Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
Migration
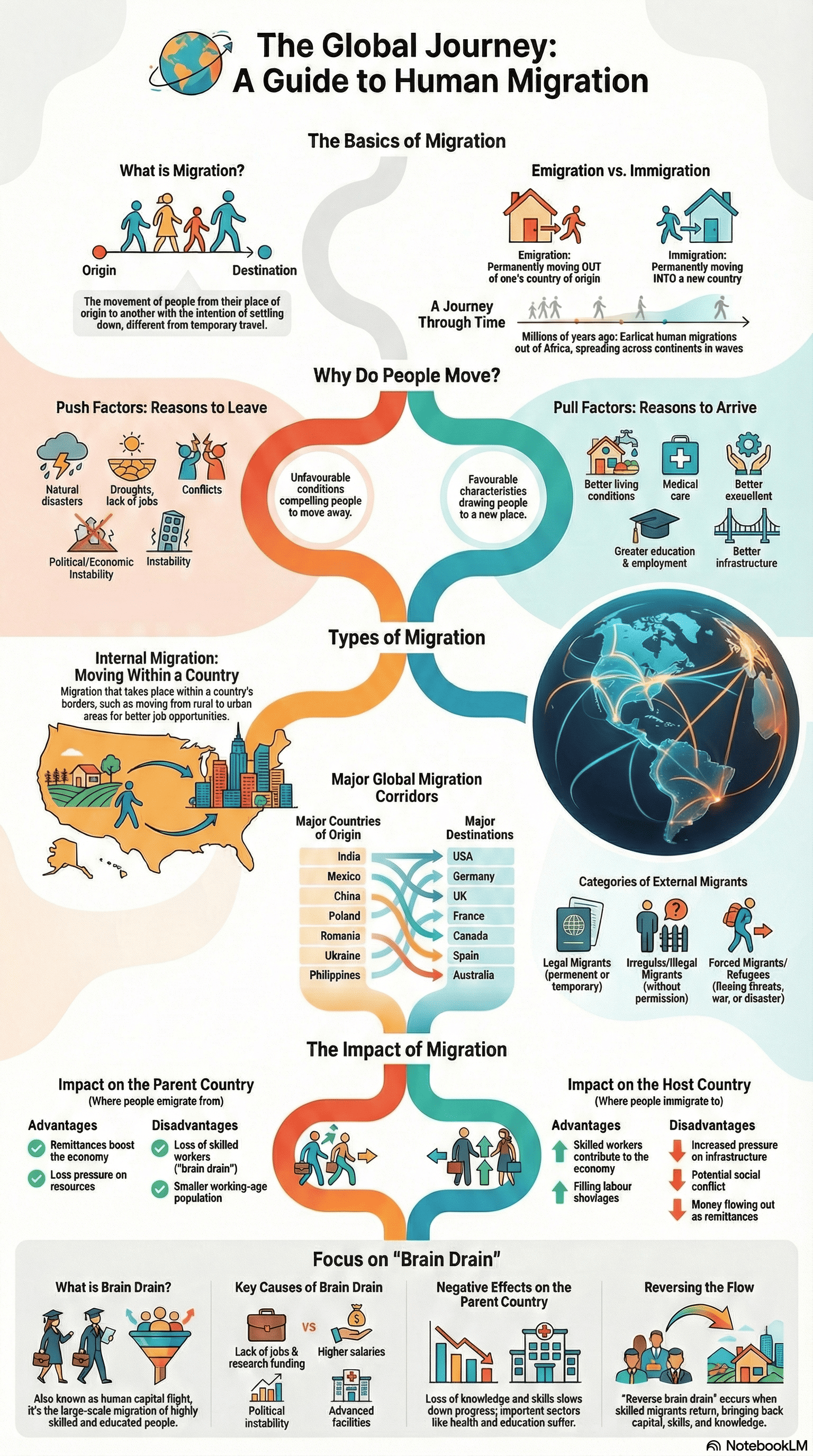
Definition and History of Migration
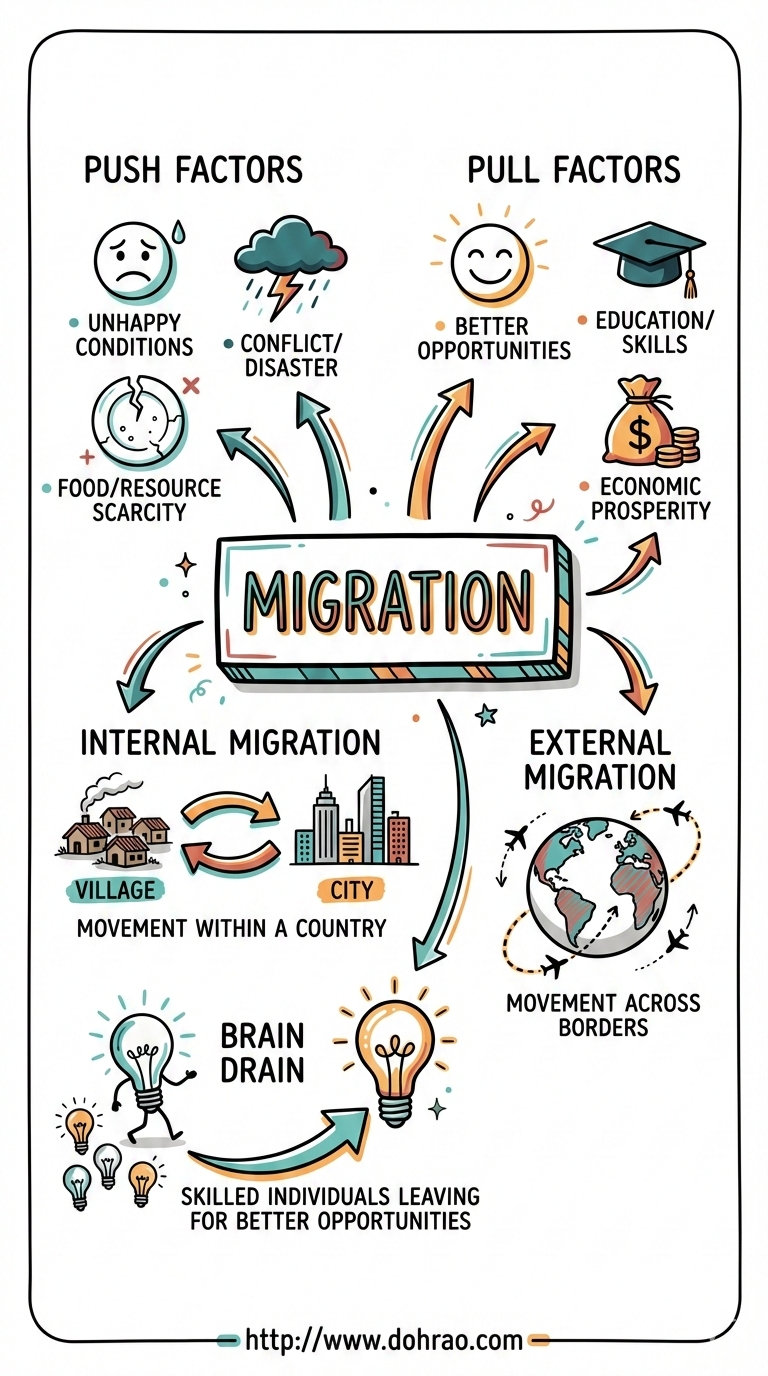
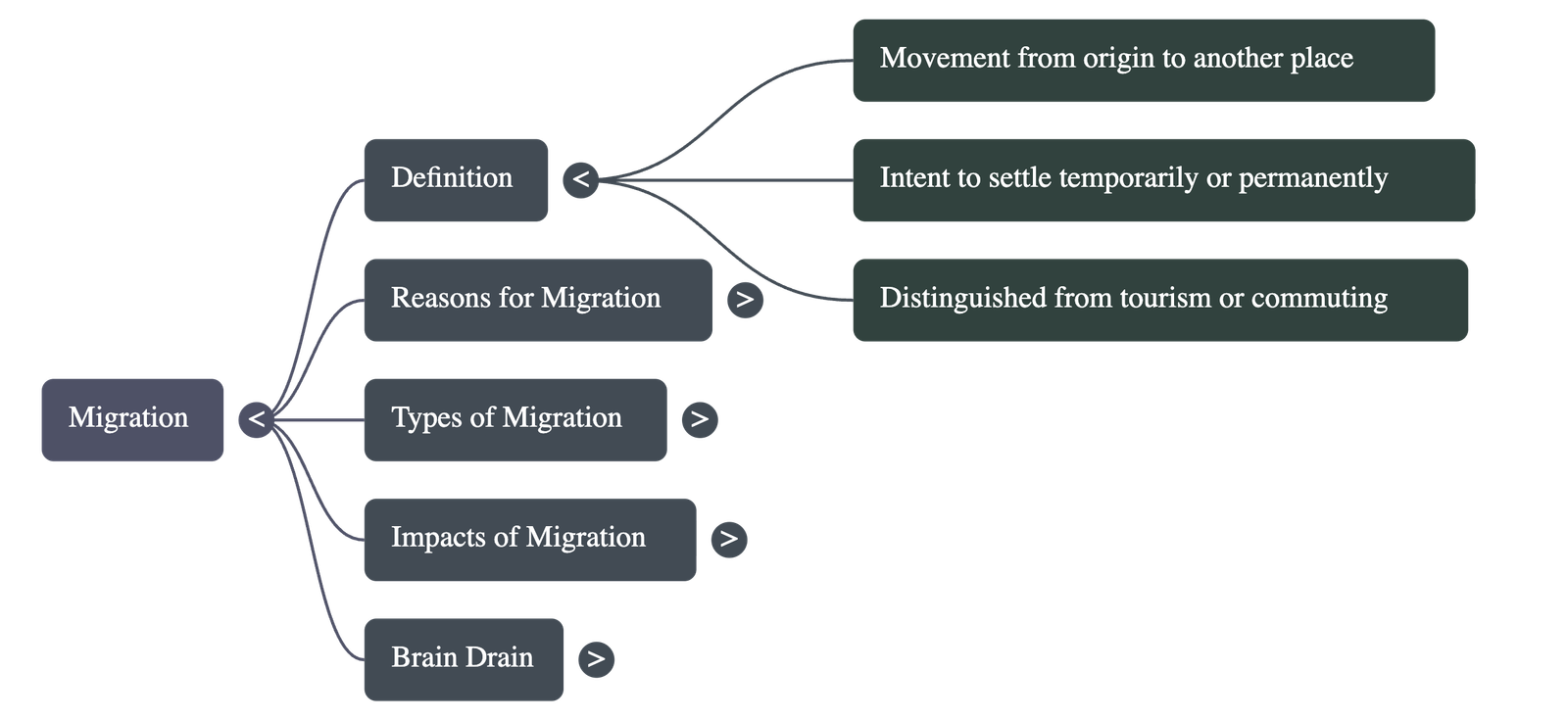
- Migration is defined as the movement of people from their place of origin to another location with the specific intention of settling temporarily or permanently.
- It is distinct from tourism, commuting for work, or herding, as these activities do not involve the intention of settling in a new place.
- Human migration has occurred throughout history, beginning with early humans moving out of Africa millions of years ago in several waves as the Ice Age retreated.
Reasons for Migration
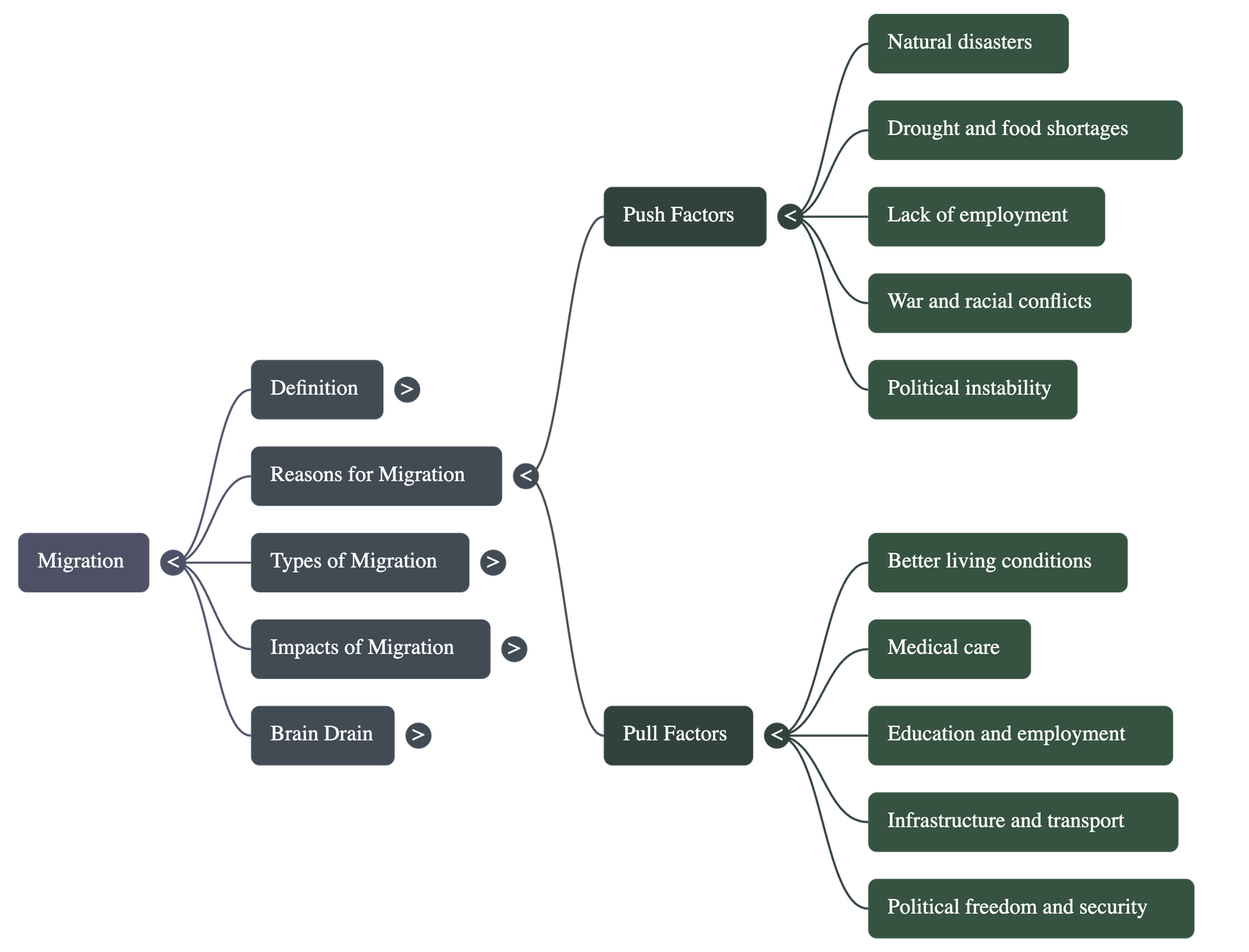
- Push Factors: These are unfavorable conditions that force or "push" people to leave a place, such as natural disasters (earthquakes, floods), lack of employment, war, communal conflicts, and political instability.
- Pull Factors: these are favorable characteristics that draw or "pull" people to a new location, including better living conditions, medical care, improved infrastructure, and higher standards of education and employment.
Types of Migration
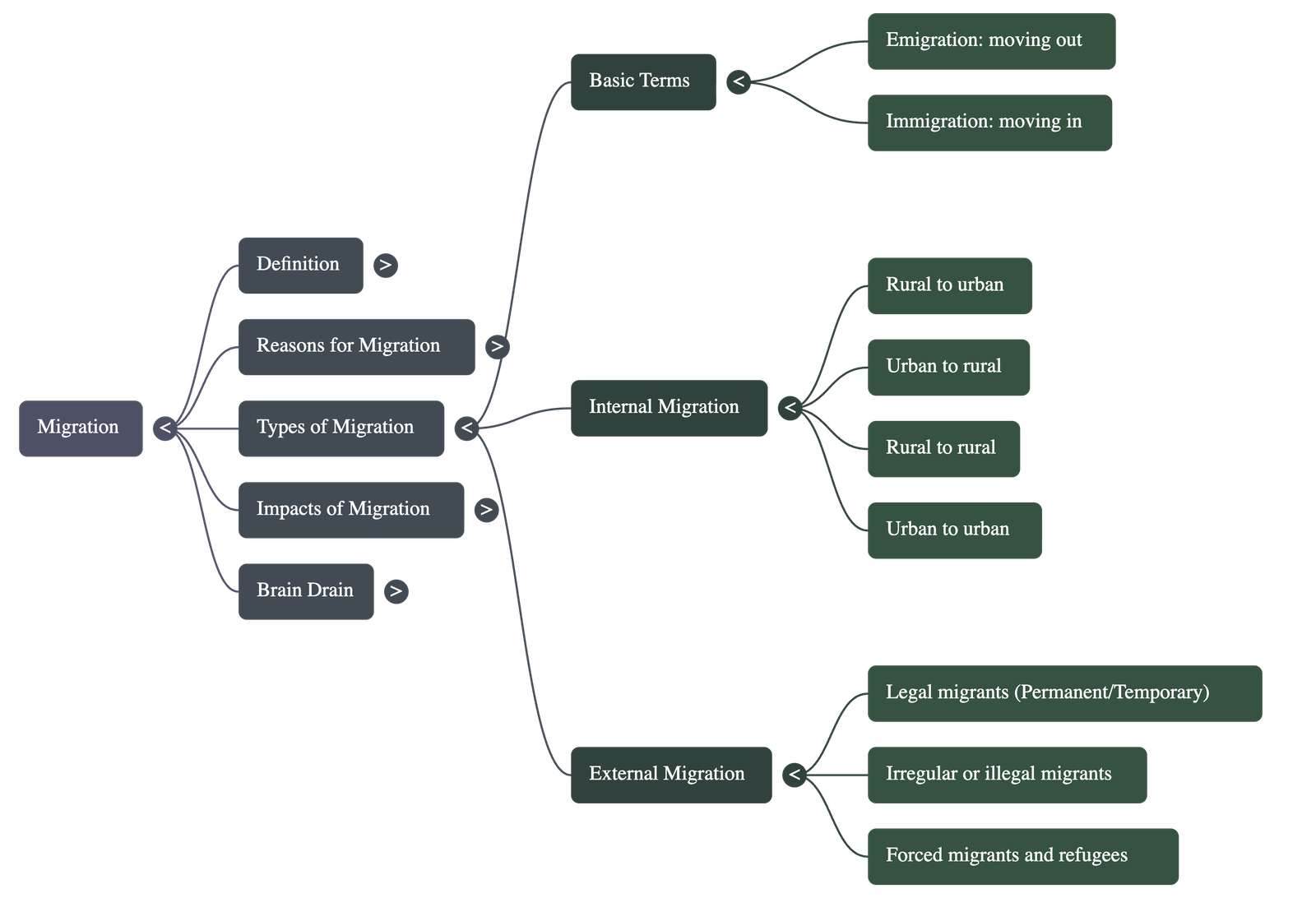
- Emigration and Immigration: Emigration is the act of permanently moving out of one place, while immigration is the act of permanently moving into a place other than one's origin.
- Internal Migration: This occurs within a country and includes movements such as rural to urban (for better infrastructure), urban to rural (to escape pollution or lack of space), rural to rural (for fertile land), and urban to urban (moving to satellite towns like Gurugram).
- External Migration: This involves crossing international borders and is classified into:
- Legal Migrants: Those granted the right of entry, who may be permanent residents or temporary workers who send remittances back home.
- Irregular (Illegal) Migrants: People living in a country without valid documentation or permission.
- Forced Migrants and Refugees: Individuals forced to flee due to threats to their lives from war, political/religious persecution, or natural disasters.
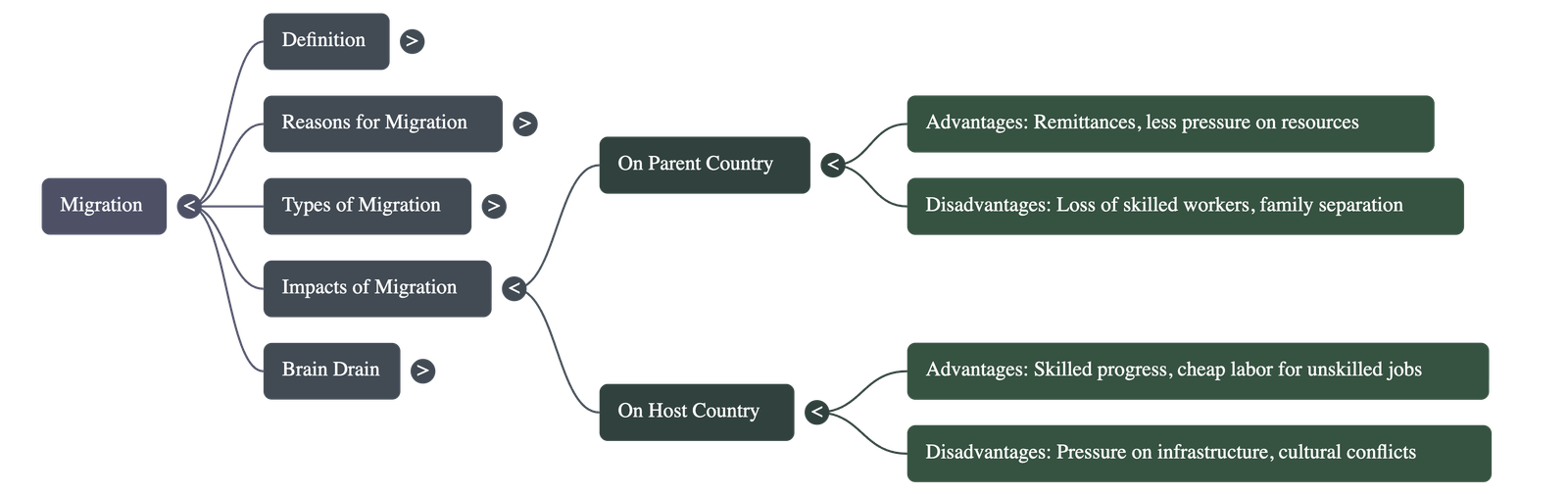
Impact of Migration
- On the Parent Country:
- Advantages: Reduced pressure on local resources, increased job availability, and an economic boost from remittances and new skills brought back by returning migrants.
- Disadvantages: Loss of skilled workers, a higher proportion of dependents as working-age people leave, and the potential for family separation to impact mental health.
- On the Host Country:
- Advantages: A gain in skills and knowledge from highly skilled immigrants and a source of unskilled labor for jobs locals may be unwilling to do.
- Disadvantages: Increased pressure on infrastructure and the standard of living, potential cultural conflicts, and the possibility of immigrants being exploited.
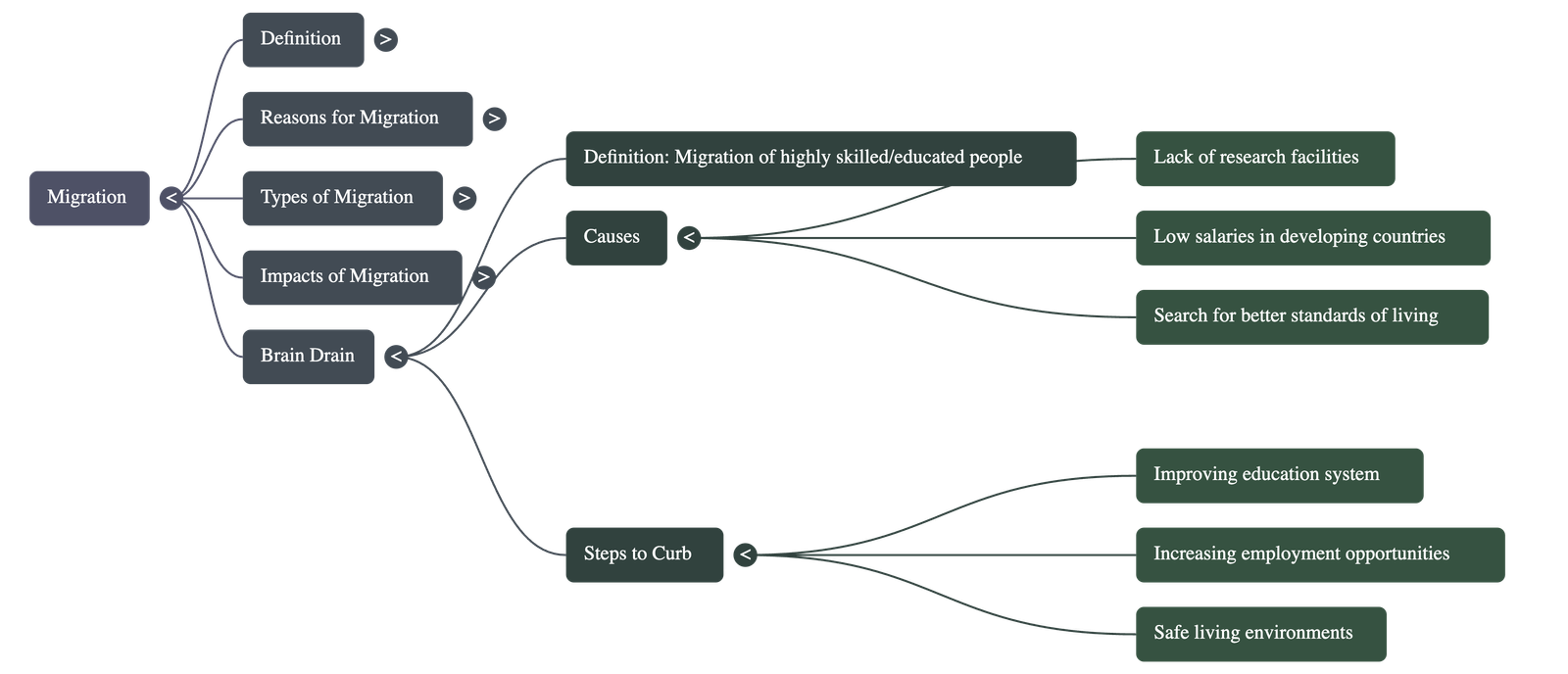
Brain Drain and Its Reversal
- Brain Drain (human capital flight) refers to the large-scale migration of highly skilled and educated professionals (like doctors and engineers) from developing countries to developed nations.
- While the host country experiences "brain gain," the parent country suffers a loss of progress, tax revenue, and the quality of work in critical sectors like health and education.
- In India, brain drain became significant around the 1950s due to a lack of research facilities and job stagnation.
- Reverse Brain Drain: Recently, many migrants have been returning to India to invest their skills and capital into start-ups, a trend encouraged by government steps to improve research facilities, employment opportunities, and the education system.
To understand the different "flows" of people, you can think of migration like a biological cell membrane: push factors are the internal pressures that force molecules out, while pull factors are the external attractions that draw them in. "Brain drain" is like the cell losing its most vital nutrients, which it must eventually try to recover through "reverse brain drain" to remain healthy and grow.
Question Bank
A. Fill in the blanks.
- Factors that cause people to migrate out of a place are called push factors.
- Internal migration takes place within a country.
- Immigrants who live in a country without permission are known as irregular or illegal migrants.
- Money sent in by migrants is known as remittances.
- Brain drain is also known as human capital flight.
B. Tick the sentences that are true. Correct the others.
- Early humans migrated from one place to another in search of better jobs.
Answer: False. Early humans migrated mainly in search of food and in response to climatic changes and natural disasters. - Migrants who are forced to leave their country owing to threats posed to their lives and freedom are known as skilled migrants.
Answer: False. They are known as refugees (or forced migrants). - Remittances sent by emigrants help the local economy.
Answer: True. - Immigration leads to a drop in the standard of living in the parent country.
Answer: False. Large-scale immigration can cause a fall in the standard of living in the host country due to pressure on infrastructure. - Countries that receive highly skilled migrants experience brain drain.
Answer: False. Countries that receive highly skilled migrants experience brain gain.
C. Multiple choice questions.
- The phenomenon of migrating out of a place is called:
Answer: b) emigration - A person migrating from India to USA to take up a job at an IT firm is an example of:
Answer: b) external migration - Gurugram is a satellite town of:
Answer: a) Delhi - The country to which one migrates is called the:
Answer: a) host country
D. Give reasons for the following.
- Migration is different from tourism.
Migration involves the intention of settling down temporarily or permanently, whereas tourism does not involve an intention to settle in a new place. - Communal or racial conflicts and war are push factors for migration.
These conditions create an unsafe environment and pose threats to life, freedom, or security, forcing people to leave their place of origin. - People migrate from urban to rural areas.
People do this to return to their place of origin, to escape urban problems like pollution and lack of space, or for economic reasons. - Employment opportunities increase in the parent country as a result of emigration.
As people leave the parent country, the job market becomes less competitive for those who remain. - In India, brain drain started from around the 1950s.
It started because highly skilled people felt they were stagnating due to inefficient organizations, a lack of jobs, and a lack of research facilities in India at that time.
E. Answer in brief.
- What is migration?
Migration is the movement of people from their place of origin to another with the intention of settling down temporarily or permanently. - Which was the earliest recorded migration in human history?
The earliest known migration occurred when early humans moved out of Africa millions of years ago. - List two advantages and two disadvantages of immigration.
Advantages: 1. Highly skilled migrants contribute to the local economy. 2. Unskilled migrants are willing to do jobs that locals may not want.
Disadvantages: 1. Pressure on infrastructure can lead to a fall in the standard of living. 2. Cultural differences may sometimes lead to conflict. - Why do migrations take place between two or more urban centres?
People move between cities for better educational and employment opportunities, or to move from crowded big cities to cleaner, satellite towns. - What do you understand by temporary workers?
Temporary workers (or migrants) move to another country to work for a specific period rather than settling there permanently; they often send money back to their families. - Give two examples of mass migrations in the history of the 20th century.
1. Migrations between India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh during Partition. 2. Migrations of Jewish people from Europe during and after the Second World War. - What are remittances? How do they help the parent country?
Remittances are money sent back to the parent country by migrants. They help boost the economy and increase the country's revenue.
F. Answer in detail.
- Explain the causes of migration.
Migration is caused by "Push" and "Pull" factors. Push factors (like natural disasters, lack of jobs, war, or instability) force people to leave a place. Pull factors (like better living conditions, medical care, education, and political freedom) attract people to a new location. - Analyse the impact of migration on the parent country and the host country.
For the parent country, emigration reduces pressure on resources and brings in remittances, but it also causes a loss of skilled labor (brain drain). For the host country, immigration provides skilled and unskilled labor but can put a strain on public infrastructure and sometimes lead to social friction. - Distinguish between the different kinds of external migrants.
External migrants include:- Legal Migrants: Granted entry by the government; can be permanent (citizens) or temporary.
- Irregular (Illegal) Migrants: Live in a country without valid permission or documents.
- Refugees (Forced Migrants): People forced to flee due to threats to their lives from war, famine, or disasters.
- What is brain drain? Evaluate the positive and negative impact of brain drain.
Brain drain is the large-scale migration of highly skilled and educated people (like doctors and engineers) from developing to developed countries. Negative: Loss of expertise, lower quality in health/education sectors, and loss of tax revenue for the parent country. Positive: Migrants send back remittances and may return later with even more advanced skills (reverse brain drain). - List the steps taken by the government and private individuals in the recent past to reverse brain drain from India.
Steps include creating a safer living environment, improving the education system, increasing employment opportunities, improving research facilities/funding, and establishing systems to improve work quality and workplace efficiency.
Look and Learn (Image Analysis)
- Identify these people.
The image (contextually) represents refugees or forced migrants fleeing hardship. - What type of migration do they illustrate?
They illustrate forced migration (refugees). - Put yourself in the place of these migrants and name the first three emotions that come to your mind.
(Student-led answer) Common emotions would include fear, hope, and sadness.
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |
1 / 1
Quick Navigation:
| | | | |