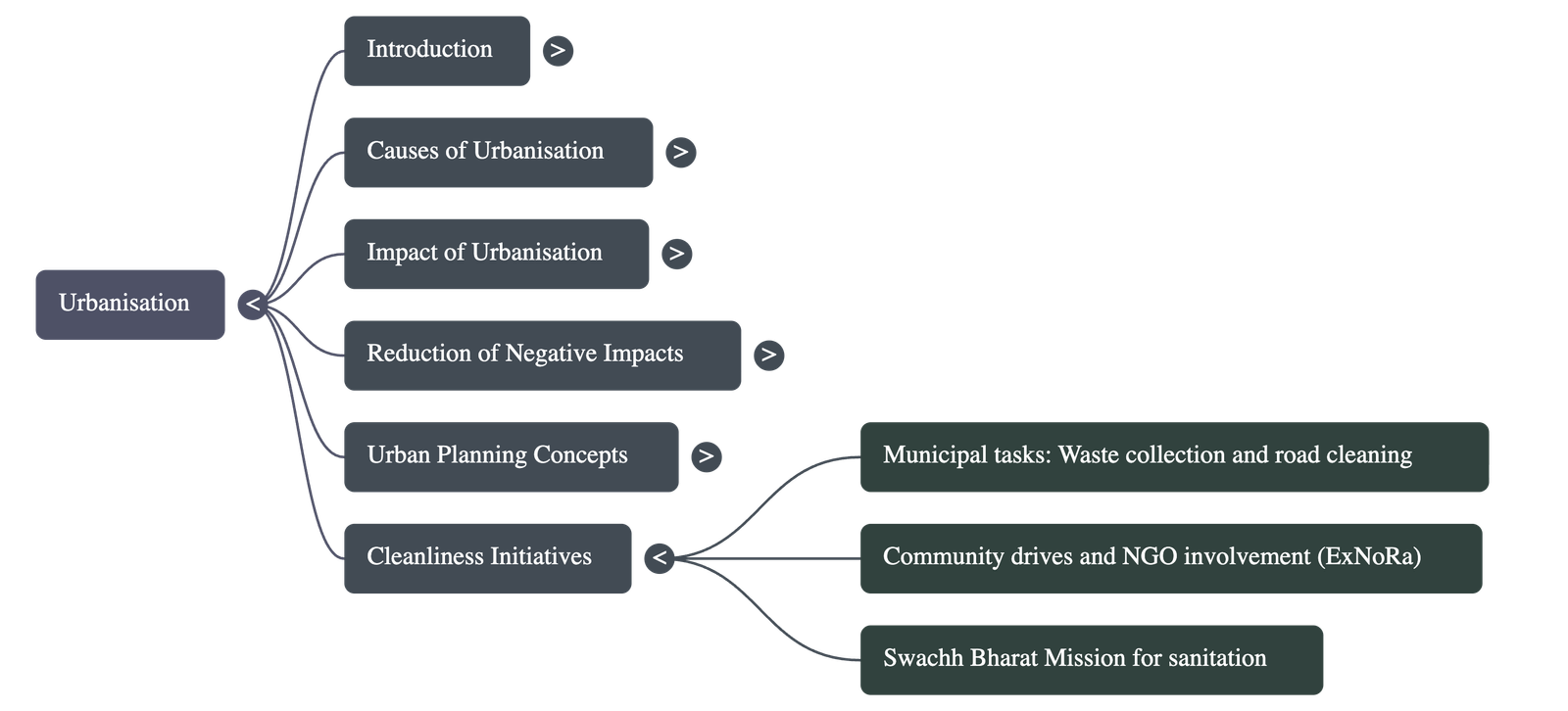
Managing and Reducing Negative Impacts
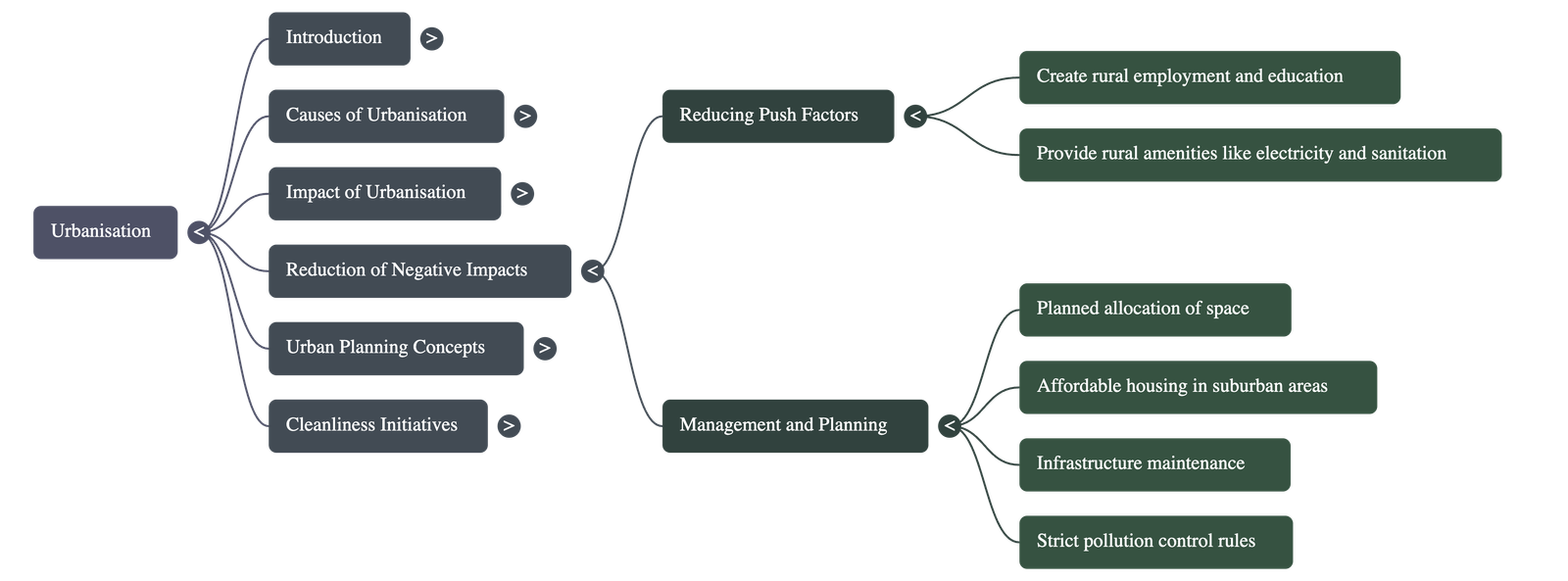
- Rural Development: To reduce migration, governments can create employment and education opportunities in rural areas and provide basic amenities like sanitation and clean water.
- Urban Planning: Authorities should plan for affordable housing in suburban areas and implement strict rules to control industrial pollution.
- Cleanliness Initiatives: Maintaining cleanliness is a challenge handled by Municipalities, NGOs (like ExNoRa), and local communities through waste collection and cleanliness drives.
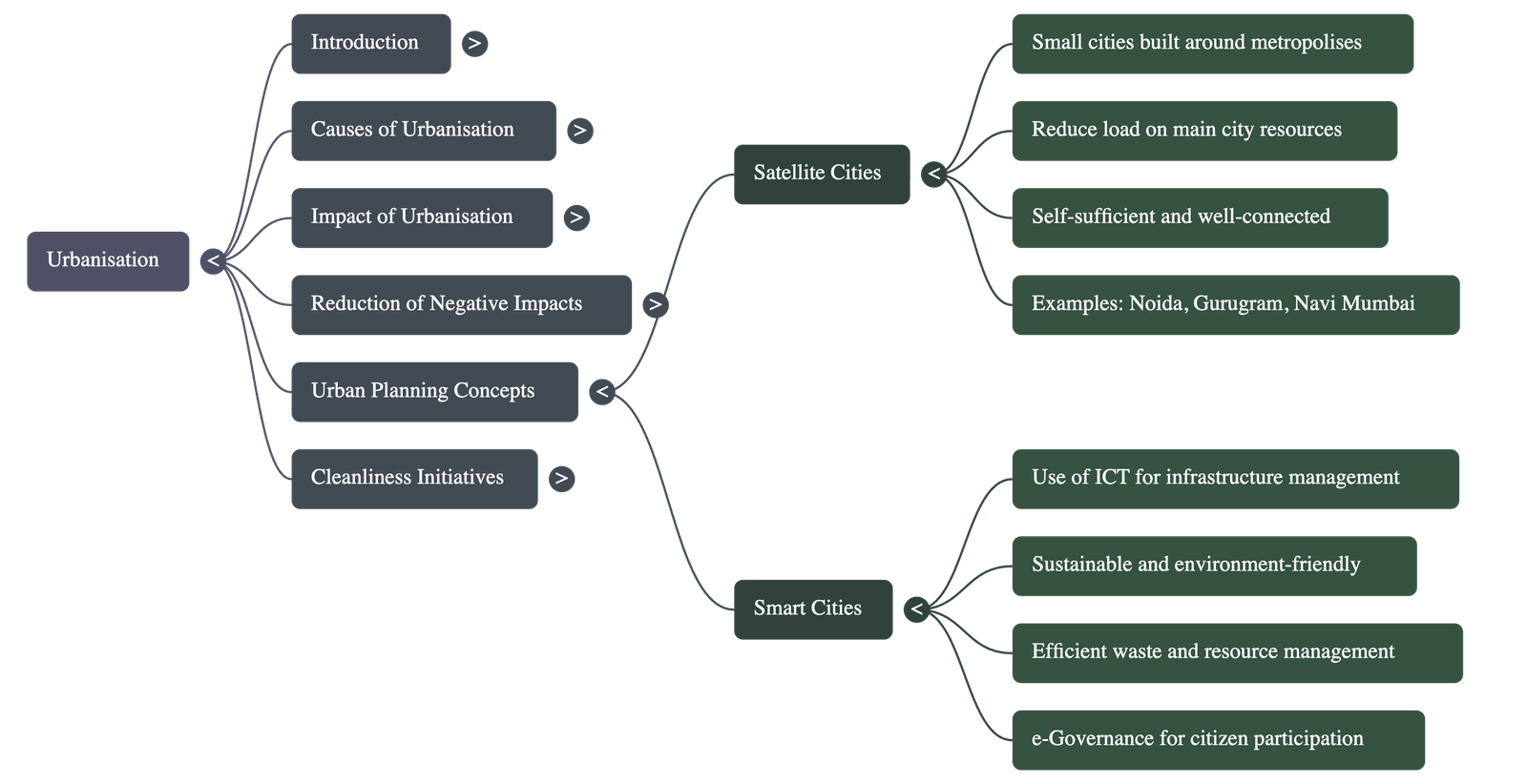
Satellite and Smart Cities
- Satellite Cities: These are small, planned cities built near a metropolis (e.g., Gurugram near New Delhi or Navi Mumbai near Mumbai) to accommodate excess population and reduce the load on the main city's resources.
- Smart Cities: These modern cities use Information and Communication Technology (ICT) and the Internet to improve infrastructure and management.
- Key Features: They focus on sustainability, renewable energy, efficient waste management, and e-Governance, which allows citizens to access government services online.
- India’s Vision: The Smart Cities Mission aims to provide core infrastructure, a clean environment, and a decent quality of life in selected cities like Kochi, Ahmedabad, and Pune.
Analogy: Urbanisation is much like a growing plant in a pot; if the pot (the city's infrastructure and planning) is large enough and the soil is well-tended, the plant thrives and provides beauty. However, if the plant grows too fast for its container without proper care, it becomes "rootbound," struggling for resources and eventually damaging the very pot it lives in.
Urbanisation - Questions and Answers
In-Text Questions
Question: Look at the satellite images of Delhi (1991 vs 2016). Delhi has grown on the banks of a river. Can you name this river?
Answer: The river is the Yamuna.
A. Fill in the blanks
- At present, around 54% of the global population lives in urban areas.
- The increasing use of machines for agricultural processes has left many agricultural workers jobless.
- Due to the lack of affordable housing, settlements with very poor living conditions called slums develop in urban areas.
- Navi Mumbai and Thane are satellite cities of Mumbai.
- A well-developed system of e-Governance allows citizens to access several government services online.
B. True or False (Correct the false statements)
-
Statement: All people who live in cities live in spacious apartments.
Answer: False. Many people in cities live in cramped spaces with minimal facilities or in slums due to the high cost of housing. -
Statement: Cities have well-developed systems of local transport.
Answer: True. -
Statement: Satellite cities are economically dependent on the metropolises they lie near.
Answer: False. Satellite cities are self-sufficient and socially and economically independent. -
Statement: E-Governance makes citizen participation in government affairs more difficult.
Answer: False. E-governance encourages citizen participation in decision-making and makes it easier to access services. -
Statement: Smart cities discourage the use of bicycles as they slow down the traffic.
Answer: False. Smart cities encourage the use of bicycles by creating bike lanes to reduce pollution and congestion.
C. Multiple Choice Questions
-
Rapid urbanisation began to take place in many countries during the:
Answer: c) Industrial Revolution -
There is an increase in crime rates in urban areas because:
Answer: b) overpopulation puts a strain on law enforcement systems -
Small cities built around or near large cities are known as:
Answer: a) satellite cities -
HITEC City is the satellite city of:
Answer: b) Hyderabad
D. Give reasons for the following
-
Skilled craftsmen like weavers and blacksmiths move to urban areas.
Answer: They move in search of better opportunities because their skills are absorbed by emerging industries and factories in cities, especially after being displaced by machines in rural areas. -
Pollution is a major problem in urban areas.
Answer: The concentration of numerous human activities, industrial activity, improper waste management, and the high use of fuel-based vehicles cause high levels of air, noise, water, and land pollution. -
People living in urban areas are often more open-minded than people who live in rural areas.
Answer: In cities, people are exposed to a variety of cultures and diverse groups of people, which usually makes them more broad-minded and tolerant. -
Vehicles in smart cities are equipped with commuter-friendly technology.
Answer: Smart cities use Information and Communication Technology (ICT) to improve efficiency, reduce congestion, and provide real-time data to improve transport services for residents.
E. Answer in brief
-
What is urbanisation?
Answer: Urbanisation is the process by which towns and cities grow, marked by a gradual increase in the proportion of people living in urban areas compared to rural areas. -
What are slums? Why do they develop?
Answer: Slums are settlements with very poor living conditions. They develop because of a lack of affordable housing and the high cost of land in cities, forcing people to live in cramped spaces with minimal facilities. -
Mention any four causes of urbanisation.
Answer: (1) Employment opportunities in factories, (2) Better access to facilities like electricity and piped water, (3) Advanced medical facilities, and (4) Better educational and training opportunities. -
What are satellite cities? Give two examples of satellite cities in India.
Answer: Satellite cities are small, planned cities built around or near a metropolis to accommodate excess population and reduce the load on the main city. Examples: Gurugram (New Delhi) and Navi Mumbai (Mumbai). -
Define smart cities. Name two cities of India that are going to be turned into smart cities.
Answer: A smart city is a modern city that uses Information and Communication Technology (ICT) and the Internet to improve infrastructure and management. Examples in India: Kochi and Pune.
F. Answer in detail
-
What was the Industrial Revolution? Assess its impact on urbanisation.
Answer: The Industrial Revolution was a period in the 18th century when goods began to be mass-produced in factories using machines instead of being made by hand at home. It triggered a major spurt in urbanisation as many workers migrated from rural areas to urban centres in search of factory employment. -
What are the causes of urbanisation?
Answer: The primary causes include the mechanization of agriculture (leaving rural workers jobless), the search for better-paying factory jobs, access to superior infrastructure (transport, communication, electricity), better healthcare, and higher-quality educational institutions. -
Discuss two negative and two positive aspects of urbanisation.
Answer: Positive: (1) Efficient use of resources through multi-storey buildings and public transport; (2) Economic development and better standards of living. Negative: (1) Pressure on limited land leading to slums; (2) Environmental degradation and high pollution levels. -
Describe ways in which we can reduce the negative impact of urbanisation.
Answer: Negative impacts can be reduced by creating employment and education in rural areas to reduce migration, building affordable housing in suburbs to curb slums, and imposing strict pollution rules on industries. -
'Keeping urban areas clean is a huge challenge.' Do you agree? Justify your answer.
Answer: Yes, because cities generate enormous amounts of waste daily. While municipalities collect garbage and clean streets, the number of dustbins and public toilets is often insufficient for the population. This requires additional efforts from NGOs and local communities through cleanliness drives. -
Why do satellite cities develop? Describe their main features.
Answer: They develop to reduce the pressure on the resources of a metropolis. Features include being smaller than the main city, being separated by a geographical barrier, having their own municipal corporations, and offering affordable housing while remaining well-connected to the metropolis. -
Discuss the features of smart cities.
Answer: Smart cities are sustainable and environment-friendly. They use renewable energy, energy-efficient technology, ICT for real-time monitoring of services, and e-Governance to allow citizens to access services online and participate in decision-making. -
Point out the differences between a smart city and an urban centre.
Answer: In a smart city, resource use is planned and sustainable, and technology is built into the infrastructure to fix inefficiencies. In a regular urban centre, resource use is often unplanned and focuses on short-term returns, with technology mostly limited to the private sector.
Analysing and Critical Thinking
Question: Why do you think the focus of smart cities is on being sustainable?
Answer: The focus is on sustainability to ensure that resources like water and energy are available for future generations. Since urban populations are growing rapidly, only sustainable practices like using renewable energy and efficient waste management can prevent total environmental collapse and resource scarcity.
Look and Learn
-
Why does the road have a cycle drawn on it?
Answer: It indicates a dedicated bike lane meant specifically for cyclists. -
What does this ensure?
Answer: It ensures the safety of cyclists and encourages people to use eco-friendly transport, which reduces traffic congestion and pollution. -
How do public bicycle systems function?
Answer: They provide bicycles on rent at various accessible points around the city. Users can pick up a bike from one point and often drop it off at another, frequently using internet-enabled apps for transactions.
Life Skills and Values
Question: What values must the citizens develop to improve the traffic situation in India? Suggest some measures that can be taken to enforce traffic rules.
Answer: Citizens must develop values like responsibility, respect for the law, and empathy for the safety of others. To enforce rules, authorities can use technology like CCTV cameras for automatic ticketing, increase fines for violations, and conduct regular awareness campaigns in schools and offices.